Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sryan Bruen: The Industrial Revolution Notes (JC History)
Uploaded by
(1A) Arran Kelly0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesOriginal Title
cb3cd328-4ef4-4e75-8b25-a398ce8f44bd
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesSryan Bruen: The Industrial Revolution Notes (JC History)
Uploaded by
(1A) Arran KellyCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Sryan Bruen
The Industrial Revolution Notes (JC History)
Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Britain?
• Improved agricultural methods provided more and better food supplies.
• Several new machines were invented in Britain at this time, which speeded up
the manufacture of industrial goods.
• Britain ruled over many countries called colonies. The colonies provided
Britain with cheap cotton and other raw materials.
• Transport improved greatly in Britain due to the construction of better roads,
canals and railways.
Changes in Textile-Making
• Textile making moved into large buildings called factories.
• Textile making came to be controlled by rich factory owners.
• Former craftsmen had to seek work in growing cities, where the factories were
situated. They were cruelly exploited by the factory owners.
Inventions during the Industrial Revolution
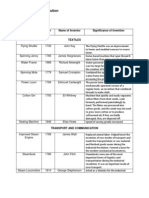
Spinning Inventions
Inventor Invention Description
James Hargreaves Spinning Jenny Could spin eight threads at
a time
Richard Arkwright Water Frame Could spin hundreds of
threads
Weaving Inventions
Inventor Invention Description
John Kay Flying Shuttle Doubled the speed of
weaving
Edmund Cartwright Power Loom Used steam power to
weave cloth quickly
Coal Mining Inventions
Inventor Invention Description
Thomas Newcomen Steam Engine Pump water out of the
mines
Abraham Darby Conversion of coal into Used to smelt iron ore to
coke make iron and steel
Steam Engine by Thomas Newcomen
• Thomas Newcomen's Steam Engine was the greatest invention of the Industrial
Revolution.
• In 1763, James Watt invented the Rotary Steam Engine which could be used
to turn other machines in factories so it mechanised and speeded up
manufacturing.
Iron and Steel
• In 1709, Abraham Darby (as above in the coal mining inventions) discovered
how to convert coal into coke which became the chief source of power for
smelting iron ore.
• In 1974, Henry Cort discovered 'Puddling and Rolling' which was a better
way of making wrought iron. Liquid pig iron was stirred and then run through
rollers to make sheets of wrought iron.
• In 1856, Henry Bessemer invented a Converter. This involved blowing hot
air through melted pig iron to burn off its impurities. Resulted in better and
cheaper steel.
What were the effects of the Industrial Revolution?
• The Growth of Cities: Poor people crowded into urban areas in search of
work.
• Trade: Britain became rich through increased overseas trade. British colonies
provided raw materials for Britain's growing factories as well as markets for
Britain's manufactured goods.
• Clothing: Cotton began to replace wool as the most popular fabric. Big
machines made cloth more cheaply than before, so the cost of clothing
decreased. However, workers were so poorly paid that they themselves could
afford few clothes.
• Working Conditions: People working in factories and mines were exploited
cruelly.
What actions did the people take to prevent the cruelty?
• Workers fought to establish trade unions.
• Many people became socialists.
