Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Medlin - Ib Chemistry SL: Design
Uploaded by
burcak gec0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageOriginal Title
9088809
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageMedlin - Ib Chemistry SL: Design
Uploaded by
burcak gecCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
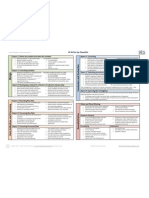
MEDLIN – IB CHEMISTRY SL INTERNAL ASSESSMENT GRADING CRITERIA
STUDENT NAME: ________________________ LAB TITLE: ________________________________________________________
TOPIC: ________________________________ TIME: ____Hrs. DATE: _______________________
INTERNAL ASSESSMENT GRADING CRITERIA
Aspect 1:
Aspect 2: Aspect 3:
Defining the Problem & Selecting
Controlling Variables Developing a Method for Collecting Data
Variables
Explicitly identified the relevant Explicitly describe how you will control the Procedure is detailed, easy to repeat
variables: control variables (or monitor them) Include a detailed apparatus diagram
Independent Justify the need to control / effect on results Reference/cite any standard techniques
Dependent Explain which variables cannot be controlled used in methods; cite sources if used for
Controlled and why procedure
Design Research Question (using variables) that Units, precision, size, formula of materials
is specific and focused Insure that sufficient data is collected and
Literature Values (or statement of none) appropriate # of trials selected, explain
Cite (MLA) sources for Literature values reasoning
Develop hypothesis based on Literature Sufficient range of independent variable
values selected
Brief explanation of the experiment Explanation of data collection leading to
data tables
C P N C P N C P N
Aspect 1: Aspect 2: Aspect 3:
Recording Raw Data Processing Raw Data Presenting Processed Data
Recorded raw quantitative data Table containing processed data Table of processed data
Recorded raw qualitative data Averages are taken of processed data Table contains title, headings, explanations
Recorded given/relevant formulas or Table containing final results, compares to Units are present and correct
values literature value Sig figs are correct
All tables contain titles, headings, Sample calculations are shown containing Every value contains uncertainty (percent
explanations equation, example, and explanation or absolute)
Units are present and correct throughout Units, sig. figs, and uncertainties are present Tables are organized and easy to follow
Significant figures are correct within 1 and correct
Data value Calculations are correct
Collection Every value contains appropriate
& uncertainty Graphs
Sig figs are consistent in uncertainties
Processing Original graph of raw data
Tables are organized and easy to follow Correct choice of graph type
Correct data was used to create graph
Title, axes, key, units, variables graphed
correctly
If linear, trend line and equation are present
Overall presentation of graph is neat, legible,
well-executed
Explanation of graph, and results of graph are
included
C P N C P N C P N
Aspect 1: Aspect 2: Aspect 3:
Concluding Evaluating Procedure(s) Improving the Investigation
Repeat results Explain the difference between expected and State explicit, realistic improvements made
Show and explain % error observed outcome to methods, and how they minimize errors
Make references to graph, explaining Make comments about the reliability of Explain equipment changes and justify
results methods Explain methods changes and justify
Restate and respond to the research Can the results be trusted? Why/why not? Suggestions to improve systematic errors if
question Evaluate outliers possible
Literature values are referenced and List errors, problems, limitation s Suggestions to improve random errors
Conclusion cited Account for error type NOT FOR IB CRITERIA – BUT REQUIRED FOR
& Describe the chemical concepts behind Discuss accuracy vs. precision ME Provide at least one relevant
Evaluation the experiment, make relevant to IB State the impact of each error on your results extension for this lab: This can be simply
curriculum Explain weaknesses in detail, state how results studying a different variable, testing the
Justify your results or lack of were affected effect of an error source, real world
Conclusion is based on your specific Explain limitations in detail, state how results examples, vocational applications, possible
results were affected extended essay topics, etc.
