Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Body Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: Digestive
Uploaded by
Dave Chadha100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
71 views4 pagesBody systems
Original Title
Body_Systems_Chart_Key
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBody systems
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
71 views4 pagesBody Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: Digestive
Uploaded by
Dave ChadhaBody systems
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Body Systems Chart
System Illustration Structures Function
Mouth: Beginning of digestion Breaks down ingested foods to tiny
Esophagus, stomach, small and large particles, which can be absorbed into
Digestive intestine and accessory structures the blood for delivery to the body’s
(teeth salivary glands, liver, cells.
gallbladder and pancreas) Undigested residue leaves the body as
feces
Heart, blood vessels, blood Primary transport system that carries
blood containing oxygen, carbon
dioxide, nutrients, wastes, ions,
Circulatory hormones and other substances to and
Or cardiovascular from the cells where exchanges are
made; pumping action of the heart
propels blood through the blood
vessels.
Protect body with blood clots,
antibodies and other protein molecules
Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, Keeps the blood continuously supplied
bronchi, and lungs. with oxygen while removing carbon
Respiratory dioxide.
Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and Rids the body of nitrogen-containing
urethra wastes (urea, uric acid, and ammonia)
Excretory which results from the breakdown of
proteins and nucleic acids by the
body’s cells
Maintains water, electrolyte and acid
base balance of blood
Lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, Picks up fluid leaded from the blood
spleen, thymus and tonsils vessels and returns it to the blood.
Immune/lymphatic Cleanses blood of pathogens and other
debris
House cells (lymphocytes and others)
that ace in the immune response to
protect the body from foreign
substances (antigens)
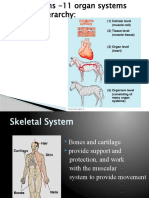
Bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, Supports and protects internal organs
and joints Provides levers for muscular action
Skeletal Stores minerals (calcium and others)
Cavities provide a site for blood cell
formations.
Muscles including voluntary and Skeletal muscles contract and shorten; in
involuntary doing so they move bones to allow
motion (running, walking etc) grasping
Muscular and manipulation of the environment and
facial expressions
Also generates heat
Brain, spinal cord, nerves and Allows body to detect changes in its
special sense organs internal and external environment and to
Nervous respond to such information by
activating appropriate muscles or glands
Helps maintain short term homeostasis of
the body via rapid transmission of
electrical signals.
Includes skin (largest organ of the Protects deeper organs from injury due to
body), hair, and fingernails, cutaneous bumps, chemical, bacteria and
organs and glands (ie sweat glands) dehydrations
Integumentary Excretes salts and urea
Helps regulate body temperature
Pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal Promotes growth and development;
and pineal glands; ovaries, testes and produces chemical messengers
Endocrine pancreas (hormones) that travel in the blood to
exert their effects on various ‘target
organs’ of the body
Plays a role in regulation of long term
homeostasis.
Female: ovaries, uterus, vagina, uterine Produces germ cells (egg); the female uterus
tubes houses a developing fetus until birth.
Reproductive
Male: testis, penis, scrotum, duct system Produces germ cells (sperm) for the
which carries sperm to the body exterior. perpetuation of the species.
You might also like
- Body Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: DigestiveDocument3 pagesBody Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: DigestiveMicaela DNo ratings yet
- Life Science ReferenceDocument2 pagesLife Science Referenceapi-291011460No ratings yet
- CirculatorySystem GizmoDocument4 pagesCirculatorySystem GizmoNashly Ramirez50% (2)
- Figures of SpeechDocument3 pagesFigures of SpeechApril J. RiveraNo ratings yet
- Body SystemsDocument116 pagesBody SystemskarunaNo ratings yet
- Brain's command center & its parts (ELACC5RI1,3,7,8Document2 pagesBrain's command center & its parts (ELACC5RI1,3,7,8Adam Yates100% (1)
- Defiency Chart and SurveyDocument2 pagesDefiency Chart and Surveyapi-232967376No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ReadingDocument32 pagesChapter 2 ReadingMarin Thompson100% (1)