You might also like
- 11 Industrial RevolutionDocument3 pages11 Industrial RevolutionEvan BrownNo ratings yet
- Industrial RevolutionDocument57 pagesIndustrial RevolutionrohanNo ratings yet
- Innovations and Inventions of The Industrial RevolutionDocument2 pagesInnovations and Inventions of The Industrial RevolutionabcNo ratings yet
- Steam, Steel and Spark: The People and Power Behind the Industrial RevolutionFrom EverandSteam, Steel and Spark: The People and Power Behind the Industrial RevolutionNo ratings yet
- How Machines Changed Cultures : Industrial Revolution for Kids - History for Kids | Timelines of History for Kids | 6th Grade Social StudiesFrom EverandHow Machines Changed Cultures : Industrial Revolution for Kids - History for Kids | Timelines of History for Kids | 6th Grade Social StudiesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- History ProjectDocument14 pagesHistory Projectvaghelashweta92No ratings yet
- Inventions and Impact of Industrial Revolution HTGHDocument9 pagesInventions and Impact of Industrial Revolution HTGHJanvi SinghiNo ratings yet
- Industrial RevolutionDocument13 pagesIndustrial RevolutionAlessia BagnascoNo ratings yet
- Industrial Revolution in Britain HandoutDocument6 pagesIndustrial Revolution in Britain HandoutAlriNo ratings yet
- Industrial RevolutionDocument26 pagesIndustrial RevolutionrrrhesariezenNo ratings yet
- Industrial RevolutionDocument22 pagesIndustrial RevolutionRyan KeeneyNo ratings yet
- Revolution and The Rise of CapitalismDocument12 pagesRevolution and The Rise of Capitalismsharma mishraNo ratings yet
- The Industrial Revolution: © Student Handouts, IncDocument65 pagesThe Industrial Revolution: © Student Handouts, IncRomeo Azriel Austria RustiaNo ratings yet
- History & Civics: TopicDocument19 pagesHistory & Civics: TopicKunshdeep Singh BediNo ratings yet
- Industrial RevolutionDocument22 pagesIndustrial RevolutionMarvinGarciaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Revolution by Ojha SirDocument12 pagesIndustrial Revolution by Ojha SirAbcdNo ratings yet
- Industrial RevolutionDocument20 pagesIndustrial RevolutionKaylie BetzlerNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLesson Planapi-588923378No ratings yet
- Industrial RevolutionDocument28 pagesIndustrial RevolutionmmillorenNo ratings yet
- Industrial RevolutionDocument41 pagesIndustrial RevolutionHakim FazNo ratings yet
- Industrial RevolutionDocument41 pagesIndustrial RevolutionRizwana MiduryNo ratings yet
- Feb10 Industrial RevolutionDocument41 pagesFeb10 Industrial RevolutionsycNo ratings yet
- The Industrial Revolution InventionsDocument2 pagesThe Industrial Revolution InventionsRoxanne GodinhoNo ratings yet
- Chandigarh University: The Industrial Revolution Soft Skills Reetesh Dhakad 18BBT1105 Palakjot Kour Sodhi 18BBT1115Document39 pagesChandigarh University: The Industrial Revolution Soft Skills Reetesh Dhakad 18BBT1105 Palakjot Kour Sodhi 18BBT1115Reetesh DhakadNo ratings yet
- Cotton Mill and Water: Factory Spinning Weaving Machinery Cotton Industrial Revolution Mechanisation Machine ToolDocument34 pagesCotton Mill and Water: Factory Spinning Weaving Machinery Cotton Industrial Revolution Mechanisation Machine ToolDhruv PatelNo ratings yet
- The First Industrial RevolutionDocument12 pagesThe First Industrial Revolutionmaria fernandez gamoNo ratings yet
- Industrial RevolutionDocument24 pagesIndustrial RevolutionHafsah SiddiquaNo ratings yet
- 1 The Beginning of IndustrializationDocument1 page1 The Beginning of IndustrializationJoshua SabuelbaNo ratings yet
- The Industrial Revolutions USD-Sogang 20170418Document79 pagesThe Industrial Revolutions USD-Sogang 20170418sadrackpagilingNo ratings yet
- The First Industrial RevolutionDocument45 pagesThe First Industrial Revolutionfauzi villegasNo ratings yet
- Western III NotesDocument74 pagesWestern III NotesRahma MohamedNo ratings yet
- The Industrial RevolutionDocument24 pagesThe Industrial RevolutionDeirdre HoughtonNo ratings yet
