Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Activity 3 - Limbang
Uploaded by
Faith WangCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Activity 3 - Limbang
Uploaded by
Faith WangCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of the Philippines
Western Mindanao State University
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
Department of Environmental
Engineering
Normal Road, Zamboanga City
ENGINEERS REPORT
AIR POLLUTION TREATMENT
SYSTEM
(COAL POWER PLANT)
Activity 3
Submitted by:
CHRISTINE FAITH R. LIMBANG
BSENE V
Submitted to:
ENGR. DEWEY J. SOJUACO
ENE 157 INSTRUCTOR
A. Objectives: At the end of the activity the student will be able to:
1. Be able to communicate information that were acquired during the virtual Plant Tour
2. Be able to extract information from the presentation (virtual Plant tour)
3. Be able to pursue further information from such a starting point and be able to present
the result of such an assessment.
B. Procedure:
1. Listen carefully and focus on what is being discussed in the video presentation
2. Make an Engineers Report.
C. Engineers Report Outline
I. Introduction
Coal-fired power plants are a major source of emissions for a number of air pollutants including
SO2, NOx, particulate matter (PM), HCl, HF, Hg, and so on. Hazardous air pollutants such as
As, Be, Cd, Cr, Pb, Mn, Ni, Se, and other metals are integral components of fine PM that are also
emitted directly from coal-fired power plants. The potential problem of coal-fired power plants
associated to the emissions of air pollutants can be treated by flue gas desulphurization (FGDs),
as the sulphur (S) will be retained in the FGD-gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O), and eventually be
disposed. Further, FGD chemistry (alkaline sorbent) allows the capture of many pollutants other
than sulphur, such as F, As, B, Cl, Se or Hg, in a gaseous form and/or as PM. The current
position of coal power generation and the generation of inorganic trace pollutants derived from it
are presented and discussed. The partitioning, speciation, and fate of inorganic trace pollutants
during pulverized coal combustion (PCC)-FGD are also reviewed.
Coal plays an essential role in our global energy scheme for power generation as most of the
world’s coal production is consumed mainly to generate electricity. However, coal is currently a
target especially for Europe, where political and social opposition to coal is mounting as efforts
intensify to limit CO2 emissions.
Coal-fired power plants currently fuel 40% of global electricity, and, in some countries, coal
fuels a higher percentage of electricity. Owing to the Paris climate agreement, in Europe, the use
of coal for power generation retreated for the fifth successive year in 2017. The European Power
Sector 2017 reported that coal’s share of Europe’s total power generation fell to 20% last year,
while the share from renewables increased to 30%. Nevertheless, Europe’s progress in reducing
the use of carbon-intensive power is gradual and uneven.
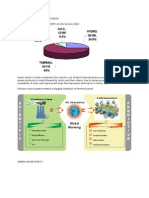
Figure 1: Configuration of a PCC plant equipped with an FGD system.
Coal is divided into three classes: anthracite, bituminous, and lignite. Empirical formulas
obtained by elemental analysis are C137H97O9NS for bituminous coal and C240H90O4NS for high-
grade anthracite. Anthracite coal is a hard rock with a metallic luster and it has jet black
appearance. Coal is used in a coal-fired power generation plant to turn water into steam and
steam drives turbine generators to generate electricity. In this process, coal is first pulverized and
the fineness achieved is as that of a talcum powder (200 mesh to 325 mesh). It is then stir
together with hot air in a skillful way and injected in the burning chamber (firebox) of a boiler.
The coal/air mixture is almost completely combusted, hence, generate maximum possible heat.
Purified water is pumped through tubes of the boiler, is converted into steam by the supplied
heat. The temperature of steam reaches up to 1,000 degrees Fahrenheit and pressures is raised up
to 3,500 psi, and this high-pressure steam is conveyed to the turbine. The huge pressure of steam
pushes the blades of turbine which move the shaft of turbine. The shaft of turbine is coupled to
the shaft of a generator. The generator magnets spin inside the wire coils to produce
electromagnetic field to produce electricity. After moving turbines, the steam is injected into a
condenser where cooling water from a nearby source is pumped in the condenser through a
network of tubes. The cooling water in the tubes transforms the steam back into water that can be
recycled in the plant or returned to its source without being contaminated (not even at high
temperature, ideally), and the steam is returned to the boiler and this cycle is repeated. Heat is
obtained by combustion operation. The combustion involves combinations of coal with oxygen.
