Professional Documents
Culture Documents
04 Laporan Genetika NONDISJUNCTION AND CROSSING OVER ON Drosophila Melanogaster
Uploaded by
hananOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
04 Laporan Genetika NONDISJUNCTION AND CROSSING OVER ON Drosophila Melanogaster
Uploaded by
hananCopyright:
Available Formats
NONDISJUNCTION AND CROSSING OVER ON Drosophila melanogaster
Genetics Class D
Study Program of Biology Education, Faculty of Teacher Training and Education, Jember University
Kalimantan Streat number 37, Kampus Tegalboto, Jember 68121
ABSTRACT
One of the topics in genetics practicum is Nondisjunction and Crossing over which discusses about
several disorders that occur due to chromosome displacement or mutations in living things. There are
movements that have positive and negative impacts on the survival of living things. Such as crossing over is an
event of exchanging segments of non-sibling chromatids from a homologous pair of chromosomes, which has
the benefit of increasing biodiversity in plants and animals with the emergence of new recombinant genes.
Meanwhile, Nondisjunction (Failure to separate) is an event that does not separate a pair of chromosomes during
cell division (meiosis). This occurs during gametogenesis, which is during meiosis. The chromosome pairs or
homologous chromosomes in gametangium stem cells will normally separate so that the gamete has half of the
number of chromosomes that an individual has. Nondisjunction can bring some negative impacts such as Down
syndrome, Turner syndrome and clinifelter syndrome for the impaired.
Keyword :Monohybrid, Dihybrid, Dominant, Recessive, Mendel
INTRODUCTION or mitosis. When nondisjunction occurs, during
Correct segregation of chromosomes during meiosis I or meiosis II, gametes are created that
the two successive meiotic divisions is essential for either contain an extra chromosome or lack a copy
the formation of haploid gametes. At least 10% of of a choromosome. Several syndromes arise from
human pregnancies produce aneuploid embryos this situation, such as Down Syndrome, Turner
with too many or too few chromosomes, the syndrome, and Klinefelter syndrome. Drosophila
majority of which are lost during pregnancy. If melanogaster is often chosen as the model
they survive to term, many have severe congenital organism in research. There are several reasons
defects and developmental and intellectual why this organism was chosen in this study, such as
disability. Thus, meiotic nondisjunction is the it has a short life cycle and easy to culture in
leading cause of pregnancy loss and birth defects in laboratory conditions. Moreover, studies of D.
humans and an important limiting factor in melanogaster and humans indicate several
women’s reproductive life span (Chernus et al, similarities in nondisjunctional mechanisms in the
2019 : 2). two species (Putri & Fauzi, 2017 : 154 - 155).
Nondisjunction (Failure to separate) is an For X kromosom nondisjunction in
event that does not separate a pair of chromosomes drosophila female meiosis, all of the normal
during cell division (meiosis). This occurs during progeny survive, while nondisjunction eggs
gametogenesis, which is during meiosis. The produce viable progeny only if fertilized by sperm
chromosome pairs or homologous chromosomes in that carry tue appropriate sex chromosome. the rate
gametangium stem cells will normally separate so of nondisjunction has traditionally been estimated
that the gamete has half of the number of by assuming a binomial process and doubling the
chromosomes that an individual has. However, the number of observed nondisjunctional progeny, to
anaphase I phase may occur when the chromosome account for the inviable classes (ScholarlyEdition,
pair does not separate due to certain influences so 2012 : 535).
