Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Guide Report
Uploaded by
Ismaeli KielOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Guide Report
Uploaded by
Ismaeli KielCopyright:
Available Formats
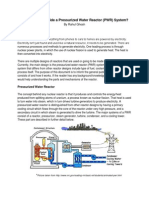
Nuclear reactor
- This hot water is then used to spin turbines that are connected to generators, producing
electricity.
- is a device used to initiate and control a self-sustained nuclear chain reaction. Nuclear
reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine
propulsion.
- The reactor is the heat source for the power plant, just like the boiler is for a coal plant.
Uranium is the dominant nuclear fuel used in nuclear reactors, and its fission reactions
are what produce the heat within a reactor. This heat is then transferred to the reactor's
coolant, which provides heat to other parts of the nuclear power plant.
Steam Generator
- They are heat exchangers where the heat produced in the reactor core is transferred to the
secondary side, the steam system, of the nuclear power plant.
- Their other important function is to provide the barrier between the reactor coolant
- Thus, there are two functional requirements placed on the steam generators. The first is to
act as a heat sink for the reactor core to prevent any core damage. The second functional
requirement is to generate the flow rate of steam from the feedwater supply at the temperature,
pressure and enthalpy conditions necessary to efficiently drive the steam turbine/electric
generating system.
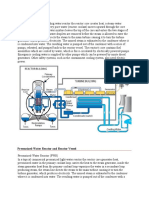
Turbine and Generator
- . The rotation of the turbines is used to spin an electric generator, which produces
electricity that is sent out the electrical grid.
- A steam turbine is a device that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and
uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft.
- Electrical Generator is a device that converts motive power (mechanical energy)
into electrical power for use in an external circuit.
Cooling Towers
- Hot water cools in contact with the air and a small portion, evaporates and raises up
through the top.
- Cooling towers are a special type of heat exchanger that allows water and air to come in
contact with each other to lower the temperature of the hot water. During this process,
small volumes of water evaporate, lowering the temperature of the water that’s being
circulated throughout the cooling tower. In a short summary, a cooling tower cools down
water that gets over heated by industrial equipment and processes.
- When the air and water come together, a small volume of water evaporates, creating an
action of cooling. The colder water gets pumped back to the process/equipment that
absorbs heat or the condenser. It repeats the loop over and over again to constantly cool
down the heated equipment or condensers.
You might also like
- ME Lab 2 Module No. 2Document17 pagesME Lab 2 Module No. 2Ismaeli Kiel86% (7)
- ME Lab 2 Module No. 2Document17 pagesME Lab 2 Module No. 2Ismaeli Kiel86% (7)
- Summer Training Report On NTPC Tanda, Ambedkar NagarDocument9 pagesSummer Training Report On NTPC Tanda, Ambedkar NagarAliraza7660% (5)
- Energy QuestionsDocument2 pagesEnergy QuestionsAbdisalaam mohamudNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers - Nuclear Power PlantDocument8 pagesQuestions and Answers - Nuclear Power PlantAkd Deshmukh100% (1)
- Homework 1 (Solution)Document8 pagesHomework 1 (Solution)Suleyman QayumNo ratings yet
- Me Lab 3Document27 pagesMe Lab 3Jerome Vega AndesNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion in A Nuclear Power Plant 46-50Document3 pagesEnergy Conversion in A Nuclear Power Plant 46-50pagal noobNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant: Definition: The Power Plant That Is Used To Warm The Water ToDocument5 pagesNuclear Power Plant: Definition: The Power Plant That Is Used To Warm The Water ToYash SoniNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power StationDocument4 pagesNuclear Power StationAnjo PepitoNo ratings yet
- Layout of Thermal Power PlantDocument21 pagesLayout of Thermal Power PlantRaj_Jai03100% (1)
- Chapter Two Literature Review 2.1 Technical Feasibility StudyDocument20 pagesChapter Two Literature Review 2.1 Technical Feasibility StudymutencoNo ratings yet
- What Happens Inside A Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) System?Document3 pagesWhat Happens Inside A Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) System?Rahul GhoshNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Power PlantDocument6 pagesGeothermal Power PlantDonabell B. MonteclarosNo ratings yet
