Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LB3 Unit 1 9781398301658
Uploaded by
Anmol Shoukat - 83197/TCHRCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LB3 Unit 1 9781398301658
Uploaded by
Anmol Shoukat - 83197/TCHRCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Life processes
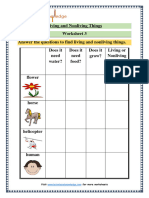
Alive or never alive?
What do you remember about living and non-living things?
n
● Talk with your partner. Which things in the pictures below are
io
alive and which have never been alive?
t
● What do things that are alive do? Use these words:
a
eat move breathe grow use senses
c
d u
E
cat child snake ruler
e r
d
car mobile phone plant
o d
H
You will need ...
● sticky notes
©
● large sheet of paper
Work with your group. living
things
a On your own sticky notes, write
how you know that something
is a living thing (alive).
b Write what living things need
to stay alive.
12
9781398301658_HCP_SCIENCE_LB3.indb 12 2021/02/23 16:56
Biology – Unit 1 Life processes
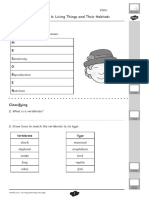
What is living?
1
What do you already know about living things?
a Are the objects below living or non-living things?
n
b Copy and complete the table for each object.
Remember to give a reason for your ideas.
t io
Object Living Not living Not sure Why? (reason)
a
wooden spoon
u c
wooden spoon fish car
E d plant baby
e r
rocks
d d monkey coin insect
H o
Think like a scientist!
All living things grow. They eat and drink
Challenge yourself!
Are there other things that
we need in order to live?
©
– this is called nutrition. They move. They
have young – this is called reproduction. Write down your ideas
These are life processes. and reasons. Share them
with the class.
Hint: Can all the
things in the
pictures above Science words
grow? living non-living
nutrition reproduction
life processes
13
9781398301658_HCP_SCIENCE_LB3.indb 13 2021/02/23 16:56
Biology – Unit 1 Life processes
Life processes
Think like a scientist!
All living things need to carry out these life processes:
io n
a t
movement – all living things move
u c
reproduction – all living
things have young
E d
e r
d d
nutrition – all living things
o
need food and water growth – all living things grow
1
H 2
©
Match the phrases to the life processes Can you remember all
in the boxes: the life processes?
a take in food growth a Close this book.
Write down the four
b increase in size movement life processes you have
c go from one place to just learnt.
reproduction b Draw a picture of an
another place
animal doing each
d produce new animals nutrition
life process.
14
9781398301658_HCP_SCIENCE_LB3.indb 14 2021/02/23 16:56
Biology – Unit 1 Life processes
Identify a living thing
Think like a scientist!
Does the object in the picture look like a living
thing? Sometimes you cannot tell! You can find
n
out by asking questions about the life processes.
io
Sami showed Ajay the photograph. Ajay asked
t
these questions to find out if it is a living thing.
a
Ajay: Does it move? Sami: Yes.
Sami: Yes. Ajay: Does it grow?
c
Ajay: Does it eat? Sami: Yes.
u
Sami: Yes. Ajay: Then it is a living thing!
Ajay: Can it have babies? Sami: Yes, it is a pufferfish.
E d
r
a Research the life processes of pufferfish.
e
b Copy and complete this table to show what you have found out.
d
Life process Question Answer
d
reproduction Does it have babies?
o
movement How does it move?
H
growth How does it grow?
nutrition What does it eat?
©
c What kind of science enquiry activity is this? Draw the symbol for this
science enquiry activity next to your table.
Let’s talk Challenge your
partner by choosing
a Find a picture of a living or non-living unusual things!
thing in your country.
b Ask a partner to ask you questions about it, using the life processes.
15
9781398301658_HCP_SCIENCE_LB3.indb 15 2021/02/23 16:56
Biology – Unit 1 Life processes
Alive, not alive, or never been alive?
Think like a scientist!
We can sort objects into three groups:
● Living things (alive): animals, including humans and plants, are living
n
things. They eat, move, have young and grow.
io
● Not alive (dead): these things were once alive. For example, twigs were
t
once part of a living thing. Bones were once part of a living thing that
moved, had young, grew and needed food and water.
a
● Never been alive: these things have never been alive, for example, things
c
made from plastic, stone, metal or glass. They have never moved, had
u
young, grown or needed food and water.
1
a Sort these objects into three groups:
E d
r
alive, not alive, never been alive.
e
b Add your own examples to the groups.
d
bird’s bones
d
fish
H o
bicycle lion
plastic bottle
tree
©
c What kind of scientific enquiry Hint: Ask yourself –
activity is this? Draw the symbol does each object carry
for this activity next to the groups out or did it carry
you sorted. out any of the life
processes.
2
Write sentences to explain the differences between Science word
something that is living, was once alive, and has never alive
been alive.
16
9781398301658_HCP_SCIENCE_LB3.indb 16 2021/02/23 16:56
Biology – Unit 1 Life processes
Life processes – movement
Think like a scientist!
Animals are living things. Animals that
are alive carry out four life processes:
n
● Movement
io
● Have young (reproduce)
t
● Need food and water
wildebeest moving to
a
● Grow. find food and water
c
Why do you think animals,
1
u
including humans, move
from place to place? How do you move
d
They move for different each day? Make a
a spider kiting
E
reasons, for example to find list of all the types
food or water, or to avoid danger. of movements you
r
Examples of movement are running, jumping, made today. Start
e
swimming, flying and crawling. Animals can also from when you woke
up. Write reasons for
d
move in other ways. For example, some beetles
roll. Some spiders move by kiting or ballooning. why you moved.
d
To do this, the spider climbs as high as it can.
o
Then it produces silk threads in the air and uses Science word
these to travel on the wind. kiting
2
H
©
a How do the animals below move?
b Choose two of these animals. Write three reasons why each animal
might move.
fish bird cricket cheetah
17
9781398301658_HCP_SCIENCE_LB3.indb 17 2021/02/23 16:56
Biology – Unit 1 Life processes
Why do animals move?
1
a Make a list of the life processes.
b Look at the box below. Which are good reasons for animals
n
moving? Which are not good reasons?
io
c Explain your answers to a partner. Use your list of life processes
in your answers.
Reasons for movement
a t
c
1 to find food
u
2 for a change
d
3 to keep warm
4 to find a mate
E
5 because it is Tuesday
r
6 to find water
e
7 to find a place to live
d
8 to hide
d
9 to get away from danger. orangutans
H o
Think like a scientist!
Cars move, and so do washing machines and robots.
Draw a robot.
Explain why you are
©
Does that mean that they are living things? a living thing and
the robot is not?
car washing machine robot
18
9781398301658_HCP_SCIENCE_LB3.indb 18 2021/02/23 16:56
Biology – Unit 1 Life processes
Living things grow
Think like a scientist!
Living things grow. Animals and plants grow.
All animals start as young. We call human young, babies.
n
Plants start as seeds and grow.
io
Something that was once alive or that has never lived, Let’s talk
t
does not grow like living things.
a
Share your
c
Memory box
1 with a partner.
u
a Create a Memory box to show the ways you have a What things
d
grown since you were a baby. Include photographs, do you both
have?
E
drawings and writing, and special objects or a toy
from when you were a baby. b What things
r
b Think about these questions: show that you
have grown?
e
● How big were you as a baby?
d
● What could you not do as a baby, compared
to what you can do now?
d
● What kind of food did you have when you
o
were born, compared to now?
H
● How old were you when you began to talk?
©
2
a What would happen if people never stopped growing?
What would be positive, minus and interesting about it?
b Copy and complete this table with your ideas.
If people never stopped growing, what would be …
Positive (good) Minus (not so good) Interesting
19
9781398301658_HCP_SCIENCE_LB3.indb 19 2021/02/23 16:56
Biology – Unit 1 Life processes
Life processes – nutrition
Think like a scientist!
Nutrition is about eating
the right foods for health
n
and growth.
io
● Living things need food
t
to grow, reproduce, move
and stay healthy.
a
● Food provides the energy
c
that keeps them moving.
u
● Living things need
d
a variety of foods for
proper growth and repair. Eating the right foods helps the body to heal
E
(get well) better after being ill or injured.
r
● Animals get their foods from plants or other animals.
d e Breakfast gives
you energy to
d
Write answers to these questions.
start the day!
o
a Why do animals, including humans, need
nutrition?
H
b What did you have for breakfast? Did the foods
come from plants or animals?
©
c What is your favourite food? Why?
d What would happen if you only ever ate your
favourite food?
e What would happen if you had nothing to eat?
Explain your answer. Use these words, and your Science words
own words:
energy
energy fruits repair repair
fruits
20
9781398301658_HCP_SCIENCE_LB3.indb 20 2021/02/23 16:57
Biology – Unit 1 Life processes
Nutrition in animals
Think like a scientist!
Animals and plants need food and water
(nutrition) to stay alive. Plants make
n
their own food. Animals must find food.
io
Different animals feed on (eat) different
foods, such as grass, seeds, nuts, fruits,
t
leaves and other animals, including
a
insects, fish and birds.
c
Some animals eat only one type of food.
u
For example, the giant panda mostly eats
bamboo shoots and stems.
d
giant panda eating bamboo
E
Animals, such as goats, eat many
r
types of plants. They eat leaves, grass,
vegetables and even flowers. Some
e
animals eat other animals. Frogs, for
d
example, feed on flies and insects.
d
Some animals eat plants and animals.
The three-toed sloth, for
o
example, eats leaves,
H
fruits, slow-moving
animals and bird’s eggs.
Humans can also eat
©
frogs eat flies and other insects plants and animals.
1
a Choose an animal and do research.
● What does it eat – plants, animals, or both?
● How does the animal move?
Science word
b Present your research in a booklet (mini book). eggs
21
9781398301658_HCP_SCIENCE_LB3.indb 21 2021/02/23 16:57
Biology – Unit 1 Life processes
Science in context
Animal nutritionists
People who help animals have a healthy diet are called animal nutritionists
(say: new-tri-shon-ists). You know that nutrition is about what we and other
animals eat to stay alive and healthy. So, what do you think an animal
n
nutritionist does?
io
Animal nutritionists do these things: Help us
t
understand how
a
Use diet can affect an
Research computers to
c
animal.
and plan diets create diets.
u
for animals. Give advice to
d
animal owners on
what to feed their
E
animal.
e r Look at what
d
health problems
animals have and
d
create diets to make
o
animals better.
H
Develop
new kinds
©
of food for
An animal nutritionist needs to: animals.
● know about nutrition.
● be a good communicator. Let’s talk
● work in a team.
● listen to other people’s ideas.
Talk with your partner. Do you
think you would make a good
● use their knowledge of science
animal nutritionist? Why?
to solve problems.
22
9781398301658_HCP_SCIENCE_LB3.indb 22 2021/02/23 16:57
Biology – Unit 1 Life processes
Life processes – reproduction
Think like a scientist!
You now know that all living things need to carry
out these four life processes:
n
● Movement – all living things move.
io
● Nutrition – all living things need food and water.
whale with its calf
t
● Growth – all living things grow.
a
● Reproduction – all living things have
c
young like themselves.
u
Reproduction is the process by which living
things produce young, called offspring.
d
A grown-up animal is called an adult. snake with its hatchling
E
Adult animals have babies. These babies
r
are called offspring.
Human parents are adults. Children are
e
their offspring.
d
Look at the pictures of adult animals and their
d
offspring. The offspring have special names. panda bear with its cub
H o
Look at these pictures of adult animals. Find
out what their offspring are called. Some
2
Adult humans reproduce
and have offspring.
©
have funny names! You are an offspring.
You were once a baby.
Bring photos to school
and put them in your
book to show what a
porcupine otter human baby looks like.
Science words
goat kangaroo offspring adult
23
9781398301658_HCP_SCIENCE_LB3.indb 23 2021/02/23 16:57
Biology – Unit 1 Life processes
Animal offspring
Think like a scientist!
Some animals lay eggs
to reproduce. Others have
n
babies called live young.
io
Vertebrates are animals sheep feeding its lamb snake hatching from egg
t
with backbones.
● Mammals are vertebrates. They have live young
a
that grow into adults. Humans are vertebrates.
c
They have live young.
u
● Birds, fish, amphibians and reptiles lay eggs.
d
Most eggs hatch young that look like tiny adults.
● Some amphibians, such as frogs, are different.
E
metamorphosis
The young go through stages before they look like
r
the adult. This is called metamorphosis.
Invertebrates are animals without backbones. Science words
e
● Many invertebrates lay eggs. The young go through
live young
d
vertebrates
metamorphosis to become adults.
mammals
d
● Not all invertebrates go through metamorphosis.
metamorphosis
o
For example, snails lay eggs that hatch into mini-snails. invertebrates
H
1
Research whether these animals have live young or lay eggs to reproduce.
©
Copy and complete the table. One example has been done for you.
cat parrot mouse antelope salamander spider snake
giraffe alligator goldfish butterfly shark
Animal Vertebrate or Live young or Does it go through
invertebrate? eggs? metamorphosis?
cat vertebrate live young no
24
9781398301658_HCP_SCIENCE_LB3.indb 24 2021/02/23 16:57
Biology – Unit 1 Life processes
Life cycles
Think like a scientist! 1
A life cycle is a diagram (model)
that shows the main stages of the
n
adult
life of a living thing. Scientists make
io
models that help to explain ideas.
They use the life cycle to show what
t
happens in the life of a plant or
a
animal. eggs
c
In the model of a life cycle (diagram)
u
below, the salamander lays eggs.
Each egg changes into a larva,
d
before becoming an adult. This is
E
an example of metamorphosis.
moult larva
r
newly
hatched larva a Above is the life cycle of a
e
dragonfly (an invertebrate).
d
It is in the wrong order.
d
b Use modelling clay to make a
model of this life cycle, but make
o
life cycle growing sure it is in the correct order.
of a
H
larva
eggs laid salamander c Write these labels next to each
in water part of your model life cycle:
©
adult eggs larva moult
Did you know that
when a dragonfly
adult larva moults, it
sheds its old skin?
Underneath is
Science words new skin.
life cycle larva moults
25
9781398301658_HCP_SCIENCE_LB3.indb 25 2021/02/23 16:57
Biology – Unit 1 Life processes
More about life cycles
1
a Work with a partner. Research the life cycle of a frog. Find out:
● Where do frogs lay their eggs – on land or in water?
n
● What are frog eggs called? What do they look like?
io
● When the eggs hatch, what does the young frog look like?
t
● How does the tadpole change?
a
● What does a froglet look like?
c
● How is the adult frog different to a froglet?
b Make a model of the life cycle of a frog, using
u
recyclable materials. Label your model.
d
c Share your model with another pair. What did Science word
they think of your model?
E
larvae
r
2
e
a Work with a partner. Research
d
the life cycle of a butterfly
d
that lives in your country.
Find out:
o
● Where do butterflies
H
lay their eggs?
● Why do they lay them there?
©
● What do the larvae look
like when they hatch from
the eggs?
● How many different stages
are there in the butterfly 3
life cycle? Think about the activities you
b Make a model of the life cycle have just been doing. What kind of
of a butterfly, using a flow scientific enquiry activities are they?
diagram. Draw the symbol next to your work.
26
9781398301658_HCP_SCIENCE_LB3.indb 26 2021/02/23 16:57
Biology – Unit 1 Life processes
What have you learnt about life processes?
1 2
Match the correct word to each Which animals have live young
statement. and which animals lay eggs?
n
nutrition reproduction
t io
growth movement
a
a Moving from place to place
toad elephant
c
b Changing in size as it gets older
u
c Food and water needed for living
d
d Produce young
E
3
r
termite eagle
True or false?
e
a Vertebrates have a backbone.
d
b Animals and plants do not need food and water to live.
d
c Metamorphosis are the stages some animals go through to
o
become adults.
d Animals move because they like the Sun.
What can you do?
H
© You have learnt about life processes. You can:
✔ describe the differences between things that are alive,
not alive, and have never been alive.
✔ name four of the life processes.
✔ describe how the offspring of different animals
grow into adults.
✔ compare the life cycles of different animals.
27
9781398301658_HCP_SCIENCE_LB3.indb 27 2021/02/23 16:57
You might also like
- Colour The Essence of YouDocument228 pagesColour The Essence of YouKIRSTIN KWOK NINGXUAN S4-10100% (4)
- Casey The Caterpillar 1Document10 pagesCasey The Caterpillar 1api-444974693No ratings yet
- Living Things and Their Life Processes WorksheetDocument9 pagesLiving Things and Their Life Processes Worksheetsylvasag90% (10)
- Diversity of Life on EarthDocument86 pagesDiversity of Life on EarthMonica Morales MaañoNo ratings yet
- Macmillan Science Level 4 Pupil S Book Unit 1 PP 11 16Document6 pagesMacmillan Science Level 4 Pupil S Book Unit 1 PP 11 16reema2050reemaNo ratings yet
- Feature Creature WorksheetDocument4 pagesFeature Creature Worksheetapi-443484889No ratings yet
- LanguageCert C1 Speaking 1.Document3 pagesLanguageCert C1 Speaking 1.TothMonikaNo ratings yet
- Animal Adaptations Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesAnimal Adaptations Lesson Planuredtech100% (3)
- Ciencias Adventure-1Document8 pagesCiencias Adventure-1victor lopezNo ratings yet
- 1-6 SencieDocument32 pages1-6 Senciedumb.ass2008No ratings yet
- Booklet 6tos Epp 73 2024 (2)Document69 pagesBooklet 6tos Epp 73 2024 (2)andreaNo ratings yet
- RH1ASB Unit 2 Marketing FINALDocument35 pagesRH1ASB Unit 2 Marketing FINALlienhusangNo ratings yet
- RH1ASB Unit 2 Marketing FINALDocument35 pagesRH1ASB Unit 2 Marketing FINALHex Dlt Jr.No ratings yet
- COT 1 Grade 3 ScienceDocument7 pagesCOT 1 Grade 3 ScienceCristine MalesNo ratings yet
- Living and Non-Living Things IdentificationDocument7 pagesLiving and Non-Living Things IdentificationManjot KaurNo ratings yet
- Quick QuizDocument2 pagesQuick QuizMohamed AbdoNo ratings yet
- Test Science - SantillanaDocument13 pagesTest Science - SantillanalindajaberchaarNo ratings yet
- RH - G1A - U2 - L1 - The - Crops - Yuki - 1127 - 191230100840Document19 pagesRH - G1A - U2 - L1 - The - Crops - Yuki - 1127 - 191230100840Krystal SorianoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet U1 Science 2 PDFDocument22 pagesWorksheet U1 Science 2 PDFCarmen De Celis CañadasNo ratings yet
- Living and Non-Living ThingsDocument4 pagesLiving and Non-Living ThingsGladys FernandezNo ratings yet
- Byme Test 3buenos PDFDocument19 pagesByme Test 3buenos PDFSilvia SerranoNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem InteractionsDocument9 pagesEcosystem InteractionsVincent Kier CablayNo ratings yet
- Taller Ciencias 2° Luz MarinaDocument14 pagesTaller Ciencias 2° Luz MarinanbNo ratings yet
- Es Int 7a QQ AspDocument2 pagesEs Int 7a QQ Aspdewonruisnor31No ratings yet
- Living Things and Nonliving ThingsDocument14 pagesLiving Things and Nonliving ThingsvicomprNo ratings yet
- II. Early Skills (Colors, Shapes, Parts of The Body, and Number Concepts)Document2 pagesII. Early Skills (Colors, Shapes, Parts of The Body, and Number Concepts)kuon_nieNo ratings yet
- Let's Check Your Attendance!Document32 pagesLet's Check Your Attendance!jm japhetNo ratings yet
- Living Non LivingDocument8 pagesLiving Non LivingDarsh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Print 1Document4 pagesPrint 1Arina KhusnaNo ratings yet
- Amazing Animals: Learning OutcomesDocument12 pagesAmazing Animals: Learning OutcomesGiovana RufiniNo ratings yet
- The Organization of Living ThingsDocument5 pagesThe Organization of Living Thingsangelsolis15No ratings yet
- T2 S 915 Y4 Living Things and Their Habitats End of Unit Assessment - Ver - 1Document9 pagesT2 S 915 Y4 Living Things and Their Habitats End of Unit Assessment - Ver - 1Primary TeachersHubNo ratings yet
- Week 26 Weekly Learning PlanDocument4 pagesWeek 26 Weekly Learning PlanSheryl RamirezNo ratings yet
