Professional Documents
Culture Documents
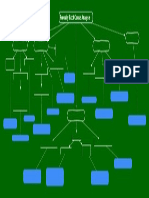
Chapter 2 - Material Behaviour
Uploaded by
Muhamad YusupCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2 - Material Behaviour
Uploaded by
Muhamad YusupCopyright:
Available Formats
Pearlite + Proeutectoid Phase Slow Cool
Material Thickness Reduced
Strain Hardening %CW = ((Ao-Ad)/Ao)*100
Bainite Medium Cool Austenite Phase Strengthening
Tempered Martensite if REHEAT Martensite Fast Cool
Grain Boundary Strengthening
Sy=So + kd^(-1/2) The finer of grain the higher the strength will be
(Hall Patch Equation)
Plain Carbon
Composite Strengthening Low-Carbon
Material Strengthening
HSLA
Intersitial
Increase Strength by induced stress
Solid Solution Strengthening Plain
from inside material
To rise the Tnr ( Minimun Temperature to recyrstalize) Subtitional Low Alloy Med-Carbon
Steel added Niobium
and decrease the Ar3(Austenite temp transformation)
Heat Treatable
Slab Reheating Temperature TMCP
Plain Weldability depend on CE
Precipitation Strengthening (Graville Diagram)
High-Carbon
Interpass Holding Temperature Process
Tool
Final Phase Matrix Transformation
Tool Steel
Austenite Carbon, Nickle, Mangan Steel Sensitization(weld decay) Addition of Ti,Nb,Ta
due heating to long in 850-500o C to reduce sensitization
Manganese SS 200 Series
Al,Ti,V,Cr,Mo,Ni Nitride Forming Element
Austenitic SS
Nickel SS 300 Series
Forming Elements Ferrite Cr,Si,Mo,W,Al Pre Heat
Ferrite SS 430 Series
Carbide, Nitride Grain Refiner
Stainless Steel
High Alloy Martensitic SS 410 Series
Commercial pure & low alloy Titanium alloys Carbide Forming Element Cr,Mo,W,V,Ta,Ti,Nb,Zr
Duplex SS 2xxx Series
contain up to 7% alumunium Titanium alpha and near alpha alloys Ferrous
Titanium is versy sensitive when welded Titanium PH SS 630 Series / 17-4 PH
must use 99,9999% Ar (ultra pure gas) contain 6% Al and beta forming
Titanium alpha-beta alloys
such as V,Cr,Mo,W,Ta,Si
High Manganese Steel Hadfield
Contain beta forming
Titanium beta alloys Maraging Steel Martensite Transformation without carbon
such as V,Cr,Mo,W,Ta,Si
Weld in Titanium Factor to be consider Gray Iron
Commercial Ductile Iron Add Mg 0,04-0,08% as grain modifier
Cast Iron
Brasses (Cu+Zn) White Iron Malleable Iron
Weld Metal Porostiy Embrittlement Contamination Cracking Main Problem Copper
Bronzes (Cu+Sn)
Chapter 2 - Metallurgy Behaviour Compacted Graphite Iron
Silicon act as Graphite Stabilizer
Cr, Mn act as Carbide Stabilizer
Other
Material surface must be cleaned no moisture, Iron causing cracking due brittleness
Low Heat Input
Zn will vapor lead to metal porosity
Titanium is material that easy to react, Oxygen,Nitrogen,Hydrogen affinity will affect High Expansion lead to High Distortion
the titanium colour Melting Point = 660o C
such small impurty will affect embrittlement Pre Heat
1/3 Density of Steel
Characteristic Prevent Crack in Weld
Low Expansion Alloys 5x thermal conductivity of steel
Slow Cooling
contain 99% Nickel Commercial
Electrical Resistance Alloy Alumunium
2,4x thermal expansion of steel
Wrought
Market name "Monel" Contain 29-33% Cu Ni-Cu Alloy
Soft Magnetic Alloys Type of Process Classified
Classification Nickel Cast Use Ni-Cu Electrode
Inconel, Incoloy, Hastelloy 15-22% Cr & 50% Fe Non HT Ni-Cr-Fe due to no sensitif
NITINOL Shape Memory Alloys
Strain Hardening of carbon pickup
15-22% Cr & 33% Fe
Heat Resistant Strengthening Method Alloying
Nimonic,Udimet,Waspalloy,Rene 41,Astroloy, Inconel X-750 HT Ni-Cr-Fe
Temper Designation
Addition of Al,Si,Be,Ti for HT Precipitation
Corrosion Resistant Precipitation Hardening
Weld Problem
Floating node
Porosity Oxide Inclusion PWHT Crack
Air Entrapment Lack of Fusion due to Strain-Age Cracking
Metal Inclusion
You might also like
