Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tesol's Work Sheets - Chapter 2
Uploaded by
sabasky0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views6 pagesOriginal Title
Tesol's work sheets - Chapter 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views6 pagesTesol's Work Sheets - Chapter 2
Uploaded by
sabaskyCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
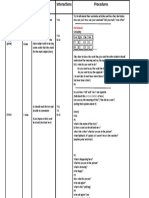
WORKSHEET: Chapter 2
Task 1 - Write 5 examples of each of the following:
Countable noun: car – egg – table – book – pen – bag – house – friend
Uncountable noun: music – advice - water – information –furniture – cheese - rice- etc.
Adjective: big – small - clean – dirty – modern – ancient - expensive – cheap –beautiful- etc.
Adverb: elegantly – happily – lazily –sharply – tediously – warmly – selfishly – slowly – etc.
Preposition: after – for – of – over – on – at – and – to – in - etc.
Verb: eat – swim – sleep – play – visit – sing – spend – stand – walk – write – fix - etc.
Pronoun: A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun. I – you – she – he – it – we - they
Infinitive: to agree -to expect – to decide - to manage- to plan- to promise –to remind- to
seem-to want –to tend - etc.
Gerund: blaming –choosing– insisting – imagining –regretting – avoiding - cooking- etc.
Comparative adjective: taller– faster - shorter – bigger – older– younger - more popular - etc.
Superlative adjective: the tallest – the fastest – the shortest – the biggest – the oldest – the
youngest – the most expensive - etc.
Article (3 only): a – an - the
Conjunction: and – or – but – because –so-since - whether – whereas - etc.
Task 2: Identify the parts of speech in the following sentence:
I usually go swimming with my best friend and his rather unusual girlfriend.
a) I – Subject Pronoun
b) usually – adverb of frequency
c) go - action verb
d) swimming - gerund
e) with - preposition
f) my - possessive adjective
g) best - adjective
h) friend - noun
i) and - conjunction
j) his - possessive adjective
k) rather – adverb of degree
l) unusual - adjective
m) girlfriend - noun
Task 3: State the differences between the following, and give an example of each:
a) Adjectives and adverbs: Adjectives describe nouns and pronouns such as people and things,
or to say how a person or thing…is, seems, becomes, looks, feels, sounds, tastes, or smells like,
He looked angry to me. Adverbs are used to describe the manner in which the action was done
or adverbs describe the verb and the action like, He looked angrily at me.
b) Nouns and pronouns: A noun names people, places, things, qualities, states, like cat, mud,
rice, water
Pronouns are words that are used instead/in place of more precise nouns or noun phrases.
Like you, he, they
Task 4: Explain the following parts of speech as you would to a student. An example sentence
would help to clarify your explanation:
a) Conjunction: It's a word that joins words, phrases, or clauses.
Words: silver and gold
Phrases: over the river and through the woods
Clauses: Sheida planted a flower, and she watched it grow.
In all of those examples, I used the conjunction and, one of the most common conjunctions.
But, of course, there are 3 types of conjunctions:
❶ Coordinating Conjunctions: There are only seven of these. (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so)
Some people remember these with the acronym FANBOYS. They glue together sentence
elements that are the same
•Two words: pie or cake
•Two phrases: in the car or on the bike
•Two independent clauses: You must study, or you won't learn grammar
❷ Subordinating Conjunctions: These conjunctions glue dependent adverb clauses to
independent clauses. (unless, whenever, since, because, if)
I will bring my cat unless you are allergic.
Whenever I see your cat, I sneeze.
Since you are coming, I won't bring my cat.
❸ Correlative Conjunctions: Correlative conjunctions are used in pairs (either...or, both...and),
but they have the same function as coordinating conjunctions. That means that they join
things that are the same.
Both David and I are allergic to cats.
Either Mom or Dad will pick you up.
He is both intelligent and good- natured
b) Gerunds: Gerunds are words that are formed from verbs but act as nouns.
we'll be able to spot them because they will be a verb + ing acting as a noun.
Swimming is fun. Swimming is a verb with an - ing ending, acting as a noun and it is the subject
of this sentence. A gerund is used in the same way as a noun, as a subject or an object. E.g.:
She denies reading the book. Flying makes me nervous.
