Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ce421 Laboratory Activity
Uploaded by
Akhemei MontealtoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ce421 Laboratory Activity
Uploaded by
Akhemei MontealtoCopyright:
Available Formats
MONTEALTO, SARAH Y. ENGR.
CIUDADANO
BSCE - 3B CE421
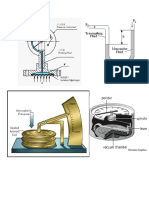
VARIOUS LABORATORY INSTRUMENTS OF PAGASA
MERCURIAL BAROMETER
Based on a principle developed by Evangelista Torricelli in 1643, the
Mercurial Barometer is an instrument used for measuring the change in
atmospheric pressure. It uses a long glass tube, open at one end and
closed at the other. Air pressure is measured by observing the height of
the column of mercury int the tube. At sea level, air pressure will push on
the mercury about 30 inches high. If you used water instead of mercury,
you would need a glass tube over 30 feet in length. As atmospheric
pressure increases, the mercury is forced from the reservoir by the
increasing air pressure and the column of mercury rises; when
atmospheric pressure decreases, the mercury flows back into the
reservoir and the column of mercury is lowered.
DIGITAL BAROMETER
A Digital Barometer measures air pressure. It is used to
predict future weather in a local region. A high pressure
reading indicates good weather and a low pressure reading
indicates bad weather. The digital barometer uses a detection
cell (i.e.a chip) to measure the air temperature. This chip will
be vital and is sensitive to atmospheric pressure which
influences its capacity to conduct/relay electricity.
BAROGRAPPH
A Barograph is a recording barometer. The pin point that
traces the pressure curve on the paper is made to move up or
down by means of a series of levers attached to aneroid cells
(metallic boxes) in tandem. The use of aneroid cells in
tandem provide a more pronounced response to changes in
atmospheric pressure than would be indicated by a single
aneroid cell of the same size.
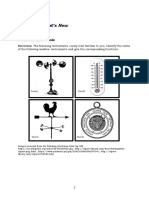
WIND VANE
A wind vane (also known as a
weathervane) is an instrument that tells
you the wind direction. Specifically, a
wind vane lets you know what direction
the wind is coming from. In other words, a
“southwest” reading on a wind vane
means that the wind is originating
southwest of your location, and heading in
a northeast direction.
LIGHTNING DETECTOR (connected to the wind vane)
The lightning detector system uses a radio that listens for
lightning at 500kHz, it listens for a particular radio signal
pattern. The lightning signal pattern is generated by the
electrical “spark”, that is the lightning itself. The lightning
detector system can be susceptible to detecting erroneous
lightning strikes. the system will not provide a perfect count
of actual lightning strikes with perfect distance estimates. In
most cases, the system will be rather accurate, but there will
always be a few discrepancies.
SUNSHINE RECORDER
A sunshine recorder is a meteorological instrument
used for recording the amount of sunlight that a
particular location receives throughout a day. Inside
the recorder’s adjustable frame are two important
pieces: a paper strip, and a glass sphere that can focus
the sunlight strongly enough to singe the paper. If the
sky is clear, the paper is slowly burned as the sun
moves across the sky. If there are clouds, the focused
light will not be strong enough to burn the paper.
THERMOMETER
A thermometer measures the degree of hotness or coldness of a given
substance. It operates on the principle of thermal expansion of the
material used, e.g., liquids like mercury and alcohol, metallic
materials, etc. Mercury is one of the liquids very sensitive to changes
of temperature. When the substance to be measured is warm,
mercury expands and rises in the capillary tube. When it cols,
mercury contracts.
MAXIMUM-MINIMUM THERMOMETER. In order to measure
the temperature range, a set of maximum and minimum
thermometers are used. A maximum thermometer has a constriction
above the bulb that permits the mercury to rise in the capillary tube
but does not allow it to descend the capillary tube unless the
thermometer is reset. The highest point that the mercury reaches
indicates the maximum temperature for the period. The minimum
thermometer, on the other hand gives the lowest temperature. It uses
colored alcohol (because of its low freezing point). it is placed at an
angle of about 20 degree from the horizontal. The black float called
index needle is pulled down-slope to the lowest temperature of the
day by two forces; (A) the surface tension at the top of the alcohol
column, and (B) the force of gravity.
