0% found this document useful (0 votes)
71 views15 pagesThyristor Fundamentals and Applications
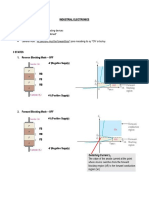
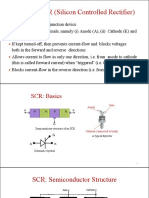
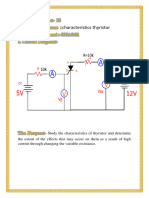
This document provides an overview of thyristors, which are semiconductor devices that can conduct current in one direction when a gate signal is applied. The document discusses thyristor characteristics such as forward and reverse blocking modes, voltage drop and conduction loss. It also covers thyristor gate drivers, forced commutation circuits, parasitic capacitance effects, protection methods, cooling types and applications. Common thyristor devices like TRIACs and GTOs are also introduced.
Uploaded by
Hoàng TúCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
71 views15 pagesThyristor Fundamentals and Applications
This document provides an overview of thyristors, which are semiconductor devices that can conduct current in one direction when a gate signal is applied. The document discusses thyristor characteristics such as forward and reverse blocking modes, voltage drop and conduction loss. It also covers thyristor gate drivers, forced commutation circuits, parasitic capacitance effects, protection methods, cooling types and applications. Common thyristor devices like TRIACs and GTOs are also introduced.
Uploaded by
Hoàng TúCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd