Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Study Guide For Module No. 3
Uploaded by
Ruby Ann MariñasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Study Guide For Module No. 3
Uploaded by
Ruby Ann MariñasCopyright:
Available Formats
FM-AA-CIA-15 Rev.
0 10-July-2020
Study Guide in (Mgt 102: Human Behavior in Organization) Module No. 3
STUDY GUIDE FOR MODULE NO. 3
LEARNING, PERCEPTION AND ATTRIBUTION
MODULE OVERVIEW
In an organization, a person needs to deal with his/her co-workers in order to reach to a certain goal
that is given by those in position. Whenever someone communicates with his/her workmates, she/he needs
to understand and respect the views and perceptions of him/her because it might have possible effects to
their work. But, how can someone do it? Well, it is simply by knowing the behavior or having a background
knowledge about that person. Through this, someone is able to know his/her limitations and will know the
appropriate treatment for that person.
Learning, perception, and attribution are important concepts that a person must to know to
effectively deal and communicate with other people. By knowing these three, one can easily identify the
proper way to deal with his/her organization effectively.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
By studying this module, you are expected to:
1. Define Learning
2. Discuss the theories of learning
3. List the factors influencing perception
4. Define what attribution is
5. Cite common attribution errors
6. List factors that influence attribution and the shortcuts used in forming impression of others
LEARNING CONTENTS
LEARNING
What is learning? What first comes into you mind whenever you hear this word. For some, they might
probably think of it as dealing with studies and academic stuff over and over again. But, actually, it is
mentioned in an article that learning involves far more than thinking. It involves the whole personality -
senses, feelings, intuition, beliefs, values and will. From this definition, we can say that through learning, a
person can change its behavior. In addition, it further widens our perspective and views on different aspects
of life.
Behavioral change happens when we gained a new knowledge or understanding on something. It has
been defined have been defined as information systems that form, alter, or reinforce attitudes, behaviors, or
acts of complying without using deception or coercion (Oinas-Kukkonen, 2013). As a result, one’s mind will
control his/her body and do what we she/he have learned or discovered.
For instance, Ms. Samantha Nathalia who used to sleep for just three hours a day because of video
games by chance have watched a video regarding the negative effects of having lack of sleep. Through the
video, she knew that it will cause bad effects on her body. And so, she was convinced and by that she
started to change her sleeping schedule.
From that situation, Ms Samantha Nathalia’s behavior change is a result of an indirect experience, in
other words by watching a video. Actually, she has two options, to continue satisfying herself for hours or to
reduce number of hours in playing video games but she chose to stick on what she had learned. By this, we
can clearly see that it is a result of change in behavior.
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 1
FM-AA-CIA-15 Rev. 0 10-July-2020
Study Guide in (Mgt 102: Human Behavior in Organization) Module No. 3
THEORIES OF LEARNING
Through studies, researcher have developed theories that help explain the process of learning.
These theories include classical conditioning, operant conditioning, and social learning .
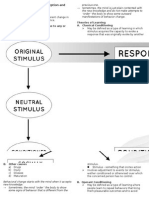
CLASSICAL CONDITIONING
Classical conditioning is also known as Pavlovian conditioning. It is leaning by association and was
discovered by a Russian psychologist, Pavlov. In other words, two stimuli are being linked together in order
to create a new response form an animal or a person.
OPERANT CONDITIONING
Operant conditioning is also referred as instrumental conditioning. It is a process of learning that
involves either reward or a punishment for a particular behavior. By this, an association is made between a
behavior and a consequence which can be positive or negative for that behavior. It can be also defined as a
learning where people might repeat the behavior or avoid the behavior based on the outcome.
This concept can be applied to workplace. Like the classical conditioning, it would help the
employees achieve a goal easily and work efficiently. A situation that can be associated with it is an
employee who submits his/her task three days before the said deadline and commended by his/her boss is
expected to repeat his/her behavior because of the positive outcome of his/her behavior.
How can we differentiate classical conditioning from operant conditioning?
In classical conditioning, it involves associating an involuntary response and stimulus, while operant
conditioning is about associating a voluntary behavior and an outcome of that said behavior.
