Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The University of The South Pacific
Uploaded by
Rex MelunOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The University of The South Pacific
Uploaded by
Rex MelunCopyright:
Available Formats
The University of the South Pacific
School of Information Technology, Engineering, Mathematics and
Physics (STEMP)
CS350 Wireless Networks
Tutorial/Lab 6: UMTS System Design And
CDMA2000 System Design
This lab covers the following course learning outcomes partially:
CLO1 - Distinguish between wireless networking principles and wired networks
CLO 2 - Evaluate emerging wireless networking technologies.
Short Answer Questions.
Question 1. What is a typical node-b sensitivity level?
The service and load determines the NodeB sensitivity; in general, in a no-load condition, the sensitivity
is between -115dBm to -125dBm. For Ericsson, the NodeB sensitivity level is calculated at around:
CS12.2: -124 dBm
PS-64: -119 dBm
PS-128: -115 dBm
PS-384: -115 dBm
Question 2. What is a typical ue sensitivity level?
The service and load determines the UE sensitivity; in general, in no-load condition, the sensitivity is
between -105dBm and -120dBm. For Ericsson, the UE sensitivity level is calculated at around:
- CS12.2: -119 dBm
- PS-64: -112 dBm
- PS-128: -110 dBm
- PS-384: -105 dBm
- HSDPA: -95 dBm
Question 3. State the typical node-b maximum output power?
The maximum NodeB output power is usually 20W or 40W, that is, 43dBm or 46dBm
Question 5. Describe a Typical Antenna Gain?
The amount of energy the antenna can “Boost” the sent and received signal by is referred to as the
antennas Gain.
Antenna gain is measured in:
1. dBi: relative to an isotropic radiator
2. dBd: relative to a dipole radiator
0 dBd = 2.15dBi
The antenna gain depends on antenna model; in link budget we use around 17dBi.
Question 6. In few sentences describe your understanding of a typical maximum path loss?
The maximum path loss is dependent on the service and vendor recommendations; typically it is in
between 135 to 140dB for urban areas and between 150 to 160dB for rural areas.
Question 10. State the pros and cons (advantages and disadvantages) of tma?
Pros:
- TMA reduces system noise, improves uplink sensitivity and leads to longer UE battery life.
Cons:
- TMA imposes an additional insertion loss (typically 0.5dB) on the downlink and increases site
installation and maintenance complexity
Question 11. Draw the different antenna types you have learned in this course and describe their
properties. This should be presented in a tabular format.
Antenna types Properties
Directional - this type of antenna has a narrow beam
width; with the power being more
directional, greater distances are usually
achieved but area coverage is sacrificed
- Yagi, Panel, Sector and Parabolic
antennae
- an EUM, NCL Station/Master will use this
type of antenna in both Point to Point
and Point to Multipoint
Omni-directional - this type of antenna has a wide beam
width and radiates 3600 ; with the power
being more spread out, shorter distances
are achieved but greater coverage
attained
- Omni antenna
- a CCU or an NCL Master will use this type
of antenna
Summary Writing
As for all mobile systems, UMTS provides wireless communication services to users on the move. The
system supports roaming, that is the UMTS users can be reached and they can place calls where ever
they are located within the coverage area of UMTS and many more.
Reflect and write a summary regarding the parent topic i.e “UMTS System Design And CDMA2000
System Design”. (Portray your understanding of the parent topic). Minimum of two paragraphs.
UMTS System Design and CDMA200 System Design
UMTS, Universal Mobile Telecommunications System is an evolution of services and data speeds from
2G. It is below the 3G mobile Networks (ITU) and one of his objectives is to increase the services that the
user demands. UMTS, use the WCDMA in the access radio (UTRAN).
The 3G systems are developed by different organizations: WCDMA (UMTS) is developed by ARIB/ETSI
and Cdma2000 is developed by TIA but there are many similarities and also very differences in the two
systems. Although exist similar concepts, the details of the physical layers are different in the two
systems because they were standardized by different associations. Nevertheless, both proposals use
concepts of IS-95. Exist also a difference between WCDMA and Cdma2000 because WDCMA has to be
compatible with GSM while cdma2000 has to be compatible with IsS-95. Cdma2000 increases the speed
of the system's 2Gs.