- Operation of A Nuclear Power PlantDocument8 pagesOperation of A Nuclear Power PlantMuhamad FaizNo ratings yet
- GeothermalDocument7 pagesGeothermalGilbert Sta BrigidaNo ratings yet
- 40.6 MW Regenerative Thermal Power PlantDocument115 pages40.6 MW Regenerative Thermal Power PlantJohn Fil PabloNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Powerplant: Dan Emil A. Bernardino Sherwin Q. Bihasa Harry Lhon B. PobleteDocument15 pagesNuclear Powerplant: Dan Emil A. Bernardino Sherwin Q. Bihasa Harry Lhon B. PobleteRonald Andrei DaguioNo ratings yet
- The Blueprint Provides An Overview of The Key Stages in Power Production in A Nuclear Power PlantDocument1 pageThe Blueprint Provides An Overview of The Key Stages in Power Production in A Nuclear Power PlantTùng Linh LêNo ratings yet
- PoweplantDocument33 pagesPoweplantAgateNo ratings yet
- تقرير محطات الطاقهDocument45 pagesتقرير محطات الطاقهعبد الرحمن إبراهيمNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine Electrical Generator Condensed Condenser: Part C Unit 1Document7 pagesSteam Turbine Electrical Generator Condensed Condenser: Part C Unit 1RichardNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant Diagram All You Need To Know About ItDocument7 pagesThermal Power Plant Diagram All You Need To Know About Itngoc hoangNo ratings yet
- Cfakepathlayoutofthermalpowerplant 091031114144 Phpapp01Document21 pagesCfakepathlayoutofthermalpowerplant 091031114144 Phpapp01Shruti GuptaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant - WikipediaDocument19 pagesNuclear Power Plant - Wikipediashrawani waghNo ratings yet
- Types of ReactorDocument3 pagesTypes of ReactorTariq AhmedNo ratings yet
- Parts of Geothermal Power PlantDocument6 pagesParts of Geothermal Power Plantpapanoggie50% (2)
- Geothermal Power Plant Types and ProcessDocument6 pagesGeothermal Power Plant Types and ProcessMaher MarquezNo ratings yet
- Boiler Temperature ControllerDocument6 pagesBoiler Temperature ControllerAlokNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument7 pagesNuclear Power PlantzzaanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3Document11 pagesLab Report 3Samsung Note 9No ratings yet
- Abhishek Kumar Asif Ahmad Niket Rakeshan Zeeshan AliDocument21 pagesAbhishek Kumar Asif Ahmad Niket Rakeshan Zeeshan AliSuphi YükselNo ratings yet
- Hydrothermal power plant physics assignmentDocument8 pagesHydrothermal power plant physics assignmentTAKIA MOSHARREFNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Power Plants in India and Abroad.: Siddhant Yadav RA1911026010043 Waste To Wealth To Wheels AssignmentDocument5 pagesDifferent Types of Power Plants in India and Abroad.: Siddhant Yadav RA1911026010043 Waste To Wealth To Wheels AssignmentSiddhant YadavNo ratings yet
- Powergeneration 190508075320Document19 pagesPowergeneration 190508075320SRINIVAS TNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2: 2.0 Rankine Cycle As A Two-Phase Power SystemDocument23 pagesThermodynamics 2: 2.0 Rankine Cycle As A Two-Phase Power SystemMarianne DevillenaNo ratings yet
- National Capital Power Station N.T.P.C: Presented by KshitijDocument25 pagesNational Capital Power Station N.T.P.C: Presented by KshitijHarshit MittalNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training PresentationDocument25 pagesIndustrial Training PresentationHarshit MittalNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PPTDocument49 pagesNuclear PPTA ABHISHEK MARSHALLNo ratings yet
- Report #1: Alternating-Current Project: Steam-Electric Power PlantDocument41 pagesReport #1: Alternating-Current Project: Steam-Electric Power PlantKian TecsonNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument4 pagesReportizni fatinNo ratings yet
- Project Report by Manish YadavDocument53 pagesProject Report by Manish Yadavmanish yaduvanshiNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant ComponentsDocument53 pagesThermal Power Plant ComponentsDhaksha AnieshNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument12 pagesLab ReportFaisal ArslanNo ratings yet
- Presented By:-: Rohit Sharma EEE 1711580Document18 pagesPresented By:-: Rohit Sharma EEE 1711580Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Thermal EngineeringDocument10 pagesThermal Engineeringlokeshdhangar842No ratings yet
- Stirling LaboratoryDocument4 pagesStirling LaboratorySilviu DnlNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant BasicsDocument5 pagesNuclear Power Plant BasicsAri HariNo ratings yet
