Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earth and Life Finals
Uploaded by
Norly Vhon Aurora0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesThe document provides an outline for an Earth and life science course, covering topics such as the origins of life on Earth, characteristics of living things, cells, evidence of evolution, and ecosystems. It describes early experiments and theories about the origins of life, including the disproving of spontaneous generation and Miller and Urey's experiment forming organic molecules. The document also defines key characteristics of living things like homeostasis, metabolism, growth, development, and response to stimuli.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides an outline for an Earth and life science course, covering topics such as the origins of life on Earth, characteristics of living things, cells, evidence of evolution, and ecosystems. It describes early experiments and theories about the origins of life, including the disproving of spontaneous generation and Miller and Urey's experiment forming organic molecules. The document also defines key characteristics of living things like homeostasis, metabolism, growth, development, and response to stimuli.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesEarth and Life Finals
Uploaded by
Norly Vhon AuroraThe document provides an outline for an Earth and life science course, covering topics such as the origins of life on Earth, characteristics of living things, cells, evidence of evolution, and ecosystems. It describes early experiments and theories about the origins of life, including the disproving of spontaneous generation and Miller and Urey's experiment forming organic molecules. The document also defines key characteristics of living things like homeostasis, metabolism, growth, development, and response to stimuli.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
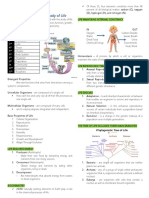
Earth and life science A.
Y 2021-2022
● He introduced electrical sparks into the mixture . After
OUTLINE a few days, molecules similar to amino acids that are
1. Introduction to life science found in all living things were formed, his experiment
2. Characteristics of life proved that the first organic molecules could have
3. Biologist been formed from primitive earth.
4. Cells
5. Evidence of evolution Characteristics of life
6. Ecosystems Wag na mag intro yawa HAHAH
All living living things are made up of cells
Introduction A cell is defined as the smallest, basic unit of life that is
❖ How did life on earth begin? responsible for all of life's processes
For some the origin of life could be explained by the Two types of cells
spontaneous generation theory which states that life forms can ● Unicellular- Single celled organism
be generated from inanimate objects. This belief had been Types:
around since the time of aristotle. ➢ prokaryotic cells/ organisms
Spontaneous generation ➢ Eukaryotic cells/ organisms
● The outmoded theory that living organism, rather than Examples: Bacteria, yeast, Amoeba
coming from the reproduction of their species, arise ● Multicellular- made up of more than one cell
from the non-living objects Examples: Humans, plant, cells
Francesco Redi Cytology- the study of cells. All living things are made up of
● Was able to disprove the spontaneous generation cells. Life starts from a cell
theory when he experimented by placing meat in a jar. All living things reproduce
Reproduction is one thing that’s a major part in life, as it is
something that every organism can do.
Two Types of reproduction
● Asexual- genetically fromed by one parent.
● Sexual- needs 2 parent to reproduce (example human
hahahah o lam mo na tawag don)
All living things are based on a universal genetic code (DNA)
DNA is the genetic code found in every cell. It also can be
inherited from parents and controls your traits.
DNA= Deoxyribonucleic acid
● DNA is pivotal to our growth, reproduction, and
health.
➢ Factors: air and smell
Living things grow and develop
Lazzaro Spallanzani, 1784 The Growth and development of living organisms are not the
● 1st artificial insemination in a dog
same things. Growth is the increase in size and mass of that
● Believed that spallanzani was the first to report the
organism. Development involves the transformation of the
effects of cooling on human sperm
organism as it goes through the growth process.
● He noted in 1776 that sperm cooled by snow became
Living things obtain and use materials and energy
motionless
Living things obtain and use material and energy to grow,
Alexander Oparin develop, and reproduce.
● In 1953, He was a russian scientist who hypothesized
Metabolism- The combination of chemical reactions through
that the atmosphere of primitive earth contained gases
which an organism builds up or breaks down materials
like ammonia, methane, hydrogen, and water vapor.
Multiple ways of getting food
He explained the energy of lightning and ultraviolet
Autotroph They make their own food
rays from chemical compounds. As they mixed with EX: Plants, lichens, and algae bakit?? Kasi nag
rain and hot seas, they formed complex organic produce sila ng photosynthesis.
molecules which was similar to what living things are Heterotroph Known as consumers EX: dogs, humans.
made of Decomposer Break down dead material for food EX: fungi,
Stainley I. Miller bacteria, worms etc.
● An American scientist, Stanley L. Miller performed an
experiment using a mixture of the glass suggested by All living things responds to their environment
oparin.
Earth and life science
● Internal stimuli- Internal stimuli are changes in He discovered the basic principles of heredity through
condition inside the body. EX: being hungry ganun experiments in his monastery’s garden
● External stimuli- external stimuli are changes in ● foundation of modern genetics and leading to the
condition outside the body. EX: sweating study of heredity.
living things maintains a stable internal environment There are seven different traits 2 types of traits
Homeostasis- also means “steady” and “same”. It helps the Shape of seed Shape of pods Dominant traits
body to maintain a stable internal environment. Color of seed Plant height Recessive traits
3 main components of homeostasis Color of pods Position of flowers
receptor Is the structure that monitors internal conditions Flower color
Control It receives and processes infos from the receptor EX: The
center nucleus is like the remote control center of the cell. It acts Charles darwin
as the cell's brain by telling it what to do, how to grow, and ● English naturalist
when to reproduce.
Contribution- the collection of a tremendous amount of genetic
effector Is any organ or tissue that receives infos from the control
data, and attempt to provide a theoretical framework for its
center and acts to bring about the changes needed to
maintain homeostasis interpretation. He formulated a developmental theory of heredity
“PANAGENISIS”
Taken as a group, living things change over time CELL
Taken as a group, living things evolve. Over generations, groups ● A cell is a fundamental unit of life
of organisms evolve, or change over time. Evolutionary change ● All the living organisms are made up of a cell
links all forms of life to a common origin more than 3.5 billion ● Known as the fundamental unit of life because it
years ago. regulates all the functions inside an organisms
Biologist ● latin= a little room
● Robert Hook (1665)
Carolus Linnaeus Two types of cells
● Father of taxonomy 1. Prokaryotic
● Swedish naturalist and explorer ● Lacks nucleus
Contributions- “development of a hierarchical system of ➢ EX: bacteria
classification of nature” it includes the 8 taxa 2. Eukaryotic
8 Taxa ● Contains nucleus
1. Domain 5. Order ➢ EX: plants and bacteria
2. Kingdom 6. Family Part of cells and its functions
3. Phylum 7. Genus Cell membrane Controls what enters and exit the cell
4. Class 8. Species Nuclear membrane Controls what enters and exit the
nucleus
Thomas Malthus nucleus Control center of the cell
● English economist and demographer chromosomes Genetic info in the nucleus
Contribution- “Population growth will always tend to outrun the Endoplasmic reticulum Transport system in the cell
food supply and that betterment of humankind is impossible Ribosome Organelle that makes protein
without strict limits on reproduction.” Golgi body Organelle that packages proteins
Vacuole Stores water or waste
Jean Baptiste De Lamarck
Lysosome Brakes down old cells parts
● French biologist and evolutionary theorist
Mitochondria (is a … charot) Organelle for cellular respiration
● Founder of invertebrate paleontology provides energy
He is best known for his idea that acquired characters are
inheritable known as “Lamarckism”. Human cells
Charles lyell ● Bone cells
● Scottish geologist ● Rbc (red blood cells)
● Author of principles of geology ● White blood cells
He introduced the theory of uniformitarianism ● Motor neuron
➢ According to him, “all features of the earth’s surface ● Intestine cells
are produced by physical, chemical, and biological ● Ovum
processes.” ● Sperm cells
Gregor Mendel
● Botanist, teacher, and agustinian prelate
● “Father of modern genetics”
Earth and life science
3. Anatomy
The female body 4. Embryology
A. Estrogen 5. Biochemistry
● Development of secondary sex characteristics
● Growth of uterus during puberty Radiocarbon dating is a method that provides objective age
● Initial growth of endometrium during estimates for carbon-based materials that originated from living
menstrual cycle organisms. An age could be present in sample and comparing
B. Progesterone this against an intentionally used reference standard
● Development of breast during puberty Patterns of evolution
● Growth of endometrium during menstrual Parallel evolution
cycle ● Two related species made similar evolutionary
● Inhibition of uterine contractions during changes after their divergence.
pregnancy ● Marsupial and placental mammals
Testosterone (male) Example
A. Optimal testosterone ➢ Sugar glider in Australia and flying squirrel in
● Sharper mind north america.
● Happy Patterns for natural selection
● Healthy heart Convergent evolution
● Plenty of energy ● When two species look alike but do not have common
● Confident ancestor
● Increased muscle mass Characteristics
● Strong erections ➢ Similar in appearance
● Strong bones ➢ Similar in function
B. Low testosterone ➢ Different in development, origin, and anatomy
● Low energy Example
● Increased fat tissue ➢ Opossum and Aye-Aye
● Increased risk of E.D and low libido
● High risk of alzheimer's disease Anatomical evidence of evolution focuses on similarities and
● Depressed differences in the body structures of different species.
● High risk of osteoporosis Homologous structure
Evidence of evolution Synonym- Homologues
In evolution, there are body parts of species that have similar
Evolution features, indicating common ancestor or same developmental
Evolution is the process of biological change by which species origin
of organisms change over time. Example
● Evolution is a central theme in all fields of biology ● Human heart and turtle heart
today. Analogous structure
Have the same functions, but have different evolutionary origins.
Example
● Bird and insect wings.
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms interacting
with each other and their nonliving environment .
What makes up an ecosystem?
● All living things
➢ Plants, animals and bacteria
● Non living things
➢ Sun, soil and rocks
Evidence Concept
1. The fossils record Everything in the natural world is connected
2. Biogeography plants and animals depend on each other to survive
● Geographic distribution of species has revealed that (biodiversity)
unrelated species in different regions of the world look
like when found in similar environments.
Earth and life science
plants and animals within an area interact with each
other with nonliving elements of the area, such as
climate, water, soil and so on.
Functions of eco systems
Habitat functions
Ecosystems provide habitat to wild plants and animals and thus
conserve biological and genetic diversity. It supports different
food chains
Production functions
Production of a wide range of goods ranging from food to raw
materials.
Regulatory functions
Ecosystems regulates essential ecological processes and life
support systems and renders stability
● Every ecosystems regulates and mountains itself and
resist any stresses disturbance upto a certain limit this
is known as cybernetic systems
Information functions
Ecosystems provide an essential “reference function” and
contribute to maintenance of human health providing
opportunities for spiritual enrichment, cognitive development,
recreation and aesthetic experience
2 types of ecosystems
Biotic
Composed of living things
Abiotic
Composed of non- living things
Roles in an ecosystems
1. Producers
Plants- they use water, carbon dioxide and sunlight to make
their own food
2. Consumers
Animals- they must eat plant or other animals for food
3. Decomposers
Bacteria and fungi- get energy by feeding on the dead bodies
of plants and animals
Earth and life science
You might also like
- Lesson 6 - Origin of Life On EarthDocument7 pagesLesson 6 - Origin of Life On EarthCindy Claire PilapilNo ratings yet
- History OF Biology: By: Ms. Maedel Joy Ventura - Escote, PH.DDocument65 pagesHistory OF Biology: By: Ms. Maedel Joy Ventura - Escote, PH.DAlbert Jade Pontimayor Legaria100% (1)
- Conversion FactorDocument3 pagesConversion FactorAniket AngreNo ratings yet
- BIO 103 Lecture 1Document25 pagesBIO 103 Lecture 1Samiul Hasan Pranto100% (1)
- Introduction To Life ScienceDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Life Sciencedivina villegasNo ratings yet
- E&L Science 8-22-19Document2 pagesE&L Science 8-22-19Borbe ClauNo ratings yet
- Origin of The UniverseDocument44 pagesOrigin of The UniverseLuis PazNo ratings yet
- Marcet Boiler ReportDocument20 pagesMarcet Boiler Reportgabrielhii1995No ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument32 pagesBiology NotesTaylor BonnetNo ratings yet
- Els (2nd Q) Unifying Theme of LifeDocument3 pagesEls (2nd Q) Unifying Theme of LifeRennelyn DimaanoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 (1st Quarter) ReviewerDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology 1 (1st Quarter) ReviewerAthena Marielle Lorenzo100% (4)
- ELS 2ndDocument4 pagesELS 2ndVenisse NapaoNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Biology ReviewerDocument5 pagesGrade 11 Biology ReviewerVen ReyNo ratings yet
- Biology 1.3 NotesDocument3 pagesBiology 1.3 NotesBino The RavenNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio ReviewerDocument10 pagesGen Bio ReviewerMarylyn MirandaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science HandoutsDocument3 pagesEarth and Life Science HandoutsbokloybrusasNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1Document4 pagesGeneral Biology 1Tapnio Glezel GolongNo ratings yet
- GenBio1 Reviewer-1Document21 pagesGenBio1 Reviewer-1Maria Keith Ericka RaguinganNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 Bio 2Document66 pagesBio 1 Bio 2Alex Jr Biñaz DoradoNo ratings yet