- OrganizedDocument5 pagesOrganizedIlaha GuseynovaNo ratings yet
- Homework T1 WK5 Science YR 7Document2 pagesHomework T1 WK5 Science YR 7Siyamala NagarajuNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 3 ScienceDocument6 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 3 ScienceRHEA MAE PABLEO100% (2)
- Grade 1 Living Things FDocument2 pagesGrade 1 Living Things FYoun La MinNo ratings yet
- Cheeky Monkey 2 Teacher's Book Unit 1Document18 pagesCheeky Monkey 2 Teacher's Book Unit 1Patricia Latrelle100% (1)
- For Demo TeachingDocument25 pagesFor Demo TeachingJayciel CantereNo ratings yet
- Inbound 3495409207234960340Document5 pagesInbound 3495409207234960340baidgenerose63No ratings yet
- Unit 6Document2 pagesUnit 6exceedstNo ratings yet
- How to Write Different Types of ParagraphsDocument25 pagesHow to Write Different Types of ParagraphsAreeba KhanNo ratings yet
- Share LP For ScienceDocument4 pagesShare LP For ScienceNielmer Gallardo100% (1)
- Characteristics of Living Things ActivityDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of Living Things ActivityPhosphoglyceric AcidNo ratings yet
- Achoo!Document28 pagesAchoo!rupshudildol100% (1)
- A Is For Ant MiniDocument8 pagesA Is For Ant MiniNathalia SalesNo ratings yet
- EIKqD7Y0 Printable Unit 25Document4 pagesEIKqD7Y0 Printable Unit 25riveracalderonandresNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Science Year 7 LB Lyp Part 2Document24 pagesCambridge Science Year 7 LB Lyp Part 2aalqadasi7No ratings yet
- Libro PDF Natural ScienceDocument20 pagesLibro PDF Natural Sciencevanesa escuderoNo ratings yet
- Science Virtual Learning: 1st Grade Living and NonlivingDocument16 pagesScience Virtual Learning: 1st Grade Living and NonlivingFranky Urahara SinagaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 715850999106857257Document8 pagesInbound 715850999106857257baidgenerose63No ratings yet
- A S 6 - Working BackwardsDocument5 pagesA S 6 - Working Backwardskkyy2266No ratings yet
- Demonstrate Understanding of Parts and Functions of Animals and Importance To HumansDocument3 pagesDemonstrate Understanding of Parts and Functions of Animals and Importance To HumansAngel AndersonNo ratings yet
- Sacred Bovines: Is An Apple Living?Document2 pagesSacred Bovines: Is An Apple Living?Maria Fabiola Pachano PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Colegio Saint Paul: Situacion de AprendizajeDocument4 pagesColegio Saint Paul: Situacion de AprendizajeAlexis ViolaNo ratings yet
- LearningLands_nivel1_ScopeandSequenceDocument2 pagesLearningLands_nivel1_ScopeandSequencePaula SarachmanNo ratings yet
- Grade 2 - Living and Non Living Things (Lived, Never Lived Things)Document15 pagesGrade 2 - Living and Non Living Things (Lived, Never Lived Things)Heena Dureja100% (1)
- Activity 1: Name: - DateDocument3 pagesActivity 1: Name: - DateJonatan Garate ArosNo ratings yet
- Nursery Scince U1-2 EditedDocument30 pagesNursery Scince U1-2 EditedAna ParkNo ratings yet
- P Pro Trad Der N Netw Work K: Spe Ecial Re EportDocument4 pagesP Pro Trad Der N Netw Work K: Spe Ecial Re Eporttawhid anamNo ratings yet
- Practice Exercises - Topic Food 2 BảnDocument7 pagesPractice Exercises - Topic Food 2 BảnPhuong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Sheltered Content Unit PlanDocument18 pagesSheltered Content Unit Planapi-542955727No ratings yet
- LB3 Unit 2 9781398301658Document14 pagesLB3 Unit 2 9781398301658Anmol Shoukat - 83197/TCHRNo ratings yet
- Sow Ee2Document13 pagesSow Ee2Anmol Shoukat - 83197/TCHRNo ratings yet
- Sow Ee2Document13 pagesSow Ee2Anmol Shoukat - 83197/TCHRNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument1 pageReproductionAnmol Shoukat - 83197/TCHRNo ratings yet
