Professional Documents
Culture Documents
I No Paleontolog: Eon Era Period Ep H
Uploaded by
Beatriz MogollonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
I No Paleontolog: Eon Era Period Ep H
Uploaded by
Beatriz MogollonCopyright:
Available Formats
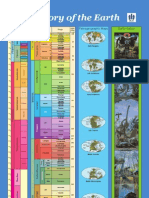
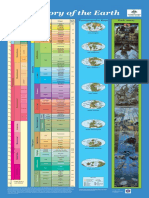
FOSSILS ANO PALEONTOLOGY
rocks found in contact with them. The final result is that the
dates often cited for a particular geologic period or for a cer- TIME UNITS OF THE GEOLOGIC TIME SCALE
tain event are not abstract dates but correspond to a rather (Numbers are absolute dates in millions of years before the present)
precise reality.
As has been seen, the strata are the praduct of the enviran- Eon Era Period Epoch
ment that existed during the time and in the place of their
formation. Environmental changes, which change the kind of Recent or
sediment, its grain size and its quantity, ha ve led to differing Holocene
Quaternary
rack formations in differing locales. Pleistocene
In reality, nowhere in the world is there a series of strata 2
that represents in continuity all the periods of the earth's his-
u
Neogene
Pliocene I
tory. To obtain this ideal series and thus to understand all the '0 5
biological events that have taken place during the geological
N
o
c: >,
Miocene I
24
eras, it is necessary to make correlations among the different <li
U '"'
strata or, even better, among different areas where they existo '.0'"
'"'
<li
¡.....
Oligocene I
37
Such correlations seek to resolve two great geological ques-
Paleogene
tions: the reconstruction of a continuous chronological succes- Eocene
I
58
sion, despite any gaps in a particular strata; and the identifi-
cation of racks of the same age deposited in different places ~ Paleocene
and enviranmental conditions. 11 66
s::
The work required to reconstruct a continuous chranological Q
u
Cretaceous
Q
succession is not easy. Erosion, active in almost all the earth' s .S:! N '0 144
o ., N
N ~ o Jurassic
environments, has often carried away sediments, and tectonic o ~ <Jl
<li
'"' <lic:
<li ¿ 208
phenomena, such as the movement of the earth's crust, have
folded, fractured and often moved entire strata in such a way
.-
c:-a
'" >
..c:
o..?
Triassic
245
that one can no longer say with certainty if they are today 11 Permian
located in the exact spot where they were originally deposited. '"
Q
'- <Jl
286
Among the various gaps in the rack record that paleontolo- '"s:: ;::l
o Pennsylvanian
gists must face, one of the most frequent is that called an un- '"
-t::
~'"'
conforrnity. During the process of sedimentation, for example
~ 'co 320
in a marine environment, undersea currents may remove lay- ...
.!:l
Mississippian
u
ers of sediment where fossils ha ve been deposited. The fossils '0 '"
U
N 360-
in these layers may be destrayed or, in other cases, may be o
<li Devonian
redeposited with sediments of a different age. The difficulties íO
e, 408-
encountered by the presence of such gaps-which can also be Silurian
difficult to identify-are understandable. The paleontologist
438-
must always be alert to avoid identifying as coeval (of the same
Ordovician
age) fossils that, due to one or another geological process, just
happen to be found together while in fact they lived in differ- 505-
ent times. Such interruptions in the strata are very common. Cambrian
Even where interruptions do not exist and one finds instead 570-
layers of strata deposited continuously, without any distur- I
bance, there is still the possibility that fossils of different ages Cryptozoic
were joined through a mechanism called non-deposition, an- Comprises
other cause of difficulty for the paleontologist. The process of About
Proterozoic
sedimentation, as is known, is very variable in intensity, and 87%
in certain moments can in fact be entirely absent. During such '"'o ofthe
e Geologic
a stasis in sedimentary activity no new material will be depos- ,
'" u
°C 0 ° Time Scale
ited, but during the same period there will be no similar dis- .!:l N
2500-
E o
ruption or organic activity. That means that the organisms that
lived during a period characterized by the absence of sedimen-
'" ~c..