Verbs: A verb is a word that expresses an action or a state of being and can be considered as
one of the most important parts of a sentence and it is used with a subject to form the basis of
a sentence and there are several types of verbs:
• Action verb: The action verb tells us what the subject of our clause or sentence is doing-
physically or mentally. (catch, play, come, work, sing, dance, write, cook …) Marie walked to
school.
•State verb: Stative verbs are often verbs connected with thinking and opinions, believe, doubt,
guess, imagine, mean, remember, think, feelings, emotions, senses. E.g.: She doesn’t know
what to do. Do you recognize him?
•Modal verbs: There is a further set of auxiliary verbs known as modal verbs or modal auxiliary
verbs. These combine with other verbs to express necessity, possibility, intention, or ability. The
modal auxiliary verbs are must, shall, will, should, would, ought (to), can, could, may, and
might. For example: You must act promptly. Can you speak Spanish? I would go if I could afford
it.
• Auxiliary verb: An auxiliary verb is a verb that determines the mood, tense, voice, or aspect of
another verb in a verb phrase. There are three auxiliary verbs in English: be, do and have.
Auxiliary verbs come before main verbs. She is reading a magazine.
• Transitive verb: Transitive verbs are action verbs that have an object to receive that action
and this verb is followed directly by an object. E.g.: She played the piano. I admire your
courage.
• Intransitive verb: Some verbs never have an object. These are called intransitive verbs.
Example: We talked for hours. I want to leave early.
*To complicate matters further, some verbs can be either transitive or intransitive, depending
on how they ‘re used.
Transitive: England lost the game.
Intransitive: England lost...
d) Comparative adjectives: One way to describe nouns (people, objects, animals, etc.) is by
comparing them to something else. We often use comparisons because we want to talk about
the differences between people, places, and things. For basic, regular comparisons: Adjective +
‘ER’ THAN
*For 1-syllable adjectives, JUST add “er” to the end. E. g: His cat is larger than my dog.
*If the 1-syllable adjective ends with the letter “e,” JUST add “r” to the end. Examples: nicer
wiser
*For adjectives that end with the letter “y,”DROP the “y” and add “ier.”
fancy = fancier pretty = prettier
*For adjectives that are 2 or more syllables, use “more” + the adjective to make the
comparative
form.
Examples: elaborate =more elaborate comfortable=more comfortable
e.g.: This chair is more comfortable than that chair
*You MUST memorize these!
Examples:
good = better than far = farther (further) than bad = worse than
e) Prepositions: Prepositions show the relationship between a noun or a pronoun and some
other word in the sentence. we can say that there are at least three categories place, time, and
movement.
■ Time/date: at, on, by, before, in, from, since, for, during, to, until, after, about
■ Movement: from, to, in, into, on, onto, by, off, out, over
■Place/position: in, at, on, by, above, over, under, below, beneath, beside, between, near, next
to, behind, in front of
*There are some common prepositions that do not neatly fit into any of the above categories
such as of and with.
f) Superlative adjectives: Superlative adjectives describe one person or thing as having more of
a quality than all other people or things in a group: for regular superlatives: THE adjective +
‘EST’ E.g.: My mother's cooking is the best in the family. The most frightening film I’ve ever
seen was Alfred Hitchcock’s ‘Psycho’.
■1 syllable adjectives. Add the /adj./ est. ...
■2+ syllable adjectives. Add the most to the adjective. ...
■Adjectives ending in –y. Remove –y and add the /adj./ iest. ...
■Adjectives ending in –e. Add the /adj./ st. ...
■Irregular adjectives. Eg: good = the best bad = worst
■Adjectives ending in a vowel and a consonant.
Task 5 : What do articles do in a sentence? Give examples of your own.
There are only 3 articles (a, an, the) and we can classify as a definite (the)and indefinite (a,an)
The – refers to a particular or definite thing; it can be used with a singular or plural noun
■ “The blue pencil is my favorite.” (a particular pencil)
A/An – refers to non-particular or indefinite nouns. The first time a noun is introduced
use a/an, then when you refer to that same noun again use the.
