Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stone Matrix Asphalt (SMA) Mixes: Mix Type: Materials For SMA
Stone Matrix Asphalt (SMA) Mixes: Mix Type: Materials For SMA
Uploaded by
Eri Susanto HariyadiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stone Matrix Asphalt (SMA) Mixes: Mix Type: Materials For SMA
Stone Matrix Asphalt (SMA) Mixes: Mix Type: Materials For SMA
Uploaded by
Eri Susanto HariyadiCopyright:
Available Formats
MIX TYPE: Materials for SMA
Stone Matrix Asphalt (SMA) Mixes SMA is a premium mix requiring high quality ma-
terials. Cubical, low abrasion, crushed stone and manu-
SMA is a gap-graded HMA that maximizes rutting factured sands are recommended because the mixture
resistance and durability with a stable stone-on-stone gains most of its strength from the stone-on-stone ag-
skeleton held together by a rich mixture of AC, filler, gregate skeleton. Aggregates should have 100 percent of
and stabilizing agents such as fibers and/or asphalt modi- the particles with one or more fractured faces. Natural
fiers. SMA was developed in Europe to resist rutting sands should not be used. Aggregates should also have
(permanent deformation) and studded tire wear. high polish values to retain good skid resistance where
SMA is often considered a premium mix because of SMA is the final surface.
higher initial costs due to increased asphalt contents and The matrix of sand, asphalt, mineral filler, and addi-
the use of more durable aggregates. However, this higher tives is also important to performance. Manufactured
initial cost may be more than offset by improved per- sands, mineral fillers, and additives (fibers and/or poly-
formance for medium and high traffic loading situations. mers) make a stiff matrix that is important to the rutting
In addition to improved durability, fatigue, and rutting resistance of these mixes. Mineral fillers and additives
resistance, other reported benefits include improved wet also reduce the amount of asphalt drain down in the mix
weather friction, due to a coarser surface texture, and during construction, increasing the amount of asphalt
lower tire noise. Reflective cracking in a SMA mixture used in the mix, improving its durability.
is often not as severe as dense-graded mixtures since Table 6 provides general guidelines for materials used
cracks have less tendency to spall 7. in SMA mixtures. See Appendix A for a complete de-
scription of materials.
Purpose
As previously mentioned, the primary purpose of
SMA mixes is improved rut resistance and durability. Mix Design
Therefore, these mixes are almost exclusively used for Marshall and Superpave compaction procedures can
surface courses on high volume interstates and U.S. be used to design SMA mixtures. For information on
highways. Special cases such as heavy, slow-moving ve- designing SMA mixtures, refer to the National Coop-
hicles may warrant the use of SMA for intermediate and erative Highway Research Program (NCHRP) Report
base layers. One state, Georgia, commonly uses SMAs 425, Designing Stone Matrix Asphalt Mixtures for Rut-
as a surface mix with an OGFC as a wearing surface. Resistant Pavements.
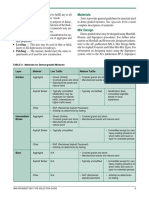
TABLE 6: Materials for SMA Mixtures
Layer Material Medium Traffic High Traffic
Surface and Aggregate • Crushed stone
Intermediate/Binder • Crushed gravel
• Manufactured sands
• Mineral filler
Asphalt Binder • Modified binder typically used • Modification likely
• Unmodified may be used • Unmodified asphalts
at lower traffic levels based on local experience
Other • Fibers
• Antistrip as determined by testing
12 HMA PAVEMENT MIX TYPE SELECTION GUIDE
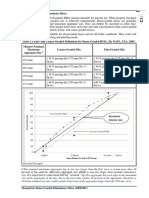
Mix Types FIGURE 6: Recommended Minimum Lift
Thickness Ranges for SMA
Figure 6 shows the range of the recommended mini-
mum lift thicknesses for the different SMA mixes.
Table 7 presents which mixes are appropriate for dif-
ferent layers and for what purpose you may use the mix. 80 75.0
Because SMA is mostly used for surface courses, choice
in mix is almost always based on lift thickness.
70
Sublayer Conditions — All Mixes
Minimum Lift Thickness Range, mm
New Construction
Moderate and High traffic — Place mix type on prop- 60
erly prepared HMA base or binder course.
Rehabilitation 50.0
Place mix type only on sound pavement structure. 50
50.0
The existing surface should have little or no crack-
ing. Structural deficiencies must be repaired prior to
placement. 40 37.5
37.5
30
20 25.0
10
9.5 12.5 19.0
Mix Type, mm
The difference in aggregate structure between dense-graded
and SMA is shown in these core samples.