DISDROMETER
A Disdrometer or so called distrometer/rain spectrometer is
a laser instrument that measures the drop size distribution
falling hydro-meteors. Based on t he principle of optical
laser active detection, the disdrometer can continuously
observe the raindrops definition size, velocity and quantity
of raindrops. It can deduce the drop size distributions,
precipitation, radar reflectivity, precipitation type, etc. It
can distinguish drizzle, rain, snow, hail snow, and mixed
precipitation. The instrument is sensitive and accurate, and
can be used in the field for a long time without
maintenance for several industries. Disdrometer can reflect
the micro-physical process of precipitation. Studying
raindrops spectra is helpful to understand the development
and evolution of precipitation and reveal the rain generator
in clouds.
RAIN GAUGE
A rain gauge is a meteorological instrument to measure
the precipitating rain in a given amount of time per unit
area. The instrument consists of a collection container
which is placed on an open. The precipitation is
measured in terms of the height of the precipitated water
accumulated in the container per given time and is
expressed in millimeters.
MANUAL RAIN GAUGES are a simple tube, closed
on one end and calibrated in inches to indicate the
amount of liquid. It must be hand-emptied after each
precipitation event in order to ensure the correct
measurements.
AUTOMATIC RAIN GAUGE SYSTEM is weather
instrument for measurements & monitoring rain rate and
total rainfall. It is constructed of high impact UV
protected plastic to provide reliable and low cost
solution.
DOCUMENTATIONS:
You might also like
- Weather PredictDocument15 pagesWeather PredictMike SyNo ratings yet
- Weather Instruments Temperature ThermometersDocument6 pagesWeather Instruments Temperature ThermometersCy Ber Allen CubonNo ratings yet
- Give Us The Different Types of Equipment, Stations or Satellites Used by PAGASA For Weather Determination and ForecastDocument5 pagesGive Us The Different Types of Equipment, Stations or Satellites Used by PAGASA For Weather Determination and ForecastArthNo ratings yet
- Measuring Weather: Instruments and FactorsDocument15 pagesMeasuring Weather: Instruments and FactorsAtul Beharwal100% (1)
- Weather InstrumentsDocument7 pagesWeather InstrumentsIza Jay Trapa DonatoNo ratings yet
- Mine Ventilation LabDocument6 pagesMine Ventilation Labzafar abbasNo ratings yet
- Geography DraftDocument11 pagesGeography Drafts.suchitra1026No ratings yet
- Safari - 10 Sep 2019 at 10:40 PMDocument1 pageSafari - 10 Sep 2019 at 10:40 PMAnn Catherine LalogNo ratings yet
- Study of Instruments Used To Measure Microclimatic VariablesDocument6 pagesStudy of Instruments Used To Measure Microclimatic VariablesH2oNo ratings yet
- Meteorological instruments guideDocument5 pagesMeteorological instruments guideArpit BarmanNo ratings yet
- 1 MET O - Shipborne Meteorological InstrumentsDocument10 pages1 MET O - Shipborne Meteorological Instrumentsjohann83% (6)
- Weather Instrument PDFDocument7 pagesWeather Instrument PDFjs cyberzoneNo ratings yet
- Measuring and Recording WeatherDocument8 pagesMeasuring and Recording WeatherzoeNo ratings yet
- Meteorological Instruments and Their UsesDocument22 pagesMeteorological Instruments and Their UsesYuvan83% (12)