that they remain together as a pair. This event is Crossing over is the exchange of chromatid
called a nondisjunction which usually occurs in the segments between homologous chromosomes and
anaphase I phase (Nusantari, 2015 : 79-80). with other chromosomes. When a cell performs
Nondisjunction the failure of sister meiotic division, the homologous chromosomes
chromatids to separate properly during mitosis or approach each other and automatically the
meiosis. the result of nondisjunction is a pair of chromatids are also close together. In this process it
aneuploid daughter cells, where one cell contains is possible that there are chromatids that stick
two copies of a chromosome and the other cell together or cross in one place, where these
posseses zero copies (Bhat & Wani, 2017: 33). intersections are called chiasms. Where the chiasm
Nondisjunction is the failure of homologous of the two chromatids can be cut off and connected
chromosomes to separate properly during meiosis again, but they are connected not to the original
segment but to the segments of the other melanogaster that can be seen from the phenotype
chromatids (non-sister chromatids) which are also are eye color, eye shape, wing shape, and body
cut, so crossovers occur. Cross-switching may color mutations so that various strains of
occur between two sibling or sister chromatids or Drosophila melanogaster are known, including
non-sibling chromatids, even with chromatids from white (w), sepia (se), eyemissing (eym), curled
other non-homologous chromosomes. Cross- (cu), taxi (tx), dumpy (dp), and vestigial (vgl). The
crossing between sibling chromatids is genetically differences in phenotypes that appear are due to
not interesting because the genetic information is changes in the genotype from normal conditions. In
the same, so there is no effect on the offspring addition to having an impact on the phenotype,
(Irawan, 2011 : 152-153). changes in the genotype will cause physiological
Chromosome linking and crossing over is a changes such as the reproductive process (Taufika
genetic concept that emerged after scientists made et al, 2020: 50).
use of crossover using D. melanogaster. Even Drosophila has different morphological
though it was not originally developed through D. characteristics between males and females. In
melanogaster, other concepts, such as multiple males Has a smaller body size when compared to
alleles and chromosome mapping can also be females. Has three segments on the abdomen and
studied through D. Melanogaster. The phenomena has a genital comb. Whereas in females the size is
of Mendelian ratio deviations that will be shown in relatively larger, has six segments in the abdomen
this study are crossovers and sex links. Through the and does not have a genital comb. Drosophila
phenomenon of crossing over, recombinant type melanogaster is a winged, small animal. Therefore,
chicks can appear in crosses involving two observing the morphology of these animals can use
different traits, even though they are on the same tools such as loops and microscopes. In Drosophila
chromosome. Through the sex-linked phenomenon, melanogaster, 4 pairs of chromosomes are found.
the F2 ratio at the cross of one or more different In general, males and females are the same, but
traits will not show the general Mendelian ratio due there is a slight difference, namely that on one of
to the absence of a particular gene on one of the sex the male chromosomes there is a curve like a hook.
chromosomes of one of the parental ones (Fauzi & Meanwhile, regarding the sexual age of females for
Corebima, 2016 : 278). mating in Drosophila melanogaster, various
Most genetic studies have used information is obtained. There are several opinions
recombination as the primary tool to assess the which state how old Drosophila melanogaster
fidelity of the meiotic process. Such studies have female reaches sexual maturity (Suparman et al,
either directly measured changes in recombination 2018: 41-42).
frequency or relied upon the fact that genome wide
reductions in exchange can increase the level of RESEARCH METHODS
nondisjunction, providing an easy read-out for This research was conducted on October 22,
recombination failure (Hughes et al, 2018 : 877). 2020, through Zoom media with laboratory
Drosophila melanogaster, is an organism assistants and lecturers from the Study Program of
that is very useful for conducting research. It is Biology Education, Faculty of Teacher Training
relatively easy to culture, has a conveniently short
and Education, Jember University. To carry out
lifespan, consists of mostly post-mitotic tissues
crosses of fruit flies with different strains, it is
(except for the reproductive system and a small part
necessary to prepare the medium, the cross stock,
of the gut), and has a fully sequenced genome and
and the cross table.
well-characterized genetics. This insect uses many
To make medium, mix banana, tape, and
mitochondrial transporters homologous to the
brown sugar in a ratio of 7: 3: 1 with added water.
human carriers, as well as the same mechanisms for
Blend until completely smooth and adjust the
transporting several metabolites from cytosol to
thickness so that it is not too runny and not too
mitochondria and vice versa. Furthermore, it offers
runny. Cook until boiling. Then, put the hot
a variety of powerful molecular genetics methods
medium that has been cooked in the culture bottle
for studying transporters, many of which would be
and immediately cover the bottle with foam. After
difficult to test in mammalian models (Curcio et al,
the medium is warm, sprinkle with 5-7 fermipan
2020: 1).