- Day ShiftDocument1 pageDay ShiftKanupriya JainNo ratings yet
- Quotation Expandable Seal ProtoDocument8 pagesQuotation Expandable Seal ProtoRohitNo ratings yet
- 4 CA4250P25K15T1NE5A80 DZ722R 哥伦比亚 维修手册 电气线路图 英文Document1 page4 CA4250P25K15T1NE5A80 DZ722R 哥伦比亚 维修手册 电气线路图 英文Jorge Elieser Sánchez RiosNo ratings yet
- F3-500-CI-PLN-PPL-0001 - AD Overall Plot PlanDocument1 pageF3-500-CI-PLN-PPL-0001 - AD Overall Plot PlanErim EsenNo ratings yet
- HV-205 (Third Floor HVAC Layout) - ModelDocument1 pageHV-205 (Third Floor HVAC Layout) - ModelMohamed AliNo ratings yet
- Christmas Medley BBC Full ScoreDocument14 pagesChristmas Medley BBC Full ScoreSpyros SpyropoulosNo ratings yet
- Internet: F.O - 50 Microns F.O - 50 MicronsDocument3 pagesInternet: F.O - 50 Microns F.O - 50 MicronsJavier CareagaNo ratings yet
- Detail Layout Plan of Proposed Fuel Filling Station at Lhs of NH 146 at Vidisha Sagar Road On Undivided Carriage Way (SCALE1 IN 500)Document1 pageDetail Layout Plan of Proposed Fuel Filling Station at Lhs of NH 146 at Vidisha Sagar Road On Undivided Carriage Way (SCALE1 IN 500)abhijeet sahu0% (1)
- PDF026Document1 pagePDF026HRS REGIONAL LAB TANJAVURNo ratings yet
- Asct Borehole Geophysics Tool Summary TableDocument1 pageAsct Borehole Geophysics Tool Summary TableAugusto PetryNo ratings yet
- Friction Loss Chart - MDPEDocument2 pagesFriction Loss Chart - MDPEManoj NairNo ratings yet
- Monthly Scrap - 11 NovemberDocument2 pagesMonthly Scrap - 11 NovemberAmirHakimRusliNo ratings yet
- Fire and Ice (Lied Phase 2) : Some Say The World Will in End Fi Re Some Say N IDocument2 pagesFire and Ice (Lied Phase 2) : Some Say The World Will in End Fi Re Some Say N IKalpattyNo ratings yet
- SLD Jaringan ULP PariamanDocument2 pagesSLD Jaringan ULP PariamanaryoNo ratings yet
- Tidal Wave: Brian Mudget Alan KeownDocument10 pagesTidal Wave: Brian Mudget Alan KeownAdib CarolineNo ratings yet
- Benedetto17 2Document1 pageBenedetto17 2Thierry QuesimuNo ratings yet
- Benja PlanDocument1 pageBenja Planmasumba patrickNo ratings yet
- Peta BTP Jatim 2021Document1 pagePeta BTP Jatim 2021denta masatoNo ratings yet
- Detail Engineering Design: PertamedikaDocument1 pageDetail Engineering Design: PertamedikaAa NaldiNo ratings yet
- Las Mañanitas Arreglo Kompleto - DireccionDocument2 pagesLas Mañanitas Arreglo Kompleto - DireccionAlexicoHumanMosqueraNo ratings yet
- Lot 129 To Lot 132Document4 pagesLot 129 To Lot 132kewcottagesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Plan of St-01: Esteban Y. Tan & AssociatesDocument1 pageDetailed Plan of St-01: Esteban Y. Tan & AssociatesRnln Sagales AmataNo ratings yet
- Monthly Scrap - 09 SeptemberDocument2 pagesMonthly Scrap - 09 SeptemberAmirHakimRusliNo ratings yet
- NewDocument1 pageNewi putu riki darmawanNo ratings yet
- AUditorium Deatils - SH4Document1 pageAUditorium Deatils - SH4PRATIMA MAHADIK50% (2)
- PR - D02111 Vie PC01 STN DWG KC FRP 02111Document1 pagePR - D02111 Vie PC01 STN DWG KC FRP 02111Ashish BhartiNo ratings yet
- Crt-Npc-Dmm-Hva-Dwg-Sd-Gn-33501 - Equipment Capacity Schedule 1-6Document1 pageCrt-Npc-Dmm-Hva-Dwg-Sd-Gn-33501 - Equipment Capacity Schedule 1-6Shah MuzzamilNo ratings yet
- Esr 18 Mahulpali 520kl 23m - RCDocument4 pagesEsr 18 Mahulpali 520kl 23m - RCGopal SinghNo ratings yet
- Part To Scrap Before Plate For Month: October Date: 1 - 15 OctoberDocument2 pagesPart To Scrap Before Plate For Month: October Date: 1 - 15 OctoberAmirHakimRusliNo ratings yet
- FF Service Si-006 Vs Si-029-R1Document12 pagesFF Service Si-006 Vs Si-029-R1Chilo InNo ratings yet
- Garbanzo Peak: Bike Park ZonesDocument2 pagesGarbanzo Peak: Bike Park ZonesNicky KiloNo ratings yet
- Letecká Mapa ČRDocument1 pageLetecká Mapa ČRSASAN MINETNo ratings yet