SOCIAL LEARNING
The third theory is social learning. Social learning theory is referred as the process of observing
behavior of other people, analyzing them, as a result we will alter those based on the outcome and
integrating those in our actions or daily living.
In society, we call those individuals who are observed as models. In society, children are surrounded by
many influential models, such as parents within the family, characters on children’s TV, friends within their
peer group and teachers at school.
Social Learning is achieved in three ways:
a.by observing what happens to other people;
b. by being told about something;
c. through direct experience
PERCEPTION
One’s behavior is not only a function of its personality, values and preferences but also of a
situation. Mostly, we evaluate the environment, interpret events, formulate responses and act accordingly.
This underscore the essentials of understanding the concept of perception.
Perception is defined as the process by which a person detect and interpret information from their
environment.
Factors Influencing Perception
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 2
FM-AA-CIA-15 Rev. 0 10-July-2020
Study Guide in (Mgt 102: Human Behavior in Organization) Module No. 3
1. the Perceiver
2. the Target
3. the Situation
The Perceiver
The person who view the target is the perceiver. His interpretation of the target is influenced by
factors that are unique to him such as:
1. past experiences
2. needs or motives
3. personality
4. values and attitudes
The Target
It is the person, object or event that is perceived by another person. The following are
characteristics of the target:
1. contrast
2. intensity
3. figure-ground separation
4. size
5. motion
6. repetition or novelty
The Situation
Surrounding environment also affects perception. The situational factors that affect perception are:
1. time
2. work setting
3. social setting
ATTRIBUTION
1. One theory that is also useful to better understand human behavior is attribution theory. It is the
process by which people assign causes to the behavior they perceive.
Common Attribution Errors
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 3
FM-AA-CIA-15 Rev. 0 10-July-2020
Study Guide in (Mgt 102: Human Behavior in Organization) Module No. 3
When people try to determine the causes of people’s behavior, errors commonly happen. These
errors maybe classified into the following types:
1. The fundamental attribution errors
2. The self-serving bias
The fundamental attribution errors also known as correspondence bias or attribution effect refers
to the tendency for people overemphasize personal characteristics and under-emphasize the
influence of external factors.
The self-serving bias is an attribution error whereby people tend to ascribe their achievements to
their good inner qualities and they associate their failures to adverse factors within the environment.
Factors that Influence Attribution
1. Distinctiveness
2. Consensus
3. Consistency
Distinctiveness is the extent to which an individual behaves in the same way across different
situations.
The chance that all those facing the same situation will have the same or similar responses.
Consistency is the measure of whether a person respond the same way across time.
SHORTCUTS USED IN FORMING IMPRESSIONS OF OTHERS
1. Selective Perception
2. Halo effect
3. Contrast effects
4. Projection
5. Stereotyping
Selective perception is a process by which individuals selectively interpret what they see on the
basis of their interests, background, experience and attitudes.
Halo effect happens when one attribute of an individual or situation is used to develop an overall
impression of the person or situation.
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 4
FM-AA-CIA-15 Rev. 0 10-July-2020
Study Guide in (Mgt 102: Human Behavior in Organization) Module No. 3
Contrast effects refers to the evaluation of a person’s characteristics that are affected by comparisons
with other people recently encountered who rank higher or lower on the same characteristics.
Projection is attributing one’s own thoughts, feelings, or motives to another.
Stereotyping refers to a generalized belief over a category pf people. It is judging someone on the
basis of one’s perception of the group to which that persons belongs.
SUMMARY
It is very essential to have a knowledge of learning, perception and attribution for understanding
people’s behavior
Change in behavior may be due to learning or other causes
Classical conditioning, operant conditioning and social learning are theories that help explain the
learning process
Perception is influenced by the characteristics of the perceiver, the target and the situation.
Attribution is the process by which people ascribe causes to the behavior they perceive
Attribution errors are fundamental attribution error and self-serving bias
Attribution is affected by several factors such as distinctiveness, consensus, and consistency
There are shortcuts in forming impression of others: selective perception, halo effect, contrast
effects, projection and stereotyping.