grains. Wait for it to cool and put in the pupation
The fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) is
paper and immediately close it again.
known to have undergone many mutations that
Stock preparation, by preparing Stock
produce intraspecific genotypic variations called
Drosophila melanogaster according to the specified
strains. Apart from normal conditions (N), several
strain. After the pupa appears, the mother or adult
strains were found which were the result of
flies are transferred to another bottle (to be
mutations and produced mutants that were different
rejuvenated). The pupa in the old bottle is isolated
from normal conditions. The differences are mainly
in an ampoule tube to produce virgin males and
related to eye color, eye shape, and wing shape.
females.
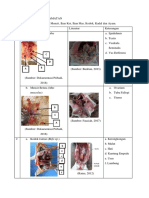
Some types of mutations in Drosophila
Crossing Over crosses, after getting male The first observation is the observation of
and female virgin, select female strain bcl with crossing over with parental male flies strain N and
male strain N along with the reciprocal. Male N female flies strain bcl.
strains with female bcl strains to be crossed in jam
♀ Strain N → KKMM
bottles, each jam bottle contains only 1 pair of
- Brownish yellow body color (KK)
Drosophila melanogaster flies. Then, wait for the
- Red compound eye color (MM)
pupa to appear. After the pupa is formed, the pupa
- The wings completely cover the body / abdomen.
ampoule is placed in the tube to observe F1. Cross
P2 by crossing strain N berina with male strain bcl. ♂ Strain bcl → kkmm
Heterozygous N strains from F1 crosses and bcl - Black body color (kk)
strains were obtained from stocks instead of F1. - Brownish compound eye color (mm)
Record the results of F2 obtained from the crosses - The wings completely cover the body / abdomen.
in the table.
Parental Crosses 1
RESULT AND DISCUSSION P1 : ♀ Strain N >< ♂ Strain bcl
The purpose of carrying out this practicum : KKMM >< kkmm
is to practice making crosses to prove the
occurrence of Crossing over and Nondisjunction in G1 : KM >< km
Drosophila Melanogaster and to calculate and F1 : KkMm (Normal Heterozygous)
observe the results of crosses of F1 and F2 Parental Crosses 2
offspring. P2 : ♀ Strain N (F1) >< ♂ Strain bcl (Stock)
The tools and materials used include, : KkMm >< kkmm
Drosophila melanogaster Strain N, w/wa/we,
bcl/bdp serves as an experimental object. A large G2 : KM, Km, kM, km >< km
hose and a small tube for suctioning and picking up F2 :
fruit flies, and transferring flies to culture bottles.
♀♂ KM Km kM km
Gauze, to cover the end of a small hose. Pupation
paper, to take pupae from the cross media. Jam km KkMm Kkmm kkMm kkmm
bottles, as culture bottles and placement media.
Banana, tape and brown sugar, as ingredients in a - KkMm (Brownish yellow body color, Red
ratio of 7: 3: 1, for the maintenance of Drosophila compound eye color) = N : 1
melanogaster. Small brush. Foam plug, as a cover - Kkmm (Brownish yellow body color, Brownish
for culture bottles. Fermipan / Yeast, for the compound eye color) : 1
manufacture of fruit fly media, which functions to - kkMm (Black body color, Red compound eye
provide air space in the medium. Scales, to measure color) : 1
the composition of the medium used. Mixer, to stir - kkmm (Black body, Brownish compound eye
the fruit fly medium that is made. Foam, as a cover. color) = bcl : 1
Label paper, label each bottle and hose.
Crossing over is an event of exchanging In parental crosses 1, female flies with strain
segments of non-sibling chromatids from a N were crossed with male flies strain bcl. The
homologous pair of chromosomes. Cross-crossing results obtained were filial (F1) where all flies had
events are very common at the time of gamete a brownish yellow body (Normal heterozygous)
formation in most creatures. Cross-moving occurs strain of N (Normal heterozygous) and red
at the end of prophase I or the beginning of compound eyes with the KkMm genotype. After
metaphase I which occurs when a chromosome has obtaining F1, a second parental cross (P2) was
doubled into two chromatids. Cross-moving carried out from a female F1 fly of Strain N
generally occurs in the middle chromatids, namely (heterozygous) with a male fly Strain bcl from the
the second and third chromatids of the chromatid stock. This is done for the testcross test, by
tetrad. However, it does not rule out the existence crossing F1 individuals with individuals who are
of cross-crossing in other chromatids. homozygous recessive (bcl).
