Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HYDROLOGY Course Covers Water Cycle
Uploaded by
Patrick AgasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HYDROLOGY Course Covers Water Cycle
Uploaded by
Patrick AgasCopyright:
Available Formats
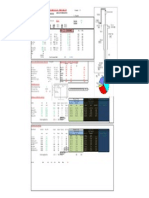
Course Name: HYDROLOGY
Course Description:
This course is concerned with the discussion of Hydrologic cycle; occurrence and analysis of
components of hydrologic cycle such as precipitation, evapotranspiration, infiltration, stream flow and
ground water; river and reservoir sedimentation; flood routing techniques; probability analysis for
hydrologic design; computer modeling for hydrologic systems.
Number of Units for Lecture, Laboratory, Fieldwork and Tutorial Lecture – 3 units
Number of Contact Hours per week Lecture – 3 hours
Prerequisite/Co-requisite: Mechanics of Fluids
Course Objectives
After completing this course, the student must be able to:
1. Develop a good understanding of the hydrologic cycle in terms of the processes and storage
relationships among its components.
2. Understand the physical meaning of different hydrologic models which capture/stimulate selected
hydrologic phenomena.
3. Solve practical problems, which involve numerical calculations from working formulas used for
hydrologic analysis and design.
4. Make solutions and decisions on a particular problem incorporating social and moral impact and put
into mind that a mediocre solution could cause a loss of life and/or property.
Course Outline
(6) 1. Hydrology and the Hydrologic Cycle
1.1 Difference Between Hydrology and Hydraulics.
1.2 The Hydrologic Cycle and the Human Impact.
1.3 Interrelationships of Phases of the Hydrologic Cycle: Evapotranspiration, Precipitation,
Infiltration/Percolation, Surface/Subsurface Runoff, Groundwater.
1.4 Philippine Watersheds: Delineation of Drainage Area, Sub-Basing/Physical Properties
Determination (Application in the Term Project).
(8) 2. Weather Basics (Meteorology): Atmospheric Waters
2.1 The Atmosphere: Composition, General Characteristics and Stability.
2.2 Introduction of Cloud Physics: Nucleation, Growth and Distribution.
2.3 Solar radiation and Earth’s Energy Balance.
2.4 General Circulation: Thermal Circulation and Earth’s Rotation.
2.5 Temperature: Geographic Distribution, Time Variation and Measurement
2.6 Humidity: Geographic Distribution, Time Variation and Measurement
(12) 3. Important Phases of Hydrologic Cycle
3.1 Precipitation: Occurrence and Measurement.
3.1.1 Formation, Forms (Philippine Setting), Types and Artificially Induced.
3.1.2 Measurement: Gages and Networks, Radar and Satellite Estimates.
3.1.3 Precipitation Data Analysis: Estimation of Missing data, Double-Mass Analysis, Mean Areal
Precipitation, Depth-Area-Duration Analysis, Frequency Analysis.
3.2 Evaporation, Transpiration, Interception and Depression Storage
3.2.1 Evaporation from Free Surface: Water Balance Method, Energy Balance Method, Mass-
Transfer Method, Penman Equation, Empirical Methods and Direct Measurement.
3.2.2 Transpiration and Evapo-transpiration.
3.2.3 Depression Storage.
3.3 Surface and Subsurface Runoff Phenomenon.
3.3.1 Rainfall-Runoff Processes: Mechanisms, Cycle, Water Stage-Discharge Relationship,
Measurement and Interpretation
3.3.2 Flood Prediction.
3.3.2.1 Graph Analysis: Characteristics, Unit Hydrograph Theory, Instantaneous Unit
Hydrograph, Synthetic Unit, Hydrographs, Applications.
3.3.2.2 Flow Routing Techniques: Channel Routing (Muskingum Method and Reservoir
Routing), Hydraulic Routing (St. Venant Equations and Numerical Solutions), Block-
Box Models.
3.4 Infiltration and Percolation: Processes and Measurements
3.5 Groundwater Storage and the Flow of Water
3.5.1 Hydrologic Investigations in Determining Subsurface Resource.
3.5.2 Hydraulics of Low of Groundwater.
3.5.3 Groundwater Exploration and Exploitation in the Philippines.
(7) 4. Concepts of Probability and Statistics Hydrology
4.1 Basic Probability Concepts and Probability Models.
4.2 Return Period, Design Storms and Design Turn-Off.
4.3 Regression and Correlation.
4.4 Risks Estimation.
(5) 5. Role of Hydrology in Water Resources Planning and Management in the Philippines.