II. Description of the existing air pollution treatment system
1. Air Pollution Treatment Flow Diagram
III. Assessment of the Air Pollution Treatment System
One of our era's greatest scourges is air pollution, on account not only of its impact on climate
change but also its impact on public and individual health due to increasing morbidity and
mortality. There are many pollutants that are major factors in disease in humans. Among them,
Particulate Matter (PM), particles of variable but very small diameter, penetrate the respiratory
system via inhalation, causing respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, reproductive and central
nervous system dysfunctions, and cancer. Despite the fact that ozone in the stratosphere plays a
protective role against ultraviolet irradiation, it is harmful when in high concentration at ground
level, also affecting the respiratory and cardiovascular system. Furthermore, nitrogen oxide,
sulfur dioxide, Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), dioxins, and polycyclic aromatic
hydrocarbons (PAHs) are all considered air pollutants that are harmful to humans. Carbon
monoxide can even provoke direct poisoning when breathed in at high levels.
IV. Recommendation for Improvement (upgrading of the existing treatment system)
Coal power plant is very useful since some other places lack energy but these plants also bring
hazard to human health, not only it affects human health, it also affects the environment and
cause global warming. There are ways to prevent air pollution, I recommend that someone or we,
environmental engineers can design and implement quality improvement solution to solve the
problem in air pollution.
V. Conclusion
Therefore, I conclude that coal power plant is very useful but it also bring hazard to
human health, affects our environment and cause global warming by emitting gas that cause air
pollution.
You might also like
- Asme section-IIDocument25 pagesAsme section-IIAmit Singh100% (10)
- List and Explain The Methods To Control Global Warming by Power PlantDocument6 pagesList and Explain The Methods To Control Global Warming by Power PlantUjjwal HiredesaiNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 BDocument4 pagesLab 6 Buzair akramNo ratings yet
- Pers Cct2003Document8 pagesPers Cct2003VIJAYPORNo ratings yet
- Big Ass ReportDocument6 pagesBig Ass ReportKudzai SaunyamaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Green House Gases (Chemistry Project Class-11)Document15 pagesEffects of Green House Gases (Chemistry Project Class-11)Anujeet Saha86% (7)
- Study of Carbon ScrubberDocument30 pagesStudy of Carbon ScrubberShaeed Bhagat Singh Yuva Club KathuraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry AirDocument2 pagesChemistry AirREAL GAMERNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact of Sawdust Briquettes Use - Experimental ApproachDocument6 pagesEnvironmental Impact of Sawdust Briquettes Use - Experimental ApproachFood CatNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of The Economic Production and Use ofDocument9 pagesAn Analysis of The Economic Production and Use ofMr PolashNo ratings yet
- Assignment of CombustionDocument9 pagesAssignment of CombustionAfiq de WinnerNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-1 (Answer)Document12 pagesTutorial-1 (Answer)sudhanshu shekharNo ratings yet
- I Would Like To Express My Special Thanks of Gratitude To My Teacher MrsDocument19 pagesI Would Like To Express My Special Thanks of Gratitude To My Teacher MrsShalini ParthipanNo ratings yet
- Progress Report 1Document24 pagesProgress Report 1Christelle Jane BeloNo ratings yet
- ENG 312 - Lecture Note 3Document6 pagesENG 312 - Lecture Note 3Kadiri DonaldNo ratings yet
