Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Qualitative
Uploaded by
Wendy Marquez TababaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Qualitative
Uploaded by
Wendy Marquez TababaCopyright:
Available Formats
Qualitative Quantitative
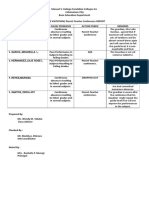
Purpose The purpose is to explain and gain insight and The purpose is to explain, predict, and/or control
understanding of phenomena through intensive phenomena through focused collection of
collection of narrative data Generate hypothesis numerical data. Test hypotheses, deductive.
to be test , inductive.
Approach to subjective, holistic, process- oriented Objective, focused, outcome- oriented
Inquiry
Hypotheses Tentative, evolving, based on particular study Specific, testable, stated prior to particular study
Research Setting Controlled setting not as important Controlled to the degree possible
Sampling Purposive: Intent to select “small, ” not Random: Intent to select “large, ” representative
necessarily representative, sample in order to sample in order to generalize results to a
get in-depth understanding population
Measurement Non-standardized, narrative (written word), Standardized, numerical (measurements,
ongoing numbers), at the end
Design and Method Flexible, specified only in general terms in Structured, inflexible, specified in detail in
advance of study Nonintervention, minimal advance of study Intervention, manipulation, and
disturbance All Descriptive— History, Biography, control Descriptive Correlation Causal-
Ethnography, Phenomenology, Grounded Comparative Experimental Consider few
Theory, Case Study, (hybrids of these) Consider variables, large group
many variable, small group
Data Collection Document and artifact (something observed) Observations (non-participant). Interviews and
Strategies that is collection (participant, non-participant). Focus Groups (semi-structured, formal).
Interviews/Focus Groups (un-/structured, Administration of tests and questionnaires (close
in-/formal). Administration of questionnaires ended).
(open ended). Taking of extensive, detailed field
notes.
Data Analysis Raw data are in words. Essentially ongoing, Raw data are numbers Performed at end of study,
involves using the observations/comments to involves statistics (using numbers to come to
come to a conclusion. conclusions).
Data Interpretation Conclusions are tentative (conclusions can Conclusions and generalizations formulated at
change), reviewed on an ongoing basis, end of study, stated with predetermined degree of
conclusions are generalizations. The validity of certainty. Inferences/generalizations are the
the inferences/generalizations are the reader’s researcher’s responsibility. Never 100% certain of
responsibility. our findings.
You might also like
- Headway Upperintermediate Teachers Guide PDFDocument240 pagesHeadway Upperintermediate Teachers Guide PDFJan Novak100% (14)
- Understanding the Difference Between Qualitative and Quantitative ResearchDocument2 pagesUnderstanding the Difference Between Qualitative and Quantitative ResearchSabhari Nath50% (2)
- Employee Salary and Benefits GuideDocument32 pagesEmployee Salary and Benefits GuideWendy Marquez Tababa75% (8)
- Difference Between Qualitative Research and Quantitative ResearchDocument3 pagesDifference Between Qualitative Research and Quantitative ResearchAcharya Krishna100% (1)
- Qualitative vs Quantitative: The Key DifferencesDocument2 pagesQualitative vs Quantitative: The Key Differencesjasmine anguloNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Research MethodDocument6 pages3.2 Research MethodsheenbergNo ratings yet
- Qualitative and quantitative research methods comparedDocument2 pagesQualitative and quantitative research methods comparedJean Gulleban100% (2)
- PDF Document PawsDocument3 pagesPDF Document PawsCarlo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Vs QuantitativeDocument2 pagesQualitative Vs QuantitativeCeejay Afinidad100% (1)
- (PS 109) ResearchDocument4 pages(PS 109) ResearchKaryfe Von OrtezaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Difference Between Qualitative and Qunatitative ResearchDocument6 pagesLESSON 3 Difference Between Qualitative and Qunatitative ResearchUlzzang girlNo ratings yet
