Professional Documents
Culture Documents
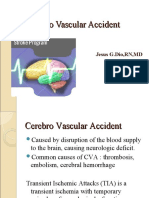
Cerebrovascular Accident or Stroke (Also: Called Brain Attack) Results From Sudden
Uploaded by
skullem180 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Sic
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views2 pagesCerebrovascular Accident or Stroke (Also: Called Brain Attack) Results From Sudden
Uploaded by
skullem18Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
System of Illness Condition
Clusters of Cues Organ/System Involved Normal Function Analysis
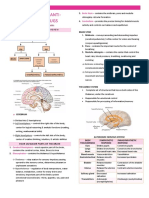
Subjective cues: The Cerebrum - The cerebrum or cortex is the My patient’s final diagnosis is CVA,
“Dih makahiwal in tunga largest part of the human brain, associated intracerebral hemorrhage left basal ganglia-
sin baran sin taymanghud with higher brain function such as thought thalamus secondary to hypertension.
ku,” as verbalized by the and action. The cerebral cortex is divided into
brother. four sections, called "lobes": the frontal lobe, Also, latest CT Scan impression include:
parietal lobe, occipital lobe, and temporal Intraparanchymal hemorrhage,
Objective cues: lobe. subcortical left temporoparietal lobe
Latest CT Scan Frontal Lobe- associated with and left capsuloganglionic area,
result: reasoning, planning, parts of speech, cortical and central cerebral atrophy.
Intraparanchymal movement, emotions, and problem
hemorrhage, solving Cerebrovascular accident or stroke (also
subcortical left Parietal Lobe- associated with called brain attack) results from sudden
temporoparietal movement, orientation, recognition, interruption of blood supply to the brain,
lobe and left perception of stimuli which precipitates neurologic dysfunction
capsuloganglionic Occipital Lobe- associated with visual lasting longer than 24 hours. Stroke are
area, cortical and processing either ischemic, caused by partial or
central cerebral Temporal Lobe- associated with complete occlusions of a cerebral blood
atrophy. perception and recognition of vessel by cerebral thrombosis or embolism or
auditory stimuli, memory, and speech hemorrhage (leakage of blood from a vessel
Right sided causes compression of brain tissue and
immobility Basal Ganglia - Processing link between spasm of adjacent vessels). Hemorrhage may
thalamus and motor cortex. Initiation and occur outside the dura (extradural), beneath
Slurred speech direction of voluntary movement. Balance the dura mater (subdural), in the
(inhibitory), Postural reflexes. subarachnoid space (subarachnoid), or within
Risk for aspiration the brain substance itself (intracerebral).
Thalamus – Receives auditory,
somatosensory, and visual signals. Relays My patient developed right sided immobility
sensory signals to the cerebral cortex and as a result of CVA. Right sided immobility or
motor control. right hemiplegia is caused by a cerebral
hemorrhage specifically on the left
Hypothalamus - pituitary gland regulation, temporoparietal lobe. This left
blood pressure regulation, hunger and salt temporoparietal lobe controls the association
cravings, feeding reflexes, thirst, body of movement on the RIGHT side of the body
temperature regulation ,hydration, heart which explains why my patient has right
rate, bladder function sided hemiplegia.
water preservation,
hormonal/neurotransmitter regulation, Furthermore, I also noted evidences of
ovarian function , testicular function, mood & slurred speech on the patient. Slurred speech
is a result of cerebral hemorrhage that might
behavioral functions, wakefulness, have affected the frontal lobe responsible for
metabolism, sleep cycles, energy levels the parts of speech.
Amygdala - The main function of amygdala is Difficulty on swallowing or dysphagia may
emotional and social processing. It processes occur in up to 65 percent of stroke patients. If
and stores memories of emotional events and not identified and managed, it can lead to
is also involved in current emotional poor nutrition, pneumonia and increased
response. disability. That is why my patient’s feeding is
Hippocampus - According to recent studies, at sitting position to prevent ASPIRATION.
its important role is in the formation of
new memories about experienced events
(episodic or autobiographical memory).
Cerebellum - The cerebellum function
involves the regulation and coordination of
movement, posture and brain.