- Industrial RevolutionDocument84 pagesIndustrial RevolutionJed BanzalesNo ratings yet
- Kens Notes Session 4Document16 pagesKens Notes Session 4Lê NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Industrial RevolutionDocument12 pagesIndustrial RevolutionDiana Cordea100% (1)
- Industrial RevolutionDocument115 pagesIndustrial RevolutionLisa Tal100% (1)
- A Brief History of The Cotton Industry: Wool Loom Shed (C. 1840)Document3 pagesA Brief History of The Cotton Industry: Wool Loom Shed (C. 1840)Muhammad ShahidNo ratings yet
- Inventions Information Handout 2017Document4 pagesInventions Information Handout 2017PRINCES SARAH REYES PERALTANo ratings yet
- Industrial Revolution NotesDocument4 pagesIndustrial Revolution Notesishanvi tripathiNo ratings yet
- The Steam EngineDocument13 pagesThe Steam EngineDaria DyabloNo ratings yet
- The Inventions of Industrial RevolutionDocument15 pagesThe Inventions of Industrial RevolutionSara QayyumNo ratings yet
- The Industrial Revolution: Investigate How Science and Technology Changed the World with 25 ProjectsFrom EverandThe Industrial Revolution: Investigate How Science and Technology Changed the World with 25 ProjectsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Ppt. by Dylan KelloggDocument14 pagesPpt. by Dylan KelloggDylan KelloggNo ratings yet
- Sssssssss DsDocument5 pagesSssssssss DsAsia VelascoNo ratings yet
- The Industrial RevolutionDocument65 pagesThe Industrial Revolutionmisssees100% (4)
- The Industrial RevolutionDocument18 pagesThe Industrial RevolutionsjkinahdujonNo ratings yet
- Isiah Rutledge: Industrial Revolution 10 EventsDocument11 pagesIsiah Rutledge: Industrial Revolution 10 EventsIsiah RutledgeNo ratings yet
- Industrial RevolutionDocument44 pagesIndustrial RevolutionRina100% (2)
- Hsslive-1H (9) INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION-signed PDFDocument162 pagesHsslive-1H (9) INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION-signed PDFAgam SinghNo ratings yet
- TechnologyDocument8 pagesTechnologyStefanus BrianNo ratings yet
- Industrial Revolution Textbook PagesDocument5 pagesIndustrial Revolution Textbook Pagesapi-306956814No ratings yet
- History Revision Agricultural Industrial Revolutions 161221155125Document7 pagesHistory Revision Agricultural Industrial Revolutions 161221155125olagunjuprecious2007No ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Outline A History of Western SocietyDocument7 pagesChapter 22 Outline A History of Western Societydrea4152No ratings yet
- Legacies of the Industrial Revolution: Steam Engine and Transportation - History Book for Kids | Children's HistoryFrom EverandLegacies of the Industrial Revolution: Steam Engine and Transportation - History Book for Kids | Children's HistoryNo ratings yet
- Innovations and Inventions During The Industrial Revolution (History Project)Document13 pagesInnovations and Inventions During The Industrial Revolution (History Project)Vansh Gupta50% (2)
- 13 Inventions - Docx HistoryDocument13 pages13 Inventions - Docx HistoryMohammed Hashim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Home Learning Project 1: The Industrial Revolution: Section 1: Setting The SceneDocument12 pagesYear 8 Home Learning Project 1: The Industrial Revolution: Section 1: Setting The SceneAnusha BhangaleNo ratings yet
- IELTS Academic Training Reading Practice Test #6. An Example Exam for You to Practise in Your Spare TimeFrom EverandIELTS Academic Training Reading Practice Test #6. An Example Exam for You to Practise in Your Spare TimeNo ratings yet
- The Industrial Revolution: © Student Handouts, IncDocument115 pagesThe Industrial Revolution: © Student Handouts, Incagent2100No ratings yet
- The Parliamentary Tradition: Key WordsDocument2 pagesThe Parliamentary Tradition: Key Words(1A) Arran KellyNo ratings yet
- The Parliamentary Tradition - FLASHCARDSDocument3 pagesThe Parliamentary Tradition - FLASHCARDS(1A) Arran KellyNo ratings yet
