Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Suggested Answers To Self Te5t: Hapter
Uploaded by
ka klklklOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Suggested Answers To Self Te5t: Hapter
Uploaded by
ka klklklCopyright:
Available Formats
Suggested answers to Self te5t b X: oxygen
Y: carbon dioxide
Chapter 7 的-40)
ii The
Section A (1 mark each) bcca
t C 2 A the I
into
Section B
1
3 a Cilium chapter 9 <p 這28')
..
11 Structure X beats to sweep mucus with
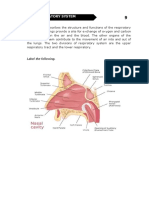
trapped bacteria towards the phary邙 1 Section A (1 mark each)
The mucus with the trapped bacteria is 2 A
then coughed up, 1 t B
or swallowed into the stomach where
Section B
most of the trapped bacteria are killed by
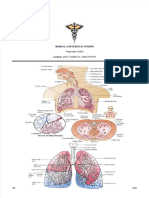
1 In the leaf, the spongy mesophyU
hydrochloric acid. 3 a Cells
1 loosely packed. In the lung, th
b ere art~
It destroys structure X. air sacs.
c The build-up of mucus narrows the trachea, This provides more air spaces for gas
reducing the airflow to and away from the diffusion and more surface area for
Cl:
lungs. 1
of gases. 、
The concentration gradient of respiratory The leaf is thin. The wall of air sacs . I
gases between the air sacs and the capillaries lung is only one-cell thick.
is less steep. 1
f I
This offers a short diffusion distance"`
The diffusion of respiratory gases slows exchange. %
down and thus gas exchange is less efficient. I
1 b (n the daytime, the rate of photos
Ynthes~,
higher than that of respiration.
I
More carbon dioxide is taken in for
Chapter 8 (p. a-49) photosynthesis than is released in
respiration. Therefore, the carbon dio頌
Section A (1 mark each) content in the air spaces is lower. /
1 A 2 0 More orygen is released in photosynthes~
than is taken .m for respiration. Therefore
Section B the orygen content in the air spaces is
1 higher.
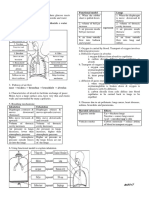
3 a P (vein) has a larger lumen.
Q (artery) has a thicker wall. 1 At night, pho:,i、ynthesis stops. The plam
carries ov· ·:-- a tion only. Oxygen is
ii The large lumen of P reduces the
taken in 」 ,, , Yb,.in dioxide is released in
resistance to the blood flow inside P. 1
respiratic: . ·. -,:·fore, the carbon dioxi也
The t.fiick wall of Q allows it to
content irt'd, . r :,paces is higher. I
withstand a high blood pressure due to
the pum1,mg action of the heart. 1
iv
You might also like
- Suggested Answers To Self Test: ApterDocument1 pageSuggested Answers To Self Test: Apterka klklklNo ratings yet
- Pipes of the Church Organ - A Selection of Classic Articles on Organ Design and ConstructionFrom EverandPipes of the Church Organ - A Selection of Classic Articles on Organ Design and ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Modul 1Document28 pagesModul 1aszmadie81No ratings yet
- Kinetics of Wastewater Treatment: Proceedings of a Post-Conference Seminar Held at the Technical University of Denmark, Copenhagen, 1978From EverandKinetics of Wastewater Treatment: Proceedings of a Post-Conference Seminar Held at the Technical University of Denmark, Copenhagen, 1978S. H. JenkinsNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answers To Self Test: Section ADocument1 pageSuggested Answers To Self Test: Section AU KILLED MY DOGNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology: Wednesday, 23 March 2022 5:54 AmDocument3 pagesRespiratory Physiology: Wednesday, 23 March 2022 5:54 AmDANA ISABELLE PILAPILNo ratings yet
- Human Biology 10th Edition Starr Test BankDocument23 pagesHuman Biology 10th Edition Starr Test Bankantheagian4p4y4100% (29)
- Suggested Answers To Exercise, Reading To Learn and Cross-Topic ExerciseDocument19 pagesSuggested Answers To Exercise, Reading To Learn and Cross-Topic ExerciseBernardNo ratings yet
- Sec 2 Science SA1 Kuo Chuan Presbyterian Sec 2018Document33 pagesSec 2 Science SA1 Kuo Chuan Presbyterian Sec 2018ok kkNo ratings yet
- The Life Process of Respiration: Biology Unit 7Document23 pagesThe Life Process of Respiration: Biology Unit 7giscaamiliaNo ratings yet