LEARNING ACTIVITIES
To be uploaded in the MS Teams Class-Assignment section
REFERENCES
Banfield Paul, Introduction to Human Resource Management, 3rd ed, , Oxford University Press,2018
Martin,Graeme, Siebet Sabina, Managing People and Organizations in Changing Context, Routledge, 2016
Medina, Roberto G., Human Behavior in Organization, Rex Bookstore,2011
Zarate, Cynthia, Organizational Behavior and Management in Philippine Organizations, Rex Bookstore
Judge, T. Robins, S.Organizational Behavior(17th ed).Pearson education limited, 2017
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 5
FM-AA-CIA-15 Rev. 0 10-July-2020
Study Guide in (Mgt 102: Human Behavior in Organization) Module No. 3
https://www.skillsyouneed.com/learn/learning.html
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/behavior-change
the book
https://www.simplypsychology.org/classical-conditioning.html
https://www.verywellmind.com/classical-vs-operant-conditioning-2794861#:~:text=Classical%20conditioning
%20involves%20associating%20an,conditioning%20involves%20no%20such%20enticements.
https://www.simplypsychology.org/bandura.html
https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-orgbehavior/chapter/3-4-perception/
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 6
You might also like
- The Gateway Experience Guidance ManualDocument45 pagesThe Gateway Experience Guidance Manualremusnic92% (12)
- Lipton (2007) - The Wisdom of Your Cells PDFDocument20 pagesLipton (2007) - The Wisdom of Your Cells PDFKlaus Fischer100% (1)
- Uncommon Ground: Radical Approaches To Artistic PracticeDocument32 pagesUncommon Ground: Radical Approaches To Artistic PracticeArtlinkEdinburghNo ratings yet
- The Scientific Basis of Energy Healing Carol L. Bowman, MDDocument12 pagesThe Scientific Basis of Energy Healing Carol L. Bowman, MDUmashankar GoudNo ratings yet
- Safety Culture AssessmentDocument11 pagesSafety Culture AssessmentViny SouzaNo ratings yet
- Learning Perception and AttributionDocument32 pagesLearning Perception and AttributionJecyl33% (3)
- Organisational Behaviour Qs.1: Explain The Importance of Studying Organisational Bahaviour?Document8 pagesOrganisational Behaviour Qs.1: Explain The Importance of Studying Organisational Bahaviour?DaminiSaraf100% (1)
- The Social Cognitive Theory With DiabetesDocument4 pagesThe Social Cognitive Theory With Diabetesnaghma28cintaNo ratings yet
- Learning, Perception, and AttributionDocument13 pagesLearning, Perception, and Attributionpedro motolaNo ratings yet
- 6 Cognitive Learning TheoryDocument3 pages6 Cognitive Learning TheoryFaiza GandapurNo ratings yet
- Bandura - Social Learning TheoryDocument5 pagesBandura - Social Learning TheoryDenise DianeNo ratings yet
- Ba Applied Management Y2 Sem 2 Principle of Performance and Professional DevelopmentDocument11 pagesBa Applied Management Y2 Sem 2 Principle of Performance and Professional DevelopmentMiron 6053No ratings yet
- MBA - (1 Year) Organizational Behavior Unit - IDocument16 pagesMBA - (1 Year) Organizational Behavior Unit - Ihemantagrawal88No ratings yet
- Hbo 3Document4 pagesHbo 3Cristine S. DayaoNo ratings yet
- Unit III CBMRDocument41 pagesUnit III CBMRBaby DasNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior (Perception)Document5 pagesHuman Behavior (Perception)Arna Francis Amor CosidoNo ratings yet
- Social Cognitive TheoryDocument3 pagesSocial Cognitive Theoryyanni estilloreNo ratings yet
- Final Practical File IGNOU Rinku JainDocument37 pagesFinal Practical File IGNOU Rinku JainRani BiswasNo ratings yet
- Attention ProcessesDocument19 pagesAttention ProcessesKaamwaalaNo ratings yet
- TheoryDocument20 pagesTheorysalons.errands0hNo ratings yet
- Part-2 Management For Rbi Grade BDocument171 pagesPart-2 Management For Rbi Grade BJYOTI PRAKASH SINGHNo ratings yet
- What Does The Phrase "Behavior Is Caused" Mean?: Montgomery, Jerald James G. Organizational BehaviorDocument10 pagesWhat Does The Phrase "Behavior Is Caused" Mean?: Montgomery, Jerald James G. Organizational Behaviorjerald james montgomeryNo ratings yet
