Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Content Outline 2
Uploaded by
api-6064777220 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pagesThis document discusses heredity and how traits are passed from parents to offspring. It introduces Gregor Mendel, the father of genetics, who studied trait inheritance in pea plants. Traits are characteristics that can be inherited, such as physical features, personality, and adaptations that help organisms survive. Adaptations are inherited traits that provide advantages, like camouflage, body shapes, or sweat glands. The environment can also influence traits in offspring. Graphs are used to compare traits between individuals.
Original Description:
Original Title
content outline 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses heredity and how traits are passed from parents to offspring. It introduces Gregor Mendel, the father of genetics, who studied trait inheritance in pea plants. Traits are characteristics that can be inherited, such as physical features, personality, and adaptations that help organisms survive. Adaptations are inherited traits that provide advantages, like camouflage, body shapes, or sweat glands. The environment can also influence traits in offspring. Graphs are used to compare traits between individuals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pagesContent Outline 2
Uploaded by
api-606477722This document discusses heredity and how traits are passed from parents to offspring. It introduces Gregor Mendel, the father of genetics, who studied trait inheritance in pea plants. Traits are characteristics that can be inherited, such as physical features, personality, and adaptations that help organisms survive. Adaptations are inherited traits that provide advantages, like camouflage, body shapes, or sweat glands. The environment can also influence traits in offspring. Graphs are used to compare traits between individuals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
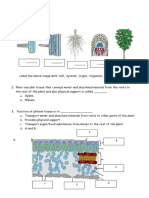
Heredity
I. Heredity- passing of traits from parents to offspring
II. Gregor Mendel
A. father of genetics
B. Studied pea plants
C. Asked the question: Why don’t the offspring look just like their parent pea plants?
Why don’t the brother/sister pea plants all look exactly the same?
III. Traits-Characteristics of an individual that can be inherited from parents.
A. Inherited- all living things receive characteristics from their parents
1. Plant examples
a) Tall v short
b) Round leaves v pointed leaves
c) Purple flowers v pink flowers
2. Animal examples
a) White fur v brown fur
b) Ears stick up v ears lay flat
c) Long snout v short snout
3. Human examples
a) Eye color
b) Height
c) Right-handed v left-handed
B. Gene- the instructions for making you
C. Different classifications of traits
1. Physical
2. Personality
3. adaptable
B. Adaptations- inherited characteristics that help an organism survive
1. Competition- 2 or more living things need the same resource to survive
2. Predator- An animal that eats other animals.
3. Prey- An animal that is eaten by other animals.
4. Advantage- a characteristic that can help an organism compete in its
environment
5. Plant examples
a) Sharp thorns on roses (to keep animals from eating them)
b) Deep roots for trees (can get water deep in the soil)
c) Waxy coating on cactus (helps hold in moisture)
d) Migration and hibernation (survive changing weather conditions)
6. Animal examples
a) Camouflage- A pattern, color, or shape that helps a living thing
blend into its environment. (chameleon)
b) Color of skin allows sunlight to be absorbed (Dark alligator)
c) Body shape (Giraffe's long neck to reach leaves at top of trees)
7. Human examples
a) Sweating (can control body temperature)
b) Different shape teeth (ability to eat a variety of foods)
c) Opposable thumbs (ability to hold tools)
8. Certain traits help predators acquire food and certain traits help prey
escape predators.
C. Environment-
1. can influence traits
2. Plants examples
a) Too little water, yellow leaves
b) Certain nutrients in soil, different color flower
c) Too little sunlight, small fruit
3. Animals examples
a) Too little food, smaller size
b) No shelter, sickness
4. Humans examples
a) Pollution, weaker lungs
b) Lack of exercise, greater chance of heart problems
c) Unhealthy food, overweight
D. Graphs will be used to compare and contrast traits amongst classmates
Standards
PA Academic Grade 4 3.1.4.B1 Describe features that are observable in both
Standards parents and their offspring.
PA Academic Grade 4 3.1.4.B5 Identify observable patterns in the physical
Standards characteristics of plants or groups of animals.
PA Academic Grade 4 3.3.4.C.2 identify physical characteristics that appear in
Standards both parents and offspring and differ between
families, strains or species.
M03.D-M.2.1.4 Translate information from one type of display to another. Limit to
pictographs, tally charts, bar graphs, and tables. Example: Convert a tally chart to a bar
graph.