- Soalan Objektif Bab 7 & Bab 8Document19 pagesSoalan Objektif Bab 7 & Bab 8SACHEETHA MoeNo ratings yet
- f3 c1 Breathing RevisionDocument2 pagesf3 c1 Breathing Revisionchinpy088464No ratings yet
- DLaboratory Actiivty 9 - Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesDLaboratory Actiivty 9 - Respiratory SystemSydney AchaiNo ratings yet
- Spațiu Despirator de DeadDocument3 pagesSpațiu Despirator de DeadAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesRespiratory SystemCarlos Enrique Pijo PerezNo ratings yet
- Human Bio S1Q1 PDFDocument10 pagesHuman Bio S1Q1 PDFAngel MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Human Bio S1Q1Document10 pagesHuman Bio S1Q1Shaira BautistaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System 11 REVISIONDocument3 pagesRespiratory System 11 REVISIONchinpy088464No ratings yet
- Respiratory System - LECDocument5 pagesRespiratory System - LECDexter DelcarmenNo ratings yet
- Mock Exam AnswersDocument6 pagesMock Exam Answersvanessaparkes123No ratings yet
- Ebook Chem 2 Chemistry in Your World 2Nd Edition Hogg Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument28 pagesEbook Chem 2 Chemistry in Your World 2Nd Edition Hogg Test Bank Full Chapter PDFalankiet45olsq100% (12)
- Unit Respiration: Ow EverDocument23 pagesUnit Respiration: Ow EverAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Learner Book AnswersDocument35 pagesScience 8 Learner Book AnswersVanished Man95% (278)
- 1Document14 pages1hanafizaNo ratings yet
- Serial 1949/29:, Inv) ! Stigatlon of Belmhoitz Resouators Report No. B.041Document26 pagesSerial 1949/29:, Inv) ! Stigatlon of Belmhoitz Resouators Report No. B.041AntonioPalloneNo ratings yet
- Workbook Answers: Unit 1 RespirationDocument30 pagesWorkbook Answers: Unit 1 RespirationYan En88% (183)
- CAPE Biology Unit 2 Past Paper Solutions 2007-2015 UpdateDocument110 pagesCAPE Biology Unit 2 Past Paper Solutions 2007-2015 Updatedevoydouglas94% (49)
- Mastering Biology BK1B NotesDocument20 pagesMastering Biology BK1B NotesAlva WongNo ratings yet
- ACHAI DLaboratory Actiivty 9 - Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesACHAI DLaboratory Actiivty 9 - Respiratory SystemSYDNEY JILL ACHAINo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Independentyanny03No ratings yet
- Respiration: Gas Transfer: Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesRespiration: Gas Transfer: Learning Objectiveshuldani-1No ratings yet
- ACFrOgC7mxGaX9liXL4MXhyIib2My7OJ2fZppJtUXaiwHAXPWv6byWDD3pHlmU1oEOp6KBWon7YU jkOlWtd JuFuLgT1S2gy3uqt5qGGQC - XMeRzHD ILMtafpI6OCKEmRORkbnWIkeZVIfnbmDocument22 pagesACFrOgC7mxGaX9liXL4MXhyIib2My7OJ2fZppJtUXaiwHAXPWv6byWDD3pHlmU1oEOp6KBWon7YU jkOlWtd JuFuLgT1S2gy3uqt5qGGQC - XMeRzHD ILMtafpI6OCKEmRORkbnWIkeZVIfnbmCenitserNo ratings yet
- Breathing and ExchangeDocument7 pagesBreathing and ExchangeRakshit ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Requirement in NCP 312 (Medical and Surgical Nursing) : Submitted By: Cadalin, Fremelen Rose CDocument4 pagesRequirement in NCP 312 (Medical and Surgical Nursing) : Submitted By: Cadalin, Fremelen Rose CFremelen Rose CadalinNo ratings yet
- 1a She Would Suck Up The Lime Water If She Breathed Through Tube X. B C DDocument4 pages1a She Would Suck Up The Lime Water If She Breathed Through Tube X. B C D李安逸No ratings yet
- Optimal Lamellar Arrangement in Fish Gills: W W W BDocument4 pagesOptimal Lamellar Arrangement in Fish Gills: W W W BvgghjiokopNo ratings yet
- Test Pitanja Iz Respiratornog Sistema Sa PrevodomDocument10 pagesTest Pitanja Iz Respiratornog Sistema Sa PrevodomzerohajdukNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology 3rd Edition Beachey Test BankDocument8 pagesRespiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology 3rd Edition Beachey Test Bankfarleykhucucc59v100% (22)
