Professional Documents
Culture Documents
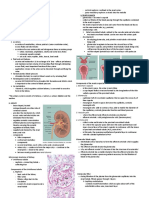
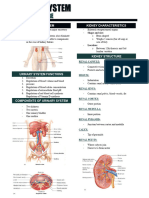
Parts of Urinary System
Uploaded by
ZHIARA MAE FACUN0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pagesThe urinary system helps remove waste from the body through urine. It contains millions of nephrons, the functional units of the kidney. Each nephron contains a renal corpuscle with a glomerulus surrounded by Bowman's capsule that filters blood to form urine. The renal tubules reabsorb water and ions from the filtered blood before it exits as urine through the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. In addition to excreting waste, the urinary system regulates fluid balance and produces hormones like erythropoietin and renin.
Original Description:
Original Title
URINARY SYTEM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe urinary system helps remove waste from the body through urine. It contains millions of nephrons, the functional units of the kidney. Each nephron contains a renal corpuscle with a glomerulus surrounded by Bowman's capsule that filters blood to form urine. The renal tubules reabsorb water and ions from the filtered blood before it exits as urine through the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. In addition to excreting waste, the urinary system regulates fluid balance and produces hormones like erythropoietin and renin.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pagesParts of Urinary System
Uploaded by
ZHIARA MAE FACUNThe urinary system helps remove waste from the body through urine. It contains millions of nephrons, the functional units of the kidney. Each nephron contains a renal corpuscle with a glomerulus surrounded by Bowman's capsule that filters blood to form urine. The renal tubules reabsorb water and ions from the filtered blood before it exits as urine through the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. In addition to excreting waste, the urinary system regulates fluid balance and produces hormones like erythropoietin and renin.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
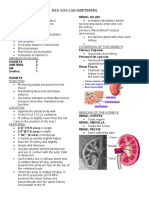
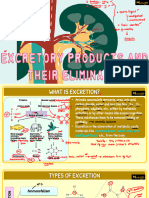
URINARY SYTEM Nephron- functional unit of a kidney, has millions of it in
the kidney.
It is important because it helps to remove our waste
products, especially urine. >> Renal tubules- tubules
Excrete excess water and waste products. Uriniferous tubule
It helps maintain normal extracellular fluid a. Proximal convoluted tubule- longer,
volume. absorbs glucose, amino acid, water (75%) +
Urinary system has endocrine function sodium chloride ion
- Releases hormone (erythropoietin acts on b. Loop of Henle (intermediate tubule)-
the bone marrow, stimulates the between the proximal and distal tubule it
production of rbc connects the proximal and distal.
- renin regulates blood pressure) - Going to distal convoluted tubule is thin;
Metabolize Vit. D.- controls the level of calcium going to proximal is thick.
in the body c. Distal convoluted tubule- shorter than the
proximal convoluted tubule, absorbs
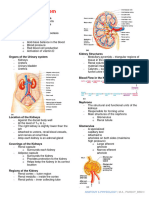
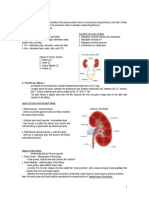
PARTS OF URINARY SYSTEM sodium ions.
- Vital for maintaining acid and base balance.
- KIDNEYS, URETER, BLADDER, URETHRA
d. Collecting tubules- absorbs water.
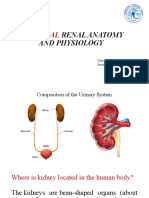
Kidney - Collects and absorbs water as much as
possible.
Renal pelvis- expanded part of the ureter.
Renal pyramid- triangular part of the medulla
(parenchyma)
Renal column- comprise of cortex
- Protruded renal column
BB- brush border- attached to the proximal
>> Renal corpuscle- capsule (pabilog)
Another part of the nephron
Other name- RENAL CORPUSCLE OF MALPHIGI
- Found within the cortex
- Spherical bodies that gives of a granular
appearance
- Comprised of Bowman’s capsule and
glomerulus.