You might also like
- Modem Specifications LTE AntennasDocument29 pagesModem Specifications LTE Antennaslimar benasoNo ratings yet
- S A T T A W A H N: Mart Ntenna Echniques and Heir Pplication To Ireless D OC EtworksDocument7 pagesS A T T A W A H N: Mart Ntenna Echniques and Heir Pplication To Ireless D OC EtworksReda BekhakhechaNo ratings yet
- Smart Antenna ReportDocument12 pagesSmart Antenna ReportfloydprinceNo ratings yet
- Saqib Ali: Report HeadingDocument52 pagesSaqib Ali: Report HeadingNishank Jain0% (1)
- Base Station Antennas For MobileDocument8 pagesBase Station Antennas For Mobilesidney TeahNo ratings yet
- Link Budget AnalysisDocument16 pagesLink Budget AnalysisIrene EmeraldNo ratings yet
- Smart AntennaDocument17 pagesSmart AntennacommunicationridersNo ratings yet
- Antenna Technology For Wireless CommunicationsDocument9 pagesAntenna Technology For Wireless Communicationskamran ashrafNo ratings yet
- Antenna KathreinDocument34 pagesAntenna Kathreinkaca011100% (1)
- Smart AntennaDocument17 pagesSmart Antennasenthil_1984No ratings yet
- Lecture 6. ComponentsDocument53 pagesLecture 6. ComponentsAmalia AzizahNo ratings yet
- Types of Smart Antenna SystemsDocument17 pagesTypes of Smart Antenna SystemsanashabirNo ratings yet
- Dual Frequency Patch Antenna: IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine January 1998Document9 pagesDual Frequency Patch Antenna: IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine January 1998lee yongzhengNo ratings yet
- Monopol AntennaDocument5 pagesMonopol Antennaia874046No ratings yet
- BeamformingDocument17 pagesBeamformingAmol MahoreNo ratings yet
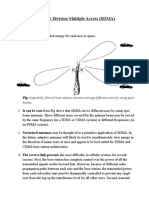
- Space Division Multiple Access (SDMA) : It Controls The Radiated Energy For Each User in SpaceDocument2 pagesSpace Division Multiple Access (SDMA) : It Controls The Radiated Energy For Each User in SpaceKrishanu ModakNo ratings yet
- CMN511 RW1Document22 pagesCMN511 RW1Sean Matthew L. OcampoNo ratings yet
- DWDM Technical ReportDocument25 pagesDWDM Technical ReportTareq QaziNo ratings yet
- Upamanyu Madhow ECE Department University of California, Santa BarbaraDocument84 pagesUpamanyu Madhow ECE Department University of California, Santa BarbaraVikash YadavNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics ReviewerDocument16 pagesFiber Optics Reviewersupermax23No ratings yet
- 5G Question and AnswersDocument11 pages5G Question and Answerssvirender_1No ratings yet
- Micro Strip Patch Antenna For Wlan/Wimax Applications: A ReviewDocument5 pagesMicro Strip Patch Antenna For Wlan/Wimax Applications: A ReviewPhương Linh TrầnNo ratings yet
- MW TransmissionDocument23 pagesMW Transmissionbonsatilahun1992No ratings yet
- Microstrip and Smart AntennaDocument6 pagesMicrostrip and Smart Antennahabtemariam mollaNo ratings yet
- Design of "Radiation Alert" Mobile PHDocument6 pagesDesign of "Radiation Alert" Mobile PHapi-20008301No ratings yet
- Smyth 2020Document9 pagesSmyth 2020Mylavarapu SriprithamNo ratings yet
- Panel Antenna PPT - Akash RayDocument19 pagesPanel Antenna PPT - Akash RayOwen HolmesNo ratings yet
- 1.5b - Cliff WhiteDocument71 pages1.5b - Cliff WhiteHilmi SanusiNo ratings yet
- Solar Power Satellites: A Seminar Report OnDocument20 pagesSolar Power Satellites: A Seminar Report Ongsudhakar14123466No ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Upena Dalal (Refer Textbook For Detailed Explanation)Document33 pagesChapter 15 Upena Dalal (Refer Textbook For Detailed Explanation)Sanjeet MalawadeNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 MCADDocument112 pagesUnit-1 MCADAbbhinav JaiinNo ratings yet
- Mobile Comm - Lec1 v1Document15 pagesMobile Comm - Lec1 v1Ahsan IqbalNo ratings yet
- Smart Antenna For Mobile Communication: Email Id:komali - Jntu@yahoo - Co.inDocument7 pagesSmart Antenna For Mobile Communication: Email Id:komali - Jntu@yahoo - Co.inARVINDNo ratings yet
- SAR With Digital Beamforming On Receive Only: Manvan - Younis@etec - Uni-Karlsruhe - deDocument3 pagesSAR With Digital Beamforming On Receive Only: Manvan - Younis@etec - Uni-Karlsruhe - defelipemaderoNo ratings yet
- Imran 2012Document28 pagesImran 2012Shaik KareemullaNo ratings yet