- E&ls Finals NotesDocument7 pagesE&ls Finals NotesMary Antonette VeronaNo ratings yet
- Nat Reviewer For Life Science 2022-2023Document6 pagesNat Reviewer For Life Science 2022-2023Johnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- Els Handout (Life)Document4 pagesEls Handout (Life)Chenee TanNo ratings yet
- Is 2 Reviewer For LT1Document10 pagesIs 2 Reviewer For LT1Lslall SjdbbhssNo ratings yet
- ST ND RD TH TH TH TH THDocument8 pagesST ND RD TH TH TH TH THOsoNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument6 pagesBiologySea are YellowNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Life Science: Unit 1: Concept of Life Lecture of Estocapio, EiaomDocument54 pagesIntroduction To Life Science: Unit 1: Concept of Life Lecture of Estocapio, EiaomEdward BelenNo ratings yet
- General Biology Reviewer-1Document16 pagesGeneral Biology Reviewer-1Katrina EstaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science SHS 15.1 The Evolving Concept of LifeDocument20 pagesEarth and Life Science SHS 15.1 The Evolving Concept of LifeWinsear VardeNo ratings yet
- 2 - Earth and Life Science 2nd Qua NotesDocument6 pages2 - Earth and Life Science 2nd Qua NotesMerce AdlaonNo ratings yet
- The Evolving Concept of LifeDocument36 pagesThe Evolving Concept of Lifechariemaegajudo0No ratings yet
- The Study of Life BiologyDocument6 pagesThe Study of Life BiologyJokher BaliliNo ratings yet
- HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF LIFE Origin and Study of LifeDocument30 pagesHISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF LIFE Origin and Study of LifeJamie Camille TanNo ratings yet
- ELIFE Second Quarter ReviewerDocument8 pagesELIFE Second Quarter ReviewerLuWiz DiazNo ratings yet
- Els - Q2 - L1 3 Origin of Life Unifying Themes CellDocument39 pagesEls - Q2 - L1 3 Origin of Life Unifying Themes CellmarkjohnmagcalengNo ratings yet
- L6S1. Introduction To Life ScienceDocument22 pagesL6S1. Introduction To Life ScienceSichayra GamotiaNo ratings yet
- Zoology LectureDocument58 pagesZoology LectureLyra Kassandra M. BorjaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Digital Notebook PDFDocument11 pagesWeek 3 Digital Notebook PDFFrancene FelipeNo ratings yet
- Els Colored PrintDocument9 pagesEls Colored PrintShein GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Concept of LifeDocument28 pagesConcept of LifeJesh RishNo ratings yet
- GenBio 1st Sem (New)Document6 pagesGenBio 1st Sem (New)anthoniorabadonNo ratings yet
- INTRO BIO and LIFEDocument33 pagesINTRO BIO and LIFEzkkpxh4dnrNo ratings yet
- Review: 1. What Is The Difference Between Needham and Spallanzani's Experiment?Document54 pagesReview: 1. What Is The Difference Between Needham and Spallanzani's Experiment?bae joohyunNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument82 pagesBiologyLewis FernandoNo ratings yet
- GenBio - 1st-Sem - LATEST GIGA UPDATEDDocument25 pagesGenBio - 1st-Sem - LATEST GIGA UPDATEDanthoniorabadonNo ratings yet
- GenBio - 1st-Sem - LATEST MEGADocument16 pagesGenBio - 1st-Sem - LATEST MEGAanthoniorabadonNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio ReviewerDocument4 pagesGen Bio ReviewerJoeselle Anne SampagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Microbiology Part 1Document23 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Microbiology Part 1If YouNo ratings yet
- Evolution and The Origin of EarthDocument3 pagesEvolution and The Origin of EarthConrado Juisan CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of LifeDocument17 pagesCharacteristics of LifeEmaleigh WhiteNo ratings yet
- EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE 4th Quarter Module 1 Lesson 1-2Document12 pagesEARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE 4th Quarter Module 1 Lesson 1-2christianaries.lapuzNo ratings yet
- Intro To Life ScienceDocument52 pagesIntro To Life ScienceBaby DarlingNo ratings yet
- The Evolving Concept of LifeDocument7 pagesThe Evolving Concept of LifeStopnaplsNo ratings yet
- Life and Its Beginnings Unifying Themes About LifeDocument44 pagesLife and Its Beginnings Unifying Themes About LifeaaNo ratings yet
- Concept of Life - ArasanDocument2 pagesConcept of Life - ArasanJhelein ArasanNo ratings yet
- Biology 1Document9 pagesBiology 1llednewigopNo ratings yet