- PART 3 - Learning, Perception, and AttributionDocument9 pagesPART 3 - Learning, Perception, and AttributionRose John SupranesNo ratings yet
- Band UraDocument27 pagesBand UraRio ReyesNo ratings yet
- Teaching Is An Integral Component of Nursing PracticeDocument4 pagesTeaching Is An Integral Component of Nursing PracticeMajorie ArimadoNo ratings yet
- OrganisationalBehaviour BookDocument316 pagesOrganisationalBehaviour BookvidhyaaravinthanNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Learning TheoryDocument2 pagesCognitive Learning TheoryMokaHanaMatsuNo ratings yet
- Social Cognitive TheoryDocument9 pagesSocial Cognitive TheoryAfshan AmjadNo ratings yet
- OB Answers MergedDocument63 pagesOB Answers MergedbgodabaNo ratings yet
- Attitude, Personality, PerceptionDocument36 pagesAttitude, Personality, PerceptionHappiness GroupNo ratings yet
- Albert Bandura's Social Cognitive TheoryDocument24 pagesAlbert Bandura's Social Cognitive TheoryMs. Huma JavedNo ratings yet
- 38 Management Process and Organization BehaviourDocument23 pages38 Management Process and Organization BehaviourTanveer DhillonNo ratings yet
- Hbo Exam Notes 1-2Document7 pagesHbo Exam Notes 1-2Joseph LapasandaNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior (OB)Document24 pagesHuman Behavior (OB)carl patNo ratings yet
- Smu Assignment Semester 1 CompleteDocument133 pagesSmu Assignment Semester 1 Completed-fbuser-79128657100% (2)
- Chapter 3:individual Perception and Decision-MakingDocument17 pagesChapter 3:individual Perception and Decision-MakingSadiqSagheerNo ratings yet
- 1st Module in Human Behavior and VictimologyDocument52 pages1st Module in Human Behavior and VictimologyNarag Krizza100% (1)
- M5 PersonalitytheoriesDocument6 pagesM5 PersonalitytheoriesFauzia SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Pro El 2 - Chapter 1Document3 pagesPro El 2 - Chapter 1JpzelleNo ratings yet
- Unit 3.1 Fundamentals of OBDocument22 pagesUnit 3.1 Fundamentals of OBPalak GuptaNo ratings yet
- ROLL531110359 Assignment Set-1 Master of Business Administration-MBA Semester 1Document16 pagesROLL531110359 Assignment Set-1 Master of Business Administration-MBA Semester 1magbool1294No ratings yet
- Week 3 Behaviour Change Models - r1Document20 pagesWeek 3 Behaviour Change Models - r1ptkabworldNo ratings yet
- Albert BanduraDocument4 pagesAlbert BanduraJonna Mae QuinoneroNo ratings yet
- Smu Assignment Semester 1 Complete 2Document134 pagesSmu Assignment Semester 1 Complete 2Subhransu PandaNo ratings yet
- FMOB Research PaperDocument25 pagesFMOB Research PaperPriyansh BachaniNo ratings yet
- Health Psychology BehaviourismDocument28 pagesHealth Psychology BehaviourismNasim AkhtarNo ratings yet
- OB Chapter TwoDocument64 pagesOB Chapter Twodameregasa08No ratings yet
- Write A Note On The Functions of Management.: Bobodoll Experiment (S)Document7 pagesWrite A Note On The Functions of Management.: Bobodoll Experiment (S)Manoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Behavior Change WebDocument7 pagesBehavior Change WebSilky GaurNo ratings yet
- Individual Differences, Mental Ability, and Personality: Study Guide For Module No. 2Document9 pagesIndividual Differences, Mental Ability, and Personality: Study Guide For Module No. 2Ruby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 HBODocument3 pagesChapter 1 HBOJoseph LapasandaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document8 pagesModule 1Kevin Von AnchetaNo ratings yet
- LAS 1 HBO (Midterms)Document6 pagesLAS 1 HBO (Midterms)Alexander AugustusNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Individual and Organisational Leadership.Document19 pagesUnit 2 - Individual and Organisational Leadership.Ganasa GowdaNo ratings yet
- UCU-HBO MOdule 1Document7 pagesUCU-HBO MOdule 1Jerlmilline Serrano Jose100% (1)