- C2022 - MED1 - TBL Lung-SoundsDocument17 pagesC2022 - MED1 - TBL Lung-SoundsJolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- Gaseous ExchangeDocument23 pagesGaseous ExchangeSsaku BoscoNo ratings yet
- Skema Pemarkahan T3T1 Skema Jawapan Markah: Struktur Mekanisme F Mekanisme GDocument2 pagesSkema Pemarkahan T3T1 Skema Jawapan Markah: Struktur Mekanisme F Mekanisme GDaniel BarnesNo ratings yet
- ANSWER Chapter 8 BIO F4Document4 pagesANSWER Chapter 8 BIO F4Izeliwani Haji IsmailNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System I. FunctionDocument6 pagesRespiratory System I. Functionjgcriste100% (3)
- Chap 11 WS1 IGCSE Bio 11.01Document6 pagesChap 11 WS1 IGCSE Bio 11.01ipradhiputriNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument6 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gasesadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- CDN Ed Human Physiology 2nd Edition Sherwood Test BankDocument34 pagesCDN Ed Human Physiology 2nd Edition Sherwood Test Banksinger.peg9nc0sg100% (24)
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument1 pagePa Tho PhysiologyJoanne JelicaNo ratings yet
- Ch.21 Notes (T)Document12 pagesCh.21 Notes (T)Kelvin LuiNo ratings yet
- Transfer FaktorDocument19 pagesTransfer FaktorJelenaJankovNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Lesson1Document9 pagesNCM 112 Lesson1Trisha LopezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Respiratory SystemDocument57 pagesChapter 2 Respiratory SystemNur AthirahNo ratings yet
- Covid NCPDocument6 pagesCovid NCPNathalia Cabalse100% (2)
- 1: Respiration Functional Model LungsDocument1 page1: Respiration Functional Model LungsNana TanNo ratings yet
- JWPN Plant RespirationDocument4 pagesJWPN Plant RespirationAs MiedaNo ratings yet
- F4Bio (C8) NotesDocument11 pagesF4Bio (C8) NotesGrace LeeNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Gas Exchange Final Version I Latest THE ONE Assessment TaskDocument10 pagesKami Export - Gas Exchange Final Version I Latest THE ONE Assessment TaskDareen FahadNo ratings yet
- 7 & 8 (Cellular Respiration, Respiratory Systems)Document19 pages7 & 8 (Cellular Respiration, Respiratory Systems)Jia YueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 PhotosynthesisDocument10 pagesChapter 10 PhotosynthesisMicky BanderaNo ratings yet
- HermanYeung DSE Chem Notes Ch5Document44 pagesHermanYeung DSE Chem Notes Ch5ka klklklNo ratings yet
- Transport in Humans: 8.1 Need For Transport SystemDocument11 pagesTransport in Humans: 8.1 Need For Transport Systemka klklklNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans: 7.1 Human Breathing SystemDocument10 pagesGas Exchange in Humans: 7.1 Human Breathing Systemka klklklNo ratings yet
- Answers To Practice: SkillDocument1 pageAnswers To Practice: Skillka klklklNo ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: Chemical Engineering and ProcessingDocument94 pagesAccepted Manuscript: Chemical Engineering and ProcessingsamiraNo ratings yet
- Bio CNGDocument23 pagesBio CNGHarshini JayaprakashNo ratings yet
- CP4Document69 pagesCP4mevansmetreelNo ratings yet
- L G L G L G 3 3: Printed: 06/08/19. 14:46. Reference: W.C.Reynolds: Thermodynamic Properties in SIDocument2 pagesL G L G L G 3 3: Printed: 06/08/19. 14:46. Reference: W.C.Reynolds: Thermodynamic Properties in SIEndel Ferraz da RrochaNo ratings yet
- Contoh Perhitungan Unit ProsesDocument4 pagesContoh Perhitungan Unit ProsesChristopher Handino KoesnoNo ratings yet
- Neeraj BPCLDocument32 pagesNeeraj BPCLAshwani Singh100% (1)
- Energy Conversion Technology 1: 2019-2020 Exercise Class 7 - 7.10.2019 - Thermochemical ConversionDocument3 pagesEnergy Conversion Technology 1: 2019-2020 Exercise Class 7 - 7.10.2019 - Thermochemical ConversionKristijanNo ratings yet
- Linde Cylinder Colors EN - Web - tcm581-582894 PDFDocument2 pagesLinde Cylinder Colors EN - Web - tcm581-582894 PDFqcmechipogNo ratings yet