- 5ad45642e4b01d108398736b 5e9a092ba8446510cc99fb5a 1615282586341Document13 pages5ad45642e4b01d108398736b 5e9a092ba8446510cc99fb5a 1615282586341Sakshi ShahNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Introduction (Cell Theor Cell Parts and Functionns)Document8 pagesLesson 1: Introduction (Cell Theor Cell Parts and Functionns)Svan Codm0% (1)
- Characteristics of LifeDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of Lifewyszynki87No ratings yet
- Characteristics of LifeDocument34 pagesCharacteristics of LifeJunfen AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Reviewer: © Angelica GarciaDocument15 pagesEarth and Life Science Reviewer: © Angelica GarciaFat AjummaNo ratings yet
- Group of Cells That Have Similar Structure and That Function Together As A UnitDocument5 pagesGroup of Cells That Have Similar Structure and That Function Together As A UnitMikachuNo ratings yet
- Microbes Mindcrobes: Human Entanglement with Microbes on a Physical, Mental, Emotional and Quantum LevelFrom EverandMicrobes Mindcrobes: Human Entanglement with Microbes on a Physical, Mental, Emotional and Quantum LevelNo ratings yet
- Science-Reviewer TyphoonsDocument10 pagesScience-Reviewer TyphoonsLaxiava VaniaNo ratings yet
- Soal-Soal KD TroDocument24 pagesSoal-Soal KD TroTita Dian NofitaNo ratings yet
- Mulat ShityeDocument130 pagesMulat ShityeShaziashah ShaziaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry CH 3 TestDocument10 pagesChemistry CH 3 TestNeoNo ratings yet
- Solution CAE-I Odd Sem 2022-23Document11 pagesSolution CAE-I Odd Sem 2022-23Dulce DeNo ratings yet
- Energy PPT (Physics)Document11 pagesEnergy PPT (Physics)phoebe100% (1)
- Abebaw ZelalemDocument97 pagesAbebaw ZelalemRebi HamzaNo ratings yet
- Adamjee Coaching - Mathematics 2006 - Past Year Paper - Class XIDocument3 pagesAdamjee Coaching - Mathematics 2006 - Past Year Paper - Class XISuneelKumarChauhanNo ratings yet
- Family and Environment EthicsDocument27 pagesFamily and Environment EthicsKrisha Nicole Go ArguellesNo ratings yet
- November 2022 (9701 - 13) QPDocument16 pagesNovember 2022 (9701 - 13) QPHung Mang ThiNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry ReviewDocument5 pagesBasic Chemistry ReviewArman Neil J. BudogNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy:: Department of Electrical Engineering, Veer Surendra Sai University of Technology BurlaDocument3 pagesSolar Energy:: Department of Electrical Engineering, Veer Surendra Sai University of Technology Burlalhr1No ratings yet
- Building Energy Estimation Report: Project InformationDocument12 pagesBuilding Energy Estimation Report: Project InformationAlex DjokaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Gravitation RevisionDocument8 pagesChapter 6 Gravitation Revision陈伟明No ratings yet
- Answer in Study Guide ScienceDocument7 pagesAnswer in Study Guide ScienceSean Campbell100% (1)
- Coal Fly AshDocument6 pagesCoal Fly AshKPCNo ratings yet
- Chapter-05 Energy Efficient Motors: 5.1 Motor Horse PowerDocument9 pagesChapter-05 Energy Efficient Motors: 5.1 Motor Horse PowerharishNo ratings yet
- Spring 2017 Registration DataDocument514 pagesSpring 2017 Registration DataKamran ButtNo ratings yet
- 0101SED16 17intro TextDocument32 pages0101SED16 17intro TextAdrian GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation On Partial Replacement of Cement by Eggshell PowderDocument6 pagesExperimental Investigation On Partial Replacement of Cement by Eggshell PowderArun anandNo ratings yet
- Design and Parametric Investigation of An Ejector - R717 - AlexisDocument14 pagesDesign and Parametric Investigation of An Ejector - R717 - AlexisAdrianUnteaNo ratings yet
- 080320184O4KQM37Annexure DocumentofEIA PDFDocument180 pages080320184O4KQM37Annexure DocumentofEIA PDFAayush tyagiNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Heat TransferDocument7 pagesTemperature and Heat TransferAhmed HashkarNo ratings yet
- Charge-Shift Bonding and Its Manifestations in Chemistry - Article - Nature ChemistryDocument9 pagesCharge-Shift Bonding and Its Manifestations in Chemistry - Article - Nature ChemistryJE49No ratings yet
- Fuel CellDocument28 pagesFuel CellRajesh ShahNo ratings yet
- Wheatering N Soil FormationDocument51 pagesWheatering N Soil FormationEdwin Yudha NugrahaNo ratings yet
- STUDY OF RELATIVE WATER QUALITY PARAMETERS IN SATAJAN BIRD SANCTURY Water MarkedDocument14 pagesSTUDY OF RELATIVE WATER QUALITY PARAMETERS IN SATAJAN BIRD SANCTURY Water MarkedJintu moni BhuyanNo ratings yet