Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CDI 6 Topic 3
Uploaded by
Stephen EstalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CDI 6 Topic 3
Uploaded by
Stephen EstalCopyright:
Available Formats
Module in CDI 6 Fire Technology & Arson Investigation 2021-2022 | HERMILINDA ORENZE
CAGAYAN STATE UNIVERSITY
College of Criminal Justice Education
Module in
CDI 6
FIRE TECHNOLOY & ARSON INVESTIGATION
Hermilinda P. Orenze, MSCrim
Topic 3: Phases of Burning/ Stages of Fire
Objective/s: Students should be able to fully understand the different stages of fire.
Lesson 1
Phases of Burning:
1. Incipient/Beginning phase – it is the initial stage of fire. The room is in normal
temperature.
2. Free burning phase – the second phase of burning in which materials or structures are
burning in the presence of adequate oxygen.
3. Smoldering phase – the final phase of burning wherein flame ceases but dense smoke
and heat completely fill the confined room.
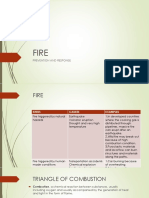
Classes of Fire:
1. Class A – materials involving vegetable fibers, wood, paper, straw, and grass. Nearly all
trash fire is considered Class A.
2. Class B – materials including petroleum products such as gasoline, fuel oils, lubricating
oils, and greases; animal fats such as butter, lard and tallow; natural gasses and
compressed gasses such as butane, propane hydrogen, and acetylene.
3. Class C – this type of fire involves electrical motors, electrical appliances and apparatus.
Use of water is usually dangerous because of the risk of electrical shock.
4. Class D – these materials involving combustible metals, alloys, or metal compounds,
either in a semi-solid or liquid state. They may further reduce in shavings, grindings,
granules, or dust.
Types of Heat Transmission:
1
Module in CDI 6 Fire Technology & Arson Investigation 2021-2022 | HERMILINDA ORENZE
1. Conduction – it is the transmission of heat through an object/medium or conductor, such
as pipe, metal, wire, or even wall.
2. Radiation – the transmission through the discharge and spread of heat from a heated or
burning source. This radiation takes place through the air or through space that cause
another flammable object to ignite.
3. Convection – it is the transmission of heat by the moving currents of liquid or gas. When
this gasses or liquids are heated, they start to move within themselves; and their free
motion, circulation starts.
Four Methods of Fire Extinguishment:
1. Cooling – the cooling process uses an extinguishing agent whose primary characteristics
are heat absorption. Water is the best general cooling agent for firefighting purposes.
2. Smothering – excludes the oxygen from the fuel so that the gases or vapors of the fuel
cannot ignite and continue the combustion.
3. Separation – the removal of the fuel in the combustion process so as not to continue the
combustion.
4. Inhibition/ Interruption of Chemical Reaction – the sequence of events in extinguishing
a fire with dry chemicals or vaporizing liquids includes some aspects of the first three
methods.
You might also like
- Cagayan State University: College of Criminal Justice Education Module in Cdi 6 Fire Technoloy & Arson InvestigationDocument3 pagesCagayan State University: College of Criminal Justice Education Module in Cdi 6 Fire Technoloy & Arson InvestigationStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Colegio de Santa Catalina de Alejandria Review Materials On Fire Tech. and Arson Investigation By: Sir Bimboy C. Cueno, CRMGST, MSCJDocument6 pagesColegio de Santa Catalina de Alejandria Review Materials On Fire Tech. and Arson Investigation By: Sir Bimboy C. Cueno, CRMGST, MSCJBimboy CuenoNo ratings yet
- Arson Prelim TopicDocument27 pagesArson Prelim TopicRALPH REVIN MALOONNo ratings yet
- WMSU Lec2Document51 pagesWMSU Lec2Kaiser CarloNo ratings yet
- Fire SafetyDocument9 pagesFire Safetysuryaa ksNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 CDI 216Document31 pagesUnit 1 CDI 216Elsa CalinayaNo ratings yet
- (Cdi 6) Fire Tech and Arson InvestigationDocument105 pages(Cdi 6) Fire Tech and Arson InvestigationCarl llagasNo ratings yet
- Fire Prevention and ProtectionDocument14 pagesFire Prevention and ProtectionvishwaNo ratings yet
- Fire Prevention Protection (Politeknik)Document39 pagesFire Prevention Protection (Politeknik)muhamad syazwan0% (1)
- Chapter 1 FireDocument11 pagesChapter 1 FireNikki Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- OSHA Module 3Document17 pagesOSHA Module 3Varsha GNo ratings yet