You might also like
- Urinary SysDocument3 pagesUrinary SysMario Antonio CarpioNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract ReciewDocument5 pagesUrinary Tract ReciewRobert LotzerNo ratings yet
- Urinary System AssessmentDocument20 pagesUrinary System Assessmentsho bartNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument4 pagesUrinary SystemCharlie CharlesNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument9 pagesUrinary SystemRaven LacsonNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesUrinary SystemKids JangNo ratings yet
- Urinary FinalsDocument4 pagesUrinary FinalsAlliana Pauline AbanNo ratings yet
- FS1 R KR7 OMu 7 VZFPL B13 XDocument4 pagesFS1 R KR7 OMu 7 VZFPL B13 Xaadeshthite476No ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesUrinary Systemshane.surigaoNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument50 pagesThe Urinary SystemDasari PrasadNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesUrinary SystemCrystal MaidenNo ratings yet
- Urinary System and Fluid BalanceDocument3 pagesUrinary System and Fluid Balanceloviamae.belizarNo ratings yet
- Urinary System NotesDocument5 pagesUrinary System NotesValerie Bete100% (4)
- Sistem Uropoetika PDFDocument33 pagesSistem Uropoetika PDFCitra FaradinaNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument10 pagesUrinary Systemapi-19824701No ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument22 pagesUrinary SystemGray Odyssey M.No ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument9 pagesUrinary SystemPrincess OrsinoNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi 07-ExcretionDocument11 pagesHsslive Xi 07-ExcretionitsansafNo ratings yet
- Vipin Sir Biology 19. Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocument55 pagesVipin Sir Biology 19. Excretory Products and Their EliminationvanshpatelssisNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesUrinary Systemydnic alykPNo ratings yet
- MC I Modular Reviewer Urinary SystemDocument12 pagesMC I Modular Reviewer Urinary SystemSteiner LimNo ratings yet
- Excretory System: BY: Evi Susanti PutriDocument19 pagesExcretory System: BY: Evi Susanti PutriFahmi Zacki MubarakNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument10 pagesUrinary SystemAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument17 pagesUrinary SystemShiela Mae SagayoNo ratings yet
- Renal Function AubfDocument11 pagesRenal Function AubfHANNA CASANDRA GARCIANo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument3 pagesExcretory Systemden mNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 18 ANAPHY TransesDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 18 ANAPHY TransesHoly HaeinNo ratings yet
- Excretory-SystemDocument90 pagesExcretory-SystemArchitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 Anaphy TransesDocument5 pagesChapter 18 Anaphy TransesHoly HaeinNo ratings yet
- Essential Anatomi and Physiologi of KidneyDocument36 pagesEssential Anatomi and Physiologi of KidneyБаттөр ОтгонбатNo ratings yet
- Urinary System (Week 16)Document11 pagesUrinary System (Week 16)Krisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- 3 Renal SystemDocument30 pages3 Renal SystemgsnehaaNo ratings yet
- Urinary System: Owned By: Johnny AlangcasDocument7 pagesUrinary System: Owned By: Johnny AlangcasAkareNo ratings yet
- 3 - Excretion NotesDocument33 pages3 - Excretion NotesJenny YoonNo ratings yet
- TH RD: - Best Time To Collect: Morning Upon AwakeningDocument9 pagesTH RD: - Best Time To Collect: Morning Upon AwakeningAngelica Kaye BuanNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument3 pagesUrinary SystemJake SimNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Urinary SystemDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Urinary SystemContented LinganNo ratings yet
- Anaphy FinalDocument22 pagesAnaphy FinalMa Sofiya Yazmin OroñaNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument4 pagesUrinary Systemvea-ann espesoNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch19 Excretory Products and Their Elimination PDFDocument3 pages11 Biology Notes ch19 Excretory Products and Their Elimination PDFRamachandranPerumalNo ratings yet