TABLE 7: Appropriate Layers and Purpose of SMA
Mix Purpose
Nominal Max. Agg. 9.5 mm 12.5 mm 19 mm
Layer
Surface • Wearing surface
• Friction
• Structure
• Smoothness
Intermediate N/A N/A • Structure
HMA PAVEMENT MIX TYPE SELECTION GUIDE 13
You might also like
- F. Reif - Fundamentals of Statistical and Thermal Physics PDFDocument333 pagesF. Reif - Fundamentals of Statistical and Thermal Physics PDFAllan SeeberNo ratings yet
- Asphalt Institute PresentationDocument43 pagesAsphalt Institute PresentationMax Cedeño De LeónNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter W4 LECTURE On Protein Synthesis in DNA and MutationDocument53 pages3rd Quarter W4 LECTURE On Protein Synthesis in DNA and MutationMorante GeraldineNo ratings yet
- Stone Matrix AsphaltDocument17 pagesStone Matrix AsphaltLilaNo ratings yet
- Sensory Aroma From Maillard Reaction of Individual and Combination of Amino Acids With Glucase in Acidic ConditionsDocument8 pagesSensory Aroma From Maillard Reaction of Individual and Combination of Amino Acids With Glucase in Acidic ConditionsAregia OviNo ratings yet
- Laundry NotesDocument16 pagesLaundry Notesjazebel3100% (4)
- MCQ Collection Nucleic Acid Dr. Mohamed Khomsi 2022Document14 pagesMCQ Collection Nucleic Acid Dr. Mohamed Khomsi 2022Abdulhadi AlhabroushNo ratings yet
- Super PaveDocument20 pagesSuper PaveHashem EL-MaRimeyNo ratings yet
- User Guidelines For Waste and Byproduct Materials in Pavement ConstructionDocument8 pagesUser Guidelines For Waste and Byproduct Materials in Pavement ConstructionRajesh KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Bituminous Mix Design & Superpave MixesDocument53 pagesBituminous Mix Design & Superpave Mixesjaffna100% (9)
- Asphalt Concrete PavementDocument9 pagesAsphalt Concrete Pavementrabia_rabiaNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, School of Engineering Cedat, Makerere UniversityDocument50 pagesDepartment of Civil and Environmental Engineering, School of Engineering Cedat, Makerere UniversityBAMSNo ratings yet
- 2019 ABCs of SMA Design & ConstructionDocument4 pages2019 ABCs of SMA Design & Constructionibrahim tanko abeNo ratings yet
- Asphalt Mix Design PDFDocument10 pagesAsphalt Mix Design PDFgelak144547No ratings yet
- HMA - Mix Design ProceduresDocument10 pagesHMA - Mix Design ProceduresbopozNo ratings yet
- Hma Pavement Mix Type Selection GuideDocument25 pagesHma Pavement Mix Type Selection GuidetymmahhNo ratings yet
- 15 Ijmtst040432Document6 pages15 Ijmtst040432Addandi Ashrith Reddy ce21b002No ratings yet
- CSE312-Topic 2-Highway Pavement Structure 2022Document53 pagesCSE312-Topic 2-Highway Pavement Structure 2022iloveminjuNo ratings yet
- Technical Note 16 Stone Mastic Asphalt: April 2004Document2 pagesTechnical Note 16 Stone Mastic Asphalt: April 2004Lutfi TofiqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 c5 FinalDocument29 pagesChapter 2 c5 FinalSamsuz ZamanNo ratings yet
- HMA (Introduction) - SICCION 2015Document54 pagesHMA (Introduction) - SICCION 2015Michael Murillo BaraquioNo ratings yet
- Kamla Nehru Institute of Technology, SultanpurDocument17 pagesKamla Nehru Institute of Technology, Sultanpursaurabh GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Stone Mastic Asphalt: A Seminar Report OnDocument17 pagesStone Mastic Asphalt: A Seminar Report Onprajakta chaudhari100% (1)
- Technical Note TN 048 Differences Between Conventional HSS SAM and SAMI TreatmentsDocument2 pagesTechnical Note TN 048 Differences Between Conventional HSS SAM and SAMI TreatmentsKarina Benavides BurgosNo ratings yet
- Suspended Slab MixDocument4 pagesSuspended Slab Mixanonymousupldr666No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Mix DesignDocument16 pagesChapter 3 - Mix DesignAbel MulugetaNo ratings yet
- B3 - Asphalt For Thin Surface CourseDocument2 pagesB3 - Asphalt For Thin Surface CourseblastmcNo ratings yet
- Section 407 - Hot Mix Asphalt: 407.01 GENERALDocument25 pagesSection 407 - Hot Mix Asphalt: 407.01 GENERALDaiNo ratings yet
- Coconut FiberDocument14 pagesCoconut Fiberrahul kumarNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document91 pagesModule 4Nitesh ShahNo ratings yet
