Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CBC With Differential, BMP
CBC With Differential, BMP
Uploaded by
MrRightOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CBC With Differential, BMP
CBC With Differential, BMP
Uploaded by
MrRightCopyright:
Available Formats
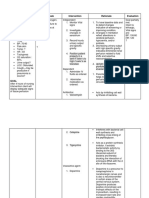
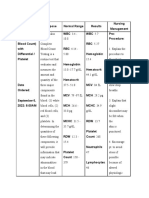
COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT WITH DIFFERENTIAL
Laboratory test Normal values Patient's Significance/Nursing
(parameters) findings interventions
White blood cells 4,500- 10,000 K/uL 8, 500 Within Normal Range
Neutrophils 54- 62% 57 Within Normal Range
Band forms 3–5 8 Significance
Band forms are an
immature form of
neutrophils, which are
the most commonly
produced white blood
cell. They are essential
for fighting disease.
That's why your body
produces them in excess
during an
infection.Laboratoey
values for high band
forms indicate Infection
Nursing interventions
Monitor temperature.
Review the importance
of breathing exercises,
effective cough,
frequent position
changes, and adequate
fluid intake.
Limit visitors; provide
masks as indicated
Encourage a balance
between activity and
rest.
Administer
antimicrobials as
indicated.
Basophils 0 – 1% 0.75 Within Normal Range
Eosinophils 0 – 3% 2 Within Normal Range
Lymphocytes 24- 44% 32 Within Normal Range
Monocytes 3 – 6% 4 Within Normal Range
Hemoglobin 13.5-16.5 g/dL 13.0 Significance
A hemoglobin t is often
used to check for
anemia, a condition in
which your body has
fewer red blood cells
than normal. If you have
anemia, your cells don't
get all the oxygen they
need. Laboratory results
for low hemoglobin
levels indicate Anemia.
Nursing interventions
Monitor hemoglobin,
hematocrit, RBC counts,
and reticulocyte counts.
Assist the client in
developing a schedule
for daily activity and
rest. Stress the
importance of frequent
rest periods.
Instruct the client about
medications that may
stimulate RBC
production in the bone
marrow.
Provide supplemental
oxygen therapy as
needed.
Anticipate the need for
the transfusion of
packed RBCs.
Hematocrit 41-50% 39.2 Significance
A hematocrit test
measures the
proportion of red blood
cells in your blood. Red
blood cells carry oxygen
throughout your body.
Having too few or too
many red blood cells can
be a sign of certain
diseases. Laboratory
results for low
hematocrit levels levels
may indicate Anemia.
Nursing interventions
Monitor hemoglobin,
hematocrit, RBC counts,
and reticulocyte counts.
Assist the client in
developing a schedule
for daily activity and
rest. Stress the
importance of frequent
rest periods.
Instruct the client about
medications that may
stimulate RBC
production in the bone
marrow.
Provide supplemental
oxygen therapy as
needed.
Anticipate the need for
the transfusion of
packed RBCs.