- Review in AUBFDocument37 pagesReview in AUBFMichelle T. MabasaNo ratings yet
- EXCRETIONDocument9 pagesEXCRETIONMaira CanashinNo ratings yet
- Kidney Function - ExcretionDocument15 pagesKidney Function - Excretionznayune82No ratings yet
- Urinary and Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesUrinary and Reproductive SystemAlther LorenNo ratings yet
- THE Urinary System: Charlotte R. Espiritu RN. MANDocument25 pagesTHE Urinary System: Charlotte R. Espiritu RN. MANLenny Ronalyn QuitorianoNo ratings yet
- Urinary System PDFDocument51 pagesUrinary System PDFYeni Vera AchmadNo ratings yet
- Basic Medical Sciences 2: Renal SystemDocument38 pagesBasic Medical Sciences 2: Renal Systemblessed23No ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument9 pagesUrinary SystemMa Ellen LumauagNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products & Their Elimination PowernotesDocument2 pagesExcretory Products & Their Elimination PowernotesSushmit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- KidneyoutlineDocument33 pagesKidneyoutlineapi-273417637No ratings yet
- PINK Cream and Green Illustrative Science Project PresentationDocument31 pagesPINK Cream and Green Illustrative Science Project Presentationereneovalerozo22No ratings yet
- Case 8 GUS - AKIDocument210 pagesCase 8 GUS - AKIGroup 12 Sofia HanaNo ratings yet
- Happ Chapter 18 TransesDocument8 pagesHapp Chapter 18 TransesFrencess Kaye SimonNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument20 pagesUrinary SystemRancesh FamoNo ratings yet
- The KidneyDocument1 pageThe KidneyMushu MunuNo ratings yet
- Urogenital System: By:Mariska Fitri Silvia (1710422003) Salsabila Luqyana (1710422023)Document26 pagesUrogenital System: By:Mariska Fitri Silvia (1710422003) Salsabila Luqyana (1710422023)Salsabila LuqyanaNo ratings yet
- Urina Rysystem: FunctionsDocument3 pagesUrina Rysystem: FunctionsGracia Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- KIDNEYDocument3 pagesKIDNEYBaJo GarnaceNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument3 pagesThe Urinary SystemOji KangjiNo ratings yet
- Module 7 POST-TASK Substance MP (Literature Value, ) Structure Main Intermolecular ForcesDocument2 pagesModule 7 POST-TASK Substance MP (Literature Value, ) Structure Main Intermolecular ForcesZHIARA MAE FACUNNo ratings yet
- Module 9 POST-TASK Substance (Acidic) Picture 1. Tannic Acid (Wine)Document4 pagesModule 9 POST-TASK Substance (Acidic) Picture 1. Tannic Acid (Wine)ZHIARA MAE FACUNNo ratings yet
- 3 Cell Populations Static-It Does Not Undergo Dna SynthesisDocument4 pages3 Cell Populations Static-It Does Not Undergo Dna SynthesisZHIARA MAE FACUNNo ratings yet
- Asian Intellectual RevolutionDocument3 pagesAsian Intellectual RevolutionZHIARA MAE FACUNNo ratings yet
- STS M1Document7 pagesSTS M1ZHIARA MAE FACUNNo ratings yet
- Question Summarize Each of The Five Sections of The Approved Harmonized National R&DDocument6 pagesQuestion Summarize Each of The Five Sections of The Approved Harmonized National R&DZHIARA MAE FACUNNo ratings yet
- GBGBGBGB GB GB GB GB: Chapter 10: Dihybrid Cross WorksheetDocument1 pageGBGBGBGB GB GB GB GB: Chapter 10: Dihybrid Cross WorksheetZHIARA MAE FACUN100% (2)
- 3 Cell Populations Static-It Does Not Undergo Dna SynthesisDocument4 pages3 Cell Populations Static-It Does Not Undergo Dna SynthesisZHIARA MAE FACUNNo ratings yet
- Developing ToothDocument3 pagesDeveloping ToothZHIARA MAE FACUNNo ratings yet
- Activity - AldehydesDocument1 pageActivity - AldehydesZHIARA MAE FACUNNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12: Properties and MetabolismDocument7 pagesVitamin B12: Properties and Metabolismkalaiarasi ravichandranNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Periodic TestDocument2 pagesFirst Quarter Periodic TestNur ShaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Jigar PatelDocument6 pagesDr. Jigar PatelJigar PatelNo ratings yet
- Patient ProfileDocument3 pagesPatient ProfileKhaled GharaibehNo ratings yet