- Compilation Air Pollution FundamentalDocument22 pagesCompilation Air Pollution FundamentalFederico Angoluan Socia Jr.No ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document4 pagesTutorial 5Yusrina AfifaNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument74 pagesAir PollutionSaneet AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Carbon Capture, Usage & Storage: AbstractDocument16 pagesCarbon Capture, Usage & Storage: AbstractPriyanshNo ratings yet
- BBSUCT1004 Environmental Science: Prepared byDocument18 pagesBBSUCT1004 Environmental Science: Prepared bygunjanNo ratings yet
- CIRED2011 0779 FinalDocument4 pagesCIRED2011 0779 FinalhalanmeloNo ratings yet
- Plant Design and Economics ProjectDocument43 pagesPlant Design and Economics Projectetayhailu100% (5)
- Unit 2 - Power Plant Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument19 pagesUnit 2 - Power Plant Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inSarvjeet ThakreNo ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide Capture, Sequestration, Compressor and Power CycleDocument10 pagesCarbon Dioxide Capture, Sequestration, Compressor and Power CycleIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- SAU1306Document93 pagesSAU1306JugarNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering: Synopsis On " "Document10 pagesMechanical Engineering: Synopsis On " "Jafar JilaniNo ratings yet
- Tackling and Reducing The Vigor Effect of Air Pollution Using Anti Smog TowerDocument6 pagesTackling and Reducing The Vigor Effect of Air Pollution Using Anti Smog TowerPriYa DharsanNo ratings yet
- A Sustainable Energy FutureDocument8 pagesA Sustainable Energy FutureJohn DambarefuNo ratings yet
- Athmosphere and Environment Research For O LevelsDocument12 pagesAthmosphere and Environment Research For O LevelsAsim HussainNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering MaterialsDocument30 pagesCivil Engineering MaterialsSiti AsmahaniNo ratings yet
- FlicDocument18 pagesFlicLima Limón LimoneroNo ratings yet
- History Thesis DefenseDocument49 pagesHistory Thesis DefenseToni CalsadoNo ratings yet
- Anurag PROJECT REPORT EVSDocument25 pagesAnurag PROJECT REPORT EVSVAA CNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 ADocument4 pagesLab 6 Auzair akramNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document58 pagesModule 4Praveen DNo ratings yet
- Lecture #3 - Understanding Air PollutionDocument63 pagesLecture #3 - Understanding Air PollutionDeep RedriffNo ratings yet
- Jesc - Ac.cn: Progress in Carbon Dioxide Separation and Capture: A ReviewDocument14 pagesJesc - Ac.cn: Progress in Carbon Dioxide Separation and Capture: A Reviewmppatilmayur1679No ratings yet
- Green TechnologyDocument3 pagesGreen TechnologyFarida TaniaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Impacts of Fossil Fuels and Alternative Energy SourcesDocument40 pagesComparative Impacts of Fossil Fuels and Alternative Energy Sourcesjubatus.libroNo ratings yet
- Course Id: ENV - 206 Sec-02: Submitted byDocument9 pagesCourse Id: ENV - 206 Sec-02: Submitted byMD. JULFIKER HASANNo ratings yet
- Civildatas - Blogspot.in: CE 2038 Scad Engineering College, Cheranmahadevi APMDocument17 pagesCivildatas - Blogspot.in: CE 2038 Scad Engineering College, Cheranmahadevi APMSURAJ RNo ratings yet
- The American University in Cairo: Environmental Science Air PollutionDocument35 pagesThe American University in Cairo: Environmental Science Air PollutionAviects Avie JaroNo ratings yet
- Young Innovators Program 2022: Greenhouse Gas Artificial PhotosynthesisDocument10 pagesYoung Innovators Program 2022: Greenhouse Gas Artificial Photosynthesisneetus creationNo ratings yet
- Environmental ChemistryDocument3 pagesEnvironmental ChemistryANDJANI ALMIRA PUTRI -No ratings yet
- Carbon Sequestration Using Microalgae-A Review: Sharmila.K, Ramya.S, Babu Ponnusami.ADocument7 pagesCarbon Sequestration Using Microalgae-A Review: Sharmila.K, Ramya.S, Babu Ponnusami.ABASKAR ENo ratings yet
- Mota MartinezDocument186 pagesMota MartinezJenni ArdiferraNo ratings yet