■ “A pencil is a useful tool.” (any pencil, not a particular one)
You might also like
- Assignment (Make A Summary)Document7 pagesAssignment (Make A Summary)Alvedro RivaldiNo ratings yet
- Grammar Guide: 1. WordsDocument16 pagesGrammar Guide: 1. WordsRania FarranNo ratings yet
- English Review 6thDocument11 pagesEnglish Review 6thDiana Patricia NavarreteNo ratings yet
- English TipsDocument21 pagesEnglish TipsLaura HallNo ratings yet
- Adjectives 22Document18 pagesAdjectives 22oussamaNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument12 pagesGrammarMuhamad Zaini MasryNo ratings yet
- English Assignment 1Document22 pagesEnglish Assignment 1katilabbuNo ratings yet
- AdjectivesDocument51 pagesAdjectivesSakshiNo ratings yet
- The Parts of Speech PPPDocument19 pagesThe Parts of Speech PPPIGCSE JourneyNo ratings yet
- UNIT 01 - Part of SpeechDocument7 pagesUNIT 01 - Part of SpeechStnrfdlhdila08 DilaaNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and Adverbs: Here Starts The Lesson!Document23 pagesAdjectives and Adverbs: Here Starts The Lesson!Katherine Caballero RiveroNo ratings yet
- The Parts of Speech: By: Syeda Rifa AnjumDocument39 pagesThe Parts of Speech: By: Syeda Rifa AnjumaNo ratings yet
- Common Types of Adverbs ExplainedDocument5 pagesCommon Types of Adverbs ExplainedIsha kaleNo ratings yet
- English 7 ReviewerDocument61 pagesEnglish 7 ReviewerDaisy OrbonNo ratings yet
- Basic English GrammarDocument78 pagesBasic English GrammarPbNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech Part 2Document8 pagesParts of Speech Part 2Ii nanda SafitriNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and AdverbsDocument25 pagesAdjectives and Adverbstanga68No ratings yet
- VERBSDocument204 pagesVERBSChenwie Mother of GodNo ratings yet
- Pronouns Dan AdjectiveDocument8 pagesPronouns Dan AdjectiveNancy IndahNo ratings yet
- The Noun: Types and Formation of Plural NounsDocument61 pagesThe Noun: Types and Formation of Plural Nounsnurfitrah azisNo ratings yet
- Determiners Interjection AdjectivesDocument9 pagesDeterminers Interjection AdjectivesJA HmiNo ratings yet
- Word Power: Guide in English Grammar For StudentsDocument54 pagesWord Power: Guide in English Grammar For Studentsjay meilyNo ratings yet
- AdjectivesDocument31 pagesAdjectivesUmmu Arba'a AuladNo ratings yet
- Grammar Notes Power PointDocument34 pagesGrammar Notes Power PointMrsAndersonLHSSNo ratings yet
- THP Practice 2Document13 pagesTHP Practice 2Dewi Astuti Purnama SariNo ratings yet
- Verbs and Subjects AgreementDocument7 pagesVerbs and Subjects AgreementAhmad FauzanNo ratings yet
- AdjectivesDocument22 pagesAdjectivesfran_corimNo ratings yet
- Eng 2Document75 pagesEng 2فراس فارس صفاقسNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech GuideDocument54 pagesParts of Speech GuideAdelina Elena Ghiuţă100% (2)
- Kinds of Nouns: Proper, Common, Countable, UncountableDocument28 pagesKinds of Nouns: Proper, Common, Countable, UncountableReddaveni Nagaraju100% (1)
- Parts of Speech - Term 3 - Notes and ActivityDocument24 pagesParts of Speech - Term 3 - Notes and ActivitySimoneNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and Adverbs GuideDocument31 pagesAdjectives and Adverbs GuideAmjad KhanNo ratings yet
- English Grammar CardDocument2 pagesEnglish Grammar CardMónica Flor100% (4)
- منهاج اللغة الانكليزيةDocument53 pagesمنهاج اللغة الانكليزيةمروان ابراهيم حمد عبدNo ratings yet
- All About GrammarDocument56 pagesAll About GrammarDeka Fab100% (1)
- Pertemuan 1 NounsDocument8 pagesPertemuan 1 NounsfelianaNo ratings yet
- Road To English BetterDocument65 pagesRoad To English BetterEko Nurhadi SatrioNo ratings yet
- GMAT® Official Guide Supplement: Sentence Correction BasicsFrom EverandGMAT® Official Guide Supplement: Sentence Correction BasicsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Lesson 01Document10 pagesLesson 01criscruzado01No ratings yet