- GB-1 Beam Details: LevelDocument1 pageGB-1 Beam Details: Levelsoe.earlvincevalerosoNo ratings yet
- A4 - Elevations and SectionsDocument1 pageA4 - Elevations and SectionsArjelyNo ratings yet
- Exaudiat Te DominusDocument5 pagesExaudiat Te DominusCatalina ʚïɞNo ratings yet
- Hold Class 2: 102B22 - W16X57 - 21'-6 5/8" - ONE REQ'DDocument1 pageHold Class 2: 102B22 - W16X57 - 21'-6 5/8" - ONE REQ'Dai ambaraNo ratings yet
- 102B25 - W21X68 - 29'-10 3/8" - ONE REQ'D CAMBER 3/4": Bill of MaterialDocument1 page102B25 - W21X68 - 29'-10 3/8" - ONE REQ'D CAMBER 3/4": Bill of Materialai ambaraNo ratings yet
- DSA DSA DSA: Guardrail - Partial ElevationDocument1 pageDSA DSA DSA: Guardrail - Partial ElevationPerr CortezNo ratings yet
- Saxaphone Section 1-Partitura - y - PartesDocument24 pagesSaxaphone Section 1-Partitura - y - PartesjuliokNo ratings yet
- Grade Wave Tom JobimDocument8 pagesGrade Wave Tom JobimThiago CassimiroNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compatibility Chart SMD Fluid ControlsDocument7 pagesChemical Compatibility Chart SMD Fluid Controlsmayur mahajanNo ratings yet
- Tampak 2 Tampak 4: A B C D E F H G A B C D E F G HDocument1 pageTampak 2 Tampak 4: A B C D E F H G A B C D E F G HAa NaldiNo ratings yet
- Residential Landscape Design KarenDocument1 pageResidential Landscape Design KarenAmosOtienohNo ratings yet
- Karjan East RWSS - R1-ModelDocument1 pageKarjan East RWSS - R1-Modeldeekarjan11No ratings yet
- BB CC DD Ee FF GG HH: Scale 1: 25Document1 pageBB CC DD Ee FF GG HH: Scale 1: 25asdNo ratings yet
- Monthly Scrap - 08 AugustDocument2 pagesMonthly Scrap - 08 AugustAmirHakimRusliNo ratings yet
- Piping & Instrumentation DiagramDocument1 pagePiping & Instrumentation DiagramSearch45No ratings yet
- Granite Porte CochereDocument11 pagesGranite Porte Cocheretanszeying8899No ratings yet
- Pragati Maidan Layout MapDocument1 pagePragati Maidan Layout Mapviv0% (1)
- B737 800 DigitalDocument1 pageB737 800 DigitalmohammedredhadjoudiNo ratings yet
- البارت بلانDocument1 pageالبارت بلانmustafamoharamNo ratings yet
- Attachment 1 (RFI 271 Rev 00)Document1 pageAttachment 1 (RFI 271 Rev 00)Ramume188No ratings yet
- Lowrider 2010-07 PDFDocument119 pagesLowrider 2010-07 PDFjonathan chenNo ratings yet
- 4355-Aa-Dc-22i10pr0900i - Checkprint For SquadDocument1 page4355-Aa-Dc-22i10pr0900i - Checkprint For Squadamit bagchiNo ratings yet
- Level, M S.P.T, N Rock Cores Grain Size Analysis Atterberg Limits Shear ParameterDocument1 pageLevel, M S.P.T, N Rock Cores Grain Size Analysis Atterberg Limits Shear Parameternandu523No ratings yet
- Black Forest-总谱与分谱Document20 pagesBlack Forest-总谱与分谱林立No ratings yet
- Ramothibe T - Stage 4-Acuv300Document2 pagesRamothibe T - Stage 4-Acuv300Monde Tidimalo Lunathi MbaluNo ratings yet
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 1: MathFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 1: MathRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 2: MathFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 2: MathNo ratings yet
- Public Expose Material 2022Document14 pagesPublic Expose Material 2022Muhamad YusupNo ratings yet
- Public Expose Material 2021Document19 pagesPublic Expose Material 2021Muhamad YusupNo ratings yet
- Pubex 2023Document48 pagesPubex 2023Muhamad YusupNo ratings yet
- Pubex 2021Document34 pagesPubex 2021Muhamad YusupNo ratings yet
- Ar 2021 SimpDocument247 pagesAr 2021 SimpMuhamad YusupNo ratings yet
- Poros Root Cause AnalysisDocument1 pagePoros Root Cause AnalysisMuhamad YusupNo ratings yet
- Porosity Root Cause Analysis: Welding Operator Welding Machine Welding Environment Material QualityDocument1 pagePorosity Root Cause Analysis: Welding Operator Welding Machine Welding Environment Material QualityMuhamad YusupNo ratings yet