You might also like
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemNo ratings yet
- Tugas Luring Jumat, 4 Desember 2020Document1 pageTugas Luring Jumat, 4 Desember 2020novaNo ratings yet
- Classification FinalDocument8 pagesClassification FinalLeonita SwandjajaNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom WorksheetDocument6 pagesPlant Kingdom WorksheetpuspaonnieNo ratings yet
- Bio Class 11 NCERTDocument168 pagesBio Class 11 NCERTCharan YadavNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer ADocument19 pagesBiology Reviewer AJane CastroNo ratings yet
- Biological Science Reviewer 2Document20 pagesBiological Science Reviewer 2Kelvin Insigne100% (1)
- Activity Pack &student Book Answers - 8Document86 pagesActivity Pack &student Book Answers - 8Eliana FalahatNo ratings yet
- Biology 1ch?Document5 pagesBiology 1ch?harshuvish009No ratings yet
- Study of Life: Biology MajorDocument21 pagesStudy of Life: Biology MajorBernard BanalNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Life Test 2fassessment Biology 1Document4 pagesCharacteristics of Life Test 2fassessment Biology 1api-375761980No ratings yet
- Wildlife Ecology Nptel Quiz AnswersDocument11 pagesWildlife Ecology Nptel Quiz AnswersBhavesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- GENBIO2Document5 pagesGENBIO2John Lloyd RaponNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 4 - Q2 - W3Document8 pagesDLL - Science 4 - Q2 - W3Judy Mae LacsonNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Biology NCERT Textbook Chapter 1 The Living World ExamplerDocument6 pagesClass 11 Biology NCERT Textbook Chapter 1 The Living World ExamplerTitan 2000No ratings yet
- 7 DiversityDocument13 pages7 Diversitytara tuitionNo ratings yet
- 11 Bio ch7-8 Quiz SolutionDocument4 pages11 Bio ch7-8 Quiz SolutionConnor BrooksNo ratings yet
- Biological Science Reviewer 2Document20 pagesBiological Science Reviewer 2Jo Hn VengzNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Biology Class 11Document168 pagesNCERT Exemplar Biology Class 11Khushboo GuptaNo ratings yet
- 3HSB ReviewDocument5 pages3HSB ReviewMelva GuerraNo ratings yet
- Wildlife EcologyDocument12 pagesWildlife Ecologysamarth.kumar2021No ratings yet
- GARINGALAO, Module 4&5 Sci102Document24 pagesGARINGALAO, Module 4&5 Sci102Shane GempasaoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3Document1 pageQuiz 3Den Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- Biological Science Reviewer 2Document20 pagesBiological Science Reviewer 2kristinebarredoNo ratings yet
- Biological Science ReviewerDocument28 pagesBiological Science Reviewerslim_101100% (1)
- Insight Link 6 - Answer Keys - WBDocument19 pagesInsight Link 6 - Answer Keys - WBElvie ColladoNo ratings yet
- 05.end of Unit Test U1Document2 pages05.end of Unit Test U1OCHANDO MARTINEZ MONICANo ratings yet
- Final Exam Worksheet With Answer Key - gr3Document5 pagesFinal Exam Worksheet With Answer Key - gr3mariaananemo666No ratings yet
- Bio Sci 2Document20 pagesBio Sci 2MARJORYNo ratings yet
- Biological Science Reviewer 2Document20 pagesBiological Science Reviewer 2Eden PatricioNo ratings yet
- PrintDocument1 pagePrintabdihusein708No ratings yet
- Juan Luis Nevarez Mrs. Catherine/BIOL 1408 July 30, 2020Document5 pagesJuan Luis Nevarez Mrs. Catherine/BIOL 1408 July 30, 2020Juan Luis Nevarez Martinez100% (1)
- Multiple Choice Questions (1 PT Each) : Ant1050 Final Fall 2009 NameDocument8 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (1 PT Each) : Ant1050 Final Fall 2009 NameChand Basha ShaikNo ratings yet
- "The Food Chain" Comprensión Lectora InglésDocument9 pages"The Food Chain" Comprensión Lectora InglésAna Basterra100% (18)
- Chapter 5 AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter 5 AnswersVladimir TrajanovikjNo ratings yet
- Xi - Biology - Work Sheet - Competency Based QNSDocument9 pagesXi - Biology - Work Sheet - Competency Based QNSSudhansu SahooNo ratings yet