Red blood cell 4.5-5.5 M/ul 4.8 Within Normal Range
RBC Distribute Width <14.5% 10.0 Within Normal Range
MCV 80-100 fL 90 Within Normal Range
MCH 26-34 pg 32 Within Normal Range
MCHC 31- 37 g/dL 33 Within Normal Range
Platelet 100,000-450,000 K/uL 200,000 Within Normal Range
BASIC METABOLIC PANEL
Laboratory test Normal values Patient's findings Significance/Nursing
(parameters) interventions
Sodium 135-147 mmol/L 136 Within Normal Range
Potassium 3.5-5.2 mmol/L 3.5 Within Normal Range
Chloride 95-107 mmol/L 100 Within Normal Range
CO2 22-30 mmol/L 28 Within Normal Range
Urea Nitrogen 7-20 mg/dL 20 Within Normal Range
Creatinine 0.5-1.2 mg/dL 1.2 Within Normal Range
Glucose 60-110 mg-dL 100 Within Normal Range
You might also like
- Sample Commissioning PlanDocument36 pagesSample Commissioning Planvan83% (18)
- Situation:: Sbar For Copd Name: MR. Gomez 68 Yr Old, M Allergies-AmpicillinDocument5 pagesSituation:: Sbar For Copd Name: MR. Gomez 68 Yr Old, M Allergies-AmpicillinMrRightNo ratings yet
- Pmls Transes Prelims 1Document5 pagesPmls Transes Prelims 1Kimberly Jean OkitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Strategic ManagementDocument28 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Strategic Managementakash borseNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Practice in Arab CountriesDocument5 pagesMental Health Practice in Arab CountriesRebecca AntoniosNo ratings yet
- Medical ManagementDocument8 pagesMedical ManagementNHICOLE YAO PORCESONo ratings yet
- Labs SVDocument10 pagesLabs SVLica_Zurriaga_9142No ratings yet
- 1 Group Case Study - NCM 107 - Group 3Document9 pages1 Group Case Study - NCM 107 - Group 3Princess Pilove GawongnaNo ratings yet
- Course in The WardDocument12 pagesCourse in The Wardmikhaela sencilNo ratings yet
- As A Student, How Do You Maintain A Healthy Lifestyle?: Topic 1: Health Care Activity 1Document4 pagesAs A Student, How Do You Maintain A Healthy Lifestyle?: Topic 1: Health Care Activity 1Elijah Mae MundocNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPDocument5 pagesAcute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPMyrvic Ortiz La OrdenNo ratings yet
- Post Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care Plan PDFDocument2 pagesPost Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care Plan PDFA sison100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Diagnosis Rationale Intervention Rationale EvaluationHerald Jones LamirezNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhage NCPDocument4 pagesHemorrhage NCPElishaNo ratings yet
- Group F DXDocument2 pagesGroup F DXmyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study UTI (Domo-Os, Belenda)Document6 pagesDrug Study UTI (Domo-Os, Belenda)Irene BungalsoNo ratings yet
- CellulitisDocument14 pagesCellulitisStephy SalvadorNo ratings yet
- FVD NCPDocument2 pagesFVD NCPJohnrick VenturaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan SampleDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Samplez6cc9vgg6nNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Anemia 2007Document25 pagesSickle Cell Anemia 2007R-o-N-n-e-lNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- Laboratory: Reference: Labtest PDFDocument6 pagesLaboratory: Reference: Labtest PDFChris Denver BancaleNo ratings yet
- Lab Result WORDDocument17 pagesLab Result WORDPrincess Pilove GawongnaNo ratings yet
- Final NCP For PostpartumDocument8 pagesFinal NCP For PostpartumJam Ali100% (1)
- Asynchronous Activity Day 1 - Dinson, Red Angela O.Document10 pagesAsynchronous Activity Day 1 - Dinson, Red Angela O.Red DinsonNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Laboratory Results: Key PointsDocument8 pagesInterpreting Laboratory Results: Key PointsMarjorie Joy GreciaNo ratings yet
- Procedure/S Indication/S Result/S Normal Values Implications Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument9 pagesProcedure/S Indication/S Result/S Normal Values Implications Nursing Responsibilitiesmyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- NCP Post PartumDocument2 pagesNCP Post PartumsteffiNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesAcute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanKrisianne Mae Lorenzo Francisco80% (5)
- ROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPDocument6 pagesROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPkimberly quitonNo ratings yet