- Solar Power Plant InstrumentsDocument6 pagesSolar Power Plant Instrumentstsrinivasan5083No ratings yet
- Barometer - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFDocument5 pagesBarometer - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFelvi anggiovennyNo ratings yet
- Bourdon GageDocument5 pagesBourdon GageTricia GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Meteorology GNU Free Documentation LicenseDocument18 pagesMeteorology GNU Free Documentation LicenseEdbert TulipasNo ratings yet
- Instruments Used To Measure PrecipitationDocument7 pagesInstruments Used To Measure PrecipitationMark Jed Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Shipborne Meteorology Instruments Barometer Reading GuideDocument39 pagesShipborne Meteorology Instruments Barometer Reading GuideKris Myka J. Eg-oganNo ratings yet
- Sectionc Climatology (A) Distinguish Between Weather and Climate (B) Explain How Any Two Elements of Weather Are Measured at A Weather StationDocument39 pagesSectionc Climatology (A) Distinguish Between Weather and Climate (B) Explain How Any Two Elements of Weather Are Measured at A Weather Stationkalule elvisNo ratings yet
- Typical InstrumentsDocument16 pagesTypical Instrumentsssuryaraj911No ratings yet
- Weather Station ExperimentDocument6 pagesWeather Station ExperimentSaadFarooqNo ratings yet
- Instrumentos de medición de temperatura, presión y volumenDocument12 pagesInstrumentos de medición de temperatura, presión y volumenMoisés Reyes SeguraNo ratings yet
- Lab Report # 2Document6 pagesLab Report # 2zainyousafzai100% (1)
- Weather Instruments, MapsDocument16 pagesWeather Instruments, MapsAshiya 21No ratings yet
- Barometer ExpositionDocument12 pagesBarometer ExpositionElda CalderónNo ratings yet
- Collecting Weather Data YEAR 10 GEODocument20 pagesCollecting Weather Data YEAR 10 GEOuffiageniusNo ratings yet
- Shipborne Meteorological InstrumentsDocument59 pagesShipborne Meteorological InstrumentsJayson CandelariaNo ratings yet
- Marine Meteorology CopyDocument120 pagesMarine Meteorology CopyprinceazulmensahNo ratings yet
- Geography ProjectDocument16 pagesGeography ProjectAbhyufay100% (1)
- Meteorology PPT InstrumentsDocument32 pagesMeteorology PPT InstrumentsSrujana Patel100% (2)
- Meteorology HandoutsDocument62 pagesMeteorology HandoutsCyrus Bumalo100% (2)
- Hydrometeorological InstrumentsDocument4 pagesHydrometeorological InstrumentsAnne WabanNo ratings yet
- Weather ObservationsDocument3 pagesWeather ObservationsIrakli ShavishviliNo ratings yet
- Hydrometeorological InstrumentsDocument7 pagesHydrometeorological InstrumentsVerra Myza Arat0% (1)
- Obinna Geo 5Document48 pagesObinna Geo 5Obinna RichardNo ratings yet
- Eseu Limba Engleză: Student:Spătaru George FlorentinDocument5 pagesEseu Limba Engleză: Student:Spătaru George FlorentinGeorge FlorentinNo ratings yet
- Pagasa Weather InsturmentsDocument28 pagesPagasa Weather InsturmentsWinard WantogNo ratings yet
- ThermometerDocument1 pageThermometerKareen JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Weather InstrumentsDocument4 pagesWeather InstrumentsLuisa Del Mundo100% (1)
- Pagasa Weather InstrumentsDocument28 pagesPagasa Weather InstrumentsMarcelito Morong92% (26)
- Weather InstumentsDocument23 pagesWeather InstumentsTakchandra JaikeshanNo ratings yet
