Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Some of Many MEP Coordination Condition's
Uploaded by
mahesh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views12 pagesOriginal Title
Some of Many MEP Coordination Condition's(1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views12 pagesSome of Many MEP Coordination Condition's
Uploaded by
maheshCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
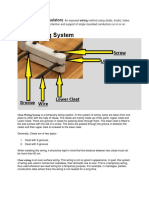
MEP Coordination Conditions
Venkatesh Muthu: Possible cases, Reasoning and Solutions
Ceiling VS MEP
Case: Ceiling to MEP clearance should be Minimum 150mm.
Reason: Often time it is less than 150mm resulting in Final stage issues such
as light head clashing with MEP containments, Diffuser neck does not have
enough length to fix Volume control damper.
Solution: All ceilings should have an imaginary boundary projecting upwards
to run clash. This boundary should be adjustable since this length may vary
from case to case.
How it is done now: We will model a temporary ceiling
Which is 150mm approx. above the actual ceiling
level.
Structure Vs MEP
Case: Structure clash with MEP is not always acceptable. It varies case by case resulting in
situation where each clash has to be reviewed .
Reason: Structure Beam less than 300 mm depth cannot be given opening due to structural
integrity failure. At the same time beams which has more than 300 mm depth cannot be given
opening in the bottom 150mm, since the strengthening rebar runs in the perimeter of the
beams.
Solution: Beams can be given opening only in the middle portions. Otherwise the MEP
elements should run below the beams as mentioned in the images below.
How it is done: Manual verification. This is a tedious process if the clash is more than 50 in
Numbers.
Lintel Beam Vs MEP
Case: Lintel Beams above the doors are not modelled in the conventional BIM process. This
beam may be 200mm thick. Although it is not modelled, it is installed in site . These beams are
either RC concrete or Steel structures which cannot be penetrated at any cost.
Reason: These beams are not given openings since the load above the door will act upon the
door head.
Solution: During MEP coordination, Care should be taken to avoid running MEP elements above
the door. Failing to do such practice may result in unwanted problems in the site execution.
How it is done?: It is done manually by checking all the available doors.
MEP Services below Light & Sensors
Case: MEP services such as Cable tray, Pipes and Ducts are not allowed below lights
and sensors.
Reason: Services below sensors may interrupt the environmental factors which are
intended to be read. Services below light will result in shadows which in turn result
in poor visibility.
Solution: Services below sensors and light should be avoided. The minimum
clearance required are mentioned in the data sheets .
How it is done?: It is done manually.
Electrical vs Electrical
Case: Spacing Between cable tray when arranged vertically should be accessible for cable pulling in
the future.
Reason: Less spacing during coordination will make cable laying very difficult. Cable pulling rollers
need to be placed on cable trays for pulling cables. At times cable trays need to be removed for this
reason.
Solution: Spacing between should be a parameter or a condition during clash coordination.
How it is done: It is done manually .
Electrical VS LC Systems
Case: Low Voltage 230V cables and Extra Low voltage cables (5V,12V,24V) should not be
placed in close vicinity to each other.
Reason: Magnetic field around the power cables will affect the signal in the ELV cable. This
will result in signal distortion.
Solution: Power cables should be placed at least 300mm away from the signal cable(AV
Intercom, PA , TV ,Access control and Telephone cables). Fiber optic signal has no impact on
its signals due to magnetic field.
How it is done?; It is done manually.
Panel Clearance:
Case: Electrical panel should have minimum clearance on the door side for future
maintenance.
Reason: As per international guidelines, Minimum spacing required for the operating
personnel's to work.
Solution: Transparent object modelled on the panel door side to make sure that the area is
cleared during clash detection.
How it is done: It is done manually or by modelling transparent object on the door side.
Plumbing Fittings vs Electrical Fixtures
Case: In kitchen , Laundry room and Toilet(Shaver socket, Oven Socket, Mixer Grinder
socket) should have a minimum clearance of 300mm on all the sides.
Reason: Plumbing fixtures and electrical sockets in close proximity is not allowed even
though the later is splash proof.
Solution: Plumbing fixtures were modelled with transparent sphere to run clash between
the electrical fixtures.