- 12 Flexible Pavement Design - From Cradle To Cradle - A, VeeraragavanDocument65 pages12 Flexible Pavement Design - From Cradle To Cradle - A, VeeraragavanSreeja SadanandanNo ratings yet
- Lec - 8 Mix Design Applications PDFDocument68 pagesLec - 8 Mix Design Applications PDFAZIMERAWNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Highway Pavement MaterialsDocument47 pagesChapter-3 Highway Pavement MaterialsZemichael AbaynehNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals: VariablesDocument8 pagesFundamentals: VariablesJalal Habib KhanNo ratings yet
- SMA-Guide Engl - 2006Document35 pagesSMA-Guide Engl - 2006Ale ChunoNo ratings yet
- Section 407 - Hot Mix Asphalt: 407.01 GeneralDocument21 pagesSection 407 - Hot Mix Asphalt: 407.01 GeneralAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Idiots' Guide To Highways Maintenance: Bituminous Mixture / Process DiagramsDocument7 pagesThe Idiots' Guide To Highways Maintenance: Bituminous Mixture / Process DiagramsEm MarNo ratings yet
- Draft TQ LetterDocument6 pagesDraft TQ LetterMotaz AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Rotor Selection Guide: For Reclamation and StabilizationDocument12 pagesRotor Selection Guide: For Reclamation and StabilizationOhana IngaNo ratings yet
- Stone Mastic AsphaltDocument9 pagesStone Mastic Asphaltsatyam lodhiNo ratings yet
- L-1 Bituminous Mix DesignDocument86 pagesL-1 Bituminous Mix DesignrajibchattarajNo ratings yet
- Granular Pavements With Thick Asphalt SurfacingDocument4 pagesGranular Pavements With Thick Asphalt SurfacingIlham FeryantoNo ratings yet
- Superpave Future HMA PavementsDocument4 pagesSuperpave Future HMA PavementsAlvin RamirezNo ratings yet
- AIB048Document4 pagesAIB048joguitarrasNo ratings yet
- Sma PavimentoDocument27 pagesSma PavimentoEdwin Garcia AredoNo ratings yet
- Chair, Infrastructure Design & Construction, EIABCDocument103 pagesChair, Infrastructure Design & Construction, EIABCabiyuNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Resilient Characteristics of Stone Matrix Asphalt (Sma)Document4 pagesEvaluation of Resilient Characteristics of Stone Matrix Asphalt (Sma)Nikhil GuptaNo ratings yet
- WorkTip 11 Bituminous Surfacing CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesWorkTip 11 Bituminous Surfacing CharacteristicsLa FoliakNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Superpave: Department of Civil EngineeringDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Superpave: Department of Civil EngineeringAjay JainNo ratings yet
- Application Description - Granular Base - User Guidelines For Waste and Byproduct Materials in Pavement Construction - FHWA-RD-97-148Document2 pagesApplication Description - Granular Base - User Guidelines For Waste and Byproduct Materials in Pavement Construction - FHWA-RD-97-148Pritha DasNo ratings yet
- Sma PMB40Document114 pagesSma PMB40Er Thyagaraj Gowda100% (1)
- Assignment 3Document16 pagesAssignment 3Wâqâr ÂnwârNo ratings yet
- Asphalt Mix Design - Superpave FundamentalsDocument27 pagesAsphalt Mix Design - Superpave FundamentalsJohn Tejada IIINo ratings yet
- Publication 1558676872 PDFDocument13 pagesPublication 1558676872 PDFHenok MebrateNo ratings yet
- 4-Highway Material Part 1 DR KhairilDocument29 pages4-Highway Material Part 1 DR Khairildanielhaikhal1No ratings yet
- Rubber Boy'sDocument14 pagesRubber Boy'sPiriyangan BNo ratings yet
- McAsphalt Asphalt Technician Training ManualDocument38 pagesMcAsphalt Asphalt Technician Training ManualRajaImran100% (1)
- Item 346: Item 346 Is A For Stone-Matrix Asphalt (SMA) and Asphalt Rubber Stone-Matrix (SMAR) MixturesDocument34 pagesItem 346: Item 346 Is A For Stone-Matrix Asphalt (SMA) and Asphalt Rubber Stone-Matrix (SMAR) MixturesLam Dao PhucNo ratings yet
- 28 - SuperpaveDocument10 pages28 - SuperpaveNagaraj PatilNo ratings yet
- OverlaysDocument11 pagesOverlaysMILON KUMAR HORENo ratings yet
- 1.construction of Subgrade Subbase and Base BBMP PDFDocument65 pages1.construction of Subgrade Subbase and Base BBMP PDFKamukwema johnNo ratings yet
