Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Philosophy
Uploaded by
blabla blablaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Philosophy
Uploaded by
blabla blablaCopyright:
Available Formats
PHILOSOPHY individuals or group of individuals or group of
individuals, regardless of the specific nature of
these ideas, views, principles, perspectives, or
beliefs.
Subtopics:
Some Common Meanings
2. Philosophy as the activity of
The Love of Wisdom
Asking Framework Questions reasoning
Philosophy as an Activity
PILOSOPO
SOME COMMON MEANINGS
-is the one who likes to reason out to engage in
the activity of reasoning
PHILOSOPHY
What pushes a person to pe a “pilosopo”?
-is the study of general and fundamental
questions about existence, knowledge, values, 1. To cover up an obvious truth
reason, mind, and language 2. To annoy or simply irritate someone
3. To engage someone in an unwelcome
-considered as the “Mother Discipline” because argumentation
most branches of science emerged from it
3. Philosophy as an academic course
Philosophy refers to:
or degree
1. Ideas, views, principles, perspectives, or
-refers to an academic subject or course that is
beliefs
taught usually in colleges, universities, and
2. The activity of reasoning
seminaries.
3. An academic course or degree
Philosophy does involve the activity of
PYTHAGORAS OF SAMOS
reasoning, but philosophy distinguishes
-He is an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher and between correct and incorrect forms of
the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism reasoning
Philosophy does involve or refer to ideas,
-His political and religious teachings were well beliefs, principles, and the like but
known in Magna Graecia and influenced the philosophy deals with them on a certain
philosophies of Plato, Aristotle, and through level
them, Western philosophy.
Philosophy as an academic course, does
study reasoning skills and the nature of
morality, knowledge, social justice and
1. Philosophy as ideas, views, others; but philosophy studies much more
perspective or beliefs
-refers to generally to ideas, views, principles,
perspectives, or beliefs held either by
SEMINARIES SOPHIST
-an institution for the training the candidates for -a wise man or one who knows
priesthood, ministry or rabbinate
-a group of intellectuals who taught oratory for
a fee to individuals aspiring to have a
successful career in politics
THEORIES
-set of ideas that served as the starting point
for making a case or conducting an ORATORY
investigation
-art of public speaking
FRAMEWORKS The Church of “Holy Wisdom”
-basic conceptual structure; or bases -Hagia Sophia
MORALITY 3R’s that describes a Sophist
-a doctrine or system of moral conduct; Relativism
conformity to ideals of right human conduct Rhetoric
Recompense
PHILOSOPHY – based on its ethymology –
Love of Wisdom RELATIVISM
-perception
PHILOSOPHY – Greek word “philosophia” –
philia means love and Sophia means wisdom
OBJECTIVE TRUTH
-it is an objective truth when its truth conditions
KINDS OF LOVE are met without bias caused by a sentient
subject
AGAPE – God’s Love for Humankind
EROS – Romantic love
STORGE – Familial love
RHETORIC
PHILIA – Brotherly love
-the art of effective and persuasive speaking or
writing to get the attention of the public
PHILOSOPHER
-one who loves wisdom RECOMPENSE
-to give something by way of compensation
Sophists believe that: PYTHAGORAS
All truths are relative in that all truths are -He is known far more for his theories and
determined by or based on human interests ideas in mathematics
Human interests varies from one another or
from one group to another -He based his teaching on how to lead a
harmonious life
PROTAGORAS
PARMENIDES
-“Man is the measure of all things”
-Known follower of Pythagoras
-A leading sophist of ancient Greece
-Unravelled the biggest question of all: Is it or
is it not?
GREEK SOPHISTS
Protagoras SOCRATES
Gorgias
-Most iconic philosopher in the history
Prodicus
Hippias -He would question people relentlessly on their
Thrasymachus beliefs and try to find definitions of virtues
Philosophers believe that: PLATO
Certain truths are universal (true for all -He combined the two major approaches of
humans) and objective (independent of pre-Socratic metaphysics and natural theology
human interests) with Socratic ethical theology
One should pursue wisdom with great
-The foundation of Plato’s philosophy is
passion and seriousness
threefold: dialects, ethics, and physics
THALES OF MILETUS
-He is hailed among historians as the “Father ARISTOTLE
of Ancient Greek Philosophy”
-Most influential among the disciples of Plato
-The first person to have investigated basic
principles such as the origin of matter -His interpretation of things was more based on
facts learnt from the experience people would
gain in their lives
ANAXIMANDER
-famous pupil of Thales SAINT THOMAS AQUINAS
-Created the 1st world image of an open -Focused much of his work on reconciling
universe Aristotelian and Christian principles
First speculative astronomer
CONFUSIUS
-Believed in the value of achieving ethical harmony through skilled judgment rather that knowledge of
rules
RENE DESCARTES
-Father of analytical geometry
-Emphasizing the understanding of that which can be known for sure
IMMANUEL KANT
-Assorted that the concepts if time and space, as well as cause and effect, are essential to the human
experience
JOHN LOCKE
-Coined the term tabula rasa (blank slate) to denote that the human mind is born unformed, and that
ideas and rules are only enforced through experience thereafter
KARL MARX
-Argued that societies develop through class struggles, and that this would ultimately lead to the
dismantling of capitalism
Who is the “Real” Wise Person?