- Environmental Education - Class II Scheme of Work 2021 - 2022 Our PhilosophyDocument14 pagesEnvironmental Education - Class II Scheme of Work 2021 - 2022 Our PhilosophyAnmol Shoukat - 83197/TCHRNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing HighlightDocument10 pagesReading and Writing HighlightMinaVheck Jimenez LayogNo ratings yet
- Metamorphosis of A ButterflyDocument1 pageMetamorphosis of A ButterflySoyoung ParkNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 5 - Q2 - Mod3Document24 pagesSCIENCE 5 - Q2 - Mod33tj internetNo ratings yet
- Soal Bing X Genap 2023Document12 pagesSoal Bing X Genap 2023intan filaniNo ratings yet
- Beautiful Butterflies of The WorldDocument4 pagesBeautiful Butterflies of The WorldUtsav SrinetNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH CLASS - THE HUNGRY CARTERPILLAR - Maternal (Reparado) PDFDocument12 pagesENGLISH CLASS - THE HUNGRY CARTERPILLAR - Maternal (Reparado) PDFMelanie OspinaNo ratings yet
- Rainforest Information Cards and WorksheetsDocument13 pagesRainforest Information Cards and Worksheetsapi-287500978No ratings yet
- English: Quarter 2 - Module 4-Week 4 - Lesson 2 Write A 4-Paragraph Composition Showing Comparison and ContrastDocument18 pagesEnglish: Quarter 2 - Module 4-Week 4 - Lesson 2 Write A 4-Paragraph Composition Showing Comparison and ContrastVicky SongcuyaNo ratings yet
- Sciennce Quiz 2Document33 pagesSciennce Quiz 2Tantan Fortaleza PingoyNo ratings yet
- Art 133 Group 3 Presntation Section 7 Fall 2107Document24 pagesArt 133 Group 3 Presntation Section 7 Fall 2107api-377880315No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2Document14 pagesLesson Plan 2Chandra MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in English Grade 1 I. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in English Grade 1 I. ObjectivesKristoff AvilaNo ratings yet
- Butterfly Metamorphosis: How Do You Define MetamorphosisDocument4 pagesButterfly Metamorphosis: How Do You Define MetamorphosismarthafitriNo ratings yet
- Larry The FrogDocument20 pagesLarry The FrogGino R. MonteloyolaNo ratings yet
- Revision - Unit 6: A-Choose The Correct AnswerDocument4 pagesRevision - Unit 6: A-Choose The Correct Answerapi-300889911No ratings yet
- Summative Math Test for Grade 5Document26 pagesSummative Math Test for Grade 5selle magatNo ratings yet
- Soal Tryout Bahasa Inggris Kelas Ix 19-20Document15 pagesSoal Tryout Bahasa Inggris Kelas Ix 19-20Arif Munandar100% (1)
- From Caterpillar To Butterfly Signature Assignment WordDocument4 pagesFrom Caterpillar To Butterfly Signature Assignment Wordapi-362322489No ratings yet
- Conservation Unit Lesson 1 Life CycleDocument9 pagesConservation Unit Lesson 1 Life Cycleapi-301720678No ratings yet
- Life Cycle of ButterflyDocument9 pagesLife Cycle of Butterflyemir6ziyanNo ratings yet
- Classification SheetDocument7 pagesClassification Sheetcarlissia wilkinsNo ratings yet
- Unit Animals Lesson 4 Life CyclesDocument8 pagesUnit Animals Lesson 4 Life Cyclesapi-545554684No ratings yet
- Life Cycle Stages and Explanation of Ant and ButterflyDocument2 pagesLife Cycle Stages and Explanation of Ant and Butterflyapi-260203422No ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test Science 5Document7 pagesDiagnostic Test Science 5Rex Russel SalemNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument24 pagesBio Projectʂɾɛɛϳɨʈɦ.v100% (1)
- Group Activities - Expressive TherapistDocument11 pagesGroup Activities - Expressive TherapistAlexandra Stancu100% (2)
- Cabbage White ButterflyDocument2 pagesCabbage White ButterflyaiktiplarNo ratings yet