- Fossil Fuels and Alternative Energy SourcesDocument40 pagesFossil Fuels and Alternative Energy SourcesOlayiwola OmiyefaNo ratings yet
- Saar Nio 2014Document13 pagesSaar Nio 2014Ardhi Angga SNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - 4 - Air Pollution - Part I - 20 - 27 Dec 2021Document87 pagesLecture 3 - 4 - Air Pollution - Part I - 20 - 27 Dec 2021Sachin YadavNo ratings yet
- Seminar LikhithaDocument18 pagesSeminar LikhithaPrajwal KRNo ratings yet
- World's Largest Science, Technology & Medicine Open Access Book PublisherDocument29 pagesWorld's Largest Science, Technology & Medicine Open Access Book Publisherlifemillion2847No ratings yet
- Coal - Dirty, Sooty, Toxic Coal-In More-Sustainable Ways Using Its New TechnologiesDocument3 pagesCoal - Dirty, Sooty, Toxic Coal-In More-Sustainable Ways Using Its New TechnologiesKat CervantesNo ratings yet
- IJETR042116Document6 pagesIJETR042116erpublicationNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle Assessment of The Process of Carbon Capture and StorageDocument8 pagesLife Cycle Assessment of The Process of Carbon Capture and Storagerajnish14feb8516No ratings yet
- Capitolul 1 Greenhouse Gases A Review of Losses andDocument24 pagesCapitolul 1 Greenhouse Gases A Review of Losses andTerkel GinaNo ratings yet
- What Is Co2Document5 pagesWhat Is Co2elinebet03No ratings yet
- Module 4 - FinalDocument24 pagesModule 4 - FinalPraveen DNo ratings yet
- 2015 tee-EIS Chapter 3 - Technology Environment PDFDocument81 pages2015 tee-EIS Chapter 3 - Technology Environment PDFYu Gen XinNo ratings yet
- Pollution Control in FoundriesDocument13 pagesPollution Control in FoundriesShabid Ashraf100% (2)
- Water Vapor, Not Carbon Dioxide, Is Major Contributor to the Earth's Greenhouse Effect: Putting the Kibosh on Global Warming AlarmistsFrom EverandWater Vapor, Not Carbon Dioxide, Is Major Contributor to the Earth's Greenhouse Effect: Putting the Kibosh on Global Warming AlarmistsNo ratings yet
- Clean Electricity Through Advanced Coal Technologies: Handbook of Pollution Prevention and Cleaner ProductionFrom EverandClean Electricity Through Advanced Coal Technologies: Handbook of Pollution Prevention and Cleaner ProductionNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 Vaccination Certificate: Joshua Cimafranca BorcesDocument1 pageCovid-19 Vaccination Certificate: Joshua Cimafranca BorcesFaith WangNo ratings yet
- Final Exam: Western Mindanao State University College of Engineering and Technology Zamboanga City, PhilippinesDocument6 pagesFinal Exam: Western Mindanao State University College of Engineering and Technology Zamboanga City, PhilippinesFaith WangNo ratings yet
- Vaccination CertificateDocument1 pageVaccination CertificateFaith WangNo ratings yet
- Liquid Tile PaintDocument1 pageLiquid Tile PaintFaith WangNo ratings yet
- Jumpshot - DawinDocument3 pagesJumpshot - DawinFaith WangNo ratings yet
- Ene - Plant Tours and Thesis Writing (Lab) : Republic of The Philippines Western Mindanao State UniversityDocument11 pagesEne - Plant Tours and Thesis Writing (Lab) : Republic of The Philippines Western Mindanao State UniversityFaith WangNo ratings yet
- Lunzuran Basketball Fiesta League 2019 Schedule of Games: Date Time Games (Biddy and Junior) Referee OfficialDocument6 pagesLunzuran Basketball Fiesta League 2019 Schedule of Games: Date Time Games (Biddy and Junior) Referee OfficialFaith WangNo ratings yet
- No. Fouls: Captain's Signature in Case of ProtestDocument1 pageNo. Fouls: Captain's Signature in Case of ProtestFaith Wang100% (1)
- ST ND ST ND ST ND ST ND ST NDDocument2 pagesST ND ST ND ST ND ST ND ST NDFaith WangNo ratings yet
- Area by Off Sets From A Straight LineDocument7 pagesArea by Off Sets From A Straight LineFaith WangNo ratings yet
- AlugbatiDocument2 pagesAlugbatiFaith WangNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Job ObjectiveDocument4 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Job ObjectiveFaith WangNo ratings yet