u
<li>,
'"' U
o.. ... Archean 1
Origin of
tation will all be deposited together and become mixed with
Earth
the remains of the organisms that lived before them, thus gen- 3800-
About
erating a heap of fossils of different ages very difficult to dis- 4.6 Billion
entangle. Years Ago
Azoic
Other sedimentary phenomenon have contributed to com-
plications in the analysis of rack strata. The partial immersion
22
You might also like
- Papa Jim's Herbal Magic Workbook by Papa JimDocument57 pagesPapa Jim's Herbal Magic Workbook by Papa JimRandom Person100% (1)
- Ferralium 2594 Mod Weld Matl Brochure A4Document22 pagesFerralium 2594 Mod Weld Matl Brochure A4Devan ShanmughaNo ratings yet
- Julie Matthews - Nourishing HopeDocument28 pagesJulie Matthews - Nourishing Hopelucaste50No ratings yet
- Waste World PDFDocument290 pagesWaste World PDFCat of Many Faces67% (3)
- FRM Part 2 - Practice Book - Volume 2 - 2021Document146 pagesFRM Part 2 - Practice Book - Volume 2 - 2021Mridul Saraf100% (1)
- Orange BookDocument43 pagesOrange BookbiosiriNo ratings yet
- Chanan - The Politics of DocumentaryDocument305 pagesChanan - The Politics of DocumentaryMauricio Rosas-HernándezNo ratings yet
- Facility Management Plan (FMP) Facilities Health, Safety & Environmental (Hse) ManagementDocument35 pagesFacility Management Plan (FMP) Facilities Health, Safety & Environmental (Hse) ManagementAhmad Saiful Ridzwan Jaharuddin100% (2)
- Chemistry ProjectDocument10 pagesChemistry ProjectVineet Agarwal50% (4)
- History of The Earth-Tower of TimeDocument1 pageHistory of The Earth-Tower of Timecatacata001100% (1)
- 24 Basic Tai Chi Chuan (Yang Style) : Relaxation and HarmonyDocument2 pages24 Basic Tai Chi Chuan (Yang Style) : Relaxation and HarmonyDharma LingamNo ratings yet
- Nanofiber Production MethodsDocument12 pagesNanofiber Production MethodsSibelKoç100% (2)
- Hydrometeorological Hazard StudentDocument26 pagesHydrometeorological Hazard StudentMargaret Nicole100% (1)
- Altered Volcanic Rocks PDFDocument288 pagesAltered Volcanic Rocks PDFErika Johanna Lozano RubioNo ratings yet
- Deep History of Life On Earth HHMI LabDocument2 pagesDeep History of Life On Earth HHMI LabNoemmy Okhman0% (1)
- Albinson 1988 PDFDocument21 pagesAlbinson 1988 PDFJavier Roberto De AndaNo ratings yet
- Albinson 1988Document21 pagesAlbinson 1988Javier Roberto De AndaNo ratings yet
- Klasifikasi BatuanDocument111 pagesKlasifikasi Batuan0710309197% (30)
- Geological Applications To Petroleum ReservoirDocument76 pagesGeological Applications To Petroleum Reservoiriqbal maratamaNo ratings yet
- PhD-Migration of Leachate Solutin Through Clay SoilDocument362 pagesPhD-Migration of Leachate Solutin Through Clay SoilHamza El FadiliNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Geology of The Nam Con Son BasinDocument11 pagesPetroleum Geology of The Nam Con Son BasinNguyen tiendungNo ratings yet
- Key Words: Polysaccharide Cy Tochemistry: Via Free AccessDocument13 pagesKey Words: Polysaccharide Cy Tochemistry: Via Free Accessnivedhitha palanirajNo ratings yet
- Energies 12 00650Document20 pagesEnergies 12 00650Babalola TomisinNo ratings yet
- Geological Applications To Petroleum ReservoirDocument76 pagesGeological Applications To Petroleum Reservoirelisabet magdalenaNo ratings yet
- Tower PDFDocument1 pageTower PDFasdNo ratings yet
- Petroleum GeologyDocument74 pagesPetroleum Geologyginozky100% (3)
- The PlioceneDocument10 pagesThe PlioceneAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Geology Oct2 StimDocument84 pagesPetroleum Geology Oct2 Stim0710309183% (6)
- Allen1985 - Field ConditionsDocument12 pagesAllen1985 - Field ConditionspedrovadaNo ratings yet
- Neogene Magmatism in The Bolivian Andes Between 16°8 and 18°8: 8tratigraphy and K/Ar GeochronologyDocument13 pagesNeogene Magmatism in The Bolivian Andes Between 16°8 and 18°8: 8tratigraphy and K/Ar GeochronologyPilar Garnica VásquezNo ratings yet
- SCTM 01 PDFDocument19 pagesSCTM 01 PDFMuhammadHaziqYussofNo ratings yet
- Charrier y MuñozDocument10 pagesCharrier y MuñozMatias Gonzalez SuazoNo ratings yet
- Paper With Sem Pictures of CementationDocument29 pagesPaper With Sem Pictures of CementationshantanurilNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics and Continental DriftDocument95 pagesPlate Tectonics and Continental DriftRudic DomencoNo ratings yet