Knows what he/she knows and he/she does not know
Holds beliefs that are not only true but which he/she can also justify
Knows a lot of things that are valuable in life
Puts his/her knowledge to practical use
Knows what should be done and acts accordingly
You might also like
- The Problems of Philosophy (Barnes & Noble Library of Essential Reading)From EverandThe Problems of Philosophy (Barnes & Noble Library of Essential Reading)No ratings yet
- Philosophy q1 Midterms Reviewer QueenDocument5 pagesPhilosophy q1 Midterms Reviewer Queen9cqzqcpqqtNo ratings yet
- Ethics ReviewerDocument7 pagesEthics ReviewerEa YangNo ratings yet
- Philosophy & Religion: Metaphysics, African Philosophy & Biblical Critical ExegesisFrom EverandPhilosophy & Religion: Metaphysics, African Philosophy & Biblical Critical ExegesisNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO THE PHILOSOPHY OF THE HUMAN PERSONDocument2 pagesINTRODUCTION TO THE PHILOSOPHY OF THE HUMAN PERSONJadzferNo ratings yet
- Philo Prelim g12Document7 pagesPhilo Prelim g12Hyakkima NasumeNo ratings yet
- Philo Reviewer!Document8 pagesPhilo Reviewer!Guessy Anthonette MulingbayanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Philosophy With Logic and Critical ThinkingDocument134 pagesIntroduction To Philosophy With Logic and Critical ThinkingRyan Merza100% (2)
- Philosophy ReviewerDocument6 pagesPhilosophy ReviewerLykaNo ratings yet
- Philo ReviewerDocument9 pagesPhilo ReviewerjorhosemiguelNo ratings yet
- PHILOSOPHY - SummaryDocument5 pagesPHILOSOPHY - SummaryCharm DenisseNo ratings yet
- PHILO ReviewerDocument4 pagesPHILO ReviewerJadzferNo ratings yet
- Philo St1 q1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesPhilo St1 q1 ReviewerCzenia BarroNo ratings yet
- PHILOSOPHYDocument18 pagesPHILOSOPHYLaurence BaguangaNo ratings yet
- What is Philosophy? Lesson 1Document7 pagesWhat is Philosophy? Lesson 1Erich MagsisiNo ratings yet
- MidtermDocument8 pagesMidtermNur-Aiza AlamhaliNo ratings yet
- Intro To Philo 1Document2 pagesIntro To Philo 1Benedict VillacrucisNo ratings yet
- Notes - PhilosophyDocument4 pagesNotes - PhilosophyGARCIA, Denmar Djasthine P.No ratings yet
- Q1 Reviewer (Philo)Document3 pagesQ1 Reviewer (Philo)kris krossNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Quarter1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesPhilosophy Quarter1 ReviewerCristine Mae MakinanoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Doing PhilosophyDocument38 pagesWeek 1 Doing PhilosophyTotchie Royze Flores Junsay100% (2)
- Philosophy Movements, Approaches, and Traditions ExplainedDocument6 pagesPhilosophy Movements, Approaches, and Traditions ExplainedMariane Gayle CaballeroNo ratings yet
- INTRO TO PHILOSOPHY OF HUMAN PERSONDocument3 pagesINTRO TO PHILOSOPHY OF HUMAN PERSONHaine Otomiya100% (1)
- Philo Hand Out Module1Document3 pagesPhilo Hand Out Module1Aaron James Bien BequilloNo ratings yet
- 6 11 PhiloDocument11 pages6 11 PhiloHannah SchwartzNo ratings yet
- Philo Week 1 NotesDocument4 pagesPhilo Week 1 NotesScarlette Beauty EnriquezNo ratings yet
- PHILOSOPHYDocument15 pagesPHILOSOPHYkreiNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greek Philosophers and the Origins of Western PhilosophyDocument5 pagesAncient Greek Philosophers and the Origins of Western PhilosophyMary Claire SodeNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Philosophy and Critical ThinkingDocument607 pagesIntroduction to Philosophy and Critical ThinkingCmay EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Philo Quarter 1 ReviewerDocument8 pagesPhilo Quarter 1 ReviewerGABRIEL LOUIS GUANONo ratings yet
- Philosophy of Man OBEDocument720 pagesPhilosophy of Man OBEKyla MarjesNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Notes Copy 2Document3 pagesPhilosophy Notes Copy 2Maria Natalia LibariosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhilosophyDocument12 pagesIntroduction To PhilosophyFria mae AbellanoNo ratings yet
- Philo Week 12 NotesDocument4 pagesPhilo Week 12 NotesScarlette Beauty EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Philosophy-Module 1Document6 pagesPhilosophy-Module 1gericj7dsNo ratings yet
