Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Levels of Structural Organization Final
Uploaded by
maxine janorasOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Levels of Structural Organization Final
Uploaded by
maxine janorasCopyright:
Available Formats
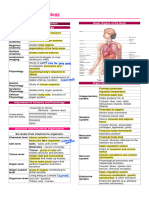
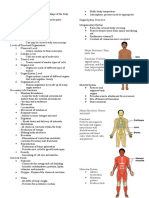
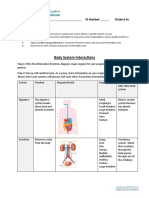
Forms the external body covering
Protects deeper tissue from injury due to bumps, chemicals, bacteria, and dehydration
Synthesizes vitamin D
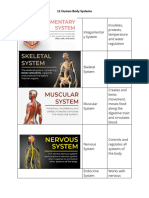
1 Integumentary System pain
Location of sensory receptors
pressure
Picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to blood Location of sweat and oil glands, which in turn excretes salt and urea
Disposes of debris in the lymphatic stream 7 Lymphatic System Hair, skin, fingernails
Houses white blood cells involved in immunity
complements each other Protects and supports body organs
Provides a framework that the muscles use to cause movement
blood carries oxygen, nutrients, hormones, carbon dioxide, wastes, etc. Blood vessels transport blood
2 Skeletal Systems Blood cells are formed within bones
Primarily a transport system that carries blood containing oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, hormones, and
6 Cardiovascular System Stores minerals
other substances to and from the cells where exchanges are made
Cartilages, joint, bones
Protects body with blood clots, antibodies, and other protein molecules in the blood
Keeps blood constantly supplied with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide
Allows manipulation of the environment, locomotion, and facial expression
The gaseous exchanges occur through the walls of the air sacs of the lungs 8 Respiratory System 3 Muscular System Maintains posture and produces heat
Contributes to the acid-base balance of the blood via its carbonic acid/ bicarbonate buffer system
Skeletal muscles
Organ System Overview
Fast-acting control system of the body
4 Nervous System Responds to internal and external changes by activating appropriate muscles and glands
Breaks food down into absorbable nutrients that enter the blood for distribution to body cells
9 Digestive System
Consists of brain, sensory receptor, spinal cord, and nerves
Indigestible foodstuffs are eliminated as feces
growth
Controls body activities
Glands secrete hormones that regulate processes such as: reproduction
nutrient use
Eliminates nitrogen-containing wastes from the body 5 Endocrine System Also the control system of the body but acts much slower
Regulates water, electrolyte, and acid-base balance of the blood 10 Urinary System
Plays a role in regulating long-term homeostasis
Filters the blood
The male testes produces sperm.
Male
Ducts and glands aid in delivery of viable sperm to the female reproductive tract
The female ovaries produce eggs or ova
Reference: Marieb, E. & Keller, S. (2018). Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology (12th ed.) Pearson Education South Asia PTE. LTD. 11 Reproductive System
Female
Other structures serve as sites for fertilization and development of the fetus
The role of this system is tp produce offspring
You might also like
- 21 Day Fix Food ListDocument1 page21 Day Fix Food Listjavi martinezNo ratings yet
- Smooth Muscle Cell Molecules: © 2012 Pearson Education, IncDocument28 pagesSmooth Muscle Cell Molecules: © 2012 Pearson Education, IncNicole EncinaresNo ratings yet
- Body Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: DigestiveDocument4 pagesBody Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: DigestiveDave Chadha100% (1)
- Oracle Apps Isourcing Process FlowDocument4 pagesOracle Apps Isourcing Process FlowRamesh GarikapatiNo ratings yet
- Body Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: DigestiveDocument3 pagesBody Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: DigestiveMicaela DNo ratings yet
- Anaphy TransesDocument21 pagesAnaphy Transesfaith A.No ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument86 pagesHuman Resource ManagementK V S PRASD REDDYNo ratings yet
- 2 - The Introduction of PHYSIOLOGY - 2Document19 pages2 - The Introduction of PHYSIOLOGY - 2Ramadan PhysiologyNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 10 Revision Material Term 2 - 2023Document28 pagesLife Sciences Grade 10 Revision Material Term 2 - 2023Linati Dawedi100% (1)
- MODULE 1 & 2 - General Biology 2Document12 pagesMODULE 1 & 2 - General Biology 2John Michael LopezNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 - Module 7 - Earth and Life ScienceDocument8 pagesQuarter 2 - Module 7 - Earth and Life ScienceKristine Alcordo100% (1)