Uncertainty compared to percent error –
justify the difference
Account for error type, explain
C P N C P N C P N
You might also like
- Practical Engineering, Process, and Reliability StatisticsFrom EverandPractical Engineering, Process, and Reliability StatisticsNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Lab Report Self-Assessment & Report FrameworkDocument6 pagesChecklist For Lab Report Self-Assessment & Report FrameworkHaritah HakimiNo ratings yet
- Ia Ess RubricDocument2 pagesIa Ess RubricCicy IrnaNo ratings yet
- IB Physics & Chemistry IA GuideDocument10 pagesIB Physics & Chemistry IA GuideAhmed SamakaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report RubricDocument2 pagesLab Report RubricjacnauNo ratings yet
- AP Lab Report RubricDocument4 pagesAP Lab Report RubricIsabela MalazarteNo ratings yet
- R A & F Analysis & Interpretation OF DataDocument4 pagesR A & F Analysis & Interpretation OF DataAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Updated Completion Practical and D D StructureDocument8 pagesUpdated Completion Practical and D D Structureapi-642709499No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument48 pagesUntitledBro KingNo ratings yet
- Estadístic A Descriptiv A: Dr. Lázaro Bustio Martínez Otoño 2023Document42 pagesEstadístic A Descriptiv A: Dr. Lázaro Bustio Martínez Otoño 2023guillermobur2310No ratings yet
- Chemistry FA2 - ISMG BreakdownDocument24 pagesChemistry FA2 - ISMG BreakdownnandiaspicyNo ratings yet
- Combine PDFDocument9 pagesCombine PDFchienikolaoNo ratings yet
- Group 7 - Result and DiscussionDocument16 pagesGroup 7 - Result and DiscussionTari AftariniNo ratings yet
- Terminal Output. StatsdocxDocument2 pagesTerminal Output. StatsdocxGabs CastilloNo ratings yet
- BC - Sodium Thiosulphate LabDocument5 pagesBC - Sodium Thiosulphate LabAkshara GuptaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document3 pagesExperiment 4mimiNo ratings yet
- Template Formal ReportDocument3 pagesTemplate Formal ReportMeow MarNo ratings yet
- Bidang KomputerDocument3 pagesBidang KomputerEmiliana ManuelNo ratings yet
- IA General Format For DevelopmentDocument5 pagesIA General Format For DevelopmentPaulina ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Ib Labs Manual-NewsyllabDocument75 pagesIb Labs Manual-NewsyllabAdnanDemirovićNo ratings yet
- CNUR 860 - FALL - 2020 Stats 2 - InstructionDocument7 pagesCNUR 860 - FALL - 2020 Stats 2 - Instructionzobia100% (1)
- KIT401 - 701 Assignment 2 - S1 - 2020Document5 pagesKIT401 - 701 Assignment 2 - S1 - 2020金雨辉No ratings yet
- General MYP4-5 Reporting Template CDocument5 pagesGeneral MYP4-5 Reporting Template Cberatmete26No ratings yet
- Ch5 - Processing Analysis of DataDocument76 pagesCh5 - Processing Analysis of Datashagun.2224mba1003No ratings yet
- Template Term PaperDocument3 pagesTemplate Term PaperGy FalcasantosNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument3 pagesReportShiela ClementeNo ratings yet
- Criterion B: Inquiring and Designing: Purpose and Background InformationDocument8 pagesCriterion B: Inquiring and Designing: Purpose and Background InformationweleviewangNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Investigation Practical Report ChecklistDocument1 pageCardiovascular Investigation Practical Report Checklistapi-632307358No ratings yet
- Subtopic 1.1: Experimental Skills: Key Ideas Intended Student Learning PurposeDocument8 pagesSubtopic 1.1: Experimental Skills: Key Ideas Intended Student Learning PurposechiggsNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis Pre Writing OrganizerDocument4 pagesData Analysis Pre Writing OrganizerbbmsscienceNo ratings yet
- 5.1. Topic 5. Part1 (Updated)Document103 pages5.1. Topic 5. Part1 (Updated)Ipek SenNo ratings yet
- Experimental Design Template IbDocument3 pagesExperimental Design Template Ibnora luisa aburto floresNo ratings yet
