Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Uygulama 1-2 & Ornek Sorular
Uygulama 1-2 & Ornek Sorular
Uploaded by
Jayson MadrigalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Uygulama 1-2 & Ornek Sorular
Uygulama 1-2 & Ornek Sorular
Uploaded by
Jayson MadrigalCopyright:
Available Formats
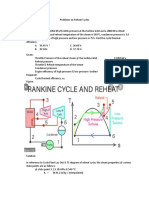
güç santralinde
o
o
o
suyu
a) ve buhar yer
-
b) T
yazarak,
c)
d)
e)
f) K alarak,
g) 0=100kPa)
Steam enters the high-pressure turbine of a steam power plant that
operates on the ideal reheat Rankine cycle at 6 MPa and 500°C and
leaves as saturated vapor. Steam is then reheated to 450°C before
it expands to a pressure of 7.5 kPa. Heat is transferred to the steam
in the boiler at a rate of 60 MW. Steam is cooled in the condenser
by the cooling water from a nearby river, which enters the condenser
at 7°C.
a) Show the cycle on a T-s diagram with respect to saturation
lines, and determine
b) write all mass, energy, entropy and exergy balance
equations,
c) find the pressure at which reheating takes place,
d) net power output and thermal efficiency,
e) the minimum mass flow rate of the cooling water required.
f) Determine the exergy destruction associated with the heat addition process. Assume a
source temperature of 1600 K and a sink temperature of 285 K.
g) Also, determine the exergy of the steam at the boiler exit. (P0=100kPa)
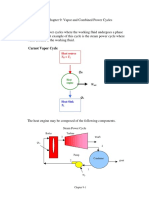
The gas-turbine portion of a combined gas-steam power plant has a
pressure ratio of 16. Air enters the compressor at 300 K at a rate of 14
kg/s and is heated to 1500 K in the combustion chamber. The
combustion gases leaving the gas turbine are used to heat the steam
to 400 ºC at 10 MPa in a heat exchanger. The combustion gases leave
the heat exchanger at 420 K. The steam leaving the turbine is
condensed at 15 kPa. Assume all the compression and expansion
processes to be isentropic. (𝑇0 = 293 𝐾, 𝑇b = 300 𝐾 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑇𝑠 = 2200 𝐾).
For air, assume constant specific heats at room temperature (cp=1.005
kJ/kg·K and k=1.4).
For water and steam;
ℎ𝑓 = 225.94 𝑘𝐽/𝑘𝑔
@ 𝑃=15 𝑘𝑃𝑎
𝑣𝑓 = 0.001014 𝑚3 /𝑘𝑔
@ 𝑃=15 𝑘𝑃𝑎
ℎ@ 𝑃=10 𝑀𝑃𝑎 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑇=400°𝐶 = 3097.0 𝑘𝐽/𝑘𝑔
𝑠@ 𝑃=10 𝑀𝑃𝑎 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑇=400°𝐶 = 6.2141 𝑘𝐽/𝑘𝑔 · 𝐾
𝑠𝑓 = 0.7549 𝑘𝐽/𝑘𝑔 · 𝐾
@ 𝑃=15 𝑘𝑃𝑎
𝑠𝑓𝑔 = 7.2522 𝑘𝐽/𝑘𝑔 · 𝐾
@ 𝑃=15 kPa
ℎ𝑓 = 225.94 𝑘𝐽/𝑘𝑔
@ 𝑃=15 𝑘𝑃𝑎
ℎ𝑓𝑔 = 2372.3 𝑘𝐽/𝑘𝑔
@ 𝑃=15 kPa
a) Draw the cycle T-s diagram.
b) Write all mass, energy, entropy and exergy balance equations for each device.
c) Determine the mass flow rate of the steam,
d) Determine the net power output,
e) Find the energy and exergy efficiencies of the combined cycle.
f) Determine entropy generation in combustion chamber and exergy destruction in condenser.
Bir birleşik gaz-buhar santralinde gaz türbininin basınç oranı 16
olup, hava kompresöre 300 K sıcaklıkta, 14 kg/s debiyle
girmektedir. Yanma odasından 1500 K sıcaklıkta çıkan gazlar,
türbinde genişledikten sonra atık ısı kazanına girmekte ve buradan
420 K sıcaklıkta çıkmaktadır. Yanma sonu gazlarının verdiği ısı ile
atık ısı kazanında 10 MPa basınç ve 400 °C sıcaklıkta buhar
üretilmektedir. Üretilen buhar bir türbinde 15 kPa basınca kadar
genişlemektedir. Tüm sıkıştırma ve genişlemelerin izantropik
olduğunu kabul ediniz. (𝑇0 = 293 𝐾, 𝑇sınır = 300 𝐾 𝑣𝑒 𝑇𝑘𝑎𝑦𝑛𝑎𝑘 =
2200 𝐾). Hava için oda sıcaklığında sabit özgül ısılar kabul ediniz
(cp=1,005 kJ/kg·K ve k=1,4).
