Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell 7
Uploaded by
XI-A Vishal Bishnoi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views6 pagesOriginal Title
cell7
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views6 pagesCell 7
Uploaded by
XI-A Vishal BishnoiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
golgi aPParatus
First discovered by Camillo Golgi.
It consist of a system of membrane- bound vesicles arranged
parallel to each other in stacks called cisterns.
The material synthesized near the ER is packaged and
dispatched to various targets inside and outside the cell
through the Golgi apparatus.
Its functions include storage , modification and packaging
of products in vesicles.
Involved in the formation of the lysosome.
lysosomes
Waste disposal system of the
cell.
Keep the cell clean by digesting
any foreign material as well as
worn out cell organelles.
Contain powerful digestive
enzymes capable of breaking
down all organic material.
When the cell gets damaged,
lysosomes may break open and
the enzymes digest their own
cell. Thus known as suicide bags
of a cell.
Mitochondria
Known as the powerhouse of the cell.
The energy required for various
chemical activities is released by the mitochondria in the
form of ATP molecules.( Adenosine triphosphate).
ATP is known as the energy currency of the cell.
Mitochondria have two membrane coverings.
Outer membrane is very porous.
Inner membrane is deeply folded.
Mitochondria are able to make their own proteins as
they have their own DNA and ribosomes .
Plastids
Present in plant cells.
Two types- 1) Chromoplasts (coloured)
2) Leucoplasts (colourless)
Plastids containing green pigment chlorophyll
are called Chloroplasts.
Leucoplasts store materials as starch, oils and
protein granules.
Plastids contain membrane layers embedded in
a material called stoma.
Has a similar structure like the mitochondria.
Have their own DNA and ribosomes.
Vacuoles
Storage sac for solid or liquid contents.
Small size vacuoles are present in animals.
Large in plants.
In plant cells, vacuoles are full of cell sap and provide turgidity
and rigidity to the cell.
Vacuoles store amino acids, sugars, various organic acids and
some proteins.
In Amoeba, the food vacuole contains the food items that the
Amoeba has consumed.
Vacuoles play an important role in expelling excess water and
some wastes from the cell.
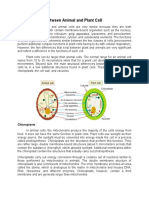
Animal cell Plant cell
Animal cells are Plants cells are usually
generally small in size. larger than animal cells.
Cell wall is absent. Cell wall is present.
Except the protozoan Plastids (Chromoplasts
Euglena, no animal cell and leucoplasts) are
possesses plastids. present.
Vacuoles are smaller in Vacuoles are larger in
size. size.
You might also like
- Ancient Indian WeaponsDocument25 pagesAncient Indian WeaponsjasmineNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 2020Document4 pagesSyllabus 2020asdfghjklNo ratings yet
- Dont Think About A ZebraDocument2 pagesDont Think About A ZebraD2WNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles: Structures and FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell Organelles: Structures and FunctionsSai Deekshita VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- CYTOLOGYDocument3 pagesCYTOLOGYJessa Mae DarulloNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles JigsawDocument10 pagesCell Organelles JigsawSusan VictoriaNo ratings yet
- MLG 2 (Part 1) The Cell Theory and Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument5 pagesMLG 2 (Part 1) The Cell Theory and Cell Structure and FunctionsJohn Tolentino LaronaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceDocument34 pagesChapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceMadhav DayareNo ratings yet
- Biology Note About CellsDocument17 pagesBiology Note About CellsEK TubeNo ratings yet
- Functions of A CellDocument4 pagesFunctions of A CellyayayanizaNo ratings yet
- Nucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticDocument5 pagesNucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticHustler ZaydeNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument4 pagesPlant CellKenneth FungoNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology GuideDocument37 pagesCell Biology GuideManuelNo ratings yet