- Modelo Reporte de LaboratorioDocument3 pagesModelo Reporte de LaboratorioNataRondonNo ratings yet
- HL Chemistry IA Checklist Updated Dec 2011Document6 pagesHL Chemistry IA Checklist Updated Dec 2011Karl Naumann100% (1)
- Unit Iv BRMDocument15 pagesUnit Iv BRMTamil piratesNo ratings yet
- MYP Science 10: Lab Report Writing GuideDocument2 pagesMYP Science 10: Lab Report Writing GuideTiberiuNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document18 pagesUnit 2rk73462002No ratings yet
- Machine Learning Project: Sneha Sharma PGPDSBA Mar'21 Group 2Document36 pagesMachine Learning Project: Sneha Sharma PGPDSBA Mar'21 Group 2preeti100% (2)
- Experimental Report Scaffold For SeniorsDocument4 pagesExperimental Report Scaffold For SeniorsJakub MarciniukNo ratings yet
- Step by Step How To Write The IaDocument11 pagesStep by Step How To Write The IaMayur VanjaniNo ratings yet
- IB Science IA: Exploration Lab RubricDocument4 pagesIB Science IA: Exploration Lab RubricJoy Ann MirandaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Research ModuleDocument3 pagesNursing Research ModuleRomeo RiveraNo ratings yet
- Standards Support Alg I MathematicsDocument93 pagesStandards Support Alg I MathematicsKrizelle Danica AmorantoNo ratings yet
- IA Write-Up Checklist: Essential Biology: Internal AssessmentDocument1 pageIA Write-Up Checklist: Essential Biology: Internal AssessmentSiddhant Kobe KothariNo ratings yet
- Research Design Quantitative Analysis For DataDocument50 pagesResearch Design Quantitative Analysis For DataHaritika ChhatwalNo ratings yet
- Basic Statistics For The Utterly ConfusedDocument45 pagesBasic Statistics For The Utterly ConfusedwaqarnasirkhanNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Handout For Statistical Writeup of Module 2 T3 2018Document14 pages5.4 Handout For Statistical Writeup of Module 2 T3 2018Anonymous 9ZIgfCdL88No ratings yet
- Deliverable 01 Worksheet: Answer and ExplanationDocument5 pagesDeliverable 01 Worksheet: Answer and ExplanationAdroit WriterNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Introduction To StatisticsDocument37 pagesWeek 1 - Introduction To StatisticsJerome MonserratNo ratings yet
- Q4-Presentation and Interpretation of DataDocument64 pagesQ4-Presentation and Interpretation of DataMa. Lourdes LazaroNo ratings yet
- Fomat For VC Doc PreparationDocument4 pagesFomat For VC Doc PreparationsatwptcNo ratings yet
- Science Process Skills PDFDocument28 pagesScience Process Skills PDFNantha Kumar Sivaperumal100% (1)
- Student I A Lab Report FormatDocument2 pagesStudent I A Lab Report FormatRyan HiraniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document5 pagesChapter 4Georcelle CarcillarNo ratings yet
- Lbosimu ReviewerDocument3 pagesLbosimu ReviewerEloise DyNo ratings yet
- Babbie Basics 5e PPT CH 14Document47 pagesBabbie Basics 5e PPT CH 14Randy CavaleraNo ratings yet
- 2016 IB TicklistDocument2 pages2016 IB TicklistAHMET KEREM AYDEMIRNo ratings yet
- New York State Regents Examination in Algebra I (Common Core)Document16 pagesNew York State Regents Examination in Algebra I (Common Core)Smita NagNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Stoichiometric Relationships - Part 2Document15 pagesTopic 1 - Stoichiometric Relationships - Part 2burcak gecNo ratings yet
- Food Science Experiments For High School Sciences: Experiment 5 Sour Cream Chemistry - Acid Titration - PH MeasurementDocument8 pagesFood Science Experiments For High School Sciences: Experiment 5 Sour Cream Chemistry - Acid Titration - PH Measurementburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Atom-Per. Table-Bond-HandoutDocument28 pagesAtom-Per. Table-Bond-Handoutburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Data Collection & Processing (DCP)Document3 pagesChecklist For Data Collection & Processing (DCP)burcak gecNo ratings yet