Hava ve buhar için;
ℎ𝑓 = 225,94 𝑘𝐽/𝑘𝑔
@ 𝑃=15 𝑘𝑃𝑎
𝑣𝑓 = 0,001014 𝑚3 /𝑘𝑔
@ 𝑃=15 𝑘𝑃𝑎
ℎ@ 𝑃=10 𝑀𝑃𝑎 𝑣𝑒 𝑇=400°𝐶 = 3097,0 𝑘𝐽/𝑘𝑔
𝑠@ 𝑃=10 𝑀𝑃𝑎 𝑣𝑒 𝑇=400°𝐶 = 6,2141 𝑘𝐽/𝑘𝑔 · 𝐾
𝑠𝑓 = 0,7549 𝑘𝐽/𝑘𝑔 · 𝐾
@ 𝑃=15 𝑘𝑃𝑎
𝑠𝑓𝑔 = 7,2522 𝑘𝐽/𝑘𝑔 · 𝐾
@ 𝑃=15 kPa
ℎ𝑓 = 225,94 𝑘𝐽/𝑘𝑔
@ 𝑃=15 𝑘𝑃𝑎
ℎ𝑓𝑔 = 2372,3 𝑘𝐽/𝑘𝑔
@ 𝑃=15 kPa
a) Çevrime ait T-s diyagramını çiziniz.
b) Tüm kütle, enerji, entropi ve ekserji denge denklemlerini her bir bileşen için yazınız.
c) Buharın kütle debisini bulunuz.
d) Santralin net gücünü bulunuz.
e) Birleşik gaz-buhar çevriminin enerji ve ekserji verimlerini hesaplayınız.
f) Yanma odasındaki entropi üretimini ve kondenserdeki ekserji yokoluşunu bulunuz.
10-73
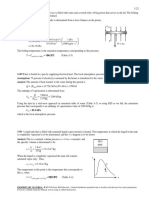
10-77 A combined gas-steam power cycle is considered. The topping cycle is a gas-turbine cycle and the bottoming cycle is
a simple ideal Rankine cycle. The mass flow rate of the steam, the net power output, and the thermal efficiency of the
combined cycle are to be determined.
Assumptions 1 Steady operating conditions exist. 2 Kinetic and potential energy changes are negligible. 3 Air is an ideal gas
with constant specific heats.
Properties The properties of air at room temperature are cp k = 1.4 (Table A-2).
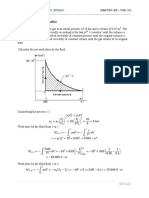
Analysis (a) The analysis of gas cycle yields
k 1 /k
P6 0.4 / 1.4
T6 T5 300 K 16 662.5 K T
P5
Qin m air h7 h6 m air c p T7 T6 1500 K 7
14 kg/s 1.005 kJ/kg K 1500 662.5 K 11,784 kW
WC , gas m air h6 h5 m air c p T6 T5 Qin GAS
CYCLE
14 kg/s 1.005 kJ/kg K 662.5 300 K 5100 kW
k 1 /k 0. 4 / 1. 4 8 3
P8 1 400 C
T8 T7 1500K 679.3 K 6
P7 16 10 MPa
WT , gas m air h7 h8 m air c p T7 T8 9 420 K
14 kg/s 1.005 kJ/kg K 1500 679.3 K 11,547 kW STEAM
W net,gas WT ,gas WC ,gas 11,547 5,100 6447 kW 300 K 2 CYCLE 15 kPa
5
1 4
From the steam tables (Tables A-4, A-5, and A-6), Qout
s
h1 h f @ 15 kPa 225.94 kJ/kg
1 f @ 15 kPa 0.001014 m 3 /kg
1 kJ
w pI,in 1 P2 P1 0.001014 m 3 /kg 10,000 15 kPa 10.12 kJ/kg
1 kPa m 3
h2 h1 wpI,in 225.94 10.13 236.06 kJ/kg
P3 10 MPa h3 3097.0 kJ/kg
T3 400 C s3 6.2141 kJ/kg K
s4 sf 6.2141 0.7549
P4 15 kPa x4 0.7528
s fg 7.2522
s4 s3
h4 hf x4 h fg 225.94 0.7528 2372.3 2011.8 kJ/kg
Noting that Q W 0 for the heat exchanger, the steady-flow energy balance equation yields
0 (steady)
E in E out E system 0 E in E out
mi hi m e he m s h3 h2 m air h8 h9
h8 h9 c p T8 T9 1.005 kJ/kg K 679.3 420 K
ms m air m air 14 kg/s 1.275 kg/s
h3 h2 h3 h2 3097.0 236.06 kJ/kg
(b) WT, steam ms h3 h4 1.275 kg/s 3097.0 2011.5 kJ/kg 1384 kW
Wp,steam ms w p 1.275 kg/s 10.12 kJ/kg 12.9 kW
Wnet,steam WT, steam Wp,steam 1384 12.9 1371 kW
and Wnet Wnet,steam Wnet,gas 1371 6448 7819 kW
Wnet 7819 kW
(c) th 66.4%
Qin 11,784 kW
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL 15 McGraw-Hill Education. Limited distribution permitted only to teachers and educators for course preparation. If
you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
You might also like
- Otto Cycle & Diesel CycleDocument36 pagesOtto Cycle & Diesel CycleNafisa AnikaNo ratings yet
- Problems On Reheat CycleDocument8 pagesProblems On Reheat CycleMurvin VillarosaNo ratings yet
- Static & Fatigue Analysis of Pressure Vessel: Project ReportDocument38 pagesStatic & Fatigue Analysis of Pressure Vessel: Project ReportHgagselim SelimNo ratings yet
