Professional Documents
Culture Documents
For Vertical and Inclined Surface
For Vertical and Inclined Surface
Uploaded by
Jade Carlo Antonio0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesThis document discusses hydrostatic pressure and buoyancy. It defines key terms like hydrostatic pressure, center of pressure, centroidal moment of inertia, and introduces formulas to calculate buoyant force and center of pressure for objects submerged in water. The document explains that buoyant force is equal to the average pressure times the surface area and provides methods to calculate average pressure and depth from the centroid to the water surface.
Original Description:
Original Title
Buoyancy and Floatation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses hydrostatic pressure and buoyancy. It defines key terms like hydrostatic pressure, center of pressure, centroidal moment of inertia, and introduces formulas to calculate buoyant force and center of pressure for objects submerged in water. The document explains that buoyant force is equal to the average pressure times the surface area and provides methods to calculate average pressure and depth from the centroid to the water surface.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesFor Vertical and Inclined Surface
For Vertical and Inclined Surface
Uploaded by
Jade Carlo AntonioThis document discusses hydrostatic pressure and buoyancy. It defines key terms like hydrostatic pressure, center of pressure, centroidal moment of inertia, and introduces formulas to calculate buoyant force and center of pressure for objects submerged in water. The document explains that buoyant force is equal to the average pressure times the surface area and provides methods to calculate average pressure and depth from the centroid to the water surface.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
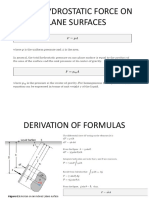
Buoyancy and Floatation HYDROSTATIC PRESSURE AND = ʃ⸹hdA x h
MANOMETRY = ⸹ʃh2 dA
Axhx⸹x hcp=⸹ʃh2 dA
Where : ʃh2 dA is the moment of inertia
about a certain axis or
surface or (Is)
For Is, using Transfer formula:
Is = I + Ah2
hcg = I + h2 cgA/hcgA or hcg = I/hcgA +
hcg
FR = Pave x A Where:
I = centroidal moment of inertia
1. If the plane surface area is considered hcg = distance from LS to the centroid of
is horizontal, then, the surface
FR =⸹ h x A A = surface area projected vertically
2. For vertical and inclined surface Derivation of the Center of Pressure
(submerged) one possible approach to
solve FR
is consider its average.
FR = Pave x A
P = ⸹havexA
= ⸹xhcg x A
Where;
h = average height, more
often is hcg
hcg = depth from the
centrroid of the
submerged substance to
the water surfaces
Taking the moment
about the liquid surface
FRx hcp = ʃpdA x h
You might also like
- 553C, 563C, and 573C Wheel Feller Buncher Hydraulic System: Front of Machine Behind CabDocument2 pages553C, 563C, and 573C Wheel Feller Buncher Hydraulic System: Front of Machine Behind Cabmrcruzito_2099No ratings yet
- Chapter2 Part2-Fluidstatic PDFDocument22 pagesChapter2 Part2-Fluidstatic PDFKhaizuran IrfanNo ratings yet
- Total Hydrostatic ForceDocument8 pagesTotal Hydrostatic ForceKenny jay DapinNo ratings yet
- dydx=tanθ dydx=ω2xg dy=ω2gx dx y=ω2x22g: Other FormulasDocument2 pagesdydx=tanθ dydx=ω2xg dy=ω2gx dx y=ω2x22g: Other Formulasangelica brongcanoNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Fluid Static Part BDocument5 pagesWeek 10 Fluid Static Part B陆昌玉No ratings yet