- 1module1introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument4 pages1module1introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonBOOM PAMIXXNo ratings yet
- Philosophy: Its Meaning and NatureDocument43 pagesPhilosophy: Its Meaning and NatureRhialyn Princess SandovalNo ratings yet
- What Is PhilosophyDocument24 pagesWhat Is Philosophylola hernandezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument6 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonArianne LaureNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Philosophy of the Human PersonDocument21 pagesIntroduction to Philosophy of the Human Personanon_254928515No ratings yet
- Ethics Midterm ReviewerDocument7 pagesEthics Midterm ReviewerAcerJun ParafinaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Philosophy Notes 1Document4 pagesIntroduction To Philosophy Notes 1Dominique FernandezNo ratings yet
- The Essential Guide to Philosophy - Its Nature, Branches, and Most Influential ThinkersDocument7 pagesThe Essential Guide to Philosophy - Its Nature, Branches, and Most Influential ThinkersManuelMarasiganMismanosNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Philosophy of the Human PersonDocument10 pagesUnderstanding the Philosophy of the Human PersonClaire TipayNo ratings yet
- Ethics Lesson 1&2Document2 pagesEthics Lesson 1&2avi kimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument23 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonnisniqtrdaNo ratings yet
- Business Logic Module 1 IntroductionDocument9 pagesBusiness Logic Module 1 IntroductioneysiNo ratings yet
- Logic Manual 1Document59 pagesLogic Manual 1James ElectrifiedNo ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument1 pagePhilosophySTEM H-Cerillano, Zcier MeiNo ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument2 pagesPhilosophySeanmyca IbitNo ratings yet
- Republic of the Philippines Ethics Chapter IntroductionDocument39 pagesRepublic of the Philippines Ethics Chapter IntroductionSophia Ann Gorospe-FerrerNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Philosophy: I. Some Common Meanings II. Love of WisdomDocument5 pagesThe Nature of Philosophy: I. Some Common Meanings II. Love of WisdomMika BeltranNo ratings yet
- Prelim LessonDocument10 pagesPrelim LessonCriszel Mae DedaseNo ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument6 pagesPhilosophygrishamcacal19No ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Introduction To Philosophy Material and Formal Object Lesson 2: Philosophy Meaning of PhilosophyDocument3 pagesLesson 1: Introduction To Philosophy Material and Formal Object Lesson 2: Philosophy Meaning of Philosophypoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- What Is Logic - WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesWhat Is Logic - WPS OfficeMelizza Fajardo BañanoNo ratings yet
- Paradigm Shift MorrisonDocument2 pagesParadigm Shift MorrisonkassandraNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Nature of PhilosophyDocument48 pagesMeaning and Nature of PhilosophyJohn Patrick Q. BarawidNo ratings yet
- EthicsDocument11 pagesEthicsLuthelle FernandezNo ratings yet
- End The CycleDocument1 pageEnd The Cycleblabla blablaNo ratings yet
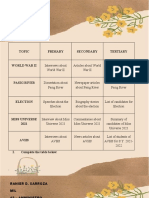
- RANIER D. SARROZA MIL 12 - AMMINISTRODocument3 pagesRANIER D. SARROZA MIL 12 - AMMINISTROblabla blablaNo ratings yet
- End The CycleDocument1 pageEnd The Cycleblabla blablaNo ratings yet
- End The Cycle 2Document1 pageEnd The Cycle 2blabla blablaNo ratings yet
- Dance Injury Risk Factors: What Are Some of The Most Common Dance Injuries?Document4 pagesDance Injury Risk Factors: What Are Some of The Most Common Dance Injuries?blabla blablaNo ratings yet
- Iphp Activity 4.2Document2 pagesIphp Activity 4.2blabla blablaNo ratings yet
- Allegory of The CaveDocument2 pagesAllegory of The Caveblabla blablaNo ratings yet
- IPHP ActivityDocument2 pagesIPHP Activityblabla blablaNo ratings yet
- Jingle LyricsDocument2 pagesJingle Lyricsblabla blablaNo ratings yet