- Heat Source TDocument24 pagesHeat Source TTemesgen ZelekeNo ratings yet
- EQA00048 Jetstream 4200 PDFDocument151 pagesEQA00048 Jetstream 4200 PDFNam TruongNo ratings yet
- MME 3334b Assignment #1: P 160 Bar, H H VP P 190.01 KJ / KGDocument5 pagesMME 3334b Assignment #1: P 160 Bar, H H VP P 190.01 KJ / KGTimNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6sol2 PDFDocument4 pagesTutorial 6sol2 PDFSohayb GattousNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) Deployment Guide: Front CoverDocument36 pagesMicrosoft Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) Deployment Guide: Front CoverСергей КовалевNo ratings yet
- Chat GPTDocument2 pagesChat GPTMaureen MainaNo ratings yet
- Uygulama 1-2 & Ornek SorularDocument16 pagesUygulama 1-2 & Ornek SorularRSS RSSNo ratings yet
- Rankine Cycle Diagram: K KG KJ K KG KJ Kpa S Kpa S S XDocument16 pagesRankine Cycle Diagram: K KG KJ K KG KJ Kpa S Kpa S S Xanon_166336005No ratings yet
- P P P P: M H H M H H H H M M H HDocument2 pagesP P P P: M H H M H H H H M M H HNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Steam Gas Turbine 2 Assignment (18%)Document12 pagesSteam Gas Turbine 2 Assignment (18%)Khairul HishamNo ratings yet
- Solution #9Document7 pagesSolution #9KinnonPangNo ratings yet
- Exercicio TermoDocument1 pageExercicio Termomcpe2793No ratings yet
- Question 1. During An Experiment Conducted in A Room at 25Document11 pagesQuestion 1. During An Experiment Conducted in A Room at 25fivos_rgNo ratings yet
- 10 90 PDFDocument2 pages10 90 PDFMarkleo AcunaNo ratings yet
- 3Document10 pages3Ariel Carlos De LeonNo ratings yet
- Sheet SolutionsDocument11 pagesSheet SolutionsMahmoud adelNo ratings yet
- Question 1. Liquid Water at 200 Kpa and 15: S S M S M T Q DT DsDocument6 pagesQuestion 1. Liquid Water at 200 Kpa and 15: S S M S M T Q DT Dsfivos_rgNo ratings yet
- c08 - Pending 8.36Document262 pagesc08 - Pending 8.36SeungMin LeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Examples&SolutionDocument42 pagesChapter 9 Examples&SolutionSami ullahNo ratings yet
- 1253-1254 TermodinamicaDocument2 pages1253-1254 TermodinamicaElbeto BerdugoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Tut-1Document5 pagesChapter 8 - Tut-1Ram AroraNo ratings yet
- I P H S V M& T: I I I I I IDocument5 pagesI P H S V M& T: I I I I I IgowthamAG07No ratings yet
- Rumus Perhitungan Turbin UapDocument17 pagesRumus Perhitungan Turbin Uapricki yusufNo ratings yet
- 12th PhysucsvipDocument3 pages12th Physucsvipphysics a2No ratings yet
- Siklus Brayton Contoh:: P P T TDocument7 pagesSiklus Brayton Contoh:: P P T TDicky PasaribuNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 7 Steam TurbineDocument5 pagesThermodynamics 7 Steam Turbinep_nicks89No ratings yet
- Tutorial 4sol PDFDocument4 pagesTutorial 4sol PDFSohayb GattousNo ratings yet
- IDL Assignment Solution 2Document5 pagesIDL Assignment Solution 2pjrfhn7596No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Vapor and Combined Power CyclesDocument29 pagesChapter 10 Vapor and Combined Power Cyclesnamsun100% (1)
- Revision SolutionDocument19 pagesRevision SolutionHassan Abo NagaNo ratings yet
- Mete 50 (Activity 1) AbaoDocument6 pagesMete 50 (Activity 1) AbaoCedric AbaoNo ratings yet