- AdjectivesDocument17 pagesAdjectivesTESLSJKC-0620 Wong Ben Lu100% (1)
- Communication SkillsDocument130 pagesCommunication Skillssayyed_hasan2006100% (1)
- A2 GrammarDocument29 pagesA2 GrammarwaldodeleonNo ratings yet
- What is an AdjectiveDocument9 pagesWhat is an AdjectiveJuan GarciaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech: Anandha, S.S., M.PDDocument28 pagesParts of Speech: Anandha, S.S., M.PDchrn nisaNo ratings yet
- Words TypesDocument23 pagesWords TypesAlejandro RochaNo ratings yet
- MKLH InggrsDocument9 pagesMKLH InggrsTekaer 2No ratings yet
- Instructional Goal 1.1:: Identifying and Forming NounsDocument8 pagesInstructional Goal 1.1:: Identifying and Forming NounsPiqih AkmalNo ratings yet
- Sentences: Independent Clauses Act As Complete Sentences, While Subordinate Clauses Cannot Stand Alone andDocument9 pagesSentences: Independent Clauses Act As Complete Sentences, While Subordinate Clauses Cannot Stand Alone andThamizhman Mani100% (1)
- Adjectives ExplainedDocument12 pagesAdjectives ExplainedFranziene BacsainNo ratings yet
- Part of Speech and Capitalization/PunctuationDocument33 pagesPart of Speech and Capitalization/PunctuationMohammad ZubairNo ratings yet
- Types of Nouns ExplainedDocument9 pagesTypes of Nouns ExplainedbobswapNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument9 pagesPart of SpeechJennifer PittmanNo ratings yet
- ADJECTIVEDocument8 pagesADJECTIVEABREHAMNo ratings yet
- English 3 Part of Speech Full OnlineDocument22 pagesEnglish 3 Part of Speech Full OnlineFalah MutilNo ratings yet
- Unit OneDocument9 pagesUnit OneMb BlackNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade English / Language Arts CRCT ReviewDocument12 pages7th Grade English / Language Arts CRCT ReviewkmschaunceyNo ratings yet
- Confusing Words, Including Heteronyms; Or Why English is Difficult to LearnFrom EverandConfusing Words, Including Heteronyms; Or Why English is Difficult to LearnNo ratings yet
- 2 5285034605794034298 PDFDocument63 pages2 5285034605794034298 PDFfernando cespedesNo ratings yet
- Example of A Good Lesson Plan: Cert Ed/PGCE Year 1Document4 pagesExample of A Good Lesson Plan: Cert Ed/PGCE Year 1sabaskyNo ratings yet
- Pictionary: ICQ: What Do You Want To Do?Document1 pagePictionary: ICQ: What Do You Want To Do?sabaskyNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1st PageDocument1 pageLesson Plan 1st PagesabaskyNo ratings yet
- My Watch My New Watch: Relative ClauseDocument6 pagesMy Watch My New Watch: Relative ClausesabaskyNo ratings yet
- Gerund and InfinitiveDocument2 pagesGerund and InfinitivesabaskyNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences Zero ConditionalDocument2 pagesConditional Sentences Zero ConditionalsabaskyNo ratings yet
- Can't /couldn't May Be or Might Be: DeductionsDocument3 pagesCan't /couldn't May Be or Might Be: DeductionssabaskyNo ratings yet
- Forex Do's and Don'ts To Make Money PDFDocument92 pagesForex Do's and Don'ts To Make Money PDFKang Yuan ShingNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument40 pagesGrammarAnonymous eWZMJD5HNo ratings yet
- Tesol's Work Sheets - Chapter 4Document8 pagesTesol's Work Sheets - Chapter 4sabaskyNo ratings yet
- Tesol's Work Sheets - Chapter 3Document5 pagesTesol's Work Sheets - Chapter 3sabaskyNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET: Chapter 1Document5 pagesWORKSHEET: Chapter 1sabaskyNo ratings yet
- Observation Task - Class 9Document14 pagesObservation Task - Class 9sabaskyNo ratings yet
- IELTS Speaking Strategies 2020 PDFDocument261 pagesIELTS Speaking Strategies 2020 PDFBalpreet Kaur100% (4)
- Discussion Starters - R PDFDocument99 pagesDiscussion Starters - R PDFSimone Groppo BucolloNo ratings yet