- Revision Pack Biology Grade 10Document62 pagesRevision Pack Biology Grade 10Dana PorterNo ratings yet
- Modules in Earth ScienceDocument22 pagesModules in Earth ScienceAlpha100% (1)
- Deed of Sale SampleDocument3 pagesDeed of Sale Samplebarbiegirl9497No ratings yet
- Organ Systems of The Human Body and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesOrgan Systems of The Human Body and Their FunctionsAsmairaNo ratings yet
- Handout # 6 Cells, Tissues, OrgansDocument5 pagesHandout # 6 Cells, Tissues, OrgansRam AugustNo ratings yet
- Differentiation: Similar in Structure Different Tissues Different Organs Different SystemsDocument13 pagesDifferentiation: Similar in Structure Different Tissues Different Organs Different SystemsShivani HiteshNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument11 pagesBIOLOGYElla May TimoteoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 AnatomyDocument3 pagesChapter 1 AnatomyinitaygracileshayneNo ratings yet
- Mod 5 Organ Systems and Animal SurvivalDocument8 pagesMod 5 Organ Systems and Animal SurvivalrasingtanyaroseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Anatomy and Physiologyfaith A.No ratings yet
- Pengantar Anatomi: Oleh DR - Edward Kosasih, MARS, PA, DKDocument41 pagesPengantar Anatomi: Oleh DR - Edward Kosasih, MARS, PA, DKSukhrian MuhdaNo ratings yet
- Living Processes of Multicellular OrganismsDocument5 pagesLiving Processes of Multicellular Organismsboloqpiau boloqbokNo ratings yet
- Anatomy AssessmentDocument7 pagesAnatomy AssessmentTrevannie EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Ch1 To Ch6Document30 pagesReviewer - Ch1 To Ch6cpagente01No ratings yet
- Physiology and Pathophysiology IntroductionDocument39 pagesPhysiology and Pathophysiology Introductionbasmala.a.zahranNo ratings yet
- S1 Human Organism Part1Document4 pagesS1 Human Organism Part1cam broquelNo ratings yet
- Elsci LT 2.2: Chapter 8: Animals' Need To SurviveDocument4 pagesElsci LT 2.2: Chapter 8: Animals' Need To SurvivelemonNo ratings yet
- Body SystemsDocument3 pagesBody SystemsA R F I J U LNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Animal's Specialized StructuresDocument58 pages1.1 Animal's Specialized StructuresNathaliabee100% (1)
- Marieb - CH - 01 - Lecture - Doc (Edited)Document3 pagesMarieb - CH - 01 - Lecture - Doc (Edited)Dustin RamosNo ratings yet
- The Human Body OrientationDocument6 pagesThe Human Body OrientationHenry BuñagNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheets Animal Cell TypesDocument4 pagesFact Sheets Animal Cell Typessamsung picturesNo ratings yet
- Funda ReviewerDocument15 pagesFunda ReviewerKate LagundiNo ratings yet
- Pedrano Page 8Document2 pagesPedrano Page 8ian laurence pedranoNo ratings yet
- Human Being Are Complex Multicellular OrganismsDocument9 pagesHuman Being Are Complex Multicellular OrganismsWilliam WongNo ratings yet
- Ass Midterm PDFDocument2 pagesAss Midterm PDFSyra May PadlanNo ratings yet
- HES 006 Lec Session #1 - SASDocument5 pagesHES 006 Lec Session #1 - SASTam BeloNo ratings yet
- Pengantar Fisiologi: Dr. Eka Bebasari, M.SC Bagian Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas RiauDocument41 pagesPengantar Fisiologi: Dr. Eka Bebasari, M.SC Bagian Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas RiauNurul Ulya RahimNo ratings yet
- Pedrano Page 8 BioDocument2 pagesPedrano Page 8 Bioian laurence pedranoNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Organs Systems P1Document8 pagesPlant and Animal Organs Systems P1ian laurence pedranoNo ratings yet
- NOTES ReportingsDocument16 pagesNOTES Reportings2240739No ratings yet
- Bioscience 1 NotesDocument21 pagesBioscience 1 NotesLulu0% (1)
- Sas 3Document1 pageSas 3zimoneNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyCHESKA LYKA ASILONo ratings yet
- Trabajo de InglesDocument3 pagesTrabajo de InglesMilagros GarciaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organisation NotesDocument15 pagesCell Organisation Notessylent gohNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue: Absorption, Transport, Excretion, Protection, SecretionDocument7 pagesEpithelial Tissue: Absorption, Transport, Excretion, Protection, SecretionKenneth Rodriguez HerminadoNo ratings yet
- Dimaculangan, Yumie F. M4Document4 pagesDimaculangan, Yumie F. M4yumie dimaculanganNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument19 pagesAnaphy ReviewerGian Paolo P. CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- System Structure Purpose Interaction With Other SystemDocument1 pageSystem Structure Purpose Interaction With Other SystemLianne LagromaNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm - Divides The Thoracic From TheDocument7 pagesDiaphragm - Divides The Thoracic From TheRizzalyn OrtizNo ratings yet