- HBO Lesson 3 LEARNING, PERCEPTION AND ATTRIBUTIONDocument10 pagesHBO Lesson 3 LEARNING, PERCEPTION AND ATTRIBUTIONJeremy Ane GoopioNo ratings yet
- MANIPULATION: Mastering the Art of Persuasion, Recognizing Manipulation, and Guarding Your Mind (2024)From EverandMANIPULATION: Mastering the Art of Persuasion, Recognizing Manipulation, and Guarding Your Mind (2024)No ratings yet
- Putting Mind Control Tactics In Your Daily Life : Exploit This Technology To Get What You Want, And Be Protected Against Its Powers!From EverandPutting Mind Control Tactics In Your Daily Life : Exploit This Technology To Get What You Want, And Be Protected Against Its Powers!No ratings yet
- Applied Human Behavioural Power and Sexual Dynamics: The Book of Social and Sexual Dominance -From EverandApplied Human Behavioural Power and Sexual Dynamics: The Book of Social and Sexual Dominance -No ratings yet
- Dynamic Dialogues: A Human-Centered Approach to Navigate the Flaws of FeedbackFrom EverandDynamic Dialogues: A Human-Centered Approach to Navigate the Flaws of FeedbackNo ratings yet
- Work Immersion Portfolio EditedDocument49 pagesWork Immersion Portfolio EditedRuby Ann Mariñas100% (1)
- House RulesDocument1 pageHouse RulesRuby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument1 pageNarrative ReportRuby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledRuby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- AnchetaDocument1 pageAnchetaRuby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- One of The Unforgettable Memories From My Life in 2022 Was When I Went To BAGBAG BEACH With My FamilyDocument1 pageOne of The Unforgettable Memories From My Life in 2022 Was When I Went To BAGBAG BEACH With My FamilyRuby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- PDF 20230117 072821 0000Document1 pagePDF 20230117 072821 0000Ruby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- Lea 3 Chapter 1 2Document28 pagesLea 3 Chapter 1 2Ruby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- Approval SheetDocument5 pagesApproval SheetRuby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- 04 Worksheet 1Document5 pages04 Worksheet 1Ruby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- Art ApreciationDocument1 pageArt ApreciationRuby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- NSTPDocument2 pagesNSTPRuby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- NSTPCEOPDocument1 pageNSTPCEOPRuby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1Ruby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document8 pagesChapter 4Ruby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- Q1 SC1 2Document4 pagesQ1 SC1 2Ruby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document6 pagesChapter 5Ruby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- Lack of EducationDocument9 pagesLack of EducationRuby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document8 pagesChapter 3Ruby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- Academic Performance of Inerangan National High School Senior High School Mobile Legends Player of SDocument1 pageAcademic Performance of Inerangan National High School Senior High School Mobile Legends Player of SRuby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- Table of ContentsDocument4 pagesTable of ContentsRuby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- Educ 1 PRELIMDocument4 pagesEduc 1 PRELIMRuby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- FABMptDocument5 pagesFABMptRuby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- Impact of Social Media To The Life of Grade 11 Pascal of Inerangan National High School SDocument3 pagesImpact of Social Media To The Life of Grade 11 Pascal of Inerangan National High School SRuby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- Monthly ProjectsDocument22 pagesMonthly ProjectsRuby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- The Efficacy of Serpentina and Aloe Vera FinalDocument21 pagesThe Efficacy of Serpentina and Aloe Vera FinalRuby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- My Portfolio in Culminating ActivityDocument9 pagesMy Portfolio in Culminating ActivityRuby Ann Mariñas100% (1)