- Bio12 Cheat Sheet RubricDocument2 pagesBio12 Cheat Sheet Rubricapi-310678040No ratings yet
- Body Systems Practice TestDocument5 pagesBody Systems Practice TestTINAIDANo ratings yet
- Organizations of the Human BodyDocument9 pagesOrganizations of the Human BodyWilliam WongNo ratings yet
- Funda ReviewerDocument15 pagesFunda ReviewerKate LagundiNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument11 pagesBIOLOGYElla May TimoteoNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Importance of Studying Anatomy and Physiology. Relate It With Your Daily ActivitiesDocument6 pagesDiscuss The Importance of Studying Anatomy and Physiology. Relate It With Your Daily ActivitiesJamaica SimanganNo ratings yet
- NOTES ReportingsDocument16 pagesNOTES Reportings2240739No ratings yet
- Differentiation: Similar in Structure Different Tissues Different Organs Different SystemsDocument13 pagesDifferentiation: Similar in Structure Different Tissues Different Organs Different SystemsShivani HiteshNo ratings yet
- Anatomy AssessmentDocument7 pagesAnatomy AssessmentTrevannie EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Integrated Function Organ - Kel 2Document20 pagesIntegrated Function Organ - Kel 2Rashif AnbiaNo ratings yet
- SYSTEM STRUCTURES AND INTERACTIONSDocument1 pageSYSTEM STRUCTURES AND INTERACTIONSLianne LagromaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Topic 1Document3 pagesAssignment Topic 1Charlyn CasabalNo ratings yet
- Physiology 1 IntroductionDocument101 pagesPhysiology 1 IntroductionBrian KipchumbaNo ratings yet
- Human BodyDocument3 pagesHuman Bodyjavier andres martinez100% (1)
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument19 pagesAnaphy ReviewerGian Paolo P. CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- Physiology and Pathophysiology IntroductionDocument39 pagesPhysiology and Pathophysiology Introductionbasmala.a.zahranNo ratings yet
- The 8 Major Organ Systems of the Human BodyDocument3 pagesThe 8 Major Organ Systems of the Human BodyAsmairaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 - Module 7 - Earth and Life ScienceDocument8 pagesQuarter 2 - Module 7 - Earth and Life ScienceKristine Alcordo100% (1)
- System of The BodyDocument2 pagesSystem of The BodyshenngggNo ratings yet
- Sci-2-Lif Parent-Guide-For-Body-SystemsDocument1 pageSci-2-Lif Parent-Guide-For-Body-Systemsapi-444425512No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology NotesDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology NotesHimiko JacksonNo ratings yet
- Handout # 6 Cells, Tissues, OrgansDocument5 pagesHandout # 6 Cells, Tissues, OrgansRam AugustNo ratings yet
- CelllllDocument9 pagesCelllllbasman1212No ratings yet
- Mod 5 Organ Systems and Animal SurvivalDocument8 pagesMod 5 Organ Systems and Animal SurvivalrasingtanyaroseNo ratings yet
- Bioscience 1 NotesDocument21 pagesBioscience 1 NotesLulu0% (1)
- Chapter 1 AnatomyDocument3 pagesChapter 1 AnatomyinitaygracileshayneNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 & 2 - General Biology 2Document12 pagesMODULE 1 & 2 - General Biology 2John Michael LopezNo ratings yet
- Body Systems, Functions, and OrgansDocument2 pagesBody Systems, Functions, and Organssandhiya padmanabanNo ratings yet
- Pengantar Anatomi: Oleh DR - Edward Kosasih, MARS, PA, DKDocument41 pagesPengantar Anatomi: Oleh DR - Edward Kosasih, MARS, PA, DKSukhrian MuhdaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Organ Systems OverviewDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Organ Systems OverviewBea PrestoNo ratings yet
- PreAP Biology CBA Review KEYDocument5 pagesPreAP Biology CBA Review KEYTom PunnenNo ratings yet
- Intro To Anaphy - ReviewerDocument5 pagesIntro To Anaphy - ReviewerEva Marie GaaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 1Document28 pagesOverview of Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 1Vincent Dajao CimafrancaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ANPH 1001 Anatomy PhysiologyDocument4 pagesChapter 1 ANPH 1001 Anatomy PhysiologyKaraNo ratings yet
- Chap-1-2 2Document20 pagesChap-1-2 2Salmone, Jhon DevonVILLARNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Notes - Lecture 1Document4 pagesAnatomy Notes - Lecture 1ellieNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy (An Orientation) : Dr. Tanveer Ahmed KhanDocument67 pagesHuman Anatomy (An Orientation) : Dr. Tanveer Ahmed KhanShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument2 pagesAnaphynaomimarielleNo ratings yet
- Bio StudyDocument12 pagesBio StudyAs If YoU dOnT kNoW tHe NaMeNo ratings yet
- The Human Body OrientationDocument6 pagesThe Human Body OrientationHenry BuñagNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheets Animal Cell TypesDocument4 pagesFact Sheets Animal Cell Typessamsung picturesNo ratings yet
