Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Iii. Analyzing Ideas: Sarah J'Nhelle G. Rocacorba 10 St. Peter
Uploaded by
Sarah Rocacorba0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesOriginal Title
III. ANALYZING IDEAS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesIii. Analyzing Ideas: Sarah J'Nhelle G. Rocacorba 10 St. Peter
Uploaded by
Sarah RocacorbaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Sarah J’Nhelle G. Rocacorba 10 St.
Peter
III. ANALYZING IDEAS
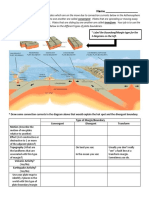
1. jUse a triple Venn diagram to describe, compare, and contrast the three plate boundaries.
CONVERGENT (COLLIDING)
Also called as destructive plate boundary.
It occurs where two plates are pushing toward each
other.
The crust is destroyed and recycled back into the interior
of Earth, while one plate dives under another.
The earthquake they produce are
They has a compression forces. stronger and devastating.
DIVERGENT They both can make a type of Are interacting and colliding with
TRANSFORM
(SPREADING) mountain. each other. FAULT
They are all
Also called as a (LATERAL)
Plate boundaries.
Constructive boundary They can cause an Also called as a Conservative
Two lithospheric plates move apart. earthquake. boundary.
The crust is generated Is a zone between two plates that slide
Is characterized by tensional stresses that horizontally past one another.
normally produce long rift zones, normal There are The transform boundary neither create nor
faults, and basaltic volcanism. volcanoes. destroys a crust.
Are generally vertical and parallel to the
direction of movement.
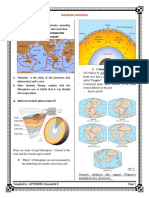
2. Why are transform faults harder to find than divergent and convergent boundaries?
>> Because of its zigzag pattern of movement, most of the faults are found in oceanic
crust, where they accommodate the lateral offset between segments of divergent
boundaries.
You might also like
- Lesson 2 - Plate BoundariesDocument24 pagesLesson 2 - Plate BoundariesArnel Jeffrey OñateNo ratings yet
- Ron Miguel Garcia 1S1Q ELS LW PlateboundariesDocument3 pagesRon Miguel Garcia 1S1Q ELS LW PlateboundariesMartin Rafael Nigel C.No ratings yet
- Science Quarter 1 Week 3.1: CapsletDocument6 pagesScience Quarter 1 Week 3.1: CapsletWesley M. PerezNo ratings yet
- LAS 4 in Science George FernandoDocument4 pagesLAS 4 in Science George Fernandogeorge fernandoNo ratings yet
- Science Saydie Savana TalangDocument4 pagesScience Saydie Savana TalangJUSWAAA LANGNo ratings yet
- Plate Boundaries NotesDocument2 pagesPlate Boundaries NotesGirli JoseeNo ratings yet
- Plate BoundaryDocument1 pagePlate BoundaryAlexa Jill MirandaNo ratings yet
- Ven Diagram: Plates Within These Plate Boundaries, Are Interacting and Colliding With Each Other, Unlike in DivergentDocument1 pageVen Diagram: Plates Within These Plate Boundaries, Are Interacting and Colliding With Each Other, Unlike in DivergentRaphael Louis CaseriaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science ReviewerDocument4 pagesEarth Science ReviewerjesusamarianegallardoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science 5-6Document3 pagesEarth and Life Science 5-6Meryl LinesesNo ratings yet
- TIMBOL, Maverick D. CE163 A2 QUIZ1 1. Explain The Different Sources of Earthquake. Differentiate ThemDocument4 pagesTIMBOL, Maverick D. CE163 A2 QUIZ1 1. Explain The Different Sources of Earthquake. Differentiate ThemMavNo ratings yet
- 6 Managing Natural HazardsDocument30 pages6 Managing Natural HazardsDrift 321No ratings yet
- Activity 5.1 Directions. Perform The Activity Below by Following The InstructionsDocument1 pageActivity 5.1 Directions. Perform The Activity Below by Following The InstructionsBenjie RamirezNo ratings yet
- Science Q1 M4Document9 pagesScience Q1 M4Vyrox MPNo ratings yet
- Sci Reviewer LT1Document15 pagesSci Reviewer LT1Parohinog, Annaiah Zane W.No ratings yet
- Study Guide AnswersDocument4 pagesStudy Guide AnswersYeashika GovilaNo ratings yet