- Application Note 23: MICRF001 Antenna Design Tutorial by Tom YestrebskyDocument8 pagesApplication Note 23: MICRF001 Antenna Design Tutorial by Tom YestrebskyIyon ManakarraNo ratings yet
- Design of A Multiband Quasi-Yagi-Type Antenna With CPW-to-CPS TransitionDocument4 pagesDesign of A Multiband Quasi-Yagi-Type Antenna With CPW-to-CPS TransitionTâm Trần ĐứcNo ratings yet
- What Is Plasma ?Document14 pagesWhat Is Plasma ?dhnsachinNo ratings yet
- E4-E5 - Text - Chapter 1. Basics of Mobile Com MunicationDocument12 pagesE4-E5 - Text - Chapter 1. Basics of Mobile Com MunicationAGM CMS&MNo ratings yet
- PMP 450M and Cnmedusa™ Technology: Technic Al Advantages and InnovationDocument11 pagesPMP 450M and Cnmedusa™ Technology: Technic Al Advantages and InnovationJuan PerezNo ratings yet
- Antenna Diversity: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesAntenna Diversity: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediawashkouletNo ratings yet
- Signal Jammer Synopsis2Document9 pagesSignal Jammer Synopsis2fogiwox149No ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Communication System:-ReferencesDocument0 pagesOptical Fiber Communication System:-Referenceswww.bhawesh.com.npNo ratings yet
- Signal Strength Enhancement Using Cellular Repeater On Three Frequency Bands For Low Signal Coverage Areas (GSM900, GSM 1800/DCS, 3G)Document6 pagesSignal Strength Enhancement Using Cellular Repeater On Three Frequency Bands For Low Signal Coverage Areas (GSM900, GSM 1800/DCS, 3G)ahmedNo ratings yet
- Basics of Mobile CommunicationDocument12 pagesBasics of Mobile CommunicationAmol DholeNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 1 What Is Transmission Media?: Name: Michael David CaparazDocument5 pagesAssignment # 1 What Is Transmission Media?: Name: Michael David CaparazMichael David CaparazNo ratings yet
- Isolation Enhancement of A Very Compact UWB-MIMO Slot Antenna With Two Defected Ground StructuresDocument4 pagesIsolation Enhancement of A Very Compact UWB-MIMO Slot Antenna With Two Defected Ground StructuresSrikar DNo ratings yet
- Documentation Sample in IEEE FormatDocument16 pagesDocumentation Sample in IEEE FormatGajjala NandiniNo ratings yet
- Smart Antennas For Mobile Communications: A. J. Paulraj, D. Gesbert, C. PapadiasDocument15 pagesSmart Antennas For Mobile Communications: A. J. Paulraj, D. Gesbert, C. PapadiasparthhsarathiNo ratings yet
- Optical Networking and Dense Wavelength Division MultiplexingDocument29 pagesOptical Networking and Dense Wavelength Division MultiplexingAshish DwivediNo ratings yet
- WDMDocument7 pagesWDMNenad VicentijevicNo ratings yet
- Compact Dual-Polarized UWB-Antenna Embedded in A Dielectric-gSsDocument8 pagesCompact Dual-Polarized UWB-Antenna Embedded in A Dielectric-gSsjulio perezNo ratings yet
- Philippine Electronics Code Book 4Document19 pagesPhilippine Electronics Code Book 4felipeNo ratings yet
- lzt1233976 02 R2ADocument44 pageslzt1233976 02 R2AMokbelNo ratings yet
- Komdat Pertemuan-02 Media Komunikasi DataDocument10 pagesKomdat Pertemuan-02 Media Komunikasi DataZulfa RangkutiNo ratings yet
- Compact MIMO Antenna Using Stepped Impedance Resonator-Based Metasurface For 5G and WIFI ApplicationsDocument6 pagesCompact MIMO Antenna Using Stepped Impedance Resonator-Based Metasurface For 5G and WIFI ApplicationsAminaMouhoucheNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Compact Dual Band U-Slot Mi 2018 Coax ProbeDocument3 pagesDesign and Analysis of Compact Dual Band U-Slot Mi 2018 Coax ProbeRaaz yousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Edited Final copy-Smart-AntennaDocument39 pagesEdited Final copy-Smart-Antennavenkataramanareddy alekhyaNo ratings yet
- Distributed Systems: Chapter 01: IntroductionDocument163 pagesDistributed Systems: Chapter 01: IntroductionRex MelunNo ratings yet
- Distributed Systems: Chapter 01: IntroductionDocument163 pagesDistributed Systems: Chapter 01: IntroductionRex MelunNo ratings yet
- Lab Week10 SolutionDocument6 pagesLab Week10 SolutionRex MelunNo ratings yet
- The University of The South PacificDocument3 pagesThe University of The South PacificRex MelunNo ratings yet