- Hamiltonian em Bruno - MurinoDocument20 pagesHamiltonian em Bruno - MurinoSahil devduttNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Force On A Plane Surface:: Tank BottomDocument25 pagesHydrostatic Force On A Plane Surface:: Tank BottomPeter Adrian NgoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document9 pagesLecture 02An SquadNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic ForceDocument27 pagesHydrostatic ForceAyumi QuiomNo ratings yet
- Ap P-PS: kJP-PaDocument8 pagesAp P-PS: kJP-PaSurabhitNo ratings yet
- FM Mod 2Document70 pagesFM Mod 2manoj kumar jainNo ratings yet
- Problem 3.58 PDFDocument2 pagesProblem 3.58 PDFKauê BrittoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Accelerated Motion of FluidsDocument7 pagesFluid Mechanics: Accelerated Motion of FluidsAnujeetMishraNo ratings yet
- Module 2.1 Hydrostatic ForcesDocument31 pagesModule 2.1 Hydrostatic ForcesAayush KNo ratings yet
- 1.4 1.5Document7 pages1.4 1.5Alexandra AlexeNo ratings yet
- Fox Fluid Mechanics 8th Solved Problem 3.14Document2 pagesFox Fluid Mechanics 8th Solved Problem 3.14Patricia RodriguesNo ratings yet
- CE271 Chap 3 PDFDocument24 pagesCE271 Chap 3 PDFMalshan NallaperumaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Hydrology: Class 2 Hydrostatic Forces On Plane SurfacesDocument5 pagesHydraulics and Hydrology: Class 2 Hydrostatic Forces On Plane SurfacesLiza KimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Hydrostatics: 2.1. PRESSUREDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Hydrostatics: 2.1. PRESSUREcemaliNo ratings yet
- Sayed Ali Asghar Zahid Mehmood Muhammad AtharDocument19 pagesSayed Ali Asghar Zahid Mehmood Muhammad AtharMuhammad HamzaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow 5f155f8d95906Document13 pagesFluid Flow 5f155f8d95906Raymart CubidNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document30 pagesCH 10Narendran KumaravelNo ratings yet
- Gradient PDFDocument1 pageGradient PDFmark carigNo ratings yet
- Pressure and Fluid StaticDocument28 pagesPressure and Fluid StaticCarolinaAndreaJimenezAngelNo ratings yet
- Pressure and Fluid StaticDocument28 pagesPressure and Fluid StaticAsad kkNo ratings yet
- Total Hydrostatic Force On Plane SurfacesDocument56 pagesTotal Hydrostatic Force On Plane SurfacesReiBañez100% (1)
- Chap 3 Sec2Document24 pagesChap 3 Sec2ZewdieNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic ForceDocument9 pagesHydrostatic ForceUMESH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document9 pagesExperiment 3Jemuel FloresNo ratings yet
- Module BaDocument12 pagesModule Bagarcialester305No ratings yet
- Hydrostatic ForcesDocument33 pagesHydrostatic ForcesAbed Alrahman QaddourNo ratings yet
- CE Module 20 - Relative Equilibrium (Principles)Document1 pageCE Module 20 - Relative Equilibrium (Principles)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Unit 3.1 - Hydrostatic ForcesDocument29 pagesUnit 3.1 - Hydrostatic ForcesIshmael MvunyiswaNo ratings yet
- Application ICalDocument18 pagesApplication ICalLouie Jean LabradorNo ratings yet
- Pressure in Stationary and Moving Fluid: Lab-On-Chip: Lecture 2Document37 pagesPressure in Stationary and Moving Fluid: Lab-On-Chip: Lecture 2Duc TranNo ratings yet
- Fluid StatisticsDocument66 pagesFluid Statisticskonetinarendra100% (1)
- Exam 1 Preparation Sheet.: ConversionsDocument4 pagesExam 1 Preparation Sheet.: ConversionskarthickNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document36 pagesModule 2swathiaabidNo ratings yet
- DGT AodDocument54 pagesDGT AodMainpal KaswanNo ratings yet
