Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rules Physics
Uploaded by
Marwan AmirOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rules Physics
Uploaded by
Marwan AmirCopyright:
Available Formats
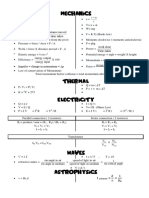
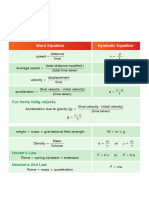
v u
Density = mass / volume a=
t
S = ut + ½ a t2 V= u + at
F = ma W= mg
total distance moved
Average speed = F = K X (Hooks law)
total time taken
Moment= force X distance from the pivot Moments clockwise = moments anticlockwise
Pressure = force / Area = F / A P = ρhg
work done
Work = force X distance moved = F . d Power =
Time taken
Kinetic energy = ½ m v2 Potential energy = mgh = weight X height
energy output
Efficiency = X 100 Momentum = mass x velocity
energy input
𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑚𝑜𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑢𝑚 𝑖𝑚𝑝𝑢𝑙𝑠𝑒 ∆𝑝
Impulse = change in momentum = Δp Force = = =𝑡
𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒
Law of conservation of Momentum:
Total momentum before collision = total momentum after collision
Q = m c T
P1 V1 = P2 V2
P x t = m c T
Q = m x Lf Q = m x Lv
P x t = m x Lf P x t = m x Lv
Q = n e- I=Q/t
V=E/Q V= I R (Ohms Law)
P=IV = I2 R = V2 / R E=IVt = I2 R t = (V2 / R) t
Parallel connection ( 2 resistors) Series connection ( 2 resistors)
Rt = product / sum = (R1 . R2) / (R1 + R2) Rt = R1 + R2
Vt = V1 = V2 Vt = V1 + V2
I = I1 + I2 I = I1 = I2
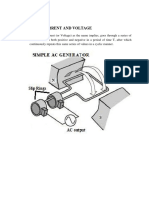
Transformer
Vin N
Iin Vin = Iout Vout = in
Vout N out
V=λf f = 1/ T , T = 1/f
sin angle in air speed of light in air 1
refractive index = = =
sin angle in medium speed of light in medium sin critical angle
V=d/t
You might also like
- Rules Physics 2023Document1 pageRules Physics 2023SalmaNo ratings yet
- Equations (Continued) : ElectricityDocument1 pageEquations (Continued) : Electricitykrishna_pipingNo ratings yet
- Exit Level Science: Texas Assessment of Knowledge and SkillsDocument36 pagesExit Level Science: Texas Assessment of Knowledge and SkillsLê DuongNo ratings yet
- EquationsDocument4 pagesEquationsyatihninhlaingNo ratings yet
- Igcse Physics FormulasDocument5 pagesIgcse Physics Formulasmohammad affan merchantNo ratings yet
- List of Data, Formulae and RelationshipsDocument5 pagesList of Data, Formulae and RelationshipsRicky ChanNo ratings yet
- Essential Formulae and SI Units SummaryDocument4 pagesEssential Formulae and SI Units SummaryAayan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Calculative Methods or Formulas 1) Speed. Average Speed 2) VelocityDocument8 pagesCalculative Methods or Formulas 1) Speed. Average Speed 2) Velocityjyoti mishraNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Formulas (Kinematic) Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 pagesAP Physics Formulas (Kinematic) Cheat Sheet: by ViaRose AimanNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS - EQUATIONS (1) KdksaklsDocument2 pagesPHYSICS - EQUATIONS (1) KdksaklsKry9No ratings yet
- Paper 2 Formula Sheet 1Document1 pagePaper 2 Formula Sheet 1mochiNo ratings yet
- A Level FormulaeDocument1 pageA Level FormulaeVarun PanickerNo ratings yet
- 2021 AP Physics I FormulasDocument1 page2021 AP Physics I FormulasRocketNo ratings yet
- Jambite.com: Improve your scores on JAMB and WAEC physics formulasDocument3 pagesJambite.com: Improve your scores on JAMB and WAEC physics formulasAhmad0% (1)
- IGCSE Equations To LearnDocument2 pagesIGCSE Equations To LearnRose SmithNo ratings yet
- Brandenz1229 - Physics Final Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesBrandenz1229 - Physics Final Cheat SheetSyeda SadiaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Equations and ConceptsDocument10 pagesMechanics Equations and ConceptsFaith Laurence SarmientoNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics FormulaeDocument2 pagesIGCSE Physics FormulaeelizabethNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument7 pagesFormula SheetCarlos GómezNo ratings yet