- Research NotesDocument7 pagesResearch NotesRaiza Eve GaniaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative ResearchDocument15 pagesQualitative ResearchmichaelgumelarNo ratings yet
- Quantitative vs. Qualitative - SummaryDocument4 pagesQuantitative vs. Qualitative - SummarySoffi LutfianaNo ratings yet
- Differences between Qualitative and Quantitative Research MethodsDocument5 pagesDifferences between Qualitative and Quantitative Research MethodsDanielle Rose Jalagat100% (1)
- Reserach Paradgms and Methods - QuantittiveDocument33 pagesReserach Paradgms and Methods - Quantittivessentume peterNo ratings yet
- Qualitative ResearchDocument17 pagesQualitative ResearchFred Wekesa Wafula100% (3)
- Quantitative vs Qualitative Research MethodsDocument15 pagesQuantitative vs Qualitative Research MethodsAn ZalNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Data AnalysisDocument51 pagesQualitative Data Analysislekha1997100% (1)
- RM Notes 2020Document111 pagesRM Notes 2020ramanvohraNo ratings yet
- Research DesignsDocument13 pagesResearch DesignsAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Quantitative and Qualitative Research: Lesson 3Document4 pagesQuantitative and Qualitative Research: Lesson 3Norania MacarayaNo ratings yet
- Selecting Scientific Procedures and Research MethodsDocument5 pagesSelecting Scientific Procedures and Research MethodsDoãn Phương LinhNo ratings yet
- So What Is The Difference Between Qualitative Research and Quantitative ResearchDocument2 pagesSo What Is The Difference Between Qualitative Research and Quantitative ResearchAbdishakur Dahir MuseNo ratings yet
- By: Ivana Tria C. TorresDocument29 pagesBy: Ivana Tria C. TorresIvana Tria TorresNo ratings yet
- Nature of Quantitative ResearchDocument15 pagesNature of Quantitative ResearchJohanna GultianoNo ratings yet
- Quantitative and Qualitative Research MethodsDocument7 pagesQuantitative and Qualitative Research MethodsAbdul Rehman ShahidNo ratings yet
- Quantitative and QualitativeDocument7 pagesQuantitative and QualitativeTifanny Shaine TomasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Concept NotesDocument2 pagesLesson 3 Concept NotesGabriel Jericho MolasNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1 Q1 M4Document20 pagesPractical Research 1 Q1 M4dv vargasNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes - Unit On A PageDocument12 pagesRevision Notes - Unit On A PageKayy LaNo ratings yet
- Prac. 1 UNIT 2Document13 pagesPrac. 1 UNIT 2Chod DandoyNo ratings yet
- 4410Document4 pages4410KATE CORPUZNo ratings yet
- Prac Research Module 2Document12 pagesPrac Research Module 2Dennis Jade Gascon NumeronNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1: Quarter 1 - : Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument9 pagesPractical Research 1: Quarter 1 - : Nature of Inquiry and Researchallliyah ashlee cubolNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1Document10 pagesPractical Research 1Mindanao Community School100% (5)
- PR2 HeDocument12 pagesPR2 HeJay-r MatibagNo ratings yet
- Quantative and Qualitative ResearchDocument3 pagesQuantative and Qualitative ResearchOliver Cayetano IINo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research & Quantitative ResearchDocument2 pagesQualitative Research & Quantitative ResearchChamali WeerasingheNo ratings yet
- Social Natural Sciences Market Research MethodsDocument6 pagesSocial Natural Sciences Market Research MethodsSaulo SauloNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Rm1 1Document3 pagesReviewer Rm1 1junnie boyNo ratings yet
- LECTURES-QUALIDocument15 pagesLECTURES-QUALIChianlee CarreonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document6 pagesChapter 3Faye EbuenNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Quantitative: DefinationDocument3 pagesQualitative Quantitative: DefinationMargo ShaezNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Mid TermDocument9 pagesStudy Guide For Mid Term455.lorenzoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Introduction Nature Scope and Process of ResearchDocument65 pagesWeek 1 Introduction Nature Scope and Process of ResearchHenry dragoNo ratings yet
- NOTES of Your Mother Research TitleDocument9 pagesNOTES of Your Mother Research TitleBlessy MamangunNo ratings yet