- Mustansiriyah University College of Sciences Atmospheric Sciences Department Dr. Sama Khalid MohammedDocument32 pagesMustansiriyah University College of Sciences Atmospheric Sciences Department Dr. Sama Khalid MohammedJeon Jungkook 전정국No ratings yet
- Maps and ChartsDocument17 pagesMaps and Chartsdheerajkumar02527289No ratings yet
- ) Wikipe: Types of Anemometer - : 1 - Cup AnemometerDocument4 pages) Wikipe: Types of Anemometer - : 1 - Cup Anemometermahmoud osamaNo ratings yet
- DRRR g1 PDFDocument39 pagesDRRR g1 PDFxyreneNo ratings yet
- BarometerDocument5 pagesBarometerdexmaxie27100% (1)
- Hydrology Lecture 2Document36 pagesHydrology Lecture 2ben joshua mercadoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Hydrology Practical Sample For WritingDocument39 pagesEngineering Hydrology Practical Sample For WritingchannelmanagementseoNo ratings yet
- Weather InstrumentsDocument6 pagesWeather InstrumentskirkemmanNo ratings yet
- DRRR 4Document11 pagesDRRR 4Noli JacksonNo ratings yet
- E-Journal in MeteorologyDocument10 pagesE-Journal in MeteorologycuthNo ratings yet
- Gas NameDocument3 pagesGas NameImamul HaqueNo ratings yet
- MeteorologyDocument42 pagesMeteorologyJeselia Sunico ArsagaNo ratings yet
- Presentation of BarometerDocument16 pagesPresentation of BarometerNabeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- WX ObservationsDocument18 pagesWX ObservationsLouie VerginoNo ratings yet
- I (Unit-II)Document44 pagesI (Unit-II)TanmaySardanaNo ratings yet
- L L L L L L L L L L: Mastrace V1.0 OnlineDocument1 pageL L L L L L L L L L: Mastrace V1.0 OnlineAkhemei MontealtoNo ratings yet
- Gaussian Elimination Review Exercises and SolutionsDocument7 pagesGaussian Elimination Review Exercises and SolutionsAkhemei MontealtoNo ratings yet
- BES7ADocument10 pagesBES7AAkhemei MontealtoNo ratings yet
- BES11Document6 pagesBES11Akhemei MontealtoNo ratings yet
- Bes7a AssignmentDocument1 pageBes7a AssignmentAkhemei MontealtoNo ratings yet
- BES7ADocument1 pageBES7AAkhemei MontealtoNo ratings yet
- BES7ADocument1 pageBES7AAkhemei MontealtoNo ratings yet
- Bes7a Final Exam (Montealto, Sarah Y. - Bsce-3b)Document5 pagesBes7a Final Exam (Montealto, Sarah Y. - Bsce-3b)Akhemei MontealtoNo ratings yet
- Ce421 Final ExaminationDocument15 pagesCe421 Final ExaminationAkhemei MontealtoNo ratings yet
- Tennis Racket Acceleration and Momentum CalculationsDocument6 pagesTennis Racket Acceleration and Momentum Calculationsertugoz100% (2)
- Zinc Clad II (85) : Inorganic Zinc Rich CoatingDocument2 pagesZinc Clad II (85) : Inorganic Zinc Rich CoatingKatherine Marimón JiménezNo ratings yet
- Inovasi Kurikulum Berdasarkan Komponen Kurikulum Strategi Dan Evaluasi Oleh: Sri MaryatiDocument16 pagesInovasi Kurikulum Berdasarkan Komponen Kurikulum Strategi Dan Evaluasi Oleh: Sri MaryatiFitroh NailulNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment 2 - Article Review - Opm530Document2 pagesIndividual Assignment 2 - Article Review - Opm530Amir HafiyNo ratings yet
- Brian Leggett (Ed) 2006 Rhetorical-Approach-To-PersuasionDocument9 pagesBrian Leggett (Ed) 2006 Rhetorical-Approach-To-PersuasionM MoralesNo ratings yet
- Lenze 8400 Electrical Shaft Technology Application - v1-0 - ENDocument50 pagesLenze 8400 Electrical Shaft Technology Application - v1-0 - ENNilo AninonNo ratings yet
- Why paraphrasing avoids plagiarismDocument3 pagesWhy paraphrasing avoids plagiarismAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Nuig Lander1Document21 pagesNuig Lander1diana meriakri100% (1)