- Basic Fire Science Chemistry of Fire: 1. Fuel 2. Heat 3. Oxygen 4. Chemical ReactionDocument3 pagesBasic Fire Science Chemistry of Fire: 1. Fuel 2. Heat 3. Oxygen 4. Chemical ReactionJaszManaloAdraoNo ratings yet
- Ship Fire Prevention and ControlDocument57 pagesShip Fire Prevention and ControlAviral Manihal 80580% (1)
- ACFrOgCHbh1EUDMjvIdmsm0wLZxSRSgg6kbM LO7hfiQDudjAfjZqCGlgS2ayt SZT5lec80 XxjbCf5eXwLfkG07cggTIRf WWUVAW0bao U Ba5iyrY3rxWXyzY HWSZ GIRAhDaTon4filuzgDocument124 pagesACFrOgCHbh1EUDMjvIdmsm0wLZxSRSgg6kbM LO7hfiQDudjAfjZqCGlgS2ayt SZT5lec80 XxjbCf5eXwLfkG07cggTIRf WWUVAW0bao U Ba5iyrY3rxWXyzY HWSZ GIRAhDaTon4filuzgMarben ViernesNo ratings yet
- CVS 467chapter 3 Fire Danger and Protection - 231025 - 070408Document37 pagesCVS 467chapter 3 Fire Danger and Protection - 231025 - 070408Benon NyabutoNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety and Indus HygieneDocument6 pagesFire Safety and Indus HygieneJohn Paul JacalanNo ratings yet
- Criminal Justice Education: La Carlota City CollegeDocument56 pagesCriminal Justice Education: La Carlota City CollegePaulo Justin Tabangcora Oropilla100% (1)
- Module 9 Fire and ArsonDocument10 pagesModule 9 Fire and ArsonJohn Carl DomingoNo ratings yet
- Cagayan State University: College of Criminal Justice Education Module in Cdi 6 Fire Technoloy & Arson InvestigationDocument3 pagesCagayan State University: College of Criminal Justice Education Module in Cdi 6 Fire Technoloy & Arson InvestigationStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Fire Prevention and Fire Fighting in Plants/Working Places.: Presentation OnDocument97 pagesFire Prevention and Fire Fighting in Plants/Working Places.: Presentation Onjamunaa83No ratings yet
- Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationDocument4 pagesFire Technology and Arson InvestigationKent Ivan LeeNo ratings yet
- Week 5 DRRRDocument12 pagesWeek 5 DRRRArianne Ysabel JuradoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Fire SafetyDocument19 pagesModule 2 Fire SafetyNaveen S BasandiNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety EducationDocument47 pagesFire Safety EducationJulie Anne Ponteres EscañoNo ratings yet
- Basic Occupatio Nal Safety & HealthDocument8 pagesBasic Occupatio Nal Safety & HealthHurty James DayonNo ratings yet
- Fire PPT CompilationDocument9 pagesFire PPT CompilationDonna Mae MartinezNo ratings yet
- Module-2 Fire SafetyDocument19 pagesModule-2 Fire SafetyBuddies Da Neeghe PuroNo ratings yet
- ArsonDocument59 pagesArsonKaizen McrayNo ratings yet
- FIREDocument8 pagesFIRERikka EstudilloNo ratings yet
- Fire Technology and Arson Investigation. Power Point PresentationDocument75 pagesFire Technology and Arson Investigation. Power Point PresentationPs Seven Neutron79% (14)
- ArsonDocument3 pagesArsonshyna2003No ratings yet
- CDI6-Week 3 and 4Document23 pagesCDI6-Week 3 and 4macypearlNo ratings yet
- CDI Fire BehaviorDocument12 pagesCDI Fire BehaviorAdrivincent A. AlegreNo ratings yet
- Fire Fighting Course - PPSXDocument58 pagesFire Fighting Course - PPSXsafety86No ratings yet
- Fire Micz Crim Review PDFDocument101 pagesFire Micz Crim Review PDFJovie MasongsongNo ratings yet
- FireDocument33 pagesFireGaille Colynne GerardoNo ratings yet
- Cdi 6 DotDocument5 pagesCdi 6 DotChella VhicNo ratings yet
- DRRR Handout FIRE HAZARDSDocument4 pagesDRRR Handout FIRE HAZARDSdharleene fionaNo ratings yet
- ArsonDocument54 pagesArsonJolly PepeNo ratings yet
- Fire InvestigationDocument126 pagesFire InvestigationAbcede IloiloNo ratings yet
- CDI-6 Fire Arson Investigation FinalDocument89 pagesCDI-6 Fire Arson Investigation FinalRochel Mae DupalcoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Fire: Prevention and ResponseDocument8 pagesLesson 3: Fire: Prevention and ResponseMicaella GuintoNo ratings yet
- Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationDocument42 pagesFire Technology and Arson InvestigationLaurenz Logmao PascuaNo ratings yet
- Cagayan State University: Fire Extinguisher Is A Mechanical Device Usually Made of Metal, Containing ChemicalsDocument2 pagesCagayan State University: Fire Extinguisher Is A Mechanical Device Usually Made of Metal, Containing ChemicalsStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- FirefightingDocument36 pagesFirefightingEugene TamposNo ratings yet