- Chương 6: 6.1. The Eye Can Be Treated, To A First Approximation, As A Thin - x0002 - Walled ElasticDocument39 pagesChương 6: 6.1. The Eye Can Be Treated, To A First Approximation, As A Thin - x0002 - Walled ElasticTran TanNo ratings yet
- Tight Binding Models: Amar Bharti February 2019Document4 pagesTight Binding Models: Amar Bharti February 2019amar bhartiNo ratings yet
- Flow NetsDocument5 pagesFlow NetsrreglosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Arches 78Document13 pagesChapter 7 Arches 78CharanNo ratings yet
- L5-Pressure Gauge and Static ForceDocument19 pagesL5-Pressure Gauge and Static ForceAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Ehrenfest's TheoremDocument4 pagesEhrenfest's TheoremAmandeep KaurNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Flow of Water Through SoilsDocument28 pages1.3 Flow of Water Through SoilsRegine DoronilaNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Study Guide For FinalDocument5 pagesSoil Mechanics Study Guide For FinalChanty CapidtoanNo ratings yet
- Darcy's Law: Week 2 Physical EquationsDocument4 pagesDarcy's Law: Week 2 Physical Equationsdownloader1983No ratings yet
- 3.5 Semi-Confined Flow: Groundwater Modeling Using Python - Bakker and PostDocument10 pages3.5 Semi-Confined Flow: Groundwater Modeling Using Python - Bakker and PostZar MaghustNo ratings yet
- Mean Curvature Flow With Triple Junctions in Higher Space DimensionsDocument31 pagesMean Curvature Flow With Triple Junctions in Higher Space Dimensionsanca irinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Total Hydrostatic Force On SurfacesDocument2 pagesChapter 3. Total Hydrostatic Force On SurfacesJames Fontanilla Cudal Jr.No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ContinuationDocument27 pagesChapter 2 ContinuationArianne Mae De Vera GallonNo ratings yet
- 10.fluid Mechanics - Properties of MatterDocument42 pages10.fluid Mechanics - Properties of MatterSanjana KumariNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic ForcesDocument9 pagesHydrostatic ForcesEhtisham RiazNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Lecture2Document15 pagesChapter Two Lecture2alaaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Prob 1Document3 pagesFluid Prob 1asafNo ratings yet
- TestaDocument1 pageTestaFoca B-ZoneNo ratings yet
- 2022-23 Ex-I CorrDocument2 pages2022-23 Ex-I CorrAzer TyuiopNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Practice Questions With SolutionDocument17 pagesFluid Mechanics Practice Questions With SolutionwebvenkyNo ratings yet
- The Equidistribution Theory of Holomorphic Curves. (AM-64), Volume 64From EverandThe Equidistribution Theory of Holomorphic Curves. (AM-64), Volume 64No ratings yet
- Heat ExchangersDocument24 pagesHeat ExchangersJade Carlo AntonioNo ratings yet
- Westphal BalanceDocument3 pagesWestphal BalanceJade Carlo AntonioNo ratings yet
- RADIATIONDocument15 pagesRADIATIONJade Carlo AntonioNo ratings yet
- Name: Antonio, Jade Carlo M. Course: BSME College: College of Engineering Year & Level: 3BDocument2 pagesName: Antonio, Jade Carlo M. Course: BSME College: College of Engineering Year & Level: 3BJade Carlo AntonioNo ratings yet
- B. FlaringDocument8 pagesB. FlaringJade Carlo AntonioNo ratings yet
- A. CobaltDocument8 pagesA. CobaltJade Carlo AntonioNo ratings yet
- A. ArborDocument3 pagesA. ArborJade Carlo AntonioNo ratings yet
- C. AnvilDocument8 pagesC. AnvilJade Carlo AntonioNo ratings yet
- DC and AC Machines: Vallerie Magne R. QuestinDocument36 pagesDC and AC Machines: Vallerie Magne R. QuestinJade Carlo AntonioNo ratings yet