How it is done: All though we can run the clash , this is an additional task to run.
Incompatible systems
Case: Kitchen Exhaust duct and Gas pipe are not compatible to each other. Similarly Gas pipe
and Electrical systems are not compatible.
Reason: As the naming indicates, these two systems in close proximity will result in fire
accidents. Heat and Fuel will leave the systems damaged beyond repair.
Solution: It is often preferred to have separate risers, corridors for systems such as this.
How it is done: This is done manually by taking enough precautions during design stage itself.
Door Swings in Egress Path
Case: Door Swings in Egress path should always be outward .
Reason: During panic hours, Inward swing will result in stampede near exits.
Solution: Door swings should be checked for swing direction which falls in
egress path.
How it is done?: It is done manually
Cable Trays vs Piping
Case: Pipes are not allowed to run in parallel with cable trays in bottom . Although pipes are
allowed to cross making sure that there is no fittings in the crossing region.
Reason: In a long run , Dripping from pipes due to condensation, leakage will result in short
circuits since wet cables has low insulation resistance.
Solution: Pipes should not be allowed to run on top of cable trays.
How it is done: It is done manually. This is a time taking process since rerouting will cause many
technical problems such as pressure loss, material loss and signal loss in ELV cables.
Note : Below installations are preferred.
You might also like
- Black&Decker. ADVANCED HOME WIRING Current With 2012-2015 Codes PDFDocument409 pagesBlack&Decker. ADVANCED HOME WIRING Current With 2012-2015 Codes PDFbandihoot100% (4)
- Electrical System of BuildingDocument86 pagesElectrical System of BuildingCatherineNo ratings yet
- A Fish Tape Is Used To Pull Stranded or Solid Wire Through Metal or PVC ConduitDocument23 pagesA Fish Tape Is Used To Pull Stranded or Solid Wire Through Metal or PVC ConduitthewhiteeagleNo ratings yet
- Safety Clearance For Transformer - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocument5 pagesSafety Clearance For Transformer - Electrical Notes & ArticlessankhaginNo ratings yet
- A Guide to the Home Electric System: Home Guide Basics Series, #2From EverandA Guide to the Home Electric System: Home Guide Basics Series, #2No ratings yet
- Potenzialausgleich FundamenterderDocument5 pagesPotenzialausgleich FundamenterderYatendra Singh HadaNo ratings yet
- Basic Residential Electrical Wiring Circuits Rough in and Codes GuideDocument10 pagesBasic Residential Electrical Wiring Circuits Rough in and Codes Guidejohnnywalker2000No ratings yet
- Digital LED Thermometer with Microcontroller AVR ATtiny13From EverandDigital LED Thermometer with Microcontroller AVR ATtiny13Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Open Wiring On InsulatorsDocument7 pagesOpen Wiring On InsulatorslouieNo ratings yet
- The First-Time Homeowner's Survival Guide: A Crash Course in Dealing with Repairs, Renovations, Property Tax Issues, and Other Potential DisastersFrom EverandThe First-Time Homeowner's Survival Guide: A Crash Course in Dealing with Repairs, Renovations, Property Tax Issues, and Other Potential DisastersRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Electrical Wiring Estimation 170529115347Document45 pagesElectrical Wiring Estimation 170529115347habib AnsariNo ratings yet
- Ee04 801-EsdeDocument20 pagesEe04 801-EsdeChandra Bose KnNo ratings yet
- Stem: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles V11From EverandStem: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles V11No ratings yet