- Fire Technology and Arson-InvestigationDocument43 pagesFire Technology and Arson-Investigationjeric deleon100% (1)
- Fire and ArsonDocument6 pagesFire and ArsonFrancheska Kate LabiosNo ratings yet
- Arson N Fire PresentationDocument135 pagesArson N Fire PresentationRoldan Bello100% (1)
- DRR Chapter 8Document3 pagesDRR Chapter 8Mary Bhabes MaestreNo ratings yet
- Fire Behavior and Arson InvestigationDocument17 pagesFire Behavior and Arson InvestigationHarold GaraoNo ratings yet
- Arson Review NotesDocument27 pagesArson Review NotesMonic BasconNo ratings yet
- Fire Behavior and Arson InvestigationDocument16 pagesFire Behavior and Arson InvestigationCherry Mie RautrautNo ratings yet
- Course Material For GCFFDocument235 pagesCourse Material For GCFFBeena BNo ratings yet
- Fire Technology and Arson Investigation ReviewerDocument11 pagesFire Technology and Arson Investigation ReviewerzachNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of FireDocument45 pagesChemistry of FireDéspoina BrieNo ratings yet
- Fire Technology and Investigation ReviewerDocument11 pagesFire Technology and Investigation ReviewerjhajhaboombeyNo ratings yet
- CDI6 (Fire Protection and Arson Investigation)Document43 pagesCDI6 (Fire Protection and Arson Investigation)Franco Angelo Reyes100% (10)
- Classification of Fire Fire ProtectionDocument2 pagesClassification of Fire Fire ProtectionKelvin SantosNo ratings yet
- Arson Module in MidtermDocument18 pagesArson Module in MidtermJasper EstevesNo ratings yet
- Fire Investigation: A Practical Guide for Students and Officers, Insurance Investigators, Loss Adjusters and Police OfficersFrom EverandFire Investigation: A Practical Guide for Students and Officers, Insurance Investigators, Loss Adjusters and Police OfficersNo ratings yet
- BulletDocument5 pagesBulletStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- ComputerDocument13 pagesComputerStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Creative NonDocument6 pagesCreative NonStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Duty DetailDocument6 pagesDuty DetailStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Counter-Action Against The Drug ProblemDocument33 pagesCounter-Action Against The Drug ProblemStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- 1st Prayer of The Year 2023Document1 page1st Prayer of The Year 2023Stephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Solo Parent ProfileDocument3 pagesSolo Parent ProfileStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Travel OrderDocument2 pagesTravel OrderStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- You Could Manipulate The PolygraphDocument2 pagesYou Could Manipulate The PolygraphStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Classroom Utilization Schedule 2 Semester 2023 Criminology 1 Year Section A Room 47 Time Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayDocument10 pagesClassroom Utilization Schedule 2 Semester 2023 Criminology 1 Year Section A Room 47 Time Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Morning PrayerDocument1 pageMorning PrayerStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Vacrec 5 11yrsDocument1 pageVacrec 5 11yrsStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- First Responder FormDocument2 pagesFirst Responder FormStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Activities in Questioned Documents ExaminationDocument23 pagesActivities in Questioned Documents ExaminationStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- MedzlistDocument2 pagesMedzlistStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Fiesta PrizesDocument2 pagesFiesta PrizesStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Deworning ListDocument7 pagesDeworning ListStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Estal Memo 2Document5 pagesEstal Memo 2Stephen EstalNo ratings yet
- BNS Form No. 7Document1 pageBNS Form No. 7Stephen Estal0% (1)
- Estal Memo 1Document5 pagesEstal Memo 1Stephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Spot IloDocument18 pagesSpot IloStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Initials Erning.Document7 pagesInitials Erning.Stephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Jose Spot ReportDocument3 pagesJose Spot ReportStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Cagayan State UniversityDocument3 pagesCagayan State UniversityStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Blotter Report SAMPLEDocument1 pageBlotter Report SAMPLEStephen Estal100% (1)