- Kami Export - Exam Booster FCE Speaking Part 3 and 4Document2 pagesKami Export - Exam Booster FCE Speaking Part 3 and 4Valen JacobNo ratings yet
- M5 - Freedom of The Human PersonDocument8 pagesM5 - Freedom of The Human PersonMarisol OtidaNo ratings yet
- AD IBS Assignment-1Document6 pagesAD IBS Assignment-1anvesha raoNo ratings yet
- School of Engineering Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument17 pagesSchool of Engineering Department of Mechanical EngineeringMohammed KawashNo ratings yet
- A Social Network Analysis of ICTD Conferences (2006-2017) : Information Technology For DevelopmentDocument24 pagesA Social Network Analysis of ICTD Conferences (2006-2017) : Information Technology For DevelopmentRjendra LamsalNo ratings yet
- Full Scale Tests of Heat Strengthened Glass With Ceramic FritDocument17 pagesFull Scale Tests of Heat Strengthened Glass With Ceramic FritKároly FurusNo ratings yet
- Cape Comm Studies Study NotesDocument28 pagesCape Comm Studies Study NotesLexi John100% (1)
- Process Costing: Cost Accounting Principles, 9eDocument17 pagesProcess Costing: Cost Accounting Principles, 9eoliver tzNo ratings yet
- Visual Division-1Document3 pagesVisual Division-1Jumran BaharNo ratings yet
- Probability Spinner WorksheetDocument2 pagesProbability Spinner WorksheetSara ShaiboonNo ratings yet
- Experiencias Cercanas A La Muerte PDFDocument18 pagesExperiencias Cercanas A La Muerte PDFGabriel MoraguesNo ratings yet
- Korea (2017) - Experimental Investigation On Massflow Characteristics of R245fa Through Electronic Expansion ValveDocument7 pagesKorea (2017) - Experimental Investigation On Massflow Characteristics of R245fa Through Electronic Expansion ValveMatias PezoNo ratings yet
- CASE-STUDY of NFPTs in Butuan CityDocument35 pagesCASE-STUDY of NFPTs in Butuan CityKizza Eyn MinguitaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Organs of Speech and Phonemic SymbolsDocument5 pagesLesson 1: Organs of Speech and Phonemic Symbolsnoah granja2No ratings yet
- MarketsandMarkets - Foresighting Research & Advisory CapabilitiesDocument44 pagesMarketsandMarkets - Foresighting Research & Advisory CapabilitiesKaranvir singhNo ratings yet
- DashaDocument2 pagesDashaSrini VasanNo ratings yet
- Watching TV ads or internet ads? Pros, cons and preferencesDocument5 pagesWatching TV ads or internet ads? Pros, cons and preferencesJiaqi LiNo ratings yet
- Armstrong ANFDocument2 pagesArmstrong ANFBramandito DamarNo ratings yet
- Ultra Low Dose CT Vs Chest X Ray in Non Traumatic Emergency D 2023 EClinicaDocument14 pagesUltra Low Dose CT Vs Chest X Ray in Non Traumatic Emergency D 2023 EClinicaronaldquezada038No ratings yet
- What is GMO - A guide to genetically modified organismsDocument14 pagesWhat is GMO - A guide to genetically modified organismsCristie Ann GuiamNo ratings yet
- Research in Educ 215 - LDM Group 7Document25 pagesResearch in Educ 215 - LDM Group 7J GATUSNo ratings yet
- A. Badal', R. Barbera, A. Bonasera, M. Gulino, A. Palmeri (Auth.), Wolfgang Bauer, Hans-Georg Ritter (Eds.) - Advances in Nuclear Dynamics 4 (1998, Springer US)Document389 pagesA. Badal', R. Barbera, A. Bonasera, M. Gulino, A. Palmeri (Auth.), Wolfgang Bauer, Hans-Georg Ritter (Eds.) - Advances in Nuclear Dynamics 4 (1998, Springer US)ramiphysicsNo ratings yet