- Understanding MEP 1st, 2nd and 3rd Fix WorksDocument4 pagesUnderstanding MEP 1st, 2nd and 3rd Fix WorksAddis MekuriaNo ratings yet
- Cabletrays Institute Technical Bulletin3Document2 pagesCabletrays Institute Technical Bulletin3ahmodahNo ratings yet
- Emes Mos e 00Document18 pagesEmes Mos e 00bpdvietNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument13 pagesUntitledvishal yaduvanshiNo ratings yet
- Objective:-Different Types of Wiring Systems and Methods of Electrical Wiring What Is Electrical Wiring?Document23 pagesObjective:-Different Types of Wiring Systems and Methods of Electrical Wiring What Is Electrical Wiring?Ateeq Ul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Ee04 801-EsdeDocument222 pagesEe04 801-EsdeChandra Bose Kn50% (2)
- Fluke - How Cables and Connectors Impact Measurement UncertaintyDocument4 pagesFluke - How Cables and Connectors Impact Measurement UncertaintyMatias RamosNo ratings yet
- Testing TET113 NOTE 444Document37 pagesTesting TET113 NOTE 444bello musaNo ratings yet
- Cabletrays Institute Technical Bulletin3Document2 pagesCabletrays Institute Technical Bulletin3MarkNo ratings yet
- HV EarthingDocument3 pagesHV EarthingarunbavaNo ratings yet
- Domestic WiringDocument22 pagesDomestic WiringDeepa Shree100% (1)
- Electrical WiringDocument8 pagesElectrical WiringRahul SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Design Report XXXDocument41 pagesDesign Report XXXashikin100% (1)
- Building Services Project (Electrical 2) Auto Saved)Document8 pagesBuilding Services Project (Electrical 2) Auto Saved)Asyraf RobaniNo ratings yet
- Foam Cutting Power SupplyDocument3 pagesFoam Cutting Power Supplyxiaoboshi100% (1)
- Method-Statement For Electrical InstallationDocument31 pagesMethod-Statement For Electrical Installationmozartjr22100% (3)
- MS For Electrical InstallationDocument31 pagesMS For Electrical InstallationPatricia Jackson100% (1)
- Cable LayoutsDocument22 pagesCable LayoutsSomnath Das100% (2)
- Basic Elect Rial - CompiledDocument73 pagesBasic Elect Rial - CompiledElsha OlegarioNo ratings yet
- HDB-Supervision Guide For Electrical Engineering WorksDocument24 pagesHDB-Supervision Guide For Electrical Engineering WorksZhu Qi Wang0% (1)
- Method StatementDocument31 pagesMethod Statementrommel duran100% (1)
- Wiring MethodsDocument9 pagesWiring MethodsSwagat Pradhan100% (1)
- Selecting the Correct Cable SizeDocument34 pagesSelecting the Correct Cable SizeSquinkle100% (1)
- Day 2 - Electrical - Q - ADocument5 pagesDay 2 - Electrical - Q - ASunil KumarNo ratings yet
- A2 Electronics CourseworkDocument8 pagesA2 Electronics Courseworkf5d17e05100% (4)
- Domestic WiringDocument43 pagesDomestic Wiringnihartn2020No ratings yet
- Service ConnDocument9 pagesService Connutpal nathNo ratings yet
- B. Electrical Systems 1. Recommended Electrical Services System For Proposed Hotel and Mall Development 1.1. Electrical Supply Distribution SystemDocument10 pagesB. Electrical Systems 1. Recommended Electrical Services System For Proposed Hotel and Mall Development 1.1. Electrical Supply Distribution SystemShanaia BualNo ratings yet
- How To:: Install An Electric ShowerDocument3 pagesHow To:: Install An Electric ShowerHoward HavElectricNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - Wiring SystemsDocument20 pagesTopic 5 - Wiring SystemsVictorNo ratings yet