- Formulea BookletDocument4 pagesFormulea Bookletalan soukeNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 1 Edexcel Physics GCSEDocument3 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 1 Edexcel Physics GCSEAli AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Tahsili Physics-Problems and QuestionsDocument75 pagesTahsili Physics-Problems and Questionsflynn riderNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Formula SheetDocument4 pagesO Level Physics Formula SheetAryan Kinger100% (1)
- Physics Important ConceptsDocument2 pagesPhysics Important Conceptsazhar aliNo ratings yet
- Physics Important ConceptsDocument2 pagesPhysics Important Conceptsazhar aliNo ratings yet
- Physics Important ConceptsDocument2 pagesPhysics Important Conceptsazhar aliNo ratings yet
- Higher Physics Formula Sheet: S. BakkeDocument5 pagesHigher Physics Formula Sheet: S. BakkeAbid RedwanNo ratings yet
- Mechanics, thermal physics, waves & optics, electricity & magentism, modern physicsDocument11 pagesMechanics, thermal physics, waves & optics, electricity & magentism, modern physicsTibra ArkaNo ratings yet
- Released Phys SciDocument24 pagesReleased Phys SciAnthony CharlesNo ratings yet
- Fis 24Document6 pagesFis 24syafrina novitaNo ratings yet
- Formulas For Phisics, 1st GradeDocument3 pagesFormulas For Phisics, 1st GradeRozalina PetrovaNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Formula Sheet 2Document2 pagesO Level Physics Formula Sheet 2Taha Maroof100% (1)
- Second condition of equilibrium; ∑τ = 0 Physics Formulas by MeasurementsDocument2 pagesSecond condition of equilibrium; ∑τ = 0 Physics Formulas by MeasurementsJan AlamNo ratings yet
- Soup EquatioonDocument2 pagesSoup EquatioonDylan LlanosNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 2 Y11Document50 pagesPhysics Paper 2 Y11Nisha zehraNo ratings yet
- Physics Uniform Circular MotionDocument4 pagesPhysics Uniform Circular MotionMica BernardoNo ratings yet
- All Physics Formulas For O Levels Physics by Ethan Wu: Celsius To KelvinDocument6 pagesAll Physics Formulas For O Levels Physics by Ethan Wu: Celsius To KelvinReuben CachiaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Fluid MechanicsDocument1 pageGeneral Physics 1 Fluid MechanicsJam JungNo ratings yet
- 105 Eq Sheet 2Document1 page105 Eq Sheet 2NadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- 105 Eq Sheet 3Document2 pages105 Eq Sheet 3NadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- A Level Physics Data+Formulae+RelationshipsDocument4 pagesA Level Physics Data+Formulae+RelationshipsAleksandarNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current FundamentalsDocument23 pagesAlternating Current FundamentalsDiane Conanan DumalaogNo ratings yet
- Midterm Review PDFDocument16 pagesMidterm Review PDFMt RushNo ratings yet
- Equations Chapters 10, 11, and 14Document1 pageEquations Chapters 10, 11, and 14Marykate SuretteNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulas: MotionDocument6 pagesPhysics Formulas: MotionfarujoyNo ratings yet
- The Physics Hypertextbook 1Document5 pagesThe Physics Hypertextbook 1govindraj87No ratings yet
- Physics Formulas Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesPhysics Formulas Cheat SheetAmal Irshad100% (1)
- A Levels Physics Formula RelationshipDocument8 pagesA Levels Physics Formula Relationships ramanNo ratings yet
- A Level Physics Data Formulae Relationships PDFDocument8 pagesA Level Physics Data Formulae Relationships PDFD-Cristen OrlandoNo ratings yet
- AS Physics EquationsDocument1 pageAS Physics EquationsAhmad MohdNo ratings yet
- AS Level Equations For PhysicsDocument1 pageAS Level Equations For PhysicsAhmad MohdNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulae 4NADocument5 pagesPhysics Formulae 4NAmuhdnurimann7No ratings yet
- List of formulae and relationshipsDocument7 pagesList of formulae and relationships王涛No ratings yet
- P53451A GCE Physics Data Booklet 8PH0Document4 pagesP53451A GCE Physics Data Booklet 8PH0Tony LiNo ratings yet
- A Level Physics Data Formulae RelationshipsDocument8 pagesA Level Physics Data Formulae RelationshipsArnav yogeshwar PurmessurNo ratings yet
- AQA A Level Physics Equation SheetDocument5 pagesAQA A Level Physics Equation SheetCamila Lorenzoni100% (2)
- 0654 IGCSE Formulae (Equations)Document3 pages0654 IGCSE Formulae (Equations)BigBoiNo ratings yet
- Physics - NotesDocument4 pagesPhysics - Notesiremkis079No ratings yet