- Business Research in 40 CharactersDocument7 pagesBusiness Research in 40 CharactersMostafa ElghifaryNo ratings yet
- English - 2nd MTDocument3 pagesEnglish - 2nd MTAaronNo ratings yet
- QualDocument39 pagesQualaigerim kazhigaliyevaNo ratings yet
- Marketing ResearchDocument40 pagesMarketing Researchartee_aggrawal4312No ratings yet
- RESEARCH-2Document2 pagesRESEARCH-2Kaela Beatrice Sy LatoNo ratings yet
- Becoming a Researcher: Guide to the Research ProcessDocument13 pagesBecoming a Researcher: Guide to the Research ProcessIvana Tria TorresNo ratings yet
- Research in Daily Life 2: Week 3Document10 pagesResearch in Daily Life 2: Week 3Abegail PanangNo ratings yet
- DissDocument8 pagesDissSummer Davz100% (1)
- Learning Activity Sheets - SedanoDocument61 pagesLearning Activity Sheets - SedanoKristine ColicoNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research MethodsDocument37 pagesQualitative Research Methodssandhya67% (3)
- Qualitative ResearchDocument15 pagesQualitative ResearchMa2FahriNo ratings yet
- Interdisciplinary Research PerspectivesDocument3 pagesInterdisciplinary Research PerspectivesSuminaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Quantitative ResearchDocument6 pagesCharacteristics of Quantitative Researchjuvylyn japosNo ratings yet
- 05 Research Methodology DesignsDocument15 pages05 Research Methodology DesignsNdaliNo ratings yet
- What Is It?: Defining The Conceptual FrameworkDocument8 pagesWhat Is It?: Defining The Conceptual FrameworkWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- Sumerian and Primitive Education InsightsDocument22 pagesSumerian and Primitive Education InsightsWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- First AidDocument56 pagesFirst AidWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- Early Egyptian Education: Prepared By: Aileen D. GonzalesDocument20 pagesEarly Egyptian Education: Prepared By: Aileen D. GonzalesWendy Marquez Tababa0% (1)
- Early Hindu Education: Aileen D. GonzalesDocument17 pagesEarly Hindu Education: Aileen D. GonzalesWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- Youtube Teorya NG WikaDocument1 pageYoutube Teorya NG WikaWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- First Aid Guide for Dressings, Bandages, Fractures & SplintingDocument29 pagesFirst Aid Guide for Dressings, Bandages, Fractures & SplintingWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- Color NotebookDocument1 pageColor NotebookWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- Basic First AidDocument64 pagesBasic First AidWendy Marquez Tababa100% (1)
- Brief History of AfpDocument10 pagesBrief History of AfpWendy Marquez Tababa100% (2)
- Report on 1st PTA MeetingDocument1 pageReport on 1st PTA MeetingWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- Basic First Aid GuideDocument64 pagesBasic First Aid GuideWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- Basic First AidDocument64 pagesBasic First AidWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- 4th PTA MinutesDocument2 pages4th PTA MinutesWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- CatDocument10 pagesCatWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- Clearance 18 19Document59 pagesClearance 18 19Wendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- Home Visit ReportDocument1 pageHome Visit ReportWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Graduation Practice Practice ScheduleDocument1 pageGuidelines For Graduation Practice Practice ScheduleWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- Home Visit ReportDocument1 pageHome Visit ReportWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- CAT Act .Document3 pagesCAT Act .Wendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- Unit Assessment Pe 9Document7 pagesUnit Assessment Pe 9Wendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- Letter For IntramsDocument1 pageLetter For IntramsWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- Community Issues and Concerns in The PhilippinesDocument11 pagesCommunity Issues and Concerns in The PhilippinesWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument2 pagesResumeWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- MarcusDocument1 pageMarcusWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- Wendy Tababa Resume - Filipino Teacher Cabanatuan CityDocument3 pagesWendy Tababa Resume - Filipino Teacher Cabanatuan CityWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- Tababa, Elaine M.: ST ND NDDocument2 pagesTababa, Elaine M.: ST ND NDWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- CWTS 1 M2 W2Document7 pagesCWTS 1 M2 W2Clark RefuerzoNo ratings yet
