Professional Documents
Culture Documents
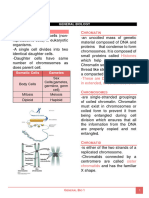
Cell division and meiosis overview
Uploaded by
SirCrumbly CookiesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell division and meiosis overview
Uploaded by
SirCrumbly CookiesCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes
Monday, 7 September 2020 7:27 pm
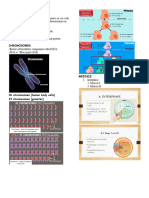
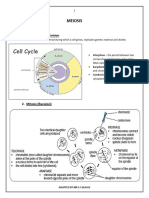
Cell Division Meiosis
- Reduces chromosome number from the diploid number
- Orderly set of stages between the time eukaryotic cell divides (2n) to haploid number (n)
and time the resulting daughter cells also divide. - 4 distinct daughter cells
- Happens only in sex cells (egg & sperm)
Types of Cells
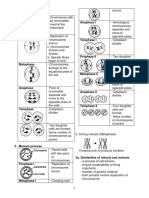
*In meiosis I (reductional division)
- Somatic Cells (haploid to diploid) n to 2n (Mitosis) PROPHASE I
- Meiotic Cells (diploid to haploid) 2n to n (Meiosis)
- Similar mitotic prophase
Binary Fission in Prokaryotes - Homologous chromosomes pair (tetrad/synapsis) and
Mitosis/Meiosis in Eukaryotes crosses over
METAPHASE I
- Homologous chromosomes align to metaphase plate
ANAPHASE I
- Homologous pairs are pulled apart and move to opposite
poles
TELOPHASE I
- Chromosomes decondense
- Nuclear membrane forms
- Cytokinesis
Screen clipping taken: 07/09/2020 7:34 pm *In Meiosis II (equatorial division)
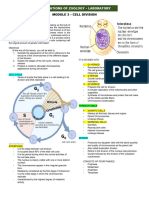
a. G1 STAGE (Growth Phase 1) - Will not undergo interphase
- G – “growth”
- Cell recovery from previous PROPHASE II
division
- Cell increases in size and - New spindle fiber forms around
doubles its organelles the chromosomes
- Accumulate materials needed
for DNA synthesis METAPHASE II
b. G1 CHECKPOINT - Chromosomes line up at the
- Checks for nutrients & growth equator
- If DNA is NOT damaged, cell goes to resting period
(GO) until it is ready to divide (mitosis) ANAPHASE II
- If damaged, it undergoes apoptosis (self-destruction)
- Centromeres divide
c. S STAGE – replication/synthesis of - Chromatids move to the
DNA opposite poles
d. G2 STAGE – protein synthesis TELOPHASE II & CYTOKINESIS
(transcription and translation)
- Nuclear envelope forms around
e. G2 CHECKPOINT – check for each set of chromosomes
DNA replicator, cell size, and if - Cytoplasm divides
protein are enough. Cell undergoes
mitosis or apoptosis Human Chromosomes
Mitosis (Mitotic Stage) Chromosomes
PROPHASE - “chroma’ – color; “soma” – body
- DNA molecules packaged via histones into
thread like structures
- visible duplication of chromosome (2 identical
- 23 pairs in humans
sister chromatids)
- The 23rd pair is the sex chromosomes
- chromatin fibers condenses into discrete chromosomes
- Arranged from largest to shortest
- spindle fiber forms and the centrosomes move toward the
opposite poles
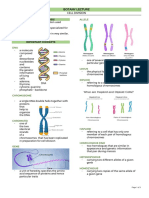
Parts
PROMETAPHASE
1. SISTER CHROMATIDS
- fragmented nuclear envelope
- 2 thread like strands that divide
- nuclear membrane gradually disintegrates
- long (q) and short arm (p)
- microtubule invades nuclear area and attaches to the
chromatids’ kinetochores
- non kinetochore microtubules lengthens the cell (opposite 2. CENTROMERE
Cell Cycle Page 1
- fragmented nuclear envelope
- 2 thread like strands that divide
- nuclear membrane gradually disintegrates
- long (q) and short arm (p)
- microtubule invades nuclear area and attaches to the
chromatids’ kinetochores
- non kinetochore microtubules lengthens the cell (opposite 2. CENTROMERE
poles)
- region where chromatids are attached
Together
METAPHASE
- where spindle fibers are attached
- chromosomes align at center
(metaphase plate) - made of cohesin proteins
- push and pull of microtubular units