- Bioknowledgy Quick Quiz On Classification of Biodiversity (5.3)Document2 pagesBioknowledgy Quick Quiz On Classification of Biodiversity (5.3)Micaela FernandezNo ratings yet
- DiversityDocument6 pagesDiversitySrijita RoyNo ratings yet
- 2021 Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organism MCQsDocument6 pages2021 Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organism MCQsGauravNo ratings yet
- Revision Test:: Long TermDocument17 pagesRevision Test:: Long Termsachin sakuNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Selection & SpeciationDocument16 pagesTopic 3 Selection & SpeciationSHASWIN RAJ A/L KARTTIKAN MoeNo ratings yet
- 1ST PERIODICAL EXAM (Envi - Sci.)Document4 pages1ST PERIODICAL EXAM (Envi - Sci.)Jevie GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Reading Explorer 2nd EditionDocument7 pagesReading Explorer 2nd EditionKurllyne Fava0% (1)
- Unit 1, Diversity of Living Things, Unit Test - 1Document7 pagesUnit 1, Diversity of Living Things, Unit Test - 1hewleet100% (1)
- Soal SMA English VersionDocument14 pagesSoal SMA English VersionNuni Rismayanti NurQalbiNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Science 10Document3 pagesSummative Test Science 10Zaifel Pacillos100% (2)
- Jasmine Castillo - Copy of PT 6Document8 pagesJasmine Castillo - Copy of PT 6api-651802534No ratings yet
- DLL Scie G4 Q2 W3Document7 pagesDLL Scie G4 Q2 W3Daniel MingoyNo ratings yet
- Evolution, Evidence and Mechanisms: Primary TEKS SupportedDocument4 pagesEvolution, Evidence and Mechanisms: Primary TEKS SupportedNoura RoseNo ratings yet
- Els - DLL - 1ST Long QuizDocument4 pagesEls - DLL - 1ST Long QuizMitze QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Science - Living Organisms QuestionsDocument3 pagesScience - Living Organisms QuestionsJay AntonyNo ratings yet
- Evolution Test Bank 1Document20 pagesEvolution Test Bank 1alshalabinezardonia96No ratings yet
- Summative TEstDocument14 pagesSummative TEstxoxkakidoxoxNo ratings yet
- Science SPL Material PDFDocument289 pagesScience SPL Material PDFViji VjNo ratings yet
- Science Quiz Bee Grade 3Document2 pagesScience Quiz Bee Grade 3Dinah Natavio Rodriguez DeGuzman88% (17)
- Jamb Syllabus For BiologyDocument26 pagesJamb Syllabus For BiologyFaithNo ratings yet
- Sma Negeri 3 Bandung: Exercise-Bio Ii Classification SystemDocument5 pagesSma Negeri 3 Bandung: Exercise-Bio Ii Classification SystemNur Almira RahardyanNo ratings yet
- Biology General ObjectivesDocument12 pagesBiology General ObjectivesRay chijiokeNo ratings yet
- Science - Classification of Living Things - QuizizzDocument3 pagesScience - Classification of Living Things - QuizizzArina KhusnaNo ratings yet
- Springhouse Middle School After School Tutoring Permission SlipDocument1 pageSpringhouse Middle School After School Tutoring Permission Slipapi-606477722No ratings yet
- Jenni Carlson Gombos Recommendation - 2023Document1 pageJenni Carlson Gombos Recommendation - 2023api-606477722No ratings yet
- TranscriptsDocument1 pageTranscriptsapi-606477722No ratings yet
- Prosem Mentor 2 EvalDocument1 pageProsem Mentor 2 Evalapi-606477722No ratings yet
- Jenni Carlson Mancini RecommendationDocument1 pageJenni Carlson Mancini Recommendationapi-606477722No ratings yet
- Pro Sem Mentor EvalDocument1 pagePro Sem Mentor Evalapi-606477722No ratings yet
- Weiler Danielson FinalDocument3 pagesWeiler Danielson Finalapi-606477722No ratings yet
- Pro Sem Supervisor 2evalDocument1 pagePro Sem Supervisor 2evalapi-606477722No ratings yet
- Pro Sem Supervisor EvalDocument1 pagePro Sem Supervisor Evalapi-606477722No ratings yet
- Stern 2nd Half Final EvalDocument4 pagesStern 2nd Half Final Evalapi-606477722No ratings yet
- Cover Letter For Student TeachingDocument2 pagesCover Letter For Student Teachingapi-606477722No ratings yet
- Text SetDocument2 pagesText Setapi-606477722No ratings yet
- Paper On LD Adhd Id AutorecoveredDocument12 pagesPaper On LD Adhd Id Autorecoveredapi-606477722No ratings yet