- New Chapter Four LastDocument36 pagesNew Chapter Four LastephremNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcome: Estimating and Costing in Electrical EngineeringDocument15 pagesLearning Outcome: Estimating and Costing in Electrical EngineeringJEFFREY BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- Wiring Systems and Types of House WiringDocument15 pagesWiring Systems and Types of House WiringpsahooNo ratings yet
- BLDNG Utilities RSW 3-1Document29 pagesBLDNG Utilities RSW 3-1Steven PadillaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Cable Laying - Electrical RevolutionDocument7 pagesMethods of Cable Laying - Electrical RevolutionjibooryNo ratings yet
- Domestic InstallatiuonDocument10 pagesDomestic InstallatiuonJoseph MvurachenaNo ratings yet
- CCTV Troubleshooting Guide for Signal Attenuation IssuesDocument49 pagesCCTV Troubleshooting Guide for Signal Attenuation IssuesAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Methods of Wiring and Different Types of Wiring Systems: o o o o o o o oDocument10 pagesMethods of Wiring and Different Types of Wiring Systems: o o o o o o o orabin ruwaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Strength DesignDocument4 pagesIndustrial Strength DesignPhạm Văn TưởngNo ratings yet
- Bim DictionaryDocument51 pagesBim DictionaryRogerNo ratings yet
- SPDCL SPDCL Solar Roof Top Application Form: Consumer DetailsDocument1 pageSPDCL SPDCL Solar Roof Top Application Form: Consumer DetailsmaheshNo ratings yet
- AMVI PREvious English PDFDocument88 pagesAMVI PREvious English PDFmaheshNo ratings yet
- 31 2022 Amvi Notifn20221231205032Document23 pages31 2022 Amvi Notifn20221231205032DILEEP COMPUTERSNo ratings yet
- Photo: ST ND RD THDocument2 pagesPhoto: ST ND RD THmaheshNo ratings yet
- Form-5 Application For Transfer of AccountDocument1 pageForm-5 Application For Transfer of AccountAishaNo ratings yet
- BIMobject Revit Style GuideDocument57 pagesBIMobject Revit Style GuideCristian Lemus BorjaNo ratings yet
- BIMobject Content Style GuideDocument22 pagesBIMobject Content Style GuidemaheshNo ratings yet
- View A-A: Ports: 2X 1/2" NPT .38 2X .33Document1 pageView A-A: Ports: 2X 1/2" NPT .38 2X .33maheshNo ratings yet
- RD3.9 Handling DocumentsDocument21 pagesRD3.9 Handling DocumentsRameshBathalaNo ratings yet
- Four Principles of Document Revision ManagementDocument4 pagesFour Principles of Document Revision ManagementmaheshNo ratings yet
- Ground Floor QUthbullapurDocument1 pageGround Floor QUthbullapurmaheshNo ratings yet
- NFPA 13 2007 Sprinkler System Checklist 0809 PDFDocument6 pagesNFPA 13 2007 Sprinkler System Checklist 0809 PDFmaheshNo ratings yet
- Bim Level 2 - StandardsDocument8 pagesBim Level 2 - StandardsmaheshNo ratings yet
- BIM Lod Requirements BasicDocument18 pagesBIM Lod Requirements BasicmaheshNo ratings yet
- Automobile Engineering TheoryDocument27 pagesAutomobile Engineering TheorymaheshNo ratings yet
- Water Pipe SizingDocument40 pagesWater Pipe SizingAfzal Khan100% (2)
- Flexible Duct Size Based On The Flow RatesDocument1 pageFlexible Duct Size Based On The Flow RatesmaheshNo ratings yet
- 10th EngLISH Toppers TipsDocument11 pages10th EngLISH Toppers TipsmaheshNo ratings yet
- 10th EngLISH Toppers TipsDocument11 pages10th EngLISH Toppers TipsmaheshNo ratings yet
- NFPA 13 2007 Sprinkler System Checklist 0809 PDFDocument6 pagesNFPA 13 2007 Sprinkler System Checklist 0809 PDFmaheshNo ratings yet
- Hindi - Numbers 1 - 100Document6 pagesHindi - Numbers 1 - 100Ganesh Lakshminarasan20% (5)
- Ufc 3 600 01-Fire Prot EngrDocument158 pagesUfc 3 600 01-Fire Prot EngrcarlcrowNo ratings yet
- Fire Fighting Design and BasicsDocument22 pagesFire Fighting Design and Basicsmahesh86% (7)
- Chilled Water VelocitiesDocument1 pageChilled Water VelocitiesmaheshNo ratings yet