- metaphase checkpoint – checks for alignment of - spindle fiber (mitotic spindle) – long
chromosome spindle microtubules used for cell division
- mitosis or apoptosis
- kinetochores – protein complex where
ANAPHASE spindle fibers attack
- sister chromatids part upon the break of the centromere Chromatin vs. Chromatid vs. Chromosome
- Chromosomes migrate towards the opposite poles
(same number and kind) - loose DNA during interphase (chromatin)
- Shortest stage - loose DNA is then tightly packed (chromatids)
- Disappearance of spindle fibers - chromatids are joined together by the centromere
(chromosome)
TELOPHASE - chromosomal conditions
- Daughter cells form (indistinct chromatin)
- Reappearance of nuclear membrane and nucleolus
CYTOKINESIS
- Cytoplasm division
- In animal cells: - cleavage furrow appears
- In plant cells – cell plate appears
Cell Cycle Page 2
You might also like
- NotesDocument2 pagesNotesSirCrumbly CookiesNo ratings yet
- Genbio Reviwer FinalsDocument5 pagesGenbio Reviwer FinalsChesley CarolinoNo ratings yet
- Genbio Reviwer FinalsDocument6 pagesGenbio Reviwer FinalsChesley CarolinoNo ratings yet
- Bio11 Campbell Chapter 12Document4 pagesBio11 Campbell Chapter 12ChristineNo ratings yet
- S4AE BiologyDocument51 pagesS4AE BiologyLeung BibiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4Document4 pagesExercise 4BARRIENTOS, MARIE NICOLENo ratings yet
- Cell Division and Chromosome ReplicationDocument5 pagesCell Division and Chromosome Replicationkami gourgaemNo ratings yet
- MEIOSISDocument2 pagesMEIOSISKim BeatrizNo ratings yet
- BiologijaDocument12 pagesBiologijablipNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell DivisionmunozayshiaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell DivisionChristina DaligconNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument9 pagesMeiosisRudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- Meiosis StagesDocument8 pagesMeiosis StagesAmelie BalibagonNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and MitosisDocument22 pagesMeiosis and Mitosisyaqoob008No ratings yet
- Anaphase I Begins When The Two Chromosomes of EachDocument4 pagesAnaphase I Begins When The Two Chromosomes of EachmatNo ratings yet
- AP BIO Unit Three Study Guide Key ConceptsDocument4 pagesAP BIO Unit Three Study Guide Key ConceptsKaycia HenryNo ratings yet
- 2020 F4 SCIENCE NOTES KSSM CHAPTER 4 6aDocument1 page2020 F4 SCIENCE NOTES KSSM CHAPTER 4 6aWani MesraNo ratings yet
- (W3) Cell CycleDocument6 pages(W3) Cell CycleRednaxela Mejico TarucNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle: Comparison Between Interphase StagesDocument3 pagesThe Cell Cycle: Comparison Between Interphase StagesBayader ALTLHINo ratings yet
- Cell DivisonsDocument2 pagesCell DivisonsharlyNo ratings yet
- KCB Biology Dept Cell Division GuideDocument11 pagesKCB Biology Dept Cell Division GuideJovia TNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Mitosis and MeiosisDocument3 pagesCell Cycle Mitosis and MeiosisjaysparklesNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument3 pagesMITOSISDaphne Ezra F. OlegarioNo ratings yet
- FOZ_LAB_M3Document7 pagesFOZ_LAB_M3jsbitsoflyfNo ratings yet
- Genetics 2019Document151 pagesGenetics 2019Joycee Jatulan-EnajeNo ratings yet
- Topic-4-Bio-1130 Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesTopic-4-Bio-1130 Cell DivisionMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- MITOSIS vs MEIOSISDocument5 pagesMITOSIS vs MEIOSISJohanna GultianoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy and Phisiology Midterm NotesDocument19 pagesAnaphy and Phisiology Midterm NotesLucy AlmonteNo ratings yet
- Bio Rev 2Document3 pagesBio Rev 2mailforprinting101No ratings yet