- Anaphy PrelimsDocument4 pagesAnaphy PrelimsKim Erida QuezonNo ratings yet
- Cell Types NotesDocument4 pagesCell Types NotesMischi Jeda ElumbaNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Cell Organisation 20.1.2016Document19 pages2.2 Cell Organisation 20.1.2016sylent gohNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Importance of Studying Anatomy and Physiology. Relate It With Your Daily ActivitiesDocument6 pagesDiscuss The Importance of Studying Anatomy and Physiology. Relate It With Your Daily ActivitiesJamaica SimanganNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument2 pagesBiologyslayer.anonymous14No ratings yet
- Orientatioin of The Human BodyDocument57 pagesOrientatioin of The Human BodyJackson JastariNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument2 pagesAnaphynaomimarielleNo ratings yet
- 11 Human Body SystemDocument3 pages11 Human Body SystemCris EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Body System Interactions: Criterion DDocument4 pagesBody System Interactions: Criterion DReem AlmeheiriNo ratings yet
- Overview (Advance)Document8 pagesOverview (Advance)GuenNo ratings yet
- Chapters 1 and 2Document20 pagesChapters 1 and 2GuenNo ratings yet
- Janoras, DM (Tissue Mind Map)Document1 pageJanoras, DM (Tissue Mind Map)maxine janorasNo ratings yet
- Janoras, DM (Tissue Mind Map)Document1 pageJanoras, DM (Tissue Mind Map)maxine janorasNo ratings yet
- Body Tissues: Connective Tissue Ephithelial TissueDocument1 pageBody Tissues: Connective Tissue Ephithelial Tissuemaxine janorasNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism Mind MapDocument1 pageElectromagnetism Mind Mapmaxine janorasNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: Upgrade Now InviteDocument1 pageSkeletal System: Upgrade Now Invitemaxine janorasNo ratings yet
- Lighting Control: Dimmerpacks ProdigiDocument1 pageLighting Control: Dimmerpacks Prodigiwcma570% (1)
- BED SyallabusDocument32 pagesBED Syallabushp4cool9660No ratings yet
- Islamic Private Debt Securities (Ipds)Document37 pagesIslamic Private Debt Securities (Ipds)Sara IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Manual Expert 7.1 - OXODocument1,324 pagesManual Expert 7.1 - OXOEduardo SilvaNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual For Medical Imaging Signals and Systems 2e by Prince 0132145189Document38 pagesSolutions Manual For Medical Imaging Signals and Systems 2e by Prince 0132145189courbheadpan22xt100% (16)
- Mvo 1965Document113 pagesMvo 1965younisNo ratings yet
- Silentknight FACP Farenhyt IFP-1000 PDFDocument220 pagesSilentknight FACP Farenhyt IFP-1000 PDFwendy vegaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 - LESSON 1 - Overview To Qualitative ResearchDocument31 pagesUNIT 2 - LESSON 1 - Overview To Qualitative ResearchmikkaellaNo ratings yet
- The Revenge of The SerpentDocument2 pagesThe Revenge of The SerpentMiyamoto MusashiNo ratings yet
- Biosash Order Form Latest - 2019-9281576348996003Document3 pagesBiosash Order Form Latest - 2019-9281576348996003Amer Suhail ShareefNo ratings yet
- Physics1ist Year Practical FilDocument27 pagesPhysics1ist Year Practical FilManish GoyalNo ratings yet
- English Compulsory (1) PrintDocument15 pagesEnglish Compulsory (1) PrintZakir KhanNo ratings yet
- The Igloo PartyDocument11 pagesThe Igloo PartyRaghav MalhotraNo ratings yet
- TOS BiologyDocument2 pagesTOS BiologyBea Noreen Ungab100% (3)
- Index of Appendices: Pmo - ConfidentialDocument149 pagesIndex of Appendices: Pmo - Confidentialonize mosesNo ratings yet
- 2019 Pathogenesis, Screening, and Diagnosis of Neonatal Hypoglycemia - UpToDateDocument14 pages2019 Pathogenesis, Screening, and Diagnosis of Neonatal Hypoglycemia - UpToDateSheyla Paola Alegre ParionaNo ratings yet
- SD 1.1.3 Design CriteriaDocument10 pagesSD 1.1.3 Design Criterianapoleonpt2No ratings yet
- Customized ListDocument6,024 pagesCustomized ListItiNo ratings yet
- AS 3 Mid-Year TestDocument2 pagesAS 3 Mid-Year TestМар'яна НагорнюкNo ratings yet
- Teaching & Learning Activities: Biology (Sb015) - PelajarDocument2 pagesTeaching & Learning Activities: Biology (Sb015) - PelajarLeevandraaNo ratings yet
- Led ZepDocument82 pagesLed Zeprfahad22926No ratings yet
- IndraneelRakshit ResumeDocument7 pagesIndraneelRakshit ResumeIndraneel RakshitNo ratings yet
- Oslo Mihai Neacsu, IcpeDocument12 pagesOslo Mihai Neacsu, IcpeMihaiNeacsuNo ratings yet
- Dzone Refcard 292 Advanced Kubernetes 2020 PDFDocument9 pagesDzone Refcard 292 Advanced Kubernetes 2020 PDFLeonardo Moreno ForeroNo ratings yet
- Entry Req EngDocument4 pagesEntry Req EngMatheus StefaniNo ratings yet
- CV Achmad AgusDocument11 pagesCV Achmad AgusWoori ConsultingNo ratings yet