- Heater SacrifiDocument2 pagesHeater SacrifiEri Susanto HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Konversi Faktor 23Document3 pagesKonversi Faktor 23Eri Susanto HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Decision Figure 234Document3 pagesDecision Figure 234Eri Susanto HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Gatepart 12Document4 pagesGatepart 12Eri Susanto HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Shear Failure VersusDocument7 pagesShear Failure VersusEri Susanto HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Provide FrametyDocument3 pagesProvide FrametyEri Susanto HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Local Shear PunchDocument9 pagesLocal Shear PunchEri Susanto HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Continuous and StripDocument1 pageContinuous and StripEri Susanto HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Ecentrivally Footing LeariearDocument5 pagesEcentrivally Footing LeariearEri Susanto HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Load and Limit StatesDocument1 pageLoad and Limit StatesEri Susanto HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Gradasi Agg AI SupDocument1 pageGradasi Agg AI SupEri Susanto HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Structural - This Is The Primary Purpose of Dense-: MaterialsDocument1 pageStructural - This Is The Primary Purpose of Dense-: MaterialsEri Susanto HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Gradasi TErbuka Bit MixDocument1 pageGradasi TErbuka Bit MixEri Susanto HariyadiNo ratings yet
- MS 4 Aspal Beton Grad AggDocument2 pagesMS 4 Aspal Beton Grad AggEri Susanto HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Lapis Perkerasan Dan Lalu LintasDocument1 pageLapis Perkerasan Dan Lalu LintasEri Susanto HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Tyfo UC StripsDocument2 pagesTyfo UC Stripsyusak santosoNo ratings yet
- Save The Penguins Storyboard UseDocument20 pagesSave The Penguins Storyboard Useapi-295900495No ratings yet
- SDS Irganox 1076 Ex-BASF (Expiry 2024)Document14 pagesSDS Irganox 1076 Ex-BASF (Expiry 2024)Arista DianaNo ratings yet
- Weinrich 2021 Model ParametersDocument8 pagesWeinrich 2021 Model ParametersKentner Chavez CorreaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science SummativeDocument3 pagesPhysical Science Summativejannette jane davidNo ratings yet
- ADV IEQEIII Ex WS kqesNAHDocument9 pagesADV IEQEIII Ex WS kqesNAHwanderedNo ratings yet
- Mustafa's Resume PDFDocument1 pageMustafa's Resume PDFmostafa mousaNo ratings yet
- Kims CopiesDocument17 pagesKims Copieszafarchem_iqbalNo ratings yet
- K69 Reducer MSDSDocument4 pagesK69 Reducer MSDSjpdahunterNo ratings yet
- Bombay HighDocument36 pagesBombay HighHarshit SharmaNo ratings yet
- COA RequirementDocument4 pagesCOA RequirementAbdul GhafoorNo ratings yet
- BSC (P) - 2020-II-IV-VI Sem (CBCS) - 1Document9 pagesBSC (P) - 2020-II-IV-VI Sem (CBCS) - 1Rahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Developing Fuels Practice QuestionsDocument39 pagesDeveloping Fuels Practice Questionssohailnoreen5062No ratings yet
- Mole ConceptDocument24 pagesMole ConceptAgriye KambojNo ratings yet
- De TopicDocument10 pagesDe TopicHet ThankiNo ratings yet
- Convection Lab 2 Thermo 2 MEE30004 PDFDocument6 pagesConvection Lab 2 Thermo 2 MEE30004 PDFBoydo HilNo ratings yet
- 2222Document5 pages2222Roberto UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- Gptms + Sio2 + Mtms + FasDocument6 pagesGptms + Sio2 + Mtms + FasTamilarasiNo ratings yet
- Solbin Brochure 2.2014RS PDFDocument12 pagesSolbin Brochure 2.2014RS PDFHandonoZchvaniaAgustyNo ratings yet
- RUBBER TECHNOLOGY - Ingredients, Activators, Fillers - Goodyear RubberDocument5 pagesRUBBER TECHNOLOGY - Ingredients, Activators, Fillers - Goodyear RubberArjun Satheesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Química Plantilla PowerPointDocument38 pagesQuímica Plantilla PowerPointJosé Rafael GuillénNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CATALOGUE VABW 2019 2020 EN RDDocument140 pagesGENERAL CATALOGUE VABW 2019 2020 EN RDdawit aregayNo ratings yet
- Meneses, Keziah F.: Cop T T T T T T Where: T T T Cop COP 1.4696 1.47Document19 pagesMeneses, Keziah F.: Cop T T T T T T Where: T T T Cop COP 1.4696 1.47Eriane GarciaNo ratings yet
- Medicine Requirement: For QuarentineDocument13 pagesMedicine Requirement: For QuarentineJahanzeb SafdarNo ratings yet
- Hydransafe FR-NSG 38Document2 pagesHydransafe FR-NSG 38Mauricio CenturionNo ratings yet