- Matching Rock LayersDocument8 pagesMatching Rock LayersJoverose Manalo VillamorNo ratings yet
- Sandweiss MoseleyFest 2009 OCRDocument16 pagesSandweiss MoseleyFest 2009 OCRDOMENICO FRANSCESC VILLAVICENCIO MERGONINo ratings yet
- Img 0015Document3 pagesImg 0015Chikonde ChikondeNo ratings yet
- cc14 Basic Principles of Chromatography + Column ChromatographyDocument10 pagescc14 Basic Principles of Chromatography + Column ChromatographyAkanksha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Janpre PDFDocument1 pageJanpre PDFMunch LabNo ratings yet
- 3-3 Geological TimescaleDocument30 pages3-3 Geological TimescaleTitat Placedes Taniog100% (1)
- Depositional and Diagenetic Histories of PDFDocument23 pagesDepositional and Diagenetic Histories of PDFkusbarotoNo ratings yet
- 2 Week - Role of Petroleum Geologist in Oil and Gas IndustryDocument10 pages2 Week - Role of Petroleum Geologist in Oil and Gas IndustryChaudry Usman Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Vestibu Lar OrgansDocument46 pagesPhysiology of The Vestibu Lar OrgansYunonNo ratings yet
- Melt Density and The Average Composition of Basalt: Contributions To Mineralogy and PetrologyDocument6 pagesMelt Density and The Average Composition of Basalt: Contributions To Mineralogy and Petrologyrael*No ratings yet
- Provenance and Sediment Dispersal in Relation To Paleotectonics and Paleogeography of Sedimentary BasinsDocument23 pagesProvenance and Sediment Dispersal in Relation To Paleotectonics and Paleogeography of Sedimentary BasinsIsidro Perez OlanNo ratings yet
- M.C. Miller, V. Alexander & R.J. Barsdate The Effects of Oil Spills On Phytoplankton in An Arctic Lake and PondsDocument27 pagesM.C. Miller, V. Alexander & R.J. Barsdate The Effects of Oil Spills On Phytoplankton in An Arctic Lake and PondsGrasicNo ratings yet
- Gip 141Document2 pagesGip 141kevin sebastianNo ratings yet
- Geologic TimeDocument127 pagesGeologic TimeMuhammad Arief Akbar100% (1)
- Iannis Xenakis - Free Stochastic Music (From Formalized Music)Document11 pagesIannis Xenakis - Free Stochastic Music (From Formalized Music)Damián NogueraNo ratings yet
- Definicion Del Denominado Complejo Igneo Basico en Colombia Y Petrogenesis de Su Parte MeridionalDocument22 pagesDefinicion Del Denominado Complejo Igneo Basico en Colombia Y Petrogenesis de Su Parte MeridionalCristina DallosNo ratings yet
- An Aborted Rift Process of Aptian-Albian Age in Central Peru, and Its Significance For The Margin GeodynamicsDocument4 pagesAn Aborted Rift Process of Aptian-Albian Age in Central Peru, and Its Significance For The Margin GeodynamicsMateo Cornejo ZezenarroNo ratings yet
- Cameron 1992Document24 pagesCameron 1992Javier Roberto De AndaNo ratings yet
- Gullierme Archaeology of Section 1989.compressedDocument33 pagesGullierme Archaeology of Section 1989.compressedmaus1945No ratings yet
- At The Edge Terminal Pleistocene HunterDocument509 pagesAt The Edge Terminal Pleistocene HunterPanorama TrabalhandoNo ratings yet
- Plunket, Patricia (Editora) - Domestic Ritual in Ancient Mesoamerica PDFDocument148 pagesPlunket, Patricia (Editora) - Domestic Ritual in Ancient Mesoamerica PDFJesus CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Basic Petroleum GeologyDocument43 pagesBasic Petroleum GeologyCARLOS RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Stratigraphic Chronological Chart History-of-the-Earth-posterDocument1 pageStratigraphic Chronological Chart History-of-the-Earth-posterUdit KumarNo ratings yet
- Out - Copiar PDFDocument11 pagesOut - Copiar PDFalbertoNo ratings yet
- Response Modification Coefficient - For Structural Systems, RDocument3 pagesResponse Modification Coefficient - For Structural Systems, RMuhammad Al MamunNo ratings yet
- Timothy C. Lindsey (1993) - Concrete IdeologyDocument9 pagesTimothy C. Lindsey (1993) - Concrete IdeologyZH0224No ratings yet
- Geochemical Correlation - JanpreDocument1 pageGeochemical Correlation - JanpreLizbethNo ratings yet
- Alteration at The Sam Copper Siler Deposits British ColumbniaDocument125 pagesAlteration at The Sam Copper Siler Deposits British ColumbniaayparraguirreNo ratings yet
- Mathews TheiaLeitourgia RomeDocument12 pagesMathews TheiaLeitourgia RomeMadalin MaticaNo ratings yet