- Problems For Chapter 8: Power Cycles: A. The Rankine CycleDocument48 pagesProblems For Chapter 8: Power Cycles: A. The Rankine CycleEUGENE AICHANo ratings yet
- Question Bank-Thermal EngineeringDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank-Thermal EngineeringIrfan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- CHME 5101, Fall 2021: Homework Assignment 3 (Due 10/13/21, 11:59 PM US Eastern Time) Problem 1Document4 pagesCHME 5101, Fall 2021: Homework Assignment 3 (Due 10/13/21, 11:59 PM US Eastern Time) Problem 1TosinNo ratings yet
- Thermo ExcerciseDocument28 pagesThermo ExcerciseAizel Jeong Aizel JeongNo ratings yet
- Ideal Rankine CycleDocument20 pagesIdeal Rankine CycleJasmin TulosaNo ratings yet
- Finalized and Edited Group 5Document12 pagesFinalized and Edited Group 5Ralph EvidenteNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics An Engineering Approach 6th Ed. (Solution) - 1240-1250Document11 pagesThermodynamics An Engineering Approach 6th Ed. (Solution) - 1240-1250Luis Felipe MartezNo ratings yet
- Closed Feed Water Heaters: Ideal Regenerative Rankine CycleDocument20 pagesClosed Feed Water Heaters: Ideal Regenerative Rankine CycleAlwendo GunawanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10xx 2Document66 pagesLecture 10xx 2King Cyruz PabloNo ratings yet
- MMAN2700ThermoProblemSheet7 - Entropy 2nd LawDocument3 pagesMMAN2700ThermoProblemSheet7 - Entropy 2nd Lawgrandw9524No ratings yet
- EXAM - (M) 2018: Mechanical Engineering Paper - IIDocument12 pagesEXAM - (M) 2018: Mechanical Engineering Paper - IISandeep PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap10 P001Document29 pagesThermo 5th Chap10 P001welberTonetoMotaNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal TermodinamikaDocument24 pagesContoh Soal TermodinamikaDea FarhaniNo ratings yet
- Boiling and Condensation PDFDocument11 pagesBoiling and Condensation PDFYeditha Satyanarayana MurthyNo ratings yet
- Thermodyancs Chapter 9 Solution ManuelDocument36 pagesThermodyancs Chapter 9 Solution ManuelFarhad MojaverNo ratings yet
- Problemario MFCDocument31 pagesProblemario MFCPonce MrlnNo ratings yet
- Problemario MFCDocument80 pagesProblemario MFCBassaldua AlfreedNo ratings yet
- AvailabilityDocument12 pagesAvailabilityanurag sahayNo ratings yet
- Solutions 4 F14Document5 pagesSolutions 4 F14nageshNo ratings yet
- Me 211 Examples SolutionsDocument30 pagesMe 211 Examples SolutionsBryan Dominic Gabriel PaduaNo ratings yet
- CalculationsDocument2 pagesCalculationsLeoNo ratings yet
- 10 27 PDFDocument1 page10 27 PDFJohn Anthony Leuterio DacanayNo ratings yet
- 10 27Document1 page10 27Feolo Riel TarayNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics Exam 2018 Wirh SolutionsDocument9 pagesApplied Thermodynamics Exam 2018 Wirh SolutionsFarouk BassaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics ProblemsDocument2 pagesThermodynamics ProblemsAlexander Salado IbrahimNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Assignment PDFDocument1 pageCH 5 Assignment PDFAftab57.No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Assignment (Answers are in parenthesis) : ΔS of theDocument1 pageChapter 5 Assignment (Answers are in parenthesis) : ΔS of theRojan PradhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Assignment (Answers are in parenthesis) : ΔS of theDocument1 pageChapter 5 Assignment (Answers are in parenthesis) : ΔS of theProtim's goNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Vapor Detector D.I.Y Kit: For Detecting Alcohol Vapor in Household or Workplace Environment Using The MQ3 SensorDocument9 pagesAlcohol Vapor Detector D.I.Y Kit: For Detecting Alcohol Vapor in Household or Workplace Environment Using The MQ3 Sensorahmed chaouki ChamiNo ratings yet