- 3x3ScoresheetENG PDFDocument1 page3x3ScoresheetENG PDFFaith WangNo ratings yet
- GEDocument25 pagesGEFaith WangNo ratings yet
- 8 M Guanidine Hydrochloride SolutionDocument2 pages8 M Guanidine Hydrochloride SolutionWater ShurikenNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 3 Atoms and MoleculesDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 3 Atoms and Moleculespavan kasaNo ratings yet
- Fuels and Combustion Part - II: DR Waqas Khalid SmmeDocument8 pagesFuels and Combustion Part - II: DR Waqas Khalid SmmeFaizan RazaNo ratings yet
- 00029487Document12 pages00029487Régis OngolloNo ratings yet
- Portable Fire ExtinguishersDocument4 pagesPortable Fire ExtinguishersShreyas MNo ratings yet
- Hozelock KillaSpray Plus Manual PDFDocument32 pagesHozelock KillaSpray Plus Manual PDFbernoullisNo ratings yet
- 5 Aquadrug With Jilani PDFDocument5 pages5 Aquadrug With Jilani PDFShamsuddin BabuNo ratings yet
- Modul Basic Aircraft Material - English Version Pak BambangDocument62 pagesModul Basic Aircraft Material - English Version Pak Bambanganandadinatha77No ratings yet
- Study Material - Engineering Chemistry MODULE 5-MODULE - 550Document12 pagesStudy Material - Engineering Chemistry MODULE 5-MODULE - 550ChanduNo ratings yet
- Defects of Ductile Iron PipeDocument8 pagesDefects of Ductile Iron PipeUma Koduri100% (1)
- Sae Ams 2759-4C-2014Document7 pagesSae Ams 2759-4C-2014Reza NooriNo ratings yet
- 2022 JC2 H2 CHEM PRELIM P3 MS - Examiners CommentsDocument33 pages2022 JC2 H2 CHEM PRELIM P3 MS - Examiners CommentsYanqiao LiNo ratings yet
- 2014 STD Test Fee - Rev2 - Feb 4 2015 PDFDocument17 pages2014 STD Test Fee - Rev2 - Feb 4 2015 PDFDon King EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Wk4b Isomer of Coordination CompoundsDocument9 pagesWk4b Isomer of Coordination CompoundsMuhammad KholidinNo ratings yet
- Pressure Technical Manual: For PVC and Polyethylene Pipe SystemsDocument107 pagesPressure Technical Manual: For PVC and Polyethylene Pipe SystemschokNo ratings yet
- Wanhua Interior Coating SolutionsDocument28 pagesWanhua Interior Coating SolutionsThanh Vu100% (1)
- Pro Therm 2017Document11 pagesPro Therm 2017jorge moraNo ratings yet
- Iron MakingDocument135 pagesIron MakingSandeep Bandyopadhyay50% (2)
- Jurnal NanoemulsiDocument12 pagesJurnal NanoemulsiulfiNo ratings yet
- Feeds and FeedingDocument58 pagesFeeds and FeedingDavid BrownNo ratings yet
- Maincote™ EC-11: Waterborne Elastomeric Acrylic Resin For Industrial Maintenance CoatingsDocument10 pagesMaincote™ EC-11: Waterborne Elastomeric Acrylic Resin For Industrial Maintenance CoatingsLong An ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Analysis of Decomposition of Thiourea and Thiourea OxidesDocument9 pagesThermodynamic Analysis of Decomposition of Thiourea and Thiourea OxidesTomás del RíoNo ratings yet
- High-Temperature Behavior of Laser ElectrodispersiDocument18 pagesHigh-Temperature Behavior of Laser Electrodispersiateer6727No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1674987123000919 MainDocument21 pages1 s2.0 S1674987123000919 MainMatteo MainoNo ratings yet
- Overview of Engg Chemistry: Assistant Professor, Dept of Applied Chemistry, Aias, Amity University, NoidaDocument14 pagesOverview of Engg Chemistry: Assistant Professor, Dept of Applied Chemistry, Aias, Amity University, Noidagaurav toppoNo ratings yet
- 5 6132006305503641751 PDFDocument23 pages5 6132006305503641751 PDFGuma KipaNo ratings yet
- SPM Kimia Jul12 PDFDocument49 pagesSPM Kimia Jul12 PDFSyazwani RadziNo ratings yet
- Selective Reduction of Organic Compounds With Al-Acetoxy-And Al-TrifluoroacetoxydiisobutylalaneDocument9 pagesSelective Reduction of Organic Compounds With Al-Acetoxy-And Al-TrifluoroacetoxydiisobutylalanelauraNo ratings yet
- Cyanide Analysis MethodsDocument11 pagesCyanide Analysis Methodsmaruf amaludin100% (1)