- FansDocument13 pagesFansmahesh0% (1)
- FP Deficision Tool Mixed Occup An CiesDocument2 pagesFP Deficision Tool Mixed Occup An CiesmaheshNo ratings yet
- BIM - 4D Modeling With Navisworks With Timeliner-01Document1 pageBIM - 4D Modeling With Navisworks With Timeliner-01maheshNo ratings yet
- Floor PlanDocument1 pageFloor PlanmaheshNo ratings yet
- Advanced Turbo MachineryDocument2 pagesAdvanced Turbo Machineryjvinod2025No ratings yet
- 26-1871-01 PaversDocument4 pages26-1871-01 Paversbanavaram1No ratings yet
- TOP/05 is flexible friction material for brake padsDocument1 pageTOP/05 is flexible friction material for brake padsMarcos LópezNo ratings yet
- Al Alloy STD Astm-B221mDocument13 pagesAl Alloy STD Astm-B221mKlas TechNo ratings yet
- Highway 2ndDocument4 pagesHighway 2ndVeronica SandersNo ratings yet
- HOSPITAL CONSTRUCTION PAYMENTDocument34 pagesHOSPITAL CONSTRUCTION PAYMENThanoseNo ratings yet
- MLC Tech Install Guide 2015Document84 pagesMLC Tech Install Guide 2015jamppajoo2No ratings yet
- Different Types of GuestDocument8 pagesDifferent Types of GuestAshutosh Sharma100% (1)
- Design of ManholeDocument8 pagesDesign of ManholeCristian Bajado100% (2)
- Decentlab Cuerda VibranteDocument2 pagesDecentlab Cuerda VibranteIsaac MonterreyNo ratings yet
- Concrete Deck SlabDocument24 pagesConcrete Deck SlabRichard ChavezNo ratings yet
- CaseDocument5 pagesCaseRedcLumsNo ratings yet
- Maytec-HT-08 Maytec Generell BrochureDocument6 pagesMaytec-HT-08 Maytec Generell BrochurezhiqianxuNo ratings yet
- Roof detail dimensions and notesDocument10 pagesRoof detail dimensions and notesardabiliNo ratings yet
- A Combined Visco Elastic Visco Plastic Behaviour of Particle Reinforced CompositesDocument15 pagesA Combined Visco Elastic Visco Plastic Behaviour of Particle Reinforced CompositesSaravanan MathiNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled Package Unit with Scroll CompressorsDocument48 pagesAir Cooled Package Unit with Scroll CompressorsMUBASHIRNo ratings yet
- 2018 06 OnlineDocument12 pages2018 06 OnlineMohamed HasikNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Properties of Cement With RHA As Replacement in ConcreteDocument6 pagesExperimental Study On Properties of Cement With RHA As Replacement in ConcreteDivya TadepalliNo ratings yet
- Beam DesignDocument3 pagesBeam DesignDeepak SahNo ratings yet
- CPP Lab Report 4Document11 pagesCPP Lab Report 4Muhammad Danial KhairuddinNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument40 pagesBrochureveloz33No ratings yet
- Product Bulletin: Model Osg Ansi ProcessDocument6 pagesProduct Bulletin: Model Osg Ansi ProcessDomingo DíazNo ratings yet
- CH-1 Pressure Vessel Design-1Document33 pagesCH-1 Pressure Vessel Design-1Kemal GetisoNo ratings yet
- Plastic - Collapse at Pipes and Vessels PDFDocument19 pagesPlastic - Collapse at Pipes and Vessels PDFElias KapaNo ratings yet
- Critical Appraisal Jami MAsjidDocument13 pagesCritical Appraisal Jami MAsjidHashim Muhammed100% (1)
- ASHRAE Report On Pre Cooling With Indirect Evaporative CoolingDocument8 pagesASHRAE Report On Pre Cooling With Indirect Evaporative CoolingAhmad Mahrous AboulsoudNo ratings yet
- Catálogo AquafinaDocument46 pagesCatálogo AquafinamarlonnormasoporteNo ratings yet
- Wire rope chart - 6x37 & 6x19, IWRC, EIPS rope specificationsDocument5 pagesWire rope chart - 6x37 & 6x19, IWRC, EIPS rope specificationsTarek HareedyNo ratings yet
- PIDS screen installation detailsDocument1 pagePIDS screen installation detailsmohamed ghazyNo ratings yet
- Silicone Encapsulants and GelsDocument12 pagesSilicone Encapsulants and GelssundarNo ratings yet