- Fluid Dynamics Part 4 Hydrodynamic Stability Theory Anatoly Ruban Full ChapterDocument60 pagesFluid Dynamics Part 4 Hydrodynamic Stability Theory Anatoly Ruban Full Chaptertom.dimaggio515100% (9)
- Hydraulics Review ProblemsDocument9 pagesHydraulics Review ProblemsrojethtrinidadNo ratings yet
- Open Channel Flow Gate Notes 65Document5 pagesOpen Channel Flow Gate Notes 65Saurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Lab Aero-2Document8 pagesLab Aero-2aty27062004No ratings yet
- Sonic Nozzle DesignDocument86 pagesSonic Nozzle Designsb ali100% (1)
- Rancang Bangun Water Seal Drainage (WSD) Khusus Thorax Dengan Pengaturan Tekanan Pada Suction PumpDocument6 pagesRancang Bangun Water Seal Drainage (WSD) Khusus Thorax Dengan Pengaturan Tekanan Pada Suction PumpDadang SaparudinNo ratings yet
- Mathemetical Physics Class NotesDocument218 pagesMathemetical Physics Class NotesSwashy Yadav50% (2)
- Cavitation Analysis CFDDocument4 pagesCavitation Analysis CFDshdjjfNo ratings yet
- Application of Visimix To The Characterization of Lab ReactorsDocument35 pagesApplication of Visimix To The Characterization of Lab ReactorsBhanu Pratap TiwariNo ratings yet
- HP Quiz - IIDocument4 pagesHP Quiz - IISaravanan AkNo ratings yet
- Dosatron - Comparativo Sistema de DosagemDocument37 pagesDosatron - Comparativo Sistema de Dosagemmarmaduke32No ratings yet
- 3-P Separator Design - 1Document10 pages3-P Separator Design - 1Naeem HussainNo ratings yet
- Pcp Абдрахманов КапитанDocument24 pagesPcp Абдрахманов КапитанЖанат МахулбеккызыNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Analysis of Oxygen As It Flows Through A NozzleDocument5 pagesThermodynamic Analysis of Oxygen As It Flows Through A NozzleEmmanuel AnakorNo ratings yet
- Mixing and Deposition of Sediment-Laden Buoyant JetsDocument262 pagesMixing and Deposition of Sediment-Laden Buoyant JetscffyauNo ratings yet
- Control Valve: Instrument Datasheet Tag No. Process ConditionsDocument1 pageControl Valve: Instrument Datasheet Tag No. Process Conditionskrishna kumarNo ratings yet
- PPO - Reservoir Performance - Part 1 - S92018Document25 pagesPPO - Reservoir Performance - Part 1 - S92018PrinCe KaleezNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument118 pagesFinal Reportdivmech1988No ratings yet
- Internship Report NestleDocument30 pagesInternship Report NestleAli RazaNo ratings yet
- Experimental Aerodynamic Analysis of Delta WingDocument9 pagesExperimental Aerodynamic Analysis of Delta WingSharan Teja ElagandulaNo ratings yet
- Discharge Through BridgeDocument2 pagesDischarge Through Bridgesirkali1973No ratings yet
- Chapter4 Part2Document18 pagesChapter4 Part2SamanAtrian0% (1)
- ME8694 Hydraulics and PneumaticsDocument79 pagesME8694 Hydraulics and PneumaticselabalajiNo ratings yet
- DR Rola ME 362 Sheet 1Document4 pagesDR Rola ME 362 Sheet 1Keroles SabryNo ratings yet
- Pre Lab Report No. 9 Friction LossDocument3 pagesPre Lab Report No. 9 Friction LossHannah AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of Viscosity in 3D, Used To Derive Navier-Stoke - Physics ForumsDocument6 pagesNewton's Law of Viscosity in 3D, Used To Derive Navier-Stoke - Physics Forumsamit kumar guptaNo ratings yet
- Reynolds AnalogyDocument1 pageReynolds AnalogymojexNo ratings yet
- Computational Fluid Dynamics With EllipSysDocument1 pageComputational Fluid Dynamics With EllipSysMahmoud MoussaNo ratings yet
- A Fundamental Study of The Flow Past A Circular Cylinder Using Abaqus/CFDDocument15 pagesA Fundamental Study of The Flow Past A Circular Cylinder Using Abaqus/CFDTodor Ivanov YankovNo ratings yet