- BCG Matrix Case Study: Malaysia Mobile TelecommunicationsDocument18 pagesBCG Matrix Case Study: Malaysia Mobile TelecommunicationsDonald YeeNo ratings yet
- 3al88354aaaa - V1 - 1359 Ioo AdministrationDocument125 pages3al88354aaaa - V1 - 1359 Ioo AdministrationRaja solaimalaiNo ratings yet
- HD781010Document4 pagesHD781010alex6832No ratings yet
- PFD SeparateurDocument1 pagePFD SeparateurTuesou MachereNo ratings yet
- Python Automation Program 2 - Syllabus - Aarav Tech SolutionsDocument14 pagesPython Automation Program 2 - Syllabus - Aarav Tech SolutionsLiba BaliNo ratings yet
- 18XX Recorder ManualDocument36 pages18XX Recorder ManualOriana LugoNo ratings yet
- Communication in Everyday Life WordDocument13 pagesCommunication in Everyday Life WordSoumyarup DebNo ratings yet
- Well CompletionDocument22 pagesWell CompletionRobot100% (1)
- Assignment BlogDocument12 pagesAssignment Blog홍석영No ratings yet
- Cyber Shield 20120801 080658 1Document1 pageCyber Shield 20120801 080658 1api-267284560No ratings yet
- Operations MGT Module #14Document5 pagesOperations MGT Module #14Jude VicenteNo ratings yet
- Quebec Now Platform NotificationsDocument397 pagesQuebec Now Platform NotificationsYKNo ratings yet
- 710, Barton Centre, M G Road, Bangalore 560 001: A.O: Against Order Tax (Vat) 5% ExtraDocument11 pages710, Barton Centre, M G Road, Bangalore 560 001: A.O: Against Order Tax (Vat) 5% ExtraKumar NagarajNo ratings yet
- In A Nutshell: EcopaperDocument2 pagesIn A Nutshell: EcopaperIIZVenomouSZIINo ratings yet
- CB2-M-ZEN-21-20003-P&ID - Symbol & Legend (33) - Rev.1Document1 pageCB2-M-ZEN-21-20003-P&ID - Symbol & Legend (33) - Rev.1ari wibowoNo ratings yet
- Cold Filter Plugging Point CFPP: Manual and Semi-Automatic Analysers: Cold BehavioursDocument1 pageCold Filter Plugging Point CFPP: Manual and Semi-Automatic Analysers: Cold Behavioursنور الزهراءNo ratings yet
- 21st Students Century Skills - Chapter 1.john Nicolas .05.10.21Document8 pages21st Students Century Skills - Chapter 1.john Nicolas .05.10.21vic markNo ratings yet
- Replace Brake FluidDocument3 pagesReplace Brake FluidGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4: Lists: - TheoryDocument52 pagesLecture 4: Lists: - TheoryAli YussufNo ratings yet
- Shopee PH RTS Shipping Fee - Seller Claim Template-2Document4 pagesShopee PH RTS Shipping Fee - Seller Claim Template-2roel rhodael samsonNo ratings yet
- Manjari Bahety CMBA2Y3-1926Document9 pagesManjari Bahety CMBA2Y3-1926Siddharth ChoudheryNo ratings yet
- Aakash Udyam Registration CertificateDocument2 pagesAakash Udyam Registration CertificateAlive DasNo ratings yet
- Database Management c2Document33 pagesDatabase Management c2Gen TagaroNo ratings yet
- DCS800 DASC TrainingDocument2 pagesDCS800 DASC TrainingGabo2040No ratings yet
- Project Report Grp-90Document30 pagesProject Report Grp-90GOURAV MAKURNo ratings yet