You might also like
- Ebook PDF The Science of Psychology An Appreciative View 5th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF The Science of Psychology An Appreciative View 5th Edition PDFmarilyn.trojanowski475100% (37)
- Brain Parts and Functions Chart KeyDocument2 pagesBrain Parts and Functions Chart Keybhihi jkgug;u75% (4)
- Neuroanatomy Guide to Cells, Fiber Tracts & Brain RegionsDocument107 pagesNeuroanatomy Guide to Cells, Fiber Tracts & Brain RegionsAlan Magpantay100% (1)
- The Twelve Core Action Values WorkbookDocument420 pagesThe Twelve Core Action Values WorkbookMouton DePanurge100% (4)
- The Myth of Autism: How a Misunderstood Epidemic Is Destroying Our ChildrenFrom EverandThe Myth of Autism: How a Misunderstood Epidemic Is Destroying Our ChildrenRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (8)
- Esoteric Anatomy - Part 1: Esoteric Anatomy, #1From EverandEsoteric Anatomy - Part 1: Esoteric Anatomy, #1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 7 Triggers To YesDocument16 pages7 Triggers To YesSaket Sharma100% (1)
- Biological MindDocument25 pagesBiological MindQuesiah González100% (1)
- Anatomy of BrainDocument9 pagesAnatomy of Brainfever_159100% (1)
- Neurological Assessment - Romeo RiveraDocument9 pagesNeurological Assessment - Romeo Riveraromeo riveraNo ratings yet
- Neurological AssessmentDocument13 pagesNeurological AssessmentLorenz Jude CańeteNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum, Thalamus, and HypothalamusDocument40 pagesCerebellum, Thalamus, and Hypothalamusasep100% (1)
- Stroke & Hemiplegia LocalizationDocument54 pagesStroke & Hemiplegia LocalizationVasu PottabatthiniNo ratings yet
- Bio PsychologyDocument30 pagesBio PsychologyNEHA JUNEJANo ratings yet
- Case 6 Revision - Cognitive Impairment: Central SulcusDocument7 pagesCase 6 Revision - Cognitive Impairment: Central SulcusCharlie WalkerNo ratings yet
- EmdrDocument33 pagesEmdrShanker Iyer100% (1)
- Neurorehabilitation 1: Stroke, TBI, MS, PD, GBS, and ALS ExaminationDocument439 pagesNeurorehabilitation 1: Stroke, TBI, MS, PD, GBS, and ALS ExaminationDuncan D'AmicoNo ratings yet
- My Book - Its Only I View My Perception Is Reality PDFDocument313 pagesMy Book - Its Only I View My Perception Is Reality PDFAndrew HannamNo ratings yet
- 2 - Chapter I - Lesson 2 - Imagery in PoetryDocument9 pages2 - Chapter I - Lesson 2 - Imagery in PoetryDave Decolas67% (49)
- The Healing Brain - The Reader's DigestDocument153 pagesThe Healing Brain - The Reader's Digestmagic_of_kali100% (2)
- Cerebellum & DiencephalonDocument21 pagesCerebellum & Diencephalonprasun_vNo ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology: Understanding How Drugs Affect the BrainDocument29 pagesPsychopharmacology: Understanding How Drugs Affect the BrainChris ZantiraNo ratings yet
- Learning To Be A Better StudentDocument15 pagesLearning To Be A Better StudentMika LavadoNo ratings yet
- Cerebro Vascular AccidentDocument82 pagesCerebro Vascular AccidentJayvee Novenario Casaljay100% (1)
- Lesson 1. Overview of Physiological PsychologyDocument8 pagesLesson 1. Overview of Physiological PsychologyMaedel Rose EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Topical Diagnosis: Department of Anatomy Medical Faculty, Hasanuddin UniversityDocument48 pagesTopical Diagnosis: Department of Anatomy Medical Faculty, Hasanuddin UniversityRey Alwiwikh100% (1)
- The Psychology of SLA - Language and The BrainDocument19 pagesThe Psychology of SLA - Language and The BrainSussanRoo100% (1)
- Lieberman (2012)Document5 pagesLieberman (2012)Renzo LanfrancoNo ratings yet
- Dr. Titis-Anatomi Fisiologi Cns - Mielum X 2022 - ProtectedDocument41 pagesDr. Titis-Anatomi Fisiologi Cns - Mielum X 2022 - ProtectedFahmi MyNo ratings yet
- CNS - Clinical Evaluation of HemiplegiaDocument36 pagesCNS - Clinical Evaluation of HemiplegiaDipin ManiNo ratings yet