- Activity Performance Worksheet: Technology and Livelihood EducationDocument6 pagesActivity Performance Worksheet: Technology and Livelihood EducationKattie Alison Lumio MacatuggalNo ratings yet
- Personhood of Counsellor in CounsellingDocument9 pagesPersonhood of Counsellor in CounsellingPrerna singhNo ratings yet
- Corporate Management OverviewDocument14 pagesCorporate Management OverviewVipin Prabhakar SinghNo ratings yet
- Midterm Examination: Henri Fayol Identified 5 Functions of Management. According To Fayol (1916), ThisDocument12 pagesMidterm Examination: Henri Fayol Identified 5 Functions of Management. According To Fayol (1916), ThisPatrizzia Ann Rose OcbinaNo ratings yet
- TR-Pharmacy Services NC IIIDocument144 pagesTR-Pharmacy Services NC IIIArjohn UrianNo ratings yet
- Stanford Executive Program: Sample Course DescriptionsDocument6 pagesStanford Executive Program: Sample Course DescriptionsAndy MengNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Language Learning Strategies On ProficiencyDocument4 pagesThe Impact of Language Learning Strategies On ProficiencyJoel Batucan Ngojo Jr.No ratings yet
- Answer Sheet - Week 8 Grade 11 Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument4 pagesAnswer Sheet - Week 8 Grade 11 Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDarie BangaoilNo ratings yet
- Zimmerman, 2002Document8 pagesZimmerman, 2002CatharinaWidiartiniNo ratings yet
- Answers-:: Organisationsal Behaviour Assignment-1Document5 pagesAnswers-:: Organisationsal Behaviour Assignment-1Avirup SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Trifa Raluca - Crossing Boundaries - A New Methodological Model For The Evaluation of Industrial HeritageDocument2 pagesTrifa Raluca - Crossing Boundaries - A New Methodological Model For The Evaluation of Industrial HeritageRaluca TrifaNo ratings yet
- Human Needs PDFDocument13 pagesHuman Needs PDFapi-33294179No ratings yet
- Difference Between Entrepreneur and ManagerDocument3 pagesDifference Between Entrepreneur and ManagerJoylyn CarisosaNo ratings yet
- Truscott (1996) The Case Against Grammar Correction L2 WritingDocument43 pagesTruscott (1996) The Case Against Grammar Correction L2 WritingChomp100% (1)
- An Analysis of Swearing Expression in A Scottish Movie Entitled Sweet Sixteen (A Socio-Pragmatics Approach)Document225 pagesAn Analysis of Swearing Expression in A Scottish Movie Entitled Sweet Sixteen (A Socio-Pragmatics Approach)Uzlifatus SaadahNo ratings yet
- Personality, Attitudes & MotivationDocument32 pagesPersonality, Attitudes & MotivationnandhiniNo ratings yet
- Interrogative SentencesDocument11 pagesInterrogative SentencesRosa Adriana Egas DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Articole StiintificeDocument4 pagesArticole StiintificeAdriana OnofreiNo ratings yet
- Practice Terhadap Hasil Belajar Siswa Pada MataDocument13 pagesPractice Terhadap Hasil Belajar Siswa Pada Mataafief Clara rianaNo ratings yet
- Laura-Perdomo ResumeDocument3 pagesLaura-Perdomo Resumeapi-313801365No ratings yet
- A Study of JokesDocument8 pagesA Study of JokesHoshang SalaiyNo ratings yet
- Productivity NinjaDocument89 pagesProductivity NinjaLeyah ChristyNo ratings yet
- Life Skills: Expressing Yourself: Ways of Giving Your OpinionDocument3 pagesLife Skills: Expressing Yourself: Ways of Giving Your OpinionAliyaNo ratings yet
- Behavioral EconomicsDocument13 pagesBehavioral EconomicsRyan Hogan100% (2)
- Learning InsightsDocument1 pageLearning InsightsSecre NeroNo ratings yet
- OriginalsDocument11 pagesOriginalsyahiaNo ratings yet
- School Playground: Its Impact On Children's Learning and DevelopmentDocument3 pagesSchool Playground: Its Impact On Children's Learning and DevelopmentAnees QaziNo ratings yet
- Rachael Nelson 22-23 - Individual Professional Development Plan 22-23Document2 pagesRachael Nelson 22-23 - Individual Professional Development Plan 22-23api-351409040No ratings yet