- The Ethnics of Surrealismedwards1998Document53 pagesThe Ethnics of Surrealismedwards1998Francisco FeioNo ratings yet
- Sal I Mullah 1992Document11 pagesSal I Mullah 1992Nyemer BaruelNo ratings yet
- Voices in the Shadows: Women and Verbal Art in Serbia and BosniaFrom EverandVoices in the Shadows: Women and Verbal Art in Serbia and BosniaNo ratings yet
- Integument, Pigments, and Hormonal Processes: Volume 9: Integument, Pigments and Hormonal ProcessesFrom EverandIntegument, Pigments, and Hormonal Processes: Volume 9: Integument, Pigments and Hormonal ProcessesNo ratings yet
- 1996 EntriesDocument26 pages1996 EntriesBeatriz MogollonNo ratings yet
- 216) Escanear0001Document1 page216) Escanear0001Beatriz MogollonNo ratings yet
- 205) Escanear0001Document1 page205) Escanear0001Beatriz MogollonNo ratings yet
- 213) Escanear0001Document1 page213) Escanear0001Beatriz MogollonNo ratings yet
- 216) Escanear0001Document1 page216) Escanear0001Beatriz MogollonNo ratings yet
- 49) Escanear0018Document1 page49) Escanear0018Beatriz MogollonNo ratings yet
- 21) Escanear0015Document1 page21) Escanear0015Beatriz MogollonNo ratings yet
- 20) Escanear0014Document1 page20) Escanear0014Beatriz MogollonNo ratings yet
- 143) Escanear0019 Pag. 143Document1 page143) Escanear0019 Pag. 143Beatriz MogollonNo ratings yet
- 18) Escanear0012Document1 page18) Escanear0012Beatriz MogollonNo ratings yet
- 16) Escanear0010Document1 page16) Escanear0010Beatriz MogollonNo ratings yet
- 11) Escanear0007Document1 page11) Escanear0007Beatriz MogollonNo ratings yet
- 13) Escanear0009Document1 page13) Escanear0009Beatriz MogollonNo ratings yet
- 238) Escanear0001Document1 page238) Escanear0001Beatriz MogollonNo ratings yet
- 236) Escanear0001Document1 page236) Escanear0001Beatriz MogollonNo ratings yet
- 2) PrefaceDocument1 page2) PrefaceBeatriz MogollonNo ratings yet
- 239) Escanear0001Document1 page239) Escanear0001Beatriz MogollonNo ratings yet
- 1a) Escanear0002Document1 page1a) Escanear0002Beatriz MogollonNo ratings yet
- Jeffrey Ansloos - Indigenous Peoples and Professional Training in Psychology in CanadaDocument17 pagesJeffrey Ansloos - Indigenous Peoples and Professional Training in Psychology in CanadaleoNo ratings yet
- Catl Exp 2018 LR PDFDocument276 pagesCatl Exp 2018 LR PDFChera IlieNo ratings yet
- 3 Agricultural PestDocument10 pages3 Agricultural Pest137 - ShubhamNo ratings yet
- Suicide by Firearm Toolkit For ChangeDocument28 pagesSuicide by Firearm Toolkit For ChangeSara WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Teacher - S Roles As A CounsellorDocument19 pagesTopic 3 Teacher - S Roles As A Counsellorlky411No ratings yet
- Personality Week 3bDocument42 pagesPersonality Week 3bAlishba Muhammad SharifNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Terapi Komprehensif HipertensiDocument4 pagesJurnal Terapi Komprehensif HipertensiismiNo ratings yet
- Biological Control Against Diseases and Pests 2011Document194 pagesBiological Control Against Diseases and Pests 2011brkica2011No ratings yet
- CDEP-Structural ReviewerDocument42 pagesCDEP-Structural ReviewerSalted EggNo ratings yet
- Kulith - The Super Pulse PDFDocument5 pagesKulith - The Super Pulse PDFChandaniNo ratings yet
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) - Symptoms - NHSDocument3 pagesIrritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) - Symptoms - NHSadni_wgNo ratings yet
- Social Studies SbaDocument20 pagesSocial Studies SbaAjay SinghNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Laminectomy IntroductionDocument4 pagesLumbar Laminectomy Introduction09194691603No ratings yet
- 4500-LSS Combined Handbook 2.2Document76 pages4500-LSS Combined Handbook 2.2Nguyễn Văn TrungNo ratings yet
- The Effect of The Cementitious Paste Thickness On The Performance of Pervious ConcreteDocument10 pagesThe Effect of The Cementitious Paste Thickness On The Performance of Pervious ConcreteEverton RenatoNo ratings yet
- ! 19 Organic Rankine CycleDocument14 pages! 19 Organic Rankine Cyclesapcuta16smenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document9 pagesChapter 13Michael KemifieldNo ratings yet
- The Perfect Male BreastDocument9 pagesThe Perfect Male BreastVandana ManeNo ratings yet
- Ed 1 XAS H 150-175JD 2001-02Document39 pagesEd 1 XAS H 150-175JD 2001-02Victor Ortega SamNo ratings yet