- Human Biology IntroductionDocument22 pagesHuman Biology IntroductionAli HarthNo ratings yet
- Anaphy TransesDocument21 pagesAnaphy Transesfaith A.No ratings yet
- Human Organ SystemDocument5 pagesHuman Organ SystemChino Paolo ChuaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology (Transes)Document9 pagesIntroduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology (Transes)Kathleen BalauagNo ratings yet
- Anatomy-An-Overview (JTO)Document79 pagesAnatomy-An-Overview (JTO)Zild DarkNo ratings yet
- Module 27 - EditedDocument15 pagesModule 27 - Editedrichard reyesNo ratings yet
- 12 Body SystemsDocument2 pages12 Body Systemsasif khanNo ratings yet
- Report in Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesReport in Anatomy and Physiologydowngrade840No ratings yet
- Marieb_ch_01_lecture_doc (edited)Document3 pagesMarieb_ch_01_lecture_doc (edited)Dustin RamosNo ratings yet
- Cells Form Tissues and Organs That Work Together in Organ SystemsDocument17 pagesCells Form Tissues and Organs That Work Together in Organ SystemsHj LifeNo ratings yet
- Lecture (Unit-I)Document59 pagesLecture (Unit-I)Misbah Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemLyka100% (1)
- Call of Cthulhu - 1990 - Delta Green - Handout - Deep One AutopsyDocument2 pagesCall of Cthulhu - 1990 - Delta Green - Handout - Deep One AutopsyFeartherNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: Section A: Roll No. INBO - 2012Document10 pagesAnswer Key: Section A: Roll No. INBO - 2012martynapetNo ratings yet
- HydraDocument5 pagesHydraBio SciencesNo ratings yet
- The Cooperative Pulling Paradigm Is AnDocument1 pageThe Cooperative Pulling Paradigm Is Anpauline gNo ratings yet
- Nervous TissueDocument7 pagesNervous TissueDavid CalaloNo ratings yet
- BibliographyDocument332 pagesBibliographyWali MahanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy terminology guideDocument16 pagesAnatomy terminology guideRika CupuNo ratings yet
- 3a - Module 3 Biodiversity Animalia Part 3b 2020Document66 pages3a - Module 3 Biodiversity Animalia Part 3b 2020Hailey McLeanNo ratings yet
- Dissection of The Amphibian Respiratory System and Mammalian Excretory SystemDocument6 pagesDissection of The Amphibian Respiratory System and Mammalian Excretory System门门No ratings yet
- Blood Groups PPT by TKR&SRDocument24 pagesBlood Groups PPT by TKR&SRseshagiriNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Classfication TableDocument1 pageAnimal Kingdom Classfication TableVishal KumarNo ratings yet
- Las Science 5 Melc 1 q2 Week1Document10 pagesLas Science 5 Melc 1 q2 Week1Marjun BartoloNo ratings yet
- Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection Part 2Document3 pagesTheory of Evolution by Natural Selection Part 2tileshadowNo ratings yet
- Fish Skeleto1Document5 pagesFish Skeleto1Ej RafaelNo ratings yet
- Cot 4Document7 pagesCot 4Jerwin Sarcia RemocalNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction For Grade 11 Worksheet 2Document8 pagesPlant Reproduction For Grade 11 Worksheet 2KISHANo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science VDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science VEric Glenn CalingaNo ratings yet
- Script Adaptive ImmunityDocument4 pagesScript Adaptive ImmunityNur KhalifahNo ratings yet
- HistologyLabManual PDFDocument110 pagesHistologyLabManual PDFIvan Rodas HuertaNo ratings yet
- Embryo Development SEDocument7 pagesEmbryo Development SEWWE FightsNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Assignment: Cnidaria and Porifera BIOL 2P92 - 09 Romil Patel (5844196) TA: Fiona Tuesday, January 24, 2017Document8 pagesLab 2 Assignment: Cnidaria and Porifera BIOL 2P92 - 09 Romil Patel (5844196) TA: Fiona Tuesday, January 24, 2017RomilPatelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy NotebookDocument39 pagesAnatomy Notebookrhowme100% (1)
- Major Body OrgansDocument28 pagesMajor Body Organsesang quettNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet No.1 VertebratesDocument4 pagesActivity Sheet No.1 VertebratesRaniey MayolNo ratings yet
- Learning Target: Module Code: Pasay-S9Lt-Q1-W1-D1Document5 pagesLearning Target: Module Code: Pasay-S9Lt-Q1-W1-D1Lady MaeNo ratings yet
- Animal AdaptationsDocument20 pagesAnimal AdaptationsDanayra PazNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Grade 10-11Document7 pagesDigestive System Grade 10-11Nandana Nayana KumaraNo ratings yet
- Cardiac MuscleDocument39 pagesCardiac MuscleAndhini Virgiannisa100% (2)
- Anaphy Reviewer For MidtermsDocument3 pagesAnaphy Reviewer For MidtermsChristianJoshuaOseaElpedesNo ratings yet