- Cagayan State University College of Criminal Justice EducationDocument2 pagesCagayan State University College of Criminal Justice EducationStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Cagayan State UniversityDocument3 pagesCagayan State UniversityStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Cagayan State University: Fire Extinguisher Is A Mechanical Device Usually Made of Metal, Containing ChemicalsDocument2 pagesCagayan State University: Fire Extinguisher Is A Mechanical Device Usually Made of Metal, Containing ChemicalsStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Cagayan State University: College of Criminal Justice Education Module in Cdi 6 Fire Technoloy & Arson InvestigationDocument3 pagesCagayan State University: College of Criminal Justice Education Module in Cdi 6 Fire Technoloy & Arson InvestigationStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Power and ElectricityDocument10 pagesPower and ElectricityElizabeth VivarNo ratings yet
- Thermoelectric Technical ReferenceDocument54 pagesThermoelectric Technical ReferenceVikram BorkhediyaNo ratings yet
- EnvisciDocument7 pagesEnvisciPrecious CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Question Answer: Free Knowledge Sharing WebsiteDocument8 pagesQuestion Answer: Free Knowledge Sharing Websitezohaib inksarNo ratings yet
- Force On Plate: Distance, MDocument32 pagesForce On Plate: Distance, MShah MohsinNo ratings yet
- Protok Realnog Fluida-3Document34 pagesProtok Realnog Fluida-3konticvNo ratings yet
- LIQUIDO-06 Quiz 1Document1 pageLIQUIDO-06 Quiz 1Krexia Mae L. LiquidoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document27 pagesLecture 1khalid mustafaNo ratings yet
- (CSEC Chemistry) Section A Notes and ESQsDocument191 pages(CSEC Chemistry) Section A Notes and ESQsNathaniel WhyteNo ratings yet
- CV Robin WaldmanetDocument4 pagesCV Robin Waldmanetyoali2326No ratings yet
- DLP in Final DemonstrationDocument10 pagesDLP in Final DemonstrationMisty MamintaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Lesson 1Document37 pagesModule 3 Lesson 1Juvy Jane DuarteNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On: "Multi-Terminal High Voltage Direct Current Transmission"Document22 pagesA Presentation On: "Multi-Terminal High Voltage Direct Current Transmission"Manish Kumar MeenaNo ratings yet
- The Differences Between Green Energy, Renewable Energy and MoreDocument1 pageThe Differences Between Green Energy, Renewable Energy and MoreroopakNo ratings yet
- Phosphorene As A Superior Gas Sensor DFT Coupled With NEGF StudyDocument21 pagesPhosphorene As A Superior Gas Sensor DFT Coupled With NEGF Study王孟謙No ratings yet
- Geo TechnicsDocument36 pagesGeo TechnicsVũ Trí MinhNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Smart GridDocument4 pagesMCQ On Smart GridJoshi RohitNo ratings yet
- AdsorptionDocument3 pagesAdsorptionali105No ratings yet
- Pollution in The OceansDocument13 pagesPollution in The OceansMory GamingNo ratings yet
- The Shepherd of Banbury's Rules To Judge of The Changes of The Weather, Grounded On Forty Years' Experience by Claridge, JohnDocument30 pagesThe Shepherd of Banbury's Rules To Judge of The Changes of The Weather, Grounded On Forty Years' Experience by Claridge, JohnGutenberg.org100% (1)
- Atomic Structure History Dalton-BohrDocument28 pagesAtomic Structure History Dalton-BohrFabrielle RafaelNo ratings yet
- Passage 1Document20 pagesPassage 1Muhammad AldiyanoorNo ratings yet
- SoilMechanics QuestionsDocument17 pagesSoilMechanics Questionsmilan subediNo ratings yet
- VTU Environmental Studies Exam Paper PDFDocument4 pagesVTU Environmental Studies Exam Paper PDFrahul_motabhaiNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and The Ocean PowerPointDocument25 pagesClimate Change and The Ocean PowerPointIslay JacksonNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Chemistry and MineralogyDocument11 pagesFundamentals of Chemistry and MineralogyEvi Intan SariNo ratings yet
- IAS Mains Geology Papers 1997: ExamraceDocument3 pagesIAS Mains Geology Papers 1997: ExamraceD DNo ratings yet
- FTC ATG Notes & QuestionsDocument301 pagesFTC ATG Notes & QuestionsGirish SreeneebusNo ratings yet
- You Searched For - SimpAsianDocument1 pageYou Searched For - SimpAsianZayar LwinNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Limiting ReactantsDocument2 pagesStudent Exploration: Limiting ReactantsaefNo ratings yet