Nondisjunction (Failure to separate) is an From the results of crossing parental 2, it
event that does not separate a pair of chromosomes can be seen that there are 4 kinds of genotypes and
during cell division (meiosis). This occurs during phenotypes, which are KkMm (brownish yellow
gametogenesis, which is during meiosis. The body, red compound eyes) and kkmm (black body,
chromosome pairs or homologous chromosomes in brownish compound eyes) are parental types while
gametangium stem cells will normally separate so kkMm (black body, red compound eyes) and
that the gamete has half of the number of Kkmm (brownish yellow body, brownish
chromosomes that an individual has. compound eyes) is a type of recombination that
results from crossing over. The phenomenon of
crossing over, recombinant type puppies can appear namely XXXw is super female, lethal. XXY is
in crosses with 2 different traits, even though on the male, sterile. Xw0 is female sterile, white. Y0 is
same 1 chromosome. male, lethal. Meanwhile, in 2 parental crosses, the
With the crossing over it can produces new event of Nondisjunction in male flies causes the
combinations of traits. Through crossing over formation of 2 types of F1, each of which has a
segments of homologous chromosomes are percentage of 50% with its genotype and
interchanged and hence provide origin of new phenotype, namely XXwY is male sterile, white. X0
characters and genetic variations. Crossingg over is a female sterile. In the Nondisjunction event, if
plays a very important role in the field of breeding the puppy (F1) has the same genotype as the
to improve the varieties of plants and animals parental, it is called Normal, whereas if the F1
The second observation is the observation of genotype is the opposite of parental it is called
Nondisjunction (NDJ) events in Drosophila experiencing Nondisjunction.
melanogaster. Observations were carried out by The occurrence of nondisjunction events can
crossing male flies strain W (XwY) with strain N result in abnormalities in their offspring. such as
(XX) berina flies and their recipients. some syndromes that arise, namely Down
syndrome, Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome
♀ Strain N → Normal (XX)
and several other effects.
- Red compound eye color
Nondisjunction in Drosophila melanogaster
- Brownish yellow body color
are influenced by several factors. Among them are
- The wings completely cover the body / abdomen.
external factors and internal factors. External
♂ Strain W → White (XwY) factors that influence the occurrence of NDJ
- White compound eye color daintaranta include high radiation energy, carbon
- Brownish yellow body color dioxide, certain chemicals and temperature. While
- The wings completely cover the body / abdomen. internal factors that influence the occurrence of
NDJ, among others, are mutant genes, age, and
Parental Crosses 1 (Female NDJ) other factors related to abnormalities in genetic
P1 : ♂ Strain W >< ♀ Strain N behavior.
: XwY >< XX
CONCLUSSION
G1 : Xw >< XX → Female NDJ
Y 0 Crossing over is an event of exchanging
F1 : segments of non-sibling chromatids from a
♀♂ Xw Y homologous pair of chromosomes. In crossing
over, you will get F1 offspring in the form of a
XX XXXw XXY combination of the genes of the two parents.
0 X 0
w
Y0 Meanwhile, when the cross-test was carried out by
crossing female F1 with male flies that were
- XXXw (25%) : Super female, Lethal homozygous rssif, there were 4 types of offspring
- XXY (25%) : Male, Steril that had different genotypes and phenotypes, each
- Xw0 (25%) : Female sterile, White with a percentage of 25%.