- G10 L1-Plate BounderiesDocument23 pagesG10 L1-Plate Bounderiesmarvs apsNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics - The Action Is at The Edges!Document2 pagesPlate Tectonics - The Action Is at The Edges!api-3808551No ratings yet
- Science Plate BoundariesDocument3 pagesScience Plate BoundariesAshley VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Earth Surface FeaturesDocument5 pagesEarth Surface FeaturesArcey Jayron TañedoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Plate BoundariesDocument46 pagesLesson 2 Plate BoundariesGian Andrei BenaguaNo ratings yet
- Why Do Plates Move?: Than Oceanic Plate) Than Continental Plate)Document2 pagesWhy Do Plates Move?: Than Oceanic Plate) Than Continental Plate)AbvernsyNo ratings yet
- Brown Aesthetic Group Project Presentation - 20231012 - 205957 - 0000Document12 pagesBrown Aesthetic Group Project Presentation - 20231012 - 205957 - 0000Precious Jewel Semillano TaladtadNo ratings yet
- Movement of Plates and Formation of Folds and FaultsDocument9 pagesMovement of Plates and Formation of Folds and FaultsHannah Maesie VelascoNo ratings yet
- Types of Plate BoundariesDocument82 pagesTypes of Plate BoundariesAllen Klein Magno100% (1)
- Science 10-Plate BoundaryDocument19 pagesScience 10-Plate BoundaryPaul LopezNo ratings yet
- Plate MovementsDocument2 pagesPlate MovementsPsalm Ezrah LavadoNo ratings yet
- Earth Life SciencesDocument109 pagesEarth Life SciencesJoenell CabungcalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Module 1 - Plate TectonicsDocument4 pagesUnit 1 - Module 1 - Plate TectonicsJell De Veas Torregoza100% (2)
- Els Advance StudyDocument3 pagesEls Advance StudyKent Joshua Garcia TanganNo ratings yet
- Earth StudyDocument28 pagesEarth Studyrewardfulgueras9No ratings yet
- G8 Q2 Week 1 1Document68 pagesG8 Q2 Week 1 1nutssdeez944No ratings yet
- Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesPlate Boundariesbridget.duncanNo ratings yet
- Een 2.1 Review PDFDocument10 pagesEen 2.1 Review PDFquandric glennNo ratings yet
- Week 5-8: MODULE 5: Divergent Plate BoundariesDocument12 pagesWeek 5-8: MODULE 5: Divergent Plate BoundariesPepito Rosario Baniqued, JrNo ratings yet
- PTR in Sci 10Document5 pagesPTR in Sci 10IanNo ratings yet
- Plate Boundaries and Mag. ReversalsDocument2 pagesPlate Boundaries and Mag. ReversalsEfren Matthew De PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Tectonic Plates NotesDocument3 pagesTectonic Plates NotesAngelica CamilonNo ratings yet
- Geography Handout 4Document14 pagesGeography Handout 4LoviNo ratings yet
- Es 2ND Week34Document27 pagesEs 2ND Week34kiyohachiroNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Plate TectonicsDocument48 pagesUnit 1: Plate TectonicsMarga IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Science Reviewer (Copy)Document3 pagesEnhanced Science Reviewer (Copy)Francis Rafael FlorNo ratings yet
- Plate Movements: (Laboratory Experiment)Document21 pagesPlate Movements: (Laboratory Experiment)Anne QuiaoitNo ratings yet
- Review For First QuarterDocument3 pagesReview For First QuarterMJ DejosNo ratings yet
- Hand-Out For EarthquakesDocument3 pagesHand-Out For EarthquakesalyssaNo ratings yet
- Valentine SlidesCarnivalDocument4 pagesValentine SlidesCarnivalnaomiNo ratings yet
- Sarah J'Nhelle G. Rocacorba 10 St. PeterDocument5 pagesSarah J'Nhelle G. Rocacorba 10 St. PeterSarah RocacorbaNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument3 pagesEarth ScienceMicsNo ratings yet
- First Quarter: Earth Science Second Quarter: Physics Third Quarter: Biology Fourth Quarter: ChemistryDocument32 pagesFirst Quarter: Earth Science Second Quarter: Physics Third Quarter: Biology Fourth Quarter: ChemistryMarieFranz ChuaNo ratings yet
- Activity Worksheet On Plate BoundariesDocument4 pagesActivity Worksheet On Plate BoundariesGlen Ruzzel Ellevera100% (1)
- Earthquake and FaultsDocument1 pageEarthquake and FaultsTricia BautistaNo ratings yet