- Lab ResultsDocument3 pagesLab ResultsKristal Cyril PolzNo ratings yet
- Blood (Notes)Document12 pagesBlood (Notes)Angel Rose BrillanteNo ratings yet
- NCP JagDocument10 pagesNCP JagArvinjohn GacutanNo ratings yet
- NCP - Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesNCP - Activity IntoleranceRoyce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- Laboratory and Diagnostic Exams: Test Result Normal Value SignficanceDocument3 pagesLaboratory and Diagnostic Exams: Test Result Normal Value SignficanceAlfrien Ivanovich LarchsonNo ratings yet
- ICS Pedia WardDocument8 pagesICS Pedia Wardsweet061991No ratings yet
- Assessment Dignosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Objective: IndependentDocument2 pagesAssessment Dignosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Objective: IndependentBenjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- Anemia: Case ScenarioDocument5 pagesAnemia: Case ScenarioGeeza Gem VicencioNo ratings yet
- Function of ErythrocytesDocument12 pagesFunction of Erythrocytesdeput_rprNo ratings yet
- Hemodialysis: Three-Year Experience: NocturnalDocument10 pagesHemodialysis: Three-Year Experience: Nocturnalerikazoku moNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 - Rle Nursing Care Plan: To Have Baseline Data. Normal Values Indicate Adequate Tissue PerfusionDocument7 pagesNCM 112 - Rle Nursing Care Plan: To Have Baseline Data. Normal Values Indicate Adequate Tissue Perfusiontherese BNo ratings yet
- NCP Decrease Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesNCP Decrease Cardiac OutputAnonymous 2hJKVrNo ratings yet
- Colle Ofn: Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesColle Ofn: Nursing Care PlanDara Sophia EncarguezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Medical TechnologyDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Medical TechnologySophia Elinor MenesesNo ratings yet
- Gi Bleeding CaseDocument28 pagesGi Bleeding CaseP BNo ratings yet
- Laboratory and Diagnostic ExaminationsDocument10 pagesLaboratory and Diagnostic ExaminationsUriel CrispinoNo ratings yet
- White Blood Cells and Differential: Normal Value Purpose and IndicationDocument1 pageWhite Blood Cells and Differential: Normal Value Purpose and IndicationKyla CasugaNo ratings yet
- Facto NCPDocument3 pagesFacto NCPkkd nyleNo ratings yet
- Peritonitis NCPDocument3 pagesPeritonitis NCPANNA V. LARITANo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Goals Adnd Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Implementation EvaluationDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Goals Adnd Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Implementation EvaluationNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Hematology Date: July1, 2010 Examination Result Normal Value Interpretations HemoglobinDocument4 pagesHematology Date: July1, 2010 Examination Result Normal Value Interpretations HemoglobinLeo_Rabacca_3610No ratings yet
- Daily ReqDocument29 pagesDaily ReqPsyche YonaNo ratings yet
- Case Pre Labs 4th FloorDocument5 pagesCase Pre Labs 4th FloorLorraine Nicolne B. CortejoNo ratings yet
- BOX 17.4 NCP Postpartum HemorrhageDocument4 pagesBOX 17.4 NCP Postpartum HemorrhageJam AliNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument1 pageImpaired Gas Exchangeruggero07No ratings yet
- Sepsis DoneDocument54 pagesSepsis DoneGiorgi PopiashviliNo ratings yet
- Assessment: Dependent RationaleDocument2 pagesAssessment: Dependent RationaleMae Navidas DigdiganNo ratings yet
- 6 Diagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresDocument12 pages6 Diagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresJanah CalitNo ratings yet
- Components of The Complete Blood Count (CBC) : © 2005 American Association For Clinical Chemistry 1Document2 pagesComponents of The Complete Blood Count (CBC) : © 2005 American Association For Clinical Chemistry 1anisa rachmitaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention-Rationale Evaluation Fluid Volume Excess Related ToDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention-Rationale Evaluation Fluid Volume Excess Related ToJen BallesterosNo ratings yet
- NCP Ca 3Document3 pagesNCP Ca 3Lalaine LocsinNo ratings yet