- Iphp Environmental Video PresentationDocument3 pagesIphp Environmental Video Presentationblabla blablaNo ratings yet
- CPARDocument2 pagesCPARblabla blablaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 4 – Skills, Techniques and Production in CRAFTSMANSHIPDocument3 pagesLESSON 4 – Skills, Techniques and Production in CRAFTSMANSHIPblabla blablaNo ratings yet
- Karl Rahner, Johannes Metz Spirit in The WorldDocument462 pagesKarl Rahner, Johannes Metz Spirit in The WorldPaulo Andrade VitóriaNo ratings yet
- Iq Eq SQ PDFDocument3 pagesIq Eq SQ PDFsukavakaNo ratings yet
- Purpose in LifeDocument1 pagePurpose in Lifeaashish95100% (1)
- A Mahamudra Invest - The Summary of MahamudraDocument10 pagesA Mahamudra Invest - The Summary of MahamudraMarquezn SantielNo ratings yet
- Merck's moral obligation to develop life-saving drugsDocument5 pagesMerck's moral obligation to develop life-saving drugsQA Domingo100% (1)
- Photo: Philosophical InsightsDocument17 pagesPhoto: Philosophical InsightsRogerio LucasNo ratings yet
- TOK Essay CriteriaDocument1 pageTOK Essay CriteriaMr_RooNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Uts 2ND QuarterDocument12 pagesReviewer in Uts 2ND QuarterJaylou BernaldezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: You, The Teacher, As A Person in Society Learning ObjectivesDocument9 pagesChapter 1: You, The Teacher, As A Person in Society Learning ObjectivesJesel QuinorNo ratings yet
- MāyāDocument3 pagesMāyāPrana Vallabha DasNo ratings yet
- Contribution of Marx and Durkheim To SociologyDocument10 pagesContribution of Marx and Durkheim To SociologyStrikerNo ratings yet
- BeckettDocument16 pagesBeckettLuca Angelo LauriNo ratings yet
- 10modernphilosophersandtheircontributiontoeducation 131021112312 Phpapp02Document14 pages10modernphilosophersandtheircontributiontoeducation 131021112312 Phpapp02Reymon SantosNo ratings yet
- Induction Reasoning ExplainedDocument5 pagesInduction Reasoning Explainedgurriaali100% (1)
- Trialectics Toward A Practical Logic of Unity Horn PDFDocument212 pagesTrialectics Toward A Practical Logic of Unity Horn PDFMaria Lysenko100% (1)
- Gender assimilation in Mao era ChinaDocument13 pagesGender assimilation in Mao era ChinaLux SlaviaNo ratings yet
- Heterotopia and The CityDocument3 pagesHeterotopia and The CityWagner de Souza Rezende100% (1)
- Law and MoralityDocument4 pagesLaw and MoralityJenifer Rose EspinaNo ratings yet
- UTS Module 1Document25 pagesUTS Module 1Neo Frank BernalNo ratings yet
- Critical Invention Autonomy: StudyDocument18 pagesCritical Invention Autonomy: Studyberubah2No ratings yet
- ETHICS - MORAL STANDARDS - MORAL DILEMMAS - Invidual - Organizatl - StructuralDocument25 pagesETHICS - MORAL STANDARDS - MORAL DILEMMAS - Invidual - Organizatl - StructuralJoy ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Universalist Grandeur, Romantic Depth, Pragmatist Cunning Richard RortyDocument13 pagesUniversalist Grandeur, Romantic Depth, Pragmatist Cunning Richard Rortyrustycarmelina108100% (1)
- Frameworks and Principle of DispositionDocument41 pagesFrameworks and Principle of DispositionCookie MonsterNo ratings yet
- Framing Indonesian Human Rights in A Perspective of Plural Society - SMA Negeri 1 Sumpiuh - Elyonai Kristina FanesDocument10 pagesFraming Indonesian Human Rights in A Perspective of Plural Society - SMA Negeri 1 Sumpiuh - Elyonai Kristina FanesSal Sabila N. KNo ratings yet
- Assignment Kadar PerubahanDocument21 pagesAssignment Kadar PerubahanSiti Hajar AjaNo ratings yet
- Speech ActsDocument3 pagesSpeech ActsJulieSanchezErsando100% (2)
- 1.1introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person (Doing Philosophy)Document41 pages1.1introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person (Doing Philosophy)Kim Anthony Supposedly VanrathNo ratings yet
- Communist Party ManufistoDocument19 pagesCommunist Party ManufistoSadaemuslim Online Book StoreNo ratings yet
- Hall Concepts of IdentityDocument8 pagesHall Concepts of IdentityCarla Cristine TedescoNo ratings yet
- Contentless IntentionalityDocument19 pagesContentless IntentionalityChris Walczak100% (1)