- 9M113 RaketaDocument7 pages9M113 RaketaJovanović DraganNo ratings yet
- Evaporation Loss During Sprinkler IrrigationDocument10 pagesEvaporation Loss During Sprinkler IrrigationAymen Al Al-BaajNo ratings yet
- Academic PressureDocument7 pagesAcademic PressureJohn Mark MontillaNo ratings yet
- Micro Cold Storage: Ecozen SolutionsDocument2 pagesMicro Cold Storage: Ecozen SolutionsVikram DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- EleDocument40 pagesEleakela_lifeNo ratings yet
- Cestodes - Summary TableDocument2 pagesCestodes - Summary TableLace Azores100% (4)
- Ahmad Nazim Ali: Personal InformationDocument3 pagesAhmad Nazim Ali: Personal InformationNazim AliNo ratings yet
- The Mathematical Gazette Volume 59 Issue 407 1975 (Doi 10.2307 - 3616804) Crockett Johnson - A Construction For A Regular HeptagonDocument6 pagesThe Mathematical Gazette Volume 59 Issue 407 1975 (Doi 10.2307 - 3616804) Crockett Johnson - A Construction For A Regular HeptagonEduardo CostaNo ratings yet
- TroxerutinDocument3 pagesTroxerutincarlosNo ratings yet
- Safed MusliDocument8 pagesSafed Muslimetro1cupidNo ratings yet
- The Story of KeeshDocument4 pagesThe Story of KeeshEmman SanoNo ratings yet
- A Healthy Man Is A Happy ManDocument2 pagesA Healthy Man Is A Happy ManYan KyawNo ratings yet
- Texts So Good He Cant Ignore Sassy Texting Secrets For Attracting High-Quality Men (And Keeping The One You Want) (Bryans, Bruce)Document167 pagesTexts So Good He Cant Ignore Sassy Texting Secrets For Attracting High-Quality Men (And Keeping The One You Want) (Bryans, Bruce)Carmen StătescuNo ratings yet
- Nekisha Taneil - Bikini Body at HomeDocument18 pagesNekisha Taneil - Bikini Body at HomeMegan86% (7)
- ECG - Check - CardiacDesign 1Document4 pagesECG - Check - CardiacDesign 1alissonafsNo ratings yet
- Guru Nadi - Full 3 PartsDocument35 pagesGuru Nadi - Full 3 Partspm plassanalNo ratings yet
- Heron of Alexandria-Math Contributions-Square Root Method and Area of A TriangleDocument11 pagesHeron of Alexandria-Math Contributions-Square Root Method and Area of A TriangleDr Srinivasan Nenmeli -KNo ratings yet
- 1314lab - Stoichiometry and Measurements LabDocument4 pages1314lab - Stoichiometry and Measurements Labapi-239310645No ratings yet
- CE Refresher Nov 2022 - Tuzon - Set 7 F2FDocument2 pagesCE Refresher Nov 2022 - Tuzon - Set 7 F2Femielyn lafortezaNo ratings yet
- A Study of Permeability and Tortuosity of Concrete: August 2005Document10 pagesA Study of Permeability and Tortuosity of Concrete: August 2005khawar aliNo ratings yet
- SHAW SADP Dewpoint Meter Specification SheetDocument4 pagesSHAW SADP Dewpoint Meter Specification SheetAyman FawzyNo ratings yet
- Magoosh Manhattan Barrron High Frequency WordsDocument25 pagesMagoosh Manhattan Barrron High Frequency WordsSalman SufiNo ratings yet
- Economic Analysis (Summary) A. Recent Economic Developments Gross Domestic Product Dynamics. Armenia Experienced Remarkable Economic GrowthDocument7 pagesEconomic Analysis (Summary) A. Recent Economic Developments Gross Domestic Product Dynamics. Armenia Experienced Remarkable Economic GrowthcarlotilloNo ratings yet
- Construction Management: Divya Negi Faculty, B.Voc., ABITDocument11 pagesConstruction Management: Divya Negi Faculty, B.Voc., ABITDIVYA NEGINo ratings yet
- Medifa 8000 Service ManuelDocument44 pagesMedifa 8000 Service ManuelhoudaNo ratings yet
- Venkat Guntipally An Accomplished IT ProfessionalDocument8 pagesVenkat Guntipally An Accomplished IT ProfessionalVenkat GuntipallyNo ratings yet
- English and Filipino HeadlinesDocument5 pagesEnglish and Filipino HeadlinesGISELLE DIMAUNNo ratings yet
- S2VNA Operating ManualDocument271 pagesS2VNA Operating ManualHever RodriguezNo ratings yet
- TsofDocument2 pagesTsofPratik RatwaniNo ratings yet
- KS3 Science 2009 Paper 2 Level 3-6Document32 pagesKS3 Science 2009 Paper 2 Level 3-6Macwise IngabireNo ratings yet