- The Great Irish Famine - FLASHCARDSDocument2 pagesThe Great Irish Famine - FLASHCARDS(1A) Arran KellyNo ratings yet
- Irish Famine WorksheetDocument1 pageIrish Famine Worksheet(1A) Arran KellyNo ratings yet
- 1st German Culture Lesson 1 2020Document20 pages1st German Culture Lesson 1 2020(1A) Arran KellyNo ratings yet
- Transportation Law SyllabusDocument17 pagesTransportation Law SyllabusIchimaru TokugawaNo ratings yet
- The Design of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) Plan For Biscuit PlantDocument7 pagesThe Design of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) Plan For Biscuit Plantttk_maniNo ratings yet
- Draconomicon 2 Metallic Dragons PDF 73Document3 pagesDraconomicon 2 Metallic Dragons PDF 73gabiNo ratings yet
- 80 MT Crawler CraneDocument40 pages80 MT Crawler CraneramyaNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutics Exam 3 - This SemesterDocument6 pagesPharmaceutics Exam 3 - This Semesterapi-3723612100% (1)
- Using The BJAC Properties Package With Aspen EDRDocument9 pagesUsing The BJAC Properties Package With Aspen EDRShitalbioNo ratings yet
- Write A Short Note On Carbon FiberDocument4 pagesWrite A Short Note On Carbon FiberMOJAHID HASAN Fall 19No ratings yet
- 17 - MiG-19 Day Interceptor & Two-Seat VariantsDocument47 pages17 - MiG-19 Day Interceptor & Two-Seat VariantsEduardoFadul100% (1)
- Petroleum Products KolkataDocument3 pagesPetroleum Products KolkatabrijeshkynNo ratings yet
- Aircraft StructureDocument11 pagesAircraft StructureVagesh VagesNo ratings yet
- GDPDocument6 pagesGDPBenedetta NardiNo ratings yet
- Asphyxia NeonatorumDocument35 pagesAsphyxia NeonatorumMuhammad RagilNo ratings yet
- Soil Resources Inventory For Land Use PlanningDocument9 pagesSoil Resources Inventory For Land Use PlanningmehNo ratings yet
- Calvino - The Daughters of The MoonDocument11 pagesCalvino - The Daughters of The MoonMar BNo ratings yet
- NU632 Unit 4 Discussion CaseDocument2 pagesNU632 Unit 4 Discussion CaseMaria Ines OrtizNo ratings yet
- Front Axle, Tie Rod and Drag Link (A21) - 20: Parts ListDocument4 pagesFront Axle, Tie Rod and Drag Link (A21) - 20: Parts ListdgloshenNo ratings yet
- Zeroing Neural Networks, An Introduction To, A Survey Of, and Predictive Computations For Time-Varying Matrix ProblemsDocument24 pagesZeroing Neural Networks, An Introduction To, A Survey Of, and Predictive Computations For Time-Varying Matrix ProblemsgoatcockNo ratings yet
- Anatomy-Head and NeckDocument94 pagesAnatomy-Head and NeckXahid IqbalNo ratings yet
- PHontDawg Vol.2 2007Document8 pagesPHontDawg Vol.2 2007Tanczos AndrasNo ratings yet
- P.B.B.SC Nsg. Syllabus Original PDFDocument57 pagesP.B.B.SC Nsg. Syllabus Original PDFRajalakshmi SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- TNSTCDocument1 pageTNSTCMohamed MNo ratings yet
- A Framework For Developing and Evaluating Utility Substation Cyber Security - Schneider ElectricDocument10 pagesA Framework For Developing and Evaluating Utility Substation Cyber Security - Schneider ElectricHugh cabNo ratings yet
- AirMAX Sector Antennas DSDocument7 pagesAirMAX Sector Antennas DSalexsdiazNo ratings yet
- Report NovelDocument12 pagesReport NovelHasan Moh'd Al AtrashNo ratings yet
- BP503T Unit 1-3Document432 pagesBP503T Unit 1-3Solomon GyampohNo ratings yet
- Sealand Equipment GuideDocument5 pagesSealand Equipment GuidePool Jaime Quispe CordovaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Origin of Khmer Land and PeopleDocument16 pagesWeek 3 - Origin of Khmer Land and PeopleAlienNo ratings yet
- Aqa CHM4 W QP Jun09Document20 pagesAqa CHM4 W QP Jun09dharmik47No ratings yet
- OOO The Word Center: Love Is Our HeadquartersDocument39 pagesOOO The Word Center: Love Is Our HeadquartersNkor IokaNo ratings yet
- Fluidization - Expansion Equations For Fluidized Solid Liquid Systems (Akgiray and Soyer, 2006)Document10 pagesFluidization - Expansion Equations For Fluidized Solid Liquid Systems (Akgiray and Soyer, 2006)Moisés MachadoNo ratings yet