- NEURO NOTESDocument5 pagesNEURO NOTESms. xxNo ratings yet
- Vascular Lesions and Review of Blood Supply: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesVascular Lesions and Review of Blood Supply: ObjectivesRigel WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- K3. Anatomi Sistem Limbik, ARAS, Saraf Tepi, Dalam Aspek Neurologis (Dr. Ahmad Azmi Nasution, M.Biomed)Document112 pagesK3. Anatomi Sistem Limbik, ARAS, Saraf Tepi, Dalam Aspek Neurologis (Dr. Ahmad Azmi Nasution, M.Biomed)AmesyahNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Cortex MappingDocument62 pagesCerebral Cortex MappingMORGAN LAMBERTNo ratings yet
- Abses SerebriDocument19 pagesAbses Serebristeve daresonNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis and Higher Brain FunctionsDocument84 pagesHomeostasis and Higher Brain Functionsbodeadumitru9261No ratings yet
- 11 Reticular Formation and Limbic SystemDocument15 pages11 Reticular Formation and Limbic SystemDavid KleinNo ratings yet
- Disorders of ConsciousnessDocument6 pagesDisorders of ConsciousnessJessa BuenoNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesNervous SystemJanica Pauline DaydayNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Cortex Areas and Their FunctionsDocument62 pagesCerebral Cortex Areas and Their FunctionsJ NNo ratings yet
- Why, . Sign and Symptom!!!: Anwar Wardy, MD - Neu Department of Neurology FKK UmjDocument29 pagesWhy, . Sign and Symptom!!!: Anwar Wardy, MD - Neu Department of Neurology FKK UmjNurul Wandasari SNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience II: CerebellumDocument13 pagesNeuroscience II: CerebellumTrina CardonaNo ratings yet
- Brain and Psychotropic Drugs ReviewDocument5 pagesBrain and Psychotropic Drugs ReviewMichaela BernadasNo ratings yet
- Brainsci 10 00584 v2 3Document15 pagesBrainsci 10 00584 v2 3Paola BuitragoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System OverviewDocument4 pagesNervous System OverviewEds SyNo ratings yet
- Neurobiologic Theories and PsychopharmacologyDocument7 pagesNeurobiologic Theories and PsychopharmacologyhoneyNo ratings yet
- Neuropsychology DetailsDocument15 pagesNeuropsychology DetailswillemrikhofspamNo ratings yet
- CerebellumDocument85 pagesCerebellumMillicent KajaraNo ratings yet
- Brain Structure and FunctionDocument61 pagesBrain Structure and FunctionBINITANo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy Overview (Inglés) (Presentación) Autor Lennart BrodinDocument60 pagesNeuroanatomy Overview (Inglés) (Presentación) Autor Lennart BrodinJulia AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Arterial Supply of The Thalamus - A Comprehensive ReviewDocument9 pagesArterial Supply of The Thalamus - A Comprehensive Reviewمحمد رؤوف خير الدينNo ratings yet
- 10 - NS3 Diencephalon Brainstem Cerebellum Conestoga (Handout) F2022 (Exported)Document37 pages10 - NS3 Diencephalon Brainstem Cerebellum Conestoga (Handout) F2022 (Exported)Lucky NguyenNo ratings yet
- Nervous System-Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument64 pagesNervous System-Anatomy & PhysiologyDeshi SportsNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: NURS 3100 Patho/Pharm 2Document37 pagesNervous System: NURS 3100 Patho/Pharm 2Malaya MilesNo ratings yet
- NEUROLOGICAL ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVESDocument75 pagesNEUROLOGICAL ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVESHarper EppsNo ratings yet
- Diencephalon, Basal Ganglia, Limbic SystemDocument56 pagesDiencephalon, Basal Ganglia, Limbic SystemJoaquin GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Disorders PresentationDocument70 pagesCognitive Disorders PresentationWasiu AfoloabiNo ratings yet
- Assessing the Neurologic SystemDocument7 pagesAssessing the Neurologic Systemjanikkakristal100% (1)