- Aspen IGCC ModelDocument19 pagesAspen IGCC ModelatisnameNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: IB Chemistry Topic 10.2Document20 pagesAlkanes: IB Chemistry Topic 10.2Ravi RanjanNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper ConversionDocument22 pagesWhitepaper ConversionarissaNo ratings yet
- Fischer Tropsch Presentation FinalDocument19 pagesFischer Tropsch Presentation FinalWaqar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Rotary Valve Fast Cycle Pressure Swing Adsorption PaperDocument14 pagesRotary Valve Fast Cycle Pressure Swing Adsorption Paperabhi_mohit2005No ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of Petcoke Steam GasificationDocument18 pagesDesign and Simulation of Petcoke Steam Gasificationsaahikrishna8100% (1)
- 'Biomass Conversion TechnologiesDocument7 pages'Biomass Conversion TechnologiesIrfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity of GasesDocument2 pagesThermal Conductivity of GasesFlorian_AngererNo ratings yet
- Ammonia - TOC (2019 Program) - 0Document10 pagesAmmonia - TOC (2019 Program) - 0oom_tgwNo ratings yet
- SSP00054020-Nr 540 SCR Exhaust Gas Treatment in The Passat 2015Document40 pagesSSP00054020-Nr 540 SCR Exhaust Gas Treatment in The Passat 2015mbutiulcaNo ratings yet
- Nitric Acid Manufacturing Flow SheetDocument2 pagesNitric Acid Manufacturing Flow Sheethana_gondokusumoNo ratings yet
- Liquefied Petroleum GasDocument2 pagesLiquefied Petroleum GasjacuzzisNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Dew PointDocument88 pagesHydrocarbon Dew PointMubarizNo ratings yet
- Saudi Technical Trade Test - Welder CategoryDocument4 pagesSaudi Technical Trade Test - Welder CategoryshabashakkimNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Fuels GTL f1 Fischer Tropsch Process2588570496085257524Document8 pagesSynthetic Fuels GTL f1 Fischer Tropsch Process2588570496085257524Ishu Vohra100% (1)
- DDG-T-P-03205 Basis of Process DesignDocument26 pagesDDG-T-P-03205 Basis of Process DesignCristinaNo ratings yet
- TRADING (Maksimal 5 Saham) : Dana Avg Down 1,790,800Document35 pagesTRADING (Maksimal 5 Saham) : Dana Avg Down 1,790,800Arya FahrevaNo ratings yet
- Capstone Design Project For Plant Design Steam Methane Reforming PlantDocument251 pagesCapstone Design Project For Plant Design Steam Methane Reforming PlantArman Jade LazarteNo ratings yet
- Solid Fuels W:oDocument3 pagesSolid Fuels W:oShane PatulotNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Ig FM200 NovecDocument1 pageComparison Between Ig FM200 NovecTun JebatNo ratings yet
- C1Document1 pageC1BenePicarNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Plant Manual - Valve - PumpDocument1 pageOxygen Plant Manual - Valve - Pumpaminata diagneNo ratings yet
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (598)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseFrom EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (52)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (217)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (517)
- Change Your Brain, Change Your Life (Before 25): Change Your Developing Mind for Real-World SuccessFrom EverandChange Your Brain, Change Your Life (Before 25): Change Your Developing Mind for Real-World SuccessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainFrom EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (111)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- The Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (633)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- Minds Make Societies: How Cognition Explains the World Humans CreateFrom EverandMinds Make Societies: How Cognition Explains the World Humans CreateRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (24)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightFrom EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- Remnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsFrom EverandRemnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- Lymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthFrom EverandLymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)