- University of Cordilleras College of Nursing NCP: Mycobacterium TuberculosisDocument3 pagesUniversity of Cordilleras College of Nursing NCP: Mycobacterium TuberculosisLyn MhoreNo ratings yet
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesRisk For Decreased Cardiac Tissue PerfusionKarina MadriagaNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument2 pagesTissuelouie roderosNo ratings yet
- High-Resolution Electrophoresis and Immunofixation: Techniques and InterpretationFrom EverandHigh-Resolution Electrophoresis and Immunofixation: Techniques and InterpretationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) VS. Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Syndrome (HHS)Document5 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) VS. Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Syndrome (HHS)MrRightNo ratings yet
- Blood Typing Lab Activity FinalDocument3 pagesBlood Typing Lab Activity FinalMrRightNo ratings yet
- Tle 9 Module 1 Final (Genyo)Document7 pagesTle 9 Module 1 Final (Genyo)MrRightNo ratings yet
- BALLON Krista - MODULE 1 - HOME VIEWING REPORTDocument2 pagesBALLON Krista - MODULE 1 - HOME VIEWING REPORTMrRightNo ratings yet
- Medieval MusicDocument13 pagesMedieval MusicMrRightNo ratings yet
- FNCPDocument2 pagesFNCPMrRightNo ratings yet
- Logbook For SGDs 1Document115 pagesLogbook For SGDs 1Shariq KhattakNo ratings yet
- 2023 BDRRMC EoDocument5 pages2023 BDRRMC EoAnilyn CelisNo ratings yet
- GHS Format-sds-Gp CleanDocument8 pagesGHS Format-sds-Gp CleanAlan TanNo ratings yet
- The 7 Biggest Mistakes Made by Singers..Document17 pagesThe 7 Biggest Mistakes Made by Singers..César De La Cruz OlivaNo ratings yet
- Final Minutes 320 RBDocument1,866 pagesFinal Minutes 320 RByasserNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliograhy: Submitted ToDocument4 pagesAnnotated Bibliograhy: Submitted ToRumela Ganguly ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal 1Document6 pagesLatihan Soal 1Simple GirlNo ratings yet
- SACS Back To School 2020Document37 pagesSACS Back To School 2020Saige DriverNo ratings yet
- Department of Physics Department of Physics Department of PhysicsDocument235 pagesDepartment of Physics Department of Physics Department of Physicstatis reyesNo ratings yet
- Insulin Therapy: by Dr. Adithya PolavarapuDocument18 pagesInsulin Therapy: by Dr. Adithya Polavarapuadithya polavarapuNo ratings yet
- Health Promotion and Primary Health CareDocument51 pagesHealth Promotion and Primary Health CareBhawna JoshiNo ratings yet
- Heitz-Mayfield Iti TG 13 en LeseprobeDocument44 pagesHeitz-Mayfield Iti TG 13 en LeseprobeS. BenzaquenNo ratings yet
- DO PBL Paper Case 16 HIV OSCEDocument4 pagesDO PBL Paper Case 16 HIV OSCESmelly RaccoonNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Study of Shilagarbha PottaliDocument8 pagesPharmaceutical Study of Shilagarbha Pottalisiva kumarNo ratings yet
- A Immediate Implant With Provisionaliztion Journal of Clinical PeriodontologyDocument12 pagesA Immediate Implant With Provisionaliztion Journal of Clinical PeriodontologyAhmed BadrNo ratings yet
- DROGAS International Narcotics Control Strategy REPORT INCSRDocument249 pagesDROGAS International Narcotics Control Strategy REPORT INCSRMauricio LemusNo ratings yet
- Dufour 2006 - Biocultural Approaches in Human Biology PDFDocument9 pagesDufour 2006 - Biocultural Approaches in Human Biology PDFFlor DarkoNo ratings yet
- Biginner's Guide To Feldenkrais PDFDocument4 pagesBiginner's Guide To Feldenkrais PDFAna Carolina PetrusNo ratings yet
- Reading 1Document17 pagesReading 1KiwiNo ratings yet
- A Regional Approach To Foot and Ankle MRIDocument17 pagesA Regional Approach To Foot and Ankle MRInior100% (1)
- Workplace Resilience Scale Winwood2013 PDFDocument8 pagesWorkplace Resilience Scale Winwood2013 PDFAmy BCNo ratings yet
- Wellness of A New Born: CHO Mentoring ProjectDocument57 pagesWellness of A New Born: CHO Mentoring ProjectAmelia ChristmasNo ratings yet
- Significance of The StudyDocument2 pagesSignificance of The StudyMiguel VienesNo ratings yet
- Health Dissertation TopicsDocument6 pagesHealth Dissertation TopicsUK100% (1)
- Prevention of Disease & Health PromotionDocument2 pagesPrevention of Disease & Health PromotionGhith WhiuNo ratings yet
- The Healing Powers of CrystalsDocument16 pagesThe Healing Powers of CrystalsATip4 EveryoneNo ratings yet