5.1 Agencies Involved in the Collection of Hydrologic Data.
5.2 Problems of Watershed Management and Watershed Protection.
Laboratory Equipment Hydrology Apparatus Software
Suggested References
1. Mays, Larry W. 2004. Water Resources Engineering, 2005 Edition. USA.
2. Mays, Larry W.; Todd, David Keith. 2004. Groundwater Engineering. USA
3. Linsley, Ray K. ; Franzini, Joseph B.; Freyberg, David L.; Tchobanoglous, David L. 1992. Water
Resources Engineering, Fourth Edition. McGraw Hill.
4. Chow, Ven Te; Maidment, David R.; Mays, Larry W. 1988. Applied Hydrology. McGraw Hill.
5. Linsley, Ray K.; Kohler Max A.; Palhus, Joseph H. 1978. Hydrology for Engineers, SI Metric Edition. New
York USA.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Design of Glass Fin for Glass FaçadeDocument4 pagesDesign of Glass Fin for Glass FaçadeZaido Al HalabiNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Composite Construction Method PDFDocument38 pagesComposite Construction Method PDFChristopher JarvinNo ratings yet
- CalculationDocument5 pagesCalculationalok_rajpoot786100% (2)
- Introduction to Operation and Maintenance of Water Distribution SystemsDocument158 pagesIntroduction to Operation and Maintenance of Water Distribution SystemsVudumula VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Importance of Transportation Engineering for Society's Economy and Quality of LifeDocument3 pagesImportance of Transportation Engineering for Society's Economy and Quality of LifePatrick AgasNo ratings yet
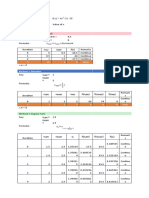
- Problem No. 1: Required: Solution:: Method 1: Incremental SearchDocument17 pagesProblem No. 1: Required: Solution:: Method 1: Incremental SearchPatrick AgasNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Examination: It Is The Agitation or Motion of Atoms and Molecules?Document7 pagesMid Term Examination: It Is The Agitation or Motion of Atoms and Molecules?Patrick AgasNo ratings yet
- SelfDocument3 pagesSelfPatrick AgasNo ratings yet
- I - Definition of TermsDocument3 pagesI - Definition of TermsPatrick AgasNo ratings yet
- Eastern Visayas State University - Ormoc City Campus Ormoc City, Leyte 6541Document3 pagesEastern Visayas State University - Ormoc City Campus Ormoc City, Leyte 6541Patrick AgasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Patrick AgasNo ratings yet
- Eastern Visayas State University - Ormoc City Campus Ormoc City, Leyte 6541Document4 pagesEastern Visayas State University - Ormoc City Campus Ormoc City, Leyte 6541Patrick AgasNo ratings yet
- Post Test #5 Measuring Capentry Work: 75 BM 73.33 BM 240 BM 288 BM 190 BM 810 BM 336 BM 1173.33 BMDocument3 pagesPost Test #5 Measuring Capentry Work: 75 BM 73.33 BM 240 BM 288 BM 190 BM 810 BM 336 BM 1173.33 BMPatrick AgasNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument1 pageNew Text DocumentPatrick AgasNo ratings yet
- Apply Technopreneurship Skills for Remote WorkDocument2 pagesApply Technopreneurship Skills for Remote WorkPatrick AgasNo ratings yet
- Finals TechnopreneurshipDocument6 pagesFinals TechnopreneurshipPatrick AgasNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere CompositionDocument3 pagesAtmosphere CompositionPatrick AgasNo ratings yet
- Nara Sean - Good JobDocument1 pageNara Sean - Good JobPatrick AgasNo ratings yet
- Example 1 ReportDocument2 pagesExample 1 ReportPatrick AgasNo ratings yet
- Vertical Parabolic Curve: Group 2 - Highway & Railroad EngineeringDocument46 pagesVertical Parabolic Curve: Group 2 - Highway & Railroad EngineeringPatrick AgasNo ratings yet
- Engineer conflict from prior workDocument6 pagesEngineer conflict from prior workPatrick AgasNo ratings yet