- DIASTROPHISMDocument37 pagesDIASTROPHISMJam Uly GastyNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM: Summary of Lessons (Part 2) : LECTURE NOTES 2.4: Endogenic ProcessDocument6 pagesMIDTERM: Summary of Lessons (Part 2) : LECTURE NOTES 2.4: Endogenic ProcessJelan ParaisoNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes: Main Menu Table of Contents BackDocument22 pagesEarthquakes: Main Menu Table of Contents BackJâdâ Â. JâçkšøñNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Week 5Document19 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Week 5Lucy Jhamaicka Maruquin IliNo ratings yet
- Q1Wk1Self Learning ActivitiesDocument5 pagesQ1Wk1Self Learning ActivitiesKent0% (1)
- Exposicion Grupo 3Document46 pagesExposicion Grupo 3OscarRomeroVasquezNo ratings yet
- I. Definition:: Endogenic ProcessesDocument10 pagesI. Definition:: Endogenic ProcessesJepoy Nisperos ReyesNo ratings yet
- dIGGIE (AutoRecovered)Document7 pagesdIGGIE (AutoRecovered)redorelle39No ratings yet
- Urine Preservatives - SLUDocument2 pagesUrine Preservatives - SLUShana Flame Haze0% (1)
- 1 - Geography and Its BranchesDocument28 pages1 - Geography and Its BranchesJan Alam100% (2)
- History of Soil MechanicsDocument9 pagesHistory of Soil Mechanicsleah yadaoNo ratings yet
- Non-Explosive Mining Systems For Hard Rock MinesDocument11 pagesNon-Explosive Mining Systems For Hard Rock MinesDimSolNo ratings yet
- Indian Roads June 2009 ExtractDocument57 pagesIndian Roads June 2009 ExtractSaurav TalukdarNo ratings yet
- 100 Geography Questions EnglishDocument4 pages100 Geography Questions EnglishWani Zahoor100% (1)
- Abstract - Seminar - Hyderabad - 3-5 Dec 2008Document107 pagesAbstract - Seminar - Hyderabad - 3-5 Dec 2008kali1No ratings yet
- Shaker Table Plans From WWW Jgokey ComDocument6 pagesShaker Table Plans From WWW Jgokey Comearthplight67% (3)
- Instructions To StudentsDocument58 pagesInstructions To StudentsNitish ShahNo ratings yet
- WTC2013 - BROX - Evaluation of Overstressing in Deep Tunnels - Feb 15 2013 PDFDocument9 pagesWTC2013 - BROX - Evaluation of Overstressing in Deep Tunnels - Feb 15 2013 PDFNicolas Cristobal Correa HernandezNo ratings yet
- Triaxial TestDocument29 pagesTriaxial Testsipil200950% (2)
- IIDocument4 pagesIIuswatun khoiriyah100% (1)
- Earthquake Resistant BuildingsDocument18 pagesEarthquake Resistant BuildingsXaid IbrahimNo ratings yet
- 2 Report Shivam ModasaDocument19 pages2 Report Shivam ModasadhwaniNo ratings yet
- B.tech. Civil Engineering Full Syllabus IndiaDocument118 pagesB.tech. Civil Engineering Full Syllabus IndiaAnubhav GargNo ratings yet
- Construction Method Statement: 6 Hereford Square, London SW7 4TTDocument65 pagesConstruction Method Statement: 6 Hereford Square, London SW7 4TTMubeen NavazNo ratings yet
- Well Logging 2Document32 pagesWell Logging 2Irish Pales CosidonNo ratings yet
- Geomechanics For Geothermal Energy DevelopmentDocument23 pagesGeomechanics For Geothermal Energy Developmentahmed el faramawyNo ratings yet
- AccentureDocument13 pagesAccenturemcaviimsNo ratings yet
- Taxonom 00 BarkDocument272 pagesTaxonom 00 Barkaddina65No ratings yet
- C 119 - 04 - QzexoqDocument7 pagesC 119 - 04 - Qzexoqsebastian novoaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Design of Fish Passage Nova ScotiaDocument95 pagesGuidelines For The Design of Fish Passage Nova ScotiaBar AvaitNo ratings yet
- Soil Forming ProcessesDocument9 pagesSoil Forming ProcessesNur IslamNo ratings yet
- Berberian and King (1981) Towards A Paleogeography and Tectonic Evolution of Lran PDFDocument56 pagesBerberian and King (1981) Towards A Paleogeography and Tectonic Evolution of Lran PDFMeisam RasoulyNo ratings yet
- Topographic Map of Olton NEDocument1 pageTopographic Map of Olton NEHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- De SiltingDocument6 pagesDe Siltingtarang001No ratings yet
- Glacial Cirque PaperDocument5 pagesGlacial Cirque PaperDylan BrazierNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Earthquakes and FaultsDocument2 pagesScience 8 Earthquakes and FaultsJohn Dwayne Angelo Pugosa100% (1)
- Fossil A-Z BookDocument6 pagesFossil A-Z Bookapi-236358005No ratings yet
- ELS Q1 Module-4 Rocks v2Document23 pagesELS Q1 Module-4 Rocks v2Dorothy HernandezNo ratings yet