- (BIOLOGY) Cell DivisionDocument12 pages(BIOLOGY) Cell DivisionHAJIRA RAMLANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 VocabularyDocument4 pagesChapter 8 Vocabularyapi-3729377100% (1)
- The Cell Cycle & Cell Division: Has One Centromere and Two ChromatidsDocument4 pagesThe Cell Cycle & Cell Division: Has One Centromere and Two ChromatidsMnemo SyneNo ratings yet
- M2-L2-Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument2 pagesM2-L2-Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionAira Estandian GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division - Short NotesDocument4 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division - Short NotesShafa SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 Cell Cycle and DivisionDocument4 pagesCh-1 Cell Cycle and DivisionHans RajNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis InfographDocument1 pageMitosis and Meiosis InfographPatricia BonganayNo ratings yet
- Fish Genetics and Breeding ExplainedDocument27 pagesFish Genetics and Breeding ExplainedHanna Beth Butiong TandayagNo ratings yet
- Cyto 3Document2 pagesCyto 3Zharlene DoloresNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument6 pagesMeiosisAbhijeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle-Mitosis - Meiosis SlidesDocument19 pagesCell Cycle-Mitosis - Meiosis SlideslkjosNo ratings yet
- Mastering Biology BK2 NotesDocument44 pagesMastering Biology BK2 NotesAlva WongNo ratings yet
- BIO C6 NOTESDocument13 pagesBIO C6 NOTESTHEN YUE PINGNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesCell DivisionMEDRANO, Hana Jhiemyka O.No ratings yet
- BT155IU Biology Lab Mitosis and MeiosisDocument15 pagesBT155IU Biology Lab Mitosis and MeiosisLý Huệ LinNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument4 pagesCell CycleJULIA AUDREY PERALTANo ratings yet
- Genetics O'level Biology NotesDocument18 pagesGenetics O'level Biology NotesBrian Obong100% (1)
- Phases of MitosisDocument11 pagesPhases of MitosiskxtnystromNo ratings yet
- MEIOSIS NotesDocument11 pagesMEIOSIS Notesnoxolo dwane100% (2)
- Reviewer in BiologyDocument2 pagesReviewer in Biology임 제리카No ratings yet
- Biology (Mitosis Cell Division)Document3 pagesBiology (Mitosis Cell Division)Harry ParconNo ratings yet
- Biology (Mitosis Cell Division)Document3 pagesBiology (Mitosis Cell Division)Harry ParconNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle ReviewerDocument2 pagesThe Cell Cycle ReviewerNcle NaborNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6-Cellular-reproductionDocument22 pagesChapter-6-Cellular-reproductionnguyenminhhuyen.workNo ratings yet
- Cell Division (Edited)Document12 pagesCell Division (Edited)Ian Karlo NuñezNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter in General Biology 1 - Grade 12: Types of Cell Somatic CellsDocument12 pagesSecond Quarter in General Biology 1 - Grade 12: Types of Cell Somatic CellsIan Karlo NuñezNo ratings yet
- 3 ScanDocument5 pages3 ScanAsadNo ratings yet
- Lumko Liberty Ntuli Student No 221015440 Gene 240 Tut 4 DoneDocument3 pagesLumko Liberty Ntuli Student No 221015440 Gene 240 Tut 4 DoneMthetheleli NxeleNo ratings yet
- Cell Division, Mitosis, Meiosis, AmitosisDocument27 pagesCell Division, Mitosis, Meiosis, AmitosisAngryBird_jinx100% (1)
- Mitosis WorksheetDocument3 pagesMitosis WorksheetHipster48No ratings yet
- Axial SkeletonDocument12 pagesAxial SkeletonSirCrumbly CookiesNo ratings yet
- 10.1.1 The Passionate Shepherd To His LoveDocument1 page10.1.1 The Passionate Shepherd To His LoveSirCrumbly CookiesNo ratings yet
- Mass Songs PDFDocument44 pagesMass Songs PDFSirCrumbly CookiesNo ratings yet
- Mass Songs PDFDocument44 pagesMass Songs PDFSirCrumbly CookiesNo ratings yet