- Me 313 (Engineering Utilities) : Mid Term ExaminationDocument7 pagesMe 313 (Engineering Utilities) : Mid Term ExaminationPatrick AgasNo ratings yet
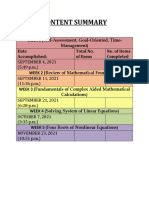
- Content SummaryDocument1 pageContent SummaryPatrick AgasNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING UTILITIES Activity 1Document2 pagesENGINEERING UTILITIES Activity 1Patrick AgasNo ratings yet
- H1 Architecture design documentDocument1 pageH1 Architecture design documentPatrick AgasNo ratings yet
- H1 Architecture design documentDocument1 pageH1 Architecture design documentPatrick AgasNo ratings yet
- H1 Architecture design documentDocument1 pageH1 Architecture design documentPatrick AgasNo ratings yet
- Lateral Load Resisting SystemsDocument55 pagesLateral Load Resisting Systemssuman33No ratings yet
- SMM7 35Document1 pageSMM7 35VimalNo ratings yet
- E Spec Guide BCI and VL PDFDocument36 pagesE Spec Guide BCI and VL PDFcphammond83No ratings yet
- 7-8 Sentrina Alaminos Cost ControlDocument60 pages7-8 Sentrina Alaminos Cost ControlQueenie PerezNo ratings yet
- Concrete Corbel Design To ACI 318-14 - Structural CalcDocument13 pagesConcrete Corbel Design To ACI 318-14 - Structural CalcĐàm ThànhNo ratings yet
- Truss BridgeDocument18 pagesTruss BridgeAkashNo ratings yet
- Construction Project TimelineDocument1 pageConstruction Project TimelineMichael HiiNo ratings yet
- (Hinze, 1955) Fundamentals of The Hydrodynamic Mechanism of Splitting in Dispersion ProcessDocument7 pages(Hinze, 1955) Fundamentals of The Hydrodynamic Mechanism of Splitting in Dispersion ProcessVeli Can CosarNo ratings yet
- Foundations On RockDocument2 pagesFoundations On RockAlaaGaballaNo ratings yet
- Northern Railway Line Doubling Project DetailsDocument6 pagesNorthern Railway Line Doubling Project DetailsPrasanta ParidaNo ratings yet
- New Series 6000Document78 pagesNew Series 6000Kintu MunabangogoNo ratings yet
- Review On Alkali-Activated Fly Ash Based Geopolymer ConcreteDocument9 pagesReview On Alkali-Activated Fly Ash Based Geopolymer ConcreteFlick TornNo ratings yet
- Case Study of The Chaq Chaq Dam FailureDocument8 pagesCase Study of The Chaq Chaq Dam FailureIjaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Determination of Flow Rate of Water in Concrete by Rilem Tube MethodDocument12 pagesDetermination of Flow Rate of Water in Concrete by Rilem Tube MethodKishore Nayak k100% (1)
- ASME and ANSI Standard Copper Water Tube and Solder-Joint Ends Valves and FittingsDocument1 pageASME and ANSI Standard Copper Water Tube and Solder-Joint Ends Valves and Fittingsaconibet9040No ratings yet
- Prefabricated Vertical DrainsDocument25 pagesPrefabricated Vertical Drainsdory.azarhotmail.comNo ratings yet
- Assignment 10CV35Document10 pagesAssignment 10CV35Abhijeeth NagarajNo ratings yet
- Eccentric Check (28-08-17) - Alson Rev.1 PDFDocument2 pagesEccentric Check (28-08-17) - Alson Rev.1 PDFAlsonChinNo ratings yet
- ADDAX PETROLEUM HYDRAULIC PROGRAMDocument1 pageADDAX PETROLEUM HYDRAULIC PROGRAMAderobaki GbengaNo ratings yet
- PUHY-P96TNU-A (-BS) 208-230V Product Data SheetDocument2 pagesPUHY-P96TNU-A (-BS) 208-230V Product Data Sheetjuraco20No ratings yet
- Stormwater Design and Specification ManuDocument20 pagesStormwater Design and Specification ManuKevin AgdumaNo ratings yet
- EAC NotesDocument105 pagesEAC NotesAyush JainNo ratings yet
- Geotech ReportDocument29 pagesGeotech ReportQasim Sultan100% (1)
- Fulltext1 PDFDocument3 pagesFulltext1 PDFvinothNo ratings yet
- LRFD Bridge Design ManualDocument26 pagesLRFD Bridge Design Manualrec serranoNo ratings yet
- Drop Formation Dynamics of Constant Low-Viscosity, Elastic FluidsDocument31 pagesDrop Formation Dynamics of Constant Low-Viscosity, Elastic FluidsoliviasaaNo ratings yet