- Designing Language Teaching On Becoming PDFDocument113 pagesDesigning Language Teaching On Becoming PDFsabaskyNo ratings yet
- Seniorcourseofen00nesfuoft PDFDocument372 pagesSeniorcourseofen00nesfuoft PDFLukeNo ratings yet
- Yule Pragmatics SearchableDocument76 pagesYule Pragmatics SearchableHoa NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Classes in C++Document15 pagesClasses in C++kishan_pant4645No ratings yet
- BAHASA INGGRIS Yes-No Questions - Kelas 6Document4 pagesBAHASA INGGRIS Yes-No Questions - Kelas 6Hendra PranotogomoNo ratings yet
- (Business Ebook) - Real Estate Investor Business PlanDocument3,841 pages(Business Ebook) - Real Estate Investor Business PlanqmapNo ratings yet
- Script Writing Templates For Students PDF Free Download PDFDocument11 pagesScript Writing Templates For Students PDF Free Download PDFGuru0% (1)
- Bauman Verbal Arts As PerformancesDocument8 pagesBauman Verbal Arts As Performancesjaviera marchantNo ratings yet
- The Rules of CapitalizationDocument3 pagesThe Rules of CapitalizationEch-chahi AbderrahimNo ratings yet
- UCINET 6 User's GuideDocument47 pagesUCINET 6 User's GuidePoonam NaiduNo ratings yet
- Creative WritingDocument18 pagesCreative WritinggermainejustincruzNo ratings yet
- Wilayat (Guardianship)Document85 pagesWilayat (Guardianship)José AntônioNo ratings yet
- Reading - A Ride To A Safari ParkDocument4 pagesReading - A Ride To A Safari ParkNur Fatin SyahirahNo ratings yet
- Digital DesignDocument532 pagesDigital DesignDuy Tiến NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Present Continous Tense Statements, Questions, Months of The YearDocument36 pagesPresent Continous Tense Statements, Questions, Months of The YearClaudya Stephanie Angeline Harman 1841100208No ratings yet
- Key Questions To Consider About SyntaxDocument3 pagesKey Questions To Consider About SyntaxShannon BlakeNo ratings yet
- Have A Great Weekend Meaning - Context & ResponsesDocument4 pagesHave A Great Weekend Meaning - Context & ResponsesmuhammadiqbalmahadNo ratings yet
- Soal Part of SpeechDocument5 pagesSoal Part of SpeechLilis YunarniNo ratings yet
- Rainbow Part - 1: (Work Book With Activities)Document72 pagesRainbow Part - 1: (Work Book With Activities)santhoshNo ratings yet
- 1 Grammar, Vocabulary, Pronunciation, and Practical English ADocument8 pages1 Grammar, Vocabulary, Pronunciation, and Practical English ANarine HovhannisyanNo ratings yet
- Kapampa Ngan Literature Historical Survey and Anthology Edna Zapanta Manlapaz 1981Document289 pagesKapampa Ngan Literature Historical Survey and Anthology Edna Zapanta Manlapaz 1981newteacher depedNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Module 2 AssignmentDocument2 pagesUnit 4 Module 2 AssignmentIvana Mucalov100% (1)
- Manual Engl CP An3 Engl PR Course TudosescuDocument114 pagesManual Engl CP An3 Engl PR Course Tudosescumonasmile86100% (5)
- Exame Normal General English RHDocument3 pagesExame Normal General English RHSilva ValigeNo ratings yet
- Singing The Kyrgyz ManasDocument175 pagesSinging The Kyrgyz ManasHüseyin AksoyNo ratings yet
- The Secrets of Body Language EssayDocument5 pagesThe Secrets of Body Language EssayCamila Mejia-QuinteroNo ratings yet
- 4) Repetition Control Structure (Part 1)Document28 pages4) Repetition Control Structure (Part 1)Bear ZOobearNo ratings yet
- EngineeringDocument44 pagesEngineeringFaiz Ahmad Faiz83% (6)
- JHS BECE PAST QUESTIONS (1990 – 2022) – Passco.org_1705526928810Document19 pagesJHS BECE PAST QUESTIONS (1990 – 2022) – Passco.org_1705526928810augustasesay4340% (1)
- Assignment OOPs & C++ (MCA-303)Document5 pagesAssignment OOPs & C++ (MCA-303)Anand BaghelNo ratings yet
- 7 Steps To Teaching A GenreDocument6 pages7 Steps To Teaching A GenreNiza Binti HarunNo ratings yet