- 11a Revision Pack T1Document36 pages11a Revision Pack T1Najat BteichNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument20 pagesCell - The Fundamental Unit of LifeKavya GoelNo ratings yet
- CellDocument23 pagesCellridabatool151214No ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Function: CellsDocument8 pagesCell Structures and Function: CellsChardean Gel BaclaanNo ratings yet
- Grade-9 Cbse Chapter-5 Revision Notes PptDocument14 pagesGrade-9 Cbse Chapter-5 Revision Notes PptNoel MammenNo ratings yet
- Cell Class Viii - 3 CompetitiveDocument23 pagesCell Class Viii - 3 Competitiverajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life: What Are Living Organisms Made Up Of?Document5 pagesChapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life: What Are Living Organisms Made Up Of?HeroNo ratings yet
- Trixie OrganellesDocument2 pagesTrixie OrganellesMir SantillanNo ratings yet
- Cell organelles functions guideDocument12 pagesCell organelles functions guideKatrina Marie Chan SalanioNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument3 pagesUntitled Documentsumedhasaha09No ratings yet
- Biology 1st DiscussionDocument52 pagesBiology 1st DiscussionBea BulasaNo ratings yet
- Biology Prelim NotesDocument47 pagesBiology Prelim NotesAmanie SidawiNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument137 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of LifeSudarshan S KNo ratings yet
- Presentation Fundamental Unit of Life 1536577024 21871Document13 pagesPresentation Fundamental Unit of Life 1536577024 21871Keerthana RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document65 pagesChapter 3Sintayehu Tsegaye100% (1)
- 1C-Tabugoc - LA2 Plant CellDocument5 pages1C-Tabugoc - LA2 Plant CellClint Jhun TabugocNo ratings yet
- Cells: Unicellular vs Multicellular OrganismsDocument6 pagesCells: Unicellular vs Multicellular Organismspraneeth satishNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cell? Describe The Functions of OrganellesDocument18 pagesWhat Is A Cell? Describe The Functions of Organellestdukes546No ratings yet
- The Basic Unit of Life: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesThe Basic Unit of Life: ObjectiveHershell ContaNo ratings yet
- BIO ReviewerDocument14 pagesBIO ReviewerRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinNo ratings yet
- CellDocument7 pagesCellnik29569No ratings yet
- Year 11 Biology NotesDocument30 pagesYear 11 Biology NotesafeefaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organeeles IDocument7 pagesCell Organeeles ISaumya GopalNo ratings yet
- Cell SamralaGDocument26 pagesCell SamralaGapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument31 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsKomalesh TheeranNo ratings yet
- Plant vs Animal Cell DifferencesDocument6 pagesPlant vs Animal Cell DifferencesYukiNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Types of CellsDocument4 pagesThe Cell: Types of CellsAllen MurilloNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1,2 - Plant Cell Structure - DFQDocument10 pagesLecture 1,2 - Plant Cell Structure - DFQUmarNo ratings yet
- BIO 001 Real Slide First SemesterDocument44 pagesBIO 001 Real Slide First Semestermarkwelly367No ratings yet
- Cell Organelles: (Text Wrapping Break)Document7 pagesCell Organelles: (Text Wrapping Break)DAKSH SACHDEVNo ratings yet
- Bayern MunchenDocument23 pagesBayern MunchenKepa KepaNo ratings yet
- Lec-8,9 CellsDocument30 pagesLec-8,9 CellsAbdullah-Al-mehedi HiraNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of Life - CW Copy Notes Class 9 PDFDocument5 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life - CW Copy Notes Class 9 PDFmanoharrish3No ratings yet
- Cell StructuresDocument25 pagesCell StructuresAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument36 pagesCell Structureapi-234891239No ratings yet
- Cellorganelles PPT 2Document20 pagesCellorganelles PPT 2Riyashika RNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell-Eukaryotic Cells Are Defined As Cells Containing Organized Nucleus and OrganellesDocument12 pagesEukaryotic Cell-Eukaryotic Cells Are Defined As Cells Containing Organized Nucleus and OrganellesgabrieleyannNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMark MagatNo ratings yet
- Animal and Cell Mini Project - MeadowDocument1 pageAnimal and Cell Mini Project - Meadowapi-394726323No ratings yet