- Brainstem Stroke SyndromesDocument43 pagesBrainstem Stroke SyndromesSarah Choo Qian RouNo ratings yet
- Review Med SurgDocument14 pagesReview Med SurgjohnpaulvidalNo ratings yet
- Neuroendocrinology of Circadian RhythmsDocument17 pagesNeuroendocrinology of Circadian RhythmsDaly DaliaNo ratings yet
- (NEURODocument20 pages(NEUROMario SutantoNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Nervous System and Brainstem AnatomyDocument30 pagesUnderstanding the Nervous System and Brainstem AnatomySatyam ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 3084 C006 PDFDocument9 pages3084 C006 PDFjuan95439No ratings yet
- Sleep Physiology 1st YrDocument45 pagesSleep Physiology 1st YrJeffrey RamosNo ratings yet
- Coma and Related Disorders of ConsciousnessDocument46 pagesComa and Related Disorders of ConsciousnessdeliarelaNo ratings yet
- The Limbic System: An Overview of its Components and FunctionsDocument38 pagesThe Limbic System: An Overview of its Components and FunctionsDr.Mukesh chandNo ratings yet
- Chapters 11 12 SingleDocument35 pagesChapters 11 12 Singlegeorgefromba100% (1)
- NervousDocument25 pagesNervousfairyzzzNo ratings yet
- Realism in The Novel of Thomas HardyDocument21 pagesRealism in The Novel of Thomas HardyAndrew LucasNo ratings yet
- The Underpinnings of Cerebellar AtaxiasDocument16 pagesThe Underpinnings of Cerebellar AtaxiasManuek GarciaNo ratings yet
- Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy in ChildrenDocument8 pagesEndoscopic Third Ventriculostomy in ChildrenCarlos Daniel Giménez MéndezNo ratings yet
- 20 Most Important Questions on Neural NetworksDocument4 pages20 Most Important Questions on Neural NetworksRashi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Explanation ExerciseDocument5 pagesExplanation Exercisejhon martin100% (1)
- Memory HTMLDocument20 pagesMemory HTMLhalleyworldNo ratings yet
- SPE-195072-MS Applications of Artificial Neural Networks in The Petroleum Industry: A ReviewDocument12 pagesSPE-195072-MS Applications of Artificial Neural Networks in The Petroleum Industry: A Reviewsaif khudhairNo ratings yet
- Neuroeconomics: Intermediate Article Kevin Mccabe, George Mason University, Fairfax, Virginia, UsaDocument5 pagesNeuroeconomics: Intermediate Article Kevin Mccabe, George Mason University, Fairfax, Virginia, UsaScrib DFbNo ratings yet
- Galvan, Hare, Voss, Glover y Casey 2007 Risk Taking and The Adolescent Brain PDFDocument7 pagesGalvan, Hare, Voss, Glover y Casey 2007 Risk Taking and The Adolescent Brain PDFSamuel Salinas ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- Causes of HypotoniaDocument2 pagesCauses of HypotoniaPutri Rahmi MaharaniNo ratings yet
- CCMP96 RD 039+腦中風之中醫證型就主流醫學觀點之研究 (2 1)Document24 pagesCCMP96 RD 039+腦中風之中醫證型就主流醫學觀點之研究 (2 1)陳瑋毅No ratings yet
- Brain Chips: Presented By: K.Jaya Sai PrasadDocument20 pagesBrain Chips: Presented By: K.Jaya Sai PrasadAnonymous 8sO4pQut0dNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Skill Related Fitness ComponentsDocument42 pagesModule 5 Skill Related Fitness Componentsjeffrey ordinalNo ratings yet
- Assumptions Underlying Motor Control-HorakDocument17 pagesAssumptions Underlying Motor Control-HorakAngela campoNo ratings yet
- The Limbic System: Emotion and Memory in the BrainDocument4 pagesThe Limbic System: Emotion and Memory in the BrainAyu NurdiyanNo ratings yet
- Zimbardo Video: The Behaving Brain AssignmentDocument10 pagesZimbardo Video: The Behaving Brain AssignmentJayNo ratings yet
- ActivationDocument1 pageActivationKatrin NovaNo ratings yet
- Protecting the nervous system through lifestyleDocument19 pagesProtecting the nervous system through lifestyleZachary me meNo ratings yet
- Unthought Meets The Assemblage Brain PDFDocument25 pagesUnthought Meets The Assemblage Brain PDFSoma BasuNo ratings yet