- Corpuz Science GeothermalDocument2 pagesCorpuz Science GeothermalArah Mae BonillaNo ratings yet
- Study of condensers in nuclear power plantsDocument8 pagesStudy of condensers in nuclear power plantsPutrii MaharaniiNo ratings yet
- Amulya Gaikwada ProjectDocument34 pagesAmulya Gaikwada ProjectHarikrishna NethaNo ratings yet
- Types of Power Plants and Energy Sources in 40 CharactersDocument71 pagesTypes of Power Plants and Energy Sources in 40 CharactersJeff Justine GeragaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic ReservoirsDocument6 pagesThermodynamic ReservoirsJosue RamirezNo ratings yet
- Power Plant FamiliarisationDocument110 pagesPower Plant FamiliarisationmrdipakwaghNo ratings yet
- Honorable Chief Engineer (Thermal) Genco, FaisalabadDocument50 pagesHonorable Chief Engineer (Thermal) Genco, FaisalabadraowaleedahmadNo ratings yet
- Paper CoolingtowersDocument6 pagesPaper CoolingtowersJane PondulanNo ratings yet
- Captive Power PlantDocument30 pagesCaptive Power PlantDeepakGawasNo ratings yet
- Physical study of the Steam-Generating UnitDocument12 pagesPhysical study of the Steam-Generating UnitIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Types of Power Plant and Their Working PrinciplesDocument11 pagesTypes of Power Plant and Their Working PrinciplesRamzi JamalNo ratings yet
- Energy Management Module IDocument18 pagesEnergy Management Module ISalikNo ratings yet
- Pressurised Water Reactor:: Hydro Electric Power PlantDocument7 pagesPressurised Water Reactor:: Hydro Electric Power PlantRajiv Ranjan SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Power Plants: For Internal Circulation OnlyDocument5 pagesUnit 1: Power Plants: For Internal Circulation OnlyRahul munthaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Thermal Power Generation: November 2020Document6 pagesFundamentals of Thermal Power Generation: November 2020Aram Nasih MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering: Steam Power Plant BasicsDocument9 pagesMechanical Engineering: Steam Power Plant BasicsMukesh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningFrom EverandThermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Sample ProblemsDocument5 pagesSample ProblemsIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- STS Midterm AnswerDocument1 pageSTS Midterm AnswerIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument4 pagesAdvantages and DisadvantagesIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Region VI Western VisayasDocument93 pagesRegion VI Western VisayasIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- ACT1 - Low Temperature RefrigerationDocument4 pagesACT1 - Low Temperature RefrigerationIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Conveyors and Conveying Systems ExplainedDocument17 pagesConveyors and Conveying Systems ExplainedIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Practice ProblemDocument3 pagesPractice ProblemIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Region VI Western VisayasDocument93 pagesRegion VI Western VisayasIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument3 pagesNuclear Power PlantIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Industrial Process Module No. 1Document16 pagesIndustrial Process Module No. 1Ismaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Classification, Applications and Operations of MachinesDocument19 pagesModule 4 - Classification, Applications and Operations of MachinesIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Industrial Process Module No. 1Document14 pagesIndustrial Process Module No. 1Ismaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Machine Shop Theory: Classification, Applications and Operations of MachinesDocument5 pagesMachine Shop Theory: Classification, Applications and Operations of MachinesIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Project 1-AnvilDesignDocument1 pageProject 1-AnvilDesignIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Machine Shop Theory: Classification, Applications and Operations of MachinesDocument5 pagesMachine Shop Theory: Classification, Applications and Operations of MachinesIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- ME Lab 2 Module No. 5 PDFDocument24 pagesME Lab 2 Module No. 5 PDFIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Industrial Processes Module on Separation and Classification of SolidsDocument17 pagesIndustrial Processes Module on Separation and Classification of SolidsIsmaeli Kiel100% (1)