- Etrepreneurship (Week7-8) Princess Velvet P. Cortez G-12 Gas Joaquin Activity 1Document1 pageEtrepreneurship (Week7-8) Princess Velvet P. Cortez G-12 Gas Joaquin Activity 1Ruby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- Mathematical ReasoningDocument10 pagesMathematical ReasoningRuby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- Print ChedDocument3 pagesPrint ChedRuby Ann MariñasNo ratings yet
- By Dr. Becky A. Bailey: Building Resilient ClassroomsDocument22 pagesBy Dr. Becky A. Bailey: Building Resilient ClassroomsBillStNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering For Machine Learning: A Case StudyDocument38 pagesSoftware Engineering For Machine Learning: A Case StudyMerciNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument15 pagesThesisGrace HernandezNo ratings yet
- TOT Manual BinderDocument177 pagesTOT Manual BinderadammarthenNo ratings yet
- Confucian or Fusion - Gutierrez&DysonDocument16 pagesConfucian or Fusion - Gutierrez&DysonFrank GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Perception: Principles of Architecture - Ii (Ar-108 C)Document44 pagesPerception: Principles of Architecture - Ii (Ar-108 C)ABHINAV SEHGALNo ratings yet
- Galactic Consciousness 28 DAY ProgramDocument45 pagesGalactic Consciousness 28 DAY ProgramAnton Tvrdik100% (1)
- Hirschman (1982) - Hedonic Consumption Emerging Concepts - Methods and PropositioDocument11 pagesHirschman (1982) - Hedonic Consumption Emerging Concepts - Methods and PropositioMarco Fernando BravoNo ratings yet
- (Practical Exam) Physiology Lab Materials For PracsDocument6 pages(Practical Exam) Physiology Lab Materials For PracsKeesha RiveraNo ratings yet
- Color Video Formation and PerceptionDocument20 pagesColor Video Formation and PerceptiontehazharrNo ratings yet
- Arghode 2012 GEJDocument10 pagesArghode 2012 GEJKatherine Uran RamirezNo ratings yet
- Richard Dotts - The 95-5 Code - For Activating The Law of AttractionDocument235 pagesRichard Dotts - The 95-5 Code - For Activating The Law of Attractionszilvi100% (4)
- Sonesson G., Pictorial SemioticsDocument70 pagesSonesson G., Pictorial SemioticsnoizfilesNo ratings yet
- Jéva, Mahat-Tattva, Ahaìkära and The Five Gross Elements. There AreDocument25 pagesJéva, Mahat-Tattva, Ahaìkära and The Five Gross Elements. There AreDāmodar DasNo ratings yet
- Question PaperDocument22 pagesQuestion Papershreekumar_scdlNo ratings yet
- Stanley Diamond - Plato and The Definition of The PrimitiveDocument19 pagesStanley Diamond - Plato and The Definition of The Primitivealeksag100% (1)
- PhilosophyDocument21 pagesPhilosophyRuffa Mae PortugalNo ratings yet
- 3 Program Outcomes and Learning OutcomesDocument13 pages3 Program Outcomes and Learning OutcomesVanessa DacumosNo ratings yet
- Cto 10 04 PDFDocument16 pagesCto 10 04 PDFAnonymous hXh1WNSZwNo ratings yet
- THE Hidden Power of The Heart - Ebook-Heart Math PDFDocument318 pagesTHE Hidden Power of The Heart - Ebook-Heart Math PDFAnonymous AHIfjTqLFl85% (13)
- Critical Listening PapersDocument8 pagesCritical Listening Papersgerakan pemudaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Age On Sensorial Response of Sri Lankan Consumers On Biscuit TypesDocument7 pagesImpact of Age On Sensorial Response of Sri Lankan Consumers On Biscuit TypesKanchana PereraNo ratings yet
- Vygotsky's Philosophy: Constructivism and Its Criticisms ExaminedDocument14 pagesVygotsky's Philosophy: Constructivism and Its Criticisms ExaminedAlejandra MonteroNo ratings yet
- Philo 101 John LockeDocument15 pagesPhilo 101 John Lockeapi-196193978No ratings yet
- Problems of Education in The 21st Century, Vol. 4, 2008Document125 pagesProblems of Education in The 21st Century, Vol. 4, 2008Scientia Socialis, Ltd.No ratings yet