- The Parts of The Cell and Their FunctionsDocument1 pageThe Parts of The Cell and Their Functionscherry.tempongNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument21 pagesMorphology of Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDhanush VNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells - De, Nition, Diagram, Structure & FunctionDocument2 pagesPlant Cells - De, Nition, Diagram, Structure & FunctionJoseph OloruntobaNo ratings yet
- Cell Part DefinitionsDocument2 pagesCell Part Definitionsyemaya hannaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell StructureDocument5 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Structureshamshad aliNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Structures in A Cell JJDocument25 pagesLesson 6 Structures in A Cell JJGemma WrigleyNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDocument13 pagesThe Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDiane CastroNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Structure and FunctionDocument8 pagesThe Cell: Structure and FunctionRajendra Chikkamath100% (1)
- Cell Organelles: The Structures that Power Plant CellsDocument10 pagesCell Organelles: The Structures that Power Plant Cellsjhariesargente05No ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- EE-260 Lecture on Electro-Mechanical Systems and Induced TorqueDocument19 pagesEE-260 Lecture on Electro-Mechanical Systems and Induced TorqueJeff HardyNo ratings yet
- Energy Security IndexDocument13 pagesEnergy Security IndexCarlos AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Grammar HFDocument7 pagesUnit 5 Grammar HFMilán Benjámin ZámbóNo ratings yet
- Grandparenting - Play With Me! Activities That Make Learning Fun 24 To 36 MonthsDocument3 pagesGrandparenting - Play With Me! Activities That Make Learning Fun 24 To 36 MonthsAmna ArshadNo ratings yet
- Quilling Letter BDocument2 pagesQuilling Letter BGueureNo ratings yet
- BMW Inyeccion 320i-325i Motronic M31 PDFDocument2 pagesBMW Inyeccion 320i-325i Motronic M31 PDFIvoo ooNo ratings yet
- JohnDocument18 pagesJohnRobert EscuadroNo ratings yet
- Bsczo 201Document280 pagesBsczo 201ishfaqqqNo ratings yet
- LugeonDocument13 pagesLugeonRojan MaghsoodifarNo ratings yet
- Resumen en Ingles Del Diario Ana Frank Chisaguano EmilyDocument16 pagesResumen en Ingles Del Diario Ana Frank Chisaguano EmilyChisaguano EmilyNo ratings yet
- ACS Sainsbury and Asda Merger Leaner 82Document26 pagesACS Sainsbury and Asda Merger Leaner 82FlareGBANo ratings yet
- Audi 6 3l w12 Fsi EngineDocument4 pagesAudi 6 3l w12 Fsi EngineMarlon100% (54)
- Area and Circumference of CircleDocument17 pagesArea and Circumference of CircleJared VallesNo ratings yet
- Lightweight Slab Shoring System - ROYALFRAME50Document6 pagesLightweight Slab Shoring System - ROYALFRAME50Renji Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- WAVES FORM 5the diagram, identify the followingDocument52 pagesWAVES FORM 5the diagram, identify the followingHuda IdrisNo ratings yet
- Sir James ChadwickDocument6 pagesSir James ChadwickMichael GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Game Theory Behavioral FinanceDocument5 pagesGame Theory Behavioral Financeplato363No ratings yet
- Analytical Reasoning Skills Part ADocument30 pagesAnalytical Reasoning Skills Part AAhmad MiftahulNo ratings yet
- Zoom Basic Functions - FinalDocument31 pagesZoom Basic Functions - FinalWenshy LavadorNo ratings yet
- U1L9 Student Guide (1) - 1Document4 pagesU1L9 Student Guide (1) - 1jonahNo ratings yet
- LNG Vessels and Their Bunkering - North America: Sean BondDocument18 pagesLNG Vessels and Their Bunkering - North America: Sean BondMaximNo ratings yet
- Northridge E250pDocument23 pagesNorthridge E250pVion VionNo ratings yet
- 1.master Techniques in Surgery - Esophageal Surgery, 1E (2014)Document456 pages1.master Techniques in Surgery - Esophageal Surgery, 1E (2014)Raul Micu ChisNo ratings yet
- 6-1 Homework Team 7Document3 pages6-1 Homework Team 7Edgar ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Geometry QuotesDocument2 pagesGeometry Quotesalecksander2005No ratings yet
- TextDocument17 pagesTextnaser zoabiNo ratings yet
- Those Who Serve - Stephen Melillo (Score)Document22 pagesThose Who Serve - Stephen Melillo (Score)Fernando RamiresNo ratings yet