- Module 3 - Classification, Applications and Operations of MachinesDocument5 pagesModule 3 - Classification, Applications and Operations of MachinesIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Classification, Applications and Operations of MachinesDocument5 pagesModule 3 - Classification, Applications and Operations of MachinesIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Physical study of the Steam-Generating UnitDocument12 pagesPhysical study of the Steam-Generating UnitIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- ME Lab 2 Module No. 3 PDFDocument36 pagesME Lab 2 Module No. 3 PDFIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Physical study of the Steam-Generating UnitDocument12 pagesPhysical study of the Steam-Generating UnitIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Conveyors and Conveying Systems ExplainedDocument17 pagesConveyors and Conveying Systems ExplainedIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Thesis Chapter 1 ReviseDocument7 pagesThesis Chapter 1 ReviseIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Industrial Process Module No. 1Document14 pagesIndustrial Process Module No. 1Ismaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Raphex QuestionsDocument25 pagesRaphex QuestionsHayrullo ShoniyozovNo ratings yet
- Towards Reactor inDocument3 pagesTowards Reactor inJAMIE ALYANNA LEGASPINo ratings yet
- Fukushima Citations PDFDocument51 pagesFukushima Citations PDFSeng LyhorNo ratings yet
- Chicago Pile 1Document14 pagesChicago Pile 1Cyrus Yu Shing ChanNo ratings yet
- Lead-Cooled Fast Reactor: Modular Nuclear Reactors Advantages Disadvantages ImplementationDocument5 pagesLead-Cooled Fast Reactor: Modular Nuclear Reactors Advantages Disadvantages Implementationapawebet-1195No ratings yet
- Persuasive EssayDocument4 pagesPersuasive Essayapi-357140302100% (1)
- The Manhattan Project and The Atomic Bomb: Second World War Franklin RooseveltDocument6 pagesThe Manhattan Project and The Atomic Bomb: Second World War Franklin RooseveltM4 TechsNo ratings yet
- CurrentDocument38 pagesCurrentMUHAMMAD ASIMNo ratings yet
- Chernobyl's Case StudyDocument4 pagesChernobyl's Case StudyVinu VelouNo ratings yet
- Liquid Metal Fast Breeder Reactor: Mona Mary Varghese Reg. No: Gcaocap008Document19 pagesLiquid Metal Fast Breeder Reactor: Mona Mary Varghese Reg. No: Gcaocap008MONA MARYNo ratings yet
- Redundant US nuclear testing and lasting environmental impactsDocument11 pagesRedundant US nuclear testing and lasting environmental impactsSneeakyAsianNo ratings yet
- Atom Bomb Lecture NotesDocument46 pagesAtom Bomb Lecture Notessn_crowley9661No ratings yet
- IAEA Activities On Research Reactor SafetyDocument26 pagesIAEA Activities On Research Reactor SafetyMohd Zulhairi Mohd NoorNo ratings yet
- P&ID Tutorial QuestionsDocument5 pagesP&ID Tutorial QuestionsshafNo ratings yet
- Technische Beschreibung KKL enDocument32 pagesTechnische Beschreibung KKL enapi-351853154100% (1)
- Seminar NuclearDocument2 pagesSeminar NuclearPanKajNo ratings yet
- Prepared by Hasin Mussayab Ahmed, Lecturer, Dept of EEE, UU: Power Plant Engineering Lecture On Nuclear Power PlantDocument26 pagesPrepared by Hasin Mussayab Ahmed, Lecturer, Dept of EEE, UU: Power Plant Engineering Lecture On Nuclear Power Plantহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- Fukushima Nuclear Disaster - ScriptDocument2 pagesFukushima Nuclear Disaster - ScriptRosa SeijasNo ratings yet
- Calculation Analysis On The Natural Circulation of A Passive Residual Heat Removal System For IPWRDocument9 pagesCalculation Analysis On The Natural Circulation of A Passive Residual Heat Removal System For IPWRGanjar GilaNo ratings yet
- How To Obtain and Extract AmericiumDocument9 pagesHow To Obtain and Extract AmericiumFrank M CNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power in PakistanDocument32 pagesNuclear Power in PakistanShahrukh SaleemNo ratings yet
- News Item Text PaperDocument6 pagesNews Item Text PaperYurii IINo ratings yet
- PSR Personal NarrativeDocument9 pagesPSR Personal Narrativeapi-315141355No ratings yet
- Notice: Reports and Guidance Documents Availability, Etc.: Amergen Energy Co., LLCDocument1 pageNotice: Reports and Guidance Documents Availability, Etc.: Amergen Energy Co., LLCJustia.comNo ratings yet
- Mark SchemeDocument12 pagesMark SchemeLeng RyanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power StationsDocument17 pagesNuclear Power StationsPrathap VuyyuruNo ratings yet
- Step 3 Fault Studies Assessment of The Edf and Areva Uk EprDocument63 pagesStep 3 Fault Studies Assessment of The Edf and Areva Uk EprEnformableNo ratings yet