- Alab Mass 2019 Lyrics Come Holy GhostDocument4 pagesAlab Mass 2019 Lyrics Come Holy GhostSirCrumbly CookiesNo ratings yet
- Mitosis QuestionsDocument10 pagesMitosis QuestionscapremaeNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument31 pagesCell CycleAlthea Angela BulaclacNo ratings yet
- General Biology Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)Document37 pagesGeneral Biology Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)shieeesh.aNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle-Mitosis - Meiosis SlidesDocument19 pagesCell Cycle-Mitosis - Meiosis SlideslkjosNo ratings yet
- CH 45 MeiosisDocument17 pagesCH 45 MeiosiserichaasNo ratings yet
- Science Quiz Bee Score SheetDocument14 pagesScience Quiz Bee Score SheetTeacher DennisNo ratings yet
- 9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument8 pages9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of Teacherswafaul_athiyyahNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Biology For Examination From 2022Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Biology For Examination From 2022bliss chipunzaNo ratings yet
- M13 Cell CycleDocument15 pagesM13 Cell CycleSamantha Kyle E. PedrigozaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis ExplainedDocument2 pagesMeiosis ExplainedGlenn GalvezNo ratings yet
- Notes in Biology Zoology LectureDocument18 pagesNotes in Biology Zoology LectureSebastian NarcisoNo ratings yet
- Cell Growth and Division: How and Why Cells DivideDocument36 pagesCell Growth and Division: How and Why Cells DivideLife with CourteneyNo ratings yet
- Tri-Fold Template-1Document2 pagesTri-Fold Template-1api-260947636No ratings yet
- Chromosomal Basis Of InheritanceDocument70 pagesChromosomal Basis Of Inheritancehailu hamesoNo ratings yet
- Biology Class 10 Icse Boards!Document10 pagesBiology Class 10 Icse Boards!nark.jf4No ratings yet
- 0 BooksDocument20 pages0 Bookslaraib zahidNo ratings yet
- Cell, Tissue & MembraneDocument24 pagesCell, Tissue & MembranehumaNo ratings yet
- Mitotic Aberrations Induced by Orange Red (A Food Additive Dye) As A Potential Genotoxicant On Root Tip Cells of Onion (Allium Cepa L.)Document10 pagesMitotic Aberrations Induced by Orange Red (A Food Additive Dye) As A Potential Genotoxicant On Root Tip Cells of Onion (Allium Cepa L.)satriaNo ratings yet
- PBL-3: Effects of Smoking and Gutka on HealthDocument8 pagesPBL-3: Effects of Smoking and Gutka on HealthRomi RajaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument31 pagesCell DivisionShin Thant Ko B10 June SectionNo ratings yet
- Bms2042 Usg Part 1Document334 pagesBms2042 Usg Part 1api-3869815No ratings yet
- Cell Biology Practice 2 Questions and AnswersDocument15 pagesCell Biology Practice 2 Questions and AnswersNgMinhHaiNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle QuizDocument3 pagesCell Cycle QuizCa RingorNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Division: Phases, Mitosis, MeiosisDocument4 pagesCell Cycle and Division: Phases, Mitosis, MeiosisRamendra SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Keystone Biology ReviewDocument53 pagesKeystone Biology ReviewTalia GelmanNo ratings yet
- Cell & Tissue StructureDocument19 pagesCell & Tissue StructureBrintha Kani KumarNo ratings yet
- IGenetics, Chapter 2 - RusselDocument73 pagesIGenetics, Chapter 2 - RusselGeorges SarkisNo ratings yet
- Science - June 24th 2011Document129 pagesScience - June 24th 2011pys009No ratings yet
- New Pattr Model Q 01.Document43 pagesNew Pattr Model Q 01.Hari Krishnan KNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 6 Study Guide AnswersDocument3 pagesBiology Unit 6 Study Guide AnswersmisterbrownerNo ratings yet