- Isaac Gcse Physics Book Teacher VersionDocument116 pagesIsaac Gcse Physics Book Teacher VersionhappyproofNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Environmental Management 0680/12Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Environmental Management 0680/12Koushik MurakundaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel May/June 2022 exam instructionsDocument2 pagesEdexcel May/June 2022 exam instructionsMarwan AmirNo ratings yet
- Biology O. Level Igcse Definitions: Downloaded by Success GroupsDocument9 pagesBiology O. Level Igcse Definitions: Downloaded by Success GroupsMarwan AmirNo ratings yet
- 10 Security MeasuresDocument1 page10 Security MeasuresMarwan AmirNo ratings yet
- Windstar 2000 U1147Document1 pageWindstar 2000 U1147adris banquethNo ratings yet
- 40 DensityandSpecificHeat Sp12Document11 pages40 DensityandSpecificHeat Sp12fernandoribeiromocNo ratings yet
- Pedestrian Stacker Truck: P-SeriesDocument4 pagesPedestrian Stacker Truck: P-SeriesTRINDADENo ratings yet
- Sci 7summative Test 4Document2 pagesSci 7summative Test 4OSZEL JUNE BALANAYNo ratings yet
- M7 Complete User Manual enDocument26 pagesM7 Complete User Manual enAnonymous qZY4l1aCEuNo ratings yet
- Hager Wiring Accessories Catalogue 1120Document64 pagesHager Wiring Accessories Catalogue 1120lizukyNo ratings yet
- 2 - Introduction To Graphic CommunicationDocument34 pages2 - Introduction To Graphic Communicationapi-3815216100% (1)
- Monograph Function: Definition and AnalysisDocument13 pagesMonograph Function: Definition and AnalysisdesignbaseNo ratings yet
- Insurance Claims Manual For Brokers and CustomersDocument43 pagesInsurance Claims Manual For Brokers and CustomersSUNIL PUJARI0% (1)
- Control M PDFDocument608 pagesControl M PDFlrcapoNo ratings yet
- Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0210008 A1Document9 pagesPatent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0210008 A1AblaqNo ratings yet
- Acceleration EnvelopingDocument2 pagesAcceleration EnvelopingNhà Đất Tân AnNo ratings yet
- Mir100 Hook DatasheetDocument2 pagesMir100 Hook DatasheetS NguyenNo ratings yet
- Kyambogo University: Examination PermitDocument1 pageKyambogo University: Examination PermitAmuronNo ratings yet
- Ser 158Document6 pagesSer 158lolaNo ratings yet
- l4 03 Measuring Purchasing PerformanceDocument150 pagesl4 03 Measuring Purchasing PerformanceMahendra Kumar Soni100% (3)
- Supplement Nice Specialty Areas and Work Role Ksas and TasksDocument548 pagesSupplement Nice Specialty Areas and Work Role Ksas and Tasksadi8066No ratings yet
- Introduction To Measurement SystemsDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Measurement SystemsAkash JamesNo ratings yet
- VTU Engineering Physics Practical (Lab) - 3.Transistor-CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesVTU Engineering Physics Practical (Lab) - 3.Transistor-CharacteristicsGaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Engineering For Steel ConstructionDocument2 pagesEngineering For Steel ConstructionBiju Muttathukatil0% (1)
- 3.2.A UnitConversionDocument6 pages3.2.A UnitConversionevan martinezNo ratings yet
- Philips Az1500 Az1505 SMDocument33 pagesPhilips Az1500 Az1505 SMJuan Carlos PerdomoNo ratings yet
- Autonomous Vehicle Implementation Predictions: Implications For Transport PlanningDocument19 pagesAutonomous Vehicle Implementation Predictions: Implications For Transport PlanningLethal11No ratings yet
- Plastic Deformation Tool Die Yield STR Ength Geometry of The Die. Stresses Applied Co Mpressive Stretch Bend Shear StressesDocument102 pagesPlastic Deformation Tool Die Yield STR Ength Geometry of The Die. Stresses Applied Co Mpressive Stretch Bend Shear StressesEbrahim AliNo ratings yet
- JLG 450 A AJ II Parts 3121243 4-15-08 Global EnglishDocument492 pagesJLG 450 A AJ II Parts 3121243 4-15-08 Global EnglishCarlos E. Delius SciaroniNo ratings yet
- QDocument27 pagesQHassanAhmedNo ratings yet
- Alphaparts REFERENCE-2013-1Document135 pagesAlphaparts REFERENCE-2013-1Georgi GeorgievNo ratings yet
- Wollam - Bryan API Q2 PDFDocument18 pagesWollam - Bryan API Q2 PDFsyedainahmadNo ratings yet
- 7 Area ComputationDocument22 pages7 Area Computationsajid khanNo ratings yet
- Understand ElectrostaticsDocument39 pagesUnderstand Electrostaticsanup vermaNo ratings yet