- Applied Sciences: Thermal and Physical Properties of Crude Palm Oil With Higher Oleic ContentDocument10 pagesApplied Sciences: Thermal and Physical Properties of Crude Palm Oil With Higher Oleic Contentburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Stoichiometric Relationships - Part 1Document22 pagesTopic 1 - Stoichiometric Relationships - Part 1burcak gecNo ratings yet
- Grade 11-Ib Chemistry Topic-5-Energetics and Thermochemistry Hess' Law Lab SheetDocument6 pagesGrade 11-Ib Chemistry Topic-5-Energetics and Thermochemistry Hess' Law Lab Sheetburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Stoichiometric Relationships - Part 1 - AnswersDocument26 pagesTopic 1 - Stoichiometric Relationships - Part 1 - Answersburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Personal Engagement: Defining The Problem and Selecting Variables Research Question and BackgroundDocument3 pagesPersonal Engagement: Defining The Problem and Selecting Variables Research Question and Backgroundburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Ap Quiz 1Document3 pagesAp Quiz 1burcak gecNo ratings yet
- Strong Interaction ÖdevDocument1 pageStrong Interaction Ödevburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Ap Unit9 WorksheetDocument5 pagesAp Unit9 Worksheetburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 3 4 p2 KeyDocument32 pagesTopic 2 3 4 p2 Keyburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Inter Molecular ForcesDocument2 pagesInter Molecular Forcesburcak gecNo ratings yet
- AP Unit10 Worksheet AnswersDocument4 pagesAP Unit10 Worksheet Answersburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Ap Unit10 WorksheetDocument4 pagesAp Unit10 Worksheetburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Ap Unit6 Worksheet AnswersDocument5 pagesAp Unit6 Worksheet Answersburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Ap Unit3 Worksheet AnswersDocument5 pagesAp Unit3 Worksheet Answersburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Ap Unit2 Worksheet AnswersDocument7 pagesAp Unit2 Worksheet Answersburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Ap Unit7 Worksheet AnswersDocument5 pagesAp Unit7 Worksheet Answersburcak gecNo ratings yet
- AP Unit9 Worksheet AnswersDocument5 pagesAP Unit9 Worksheet AnswersAAVANINo ratings yet
- Ap Unit6 WorksheetDocument4 pagesAp Unit6 Worksheetburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Ap Unit7 WorksheetDocument4 pagesAp Unit7 Worksheetburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Name - Period - AP Chemistry Unit 2 WorksheetDocument4 pagesName - Period - AP Chemistry Unit 2 Worksheetburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Ap Unit10 WorksheetDocument4 pagesAp Unit10 Worksheetburcak gecNo ratings yet
- AP Unit1 WorksheetDocument4 pagesAP Unit1 Worksheetburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Ap Unit3 WorksheetDocument4 pagesAp Unit3 Worksheetburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Ap Unit3 Worksheet AnswersDocument5 pagesAp Unit3 Worksheet Answersburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Ap Unit7 WorksheetDocument4 pagesAp Unit7 Worksheetburcak gecNo ratings yet
- AP Unit10 Worksheet AnswersDocument4 pagesAP Unit10 Worksheet Answersburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Botox Research PaperDocument9 pagesBotox Research PaperMarinaNo ratings yet
- Delivery Room ChecklistDocument2 pagesDelivery Room Checklistapi-3739910100% (5)
- Lesson 4 - Qualitative Research in Different Areas of KnowledgeDocument18 pagesLesson 4 - Qualitative Research in Different Areas of KnowledgePrincess AguiNo ratings yet
- Hume's Problems With InductionDocument188 pagesHume's Problems With InductionAvi Sion100% (2)
- 1b. Havik, Tielens in Conversation With J.Palaasmaa - Atmosphere - Compassion - and - Embodied - ExperienceDocument10 pages1b. Havik, Tielens in Conversation With J.Palaasmaa - Atmosphere - Compassion - and - Embodied - ExperienceLOGAN LEYTONNo ratings yet