- Lab Week10 SolutionDocument6 pagesLab Week10 SolutionRex MelunNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Lab 7 - IDL - Interface Description Language: Section 2: Planning and PreparationDocument4 pagesWeek 10 Lab 7 - IDL - Interface Description Language: Section 2: Planning and PreparationRex MelunNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Marriage and Marriage PaymentsDocument11 pagesLecture 3 - Marriage and Marriage PaymentsGrace MguniNo ratings yet
- AMCHAM Press ReleaseDocument1 pageAMCHAM Press ReleaseAnonymous FnM14a0No ratings yet
- Book Notes Covering: Andy Kirk's Book, Data Visualization - A Successful Design ProcessDocument10 pagesBook Notes Covering: Andy Kirk's Book, Data Visualization - A Successful Design ProcessDataVersed100% (1)
- Grade 5 Olympiad: Answer The QuestionsDocument14 pagesGrade 5 Olympiad: Answer The QuestionsVinieysha LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Guide To Networking Essentials Fifth Edition: Making Networks WorkDocument33 pagesGuide To Networking Essentials Fifth Edition: Making Networks WorkKhamis SeifNo ratings yet
- Capitol Medical Center, Inc. v. NLRCDocument14 pagesCapitol Medical Center, Inc. v. NLRCFidel Rico NiniNo ratings yet
- Finman General Assurance Corporation Vs - The Honorable Court of AppealsDocument2 pagesFinman General Assurance Corporation Vs - The Honorable Court of AppealsNorie De los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Germany's Three-Pillar Banking SystemDocument7 pagesGermany's Three-Pillar Banking Systemmladen_nbNo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics and Statistics: Fundamentals ofDocument468 pagesBusiness Mathematics and Statistics: Fundamentals ofSamirNo ratings yet
- University of Nottingham Department of Architecture and Built EnvironmentDocument43 pagesUniversity of Nottingham Department of Architecture and Built EnvironmentDaniahNo ratings yet
- Keywords: Communication, Technology, Collaborative, Evaluative Learning, InnovativeDocument11 pagesKeywords: Communication, Technology, Collaborative, Evaluative Learning, InnovativeNnamani EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Cosare V BroadcomDocument2 pagesCosare V BroadcomapbueraNo ratings yet
- Hilti AnchorDocument5 pagesHilti AnchorGopi KrishnanNo ratings yet
- 7MWTW1710YM0Document8 pages7MWTW1710YM0Izack-Dy JimZitNo ratings yet
- Subsistence and Travel FormsDocument3 pagesSubsistence and Travel FormsAnonymous YRLhQY6G6jNo ratings yet
- 201183-B-00-20 Part ListDocument19 pages201183-B-00-20 Part ListMohamed IsmailNo ratings yet
- Q3 Week 1 Homeroom Guidance JGRDocument9 pagesQ3 Week 1 Homeroom Guidance JGRJasmin Goot Rayos50% (4)
- A88438-23 Critical Procedure 11-01 - Pipeline Cut Outs - A5X9W9Document7 pagesA88438-23 Critical Procedure 11-01 - Pipeline Cut Outs - A5X9W9mahmoudNo ratings yet
- E14r50p01 800 MhaDocument4 pagesE14r50p01 800 Mha'Theodora GeorgianaNo ratings yet
- Power Dense and Robust Traction Power Inverter For The Second Generation Chevrolet Volt Extended Range EDocument8 pagesPower Dense and Robust Traction Power Inverter For The Second Generation Chevrolet Volt Extended Range Ejrz000No ratings yet
- TM9-238 Deepwater Fording of Ordnance Materiel PDFDocument35 pagesTM9-238 Deepwater Fording of Ordnance Materiel PDFdieudecafeNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument61 pagesProblem SetEmily FungNo ratings yet
- Risk, Return & Capital BudgetingDocument18 pagesRisk, Return & Capital BudgetingMuhammad Akmal HussainNo ratings yet
- Transportation Problem VAMDocument16 pagesTransportation Problem VAMLia AmmuNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials-Istanbul .Technical UniversityDocument40 pagesEngineering Materials-Istanbul .Technical UniversitybuggrraaNo ratings yet
- Item No. 6 Diary No 6856 2024 ConsolidatedDocument223 pagesItem No. 6 Diary No 6856 2024 Consolidatedisha NagpalNo ratings yet
- Latifi LAMY Catalog 2013 PDFDocument76 pagesLatifi LAMY Catalog 2013 PDFWang LinusNo ratings yet
- CRM Module 1Document58 pagesCRM Module 1Dhrupal TripathiNo ratings yet
- Median FilteringDocument30 pagesMedian FilteringK.R.RaguramNo ratings yet
- Evaluating The Policy Outcomes For Urban Resiliency in Informal Settlements Since Independence in Dhaka, Bangladesh: A ReviewDocument14 pagesEvaluating The Policy Outcomes For Urban Resiliency in Informal Settlements Since Independence in Dhaka, Bangladesh: A ReviewJaber AbdullahNo ratings yet