- Burn PPT VCMC 1Document70 pagesBurn PPT VCMC 1feva55100% (2)
- A2 Student Unit Guide Edexcel Biology Unit 5 PDFDocument95 pagesA2 Student Unit Guide Edexcel Biology Unit 5 PDFRishita Singh100% (2)
- Medmicro 32 2 135Document7 pagesMedmicro 32 2 135vinty permatasariNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic PathologyDocument2 pagesOrthopedic PathologyvetpathforumNo ratings yet
- Listeria MonocytogenesDocument28 pagesListeria Monocytogenestummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (1)
- Denagard Amoxicillin MICs For Respiratory PathogensDocument2 pagesDenagard Amoxicillin MICs For Respiratory Pathogensnick224No ratings yet
- Psy Book ResearchDocument6 pagesPsy Book Researchshankl1088No ratings yet
- Biology ChallengeDocument7 pagesBiology Challengemartynapet50% (2)
- Lung Cancer Case StudyDocument38 pagesLung Cancer Case StudyAna Marie Besa Battung-Zalun100% (2)
- Seminar Activity and Narrative Proposal 1Document15 pagesSeminar Activity and Narrative Proposal 1robucadjNo ratings yet
- Oxygen PresentationDocument26 pagesOxygen PresentationPennyStevana100% (1)
- Planescape 4e - Ecology of The ModronDocument9 pagesPlanescape 4e - Ecology of The ModronProfDrPepper100% (2)
- Adoption Foster ApplicationDocument4 pagesAdoption Foster Applicationlb8757No ratings yet
- Literatura 6Document4 pagesLiteratura 6Анастасія КарпенкоNo ratings yet
- Orbital Cellulitis PEDIADocument49 pagesOrbital Cellulitis PEDIACarmela VargasNo ratings yet
- Bio DoopDocument6 pagesBio DoopAnaconda Warriors 12 ANo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Mosquito Trivia: Anopheles Quadrimaculatus Culex Pipiens, Aedes Aegypti Aedes Albopictus AnophelesDocument3 pagesThe Ultimate Mosquito Trivia: Anopheles Quadrimaculatus Culex Pipiens, Aedes Aegypti Aedes Albopictus Anophelespixol9339No ratings yet
- Below-Knee Amputation Surgery: Henry E. Loon, M.DDocument14 pagesBelow-Knee Amputation Surgery: Henry E. Loon, M.Ddinda salmahellaNo ratings yet
- November 3, 2017 Strathmore TimesDocument24 pagesNovember 3, 2017 Strathmore TimesStrathmore TimesNo ratings yet
- Science Form 2Document4 pagesScience Form 2lembu_sihat77100% (1)
- Legal Medicine NewDocument19 pagesLegal Medicine Newmhilet_chiNo ratings yet
- Animal HusbandryDocument21 pagesAnimal Husbandrysasi00027No ratings yet
- Diagnosa Ultrasonografi Untuk Mendeteksi Kelainan Pada Organ Urogenitalia Anjing Jantan (Canis Lupus)Document54 pagesDiagnosa Ultrasonografi Untuk Mendeteksi Kelainan Pada Organ Urogenitalia Anjing Jantan (Canis Lupus)tubagus fauzul adzimNo ratings yet
- A1 Vs A2 Milk and Its SourceDocument1 pageA1 Vs A2 Milk and Its SourcecrneeteshNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka: Universitas Sumatera UtaraDocument3 pagesDaftar Pustaka: Universitas Sumatera UtaraAdisti ZakyatunnisaNo ratings yet
- Cumitech 23 - Infections of The Skin and Subcutaneous Tissues PDFDocument16 pagesCumitech 23 - Infections of The Skin and Subcutaneous Tissues PDFAnjali MohanNo ratings yet
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (84)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeFrom EverandThe Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (39)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (267)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- I Shouldn't Feel This Way: Name What’s Hard, Tame Your Guilt, and Transform Self-Sabotage into Brave ActionFrom EverandI Shouldn't Feel This Way: Name What’s Hard, Tame Your Guilt, and Transform Self-Sabotage into Brave ActionNo ratings yet
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (170)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (46)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceFrom EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (51)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesFrom EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1412)
- Self-Care for Autistic People: 100+ Ways to Recharge, De-Stress, and Unmask!From EverandSelf-Care for Autistic People: 100+ Ways to Recharge, De-Stress, and Unmask!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)