- Aula 7 Cochran SmithDocument8 pagesAula 7 Cochran SmithVanderson MenezesNo ratings yet
- Group Counseling Strategies and Skills 8th Edition Jacobs Test BankDocument8 pagesGroup Counseling Strategies and Skills 8th Edition Jacobs Test Bankadelarichard7bai100% (26)
- Scheduling Content On Social Media Theory Evidence PDFDocument21 pagesScheduling Content On Social Media Theory Evidence PDFPaula MarquesNo ratings yet
- The (Re) Genesis of Values: Examining The Importance of Values For ActionDocument25 pagesThe (Re) Genesis of Values: Examining The Importance of Values For ActionJ LopezNo ratings yet
- Lead Workplace CommunicationDocument42 pagesLead Workplace CommunicationOliver BC Sanchez100% (1)
- Institutional Knowledge at Singapore Management University Institutional Knowledge at Singapore Management UniversityDocument25 pagesInstitutional Knowledge at Singapore Management University Institutional Knowledge at Singapore Management UniversityGianinaNo ratings yet
- Arrow Sisters - Tarot Ebook Masterclass For BeginnersDocument24 pagesArrow Sisters - Tarot Ebook Masterclass For BeginnersBharti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Managing Children With Challenging Behaviours Parents Meaning Making Processes in Relation To Their Children S ADHD DiagnosisDocument18 pagesManaging Children With Challenging Behaviours Parents Meaning Making Processes in Relation To Their Children S ADHD Diagnosispf36No ratings yet
- Service Marketing Triangle & SERVQUAL MODELDocument7 pagesService Marketing Triangle & SERVQUAL MODELSakshi ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Wiliam (2018) - Chapter 5 (Providing Feedback That Moves Learning Forward)Document32 pagesWiliam (2018) - Chapter 5 (Providing Feedback That Moves Learning Forward)JalNo ratings yet
- Effect of Organizational Structure On The Performance of OrganizationDocument40 pagesEffect of Organizational Structure On The Performance of OrganizationArren Khan100% (1)
- 5 Senses Lesson PlanDocument3 pages5 Senses Lesson Planapi-576257821No ratings yet
- FinalseniorprojectDocument15 pagesFinalseniorprojectapi-670716653No ratings yet
- Comunication ProcessDocument23 pagesComunication ProcessUmairNo ratings yet
- All SSC CGL (2020) 21 Shifts Vocab in One PDFDocument11 pagesAll SSC CGL (2020) 21 Shifts Vocab in One PDFpawan16796kumarNo ratings yet
- Proverbs 29:18a: Corporate Social Responsibility and Good Governance Second EditionDocument8 pagesProverbs 29:18a: Corporate Social Responsibility and Good Governance Second EditionLouelie Jean AlfornonNo ratings yet
- Middle School Research Paper Graphic OrganizerDocument8 pagesMiddle School Research Paper Graphic Organizerwonopwwgf100% (1)
- Lecture 2. Linear Classification: Prof. Simone FormentinDocument10 pagesLecture 2. Linear Classification: Prof. Simone FormentinCarlos Andres Pinzon LoaizaNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.3 Metacognitive Reading ReportDocument3 pagesAssignment No.3 Metacognitive Reading ReportNathaniel MateoNo ratings yet
- Jaspers Resume 4Document1 pageJaspers Resume 4api-531828040No ratings yet
- MATERI KD 3.26 BAHASA INGGRIS KELAS XII SEMESTER GANJIL-ARIF N Bagian 1 PDFDocument8 pagesMATERI KD 3.26 BAHASA INGGRIS KELAS XII SEMESTER GANJIL-ARIF N Bagian 1 PDFArif Nurrahman100% (1)
- PerfectionismDocument15 pagesPerfectionismNatacha Cabete100% (1)
- Kono Subarashii Sekai Ni Shukufuku Wo! - Volume 11Document227 pagesKono Subarashii Sekai Ni Shukufuku Wo! - Volume 11Gusti Ahmad Faiz67% (3)
- WNL Why You Should Start Work at 10am Adv PDFDocument5 pagesWNL Why You Should Start Work at 10am Adv PDFAndrzej0% (1)
- Mac 217 Investigative and Interpretive Reporting PDFDocument12 pagesMac 217 Investigative and Interpretive Reporting PDFDr. Nick IdokoNo ratings yet