- Y0 (25%) : Male, Lethal Nondisjunction (Failure to separate) is an
event that does not separate a pair of chromosomes
Parental Crosses 2 (Male NDJ)
during cell division (meiosis). This occurs during
P1 : ♂ Strain W >< ♀ Strain N
gametogenesis, which is during meiosis. The
: XwY >< XX
chromosome pairs or homologous chromosomes in
G1 : XwY >< X → Male NDJ gametangium stem cells will normally separate so
0 .X that the gamete has half of the number of
F1 : chromosomes that an individual has. In a
nondisjunction cross, if an NDJ individual is a
♀♂ X wY 0 female parent, 4 types of offspring will be obtained
X XX Y
w
X0 which have different genotypes and phenotypes and
each has a percentage of 25%. Meanwhile, if the
X XX Y
w
X0
one experiencing nondisjunction is a male parent,
- XXwY (50%) : Male steril, White there will be two kinds of offspring that have
- X0 (50%) : Female Steril different genotypes and phenotypes, each with a
percentage of 50%.
In parental crossing 1, the event of REFFERENCES
Nondisjunction in female flies causes the formation
of 4 types of F1, each of which has a percentage of
25% or 1: 1: 1: 1 with the genotype and phenotype,
Bhat, Tariq Ahmad., A. A. Wani. 2017.
Chromosome Structure and Aberrations. India
: Spreinger.
Chernus, Jonathan M., E. G. Allen., Z. Zeng., E. R.
Hoffman., T. J. Hassold., E. Feingold., S. L.
Sherman. 2019. A candidate gene analysis and
GWAS for genes associated with maternal
nondisjunction of chromosome 21. PLOS
Genetics. December 12, 2019 : 1-38.
Curcio, Rosita., P. Lunetti., V. Zara., A.
Ferramosca., F. Marra., G. Fiermonte., A. R.
Carpello., F. D. Leonardis., L. Capobianco.,
V. Dolce. 2020. Drosophila melanogaster
mitochondrial carriers: similarities and
differences with the human carriers.
International Jurnal of Molecular Sciences.
21(17): 1
Fauzi, Ahmad., A. D. Corebima. 2016.
Pemanfaatan Drosophila melanogaster
sebagai organisme model dalam mengungkap
berbagai fenomena penyimpangan rasio
mendel. Prosiding Seminar Nasional Biologi.
278-282.
Hughes, Stacie E., D. E. Miller., A. L. Miller., R. S.
Hawley. 2018. Female meiosis: Synapsis,
recombination, and segregation in Drosophila
melanogaster. Genetics. 208(3) : 875-908.
Irawan, Bambang. 2011. Genetika Penjelasan
Mekanisme Pewarisan Sifat. Surabaya : Pusat
penerbitan dan percetakan Unair (AUP).
Nusantari, Elya. 2015. Genetika : Belajar Genetika
Dengan Mudah & Komprehensif.
Yogyakarta : Deepublish.
Putri, Eka Pratama., A. Fauzi. 2017. Sodium
Cyclamate Effect on Nondisjunction
Frequency of Drosophila melanogaster
Meigen. Proceeding of International
Conference on Green Technology. October
2017. 8(1) : 154-158.
ScholarlyEdition. 2012. Issues in Genetic
Medicine. 2011 Edition. Georgia : Scholarly
Edition.
Suparman., C. Roini., J. Saban. 2018. Indeks isolasi
sexual antara lalat buah (Drosophila
melanogaster (Meigen)) dari Moya, Pulau
Ternate dan Gurabunga, Pulau Tidore. Jurnal
Ilmiah MIPA. 3(1): 41-42.
Tufika, Ramadhan., S. A. Nugroho., A. Nuraisyah.
2020. Perbedaan strain dan umur betina
terhadap jumlah keturunan lalat buah
(Drosophila melanogaster Meigin). Jurnal
Tambora. 4(1): 50.
You might also like
- Staghorn Corals of the World: A Revision of the Genus AcroporaFrom EverandStaghorn Corals of the World: A Revision of the Genus AcroporaNo ratings yet
- Invertebrate Taxonomy Test AnswersDocument3 pagesInvertebrate Taxonomy Test AnswersGresia FalentinaNo ratings yet
- Gambar Praktikum 1 PROTOZOADocument3 pagesGambar Praktikum 1 PROTOZOANajmi AuliaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document32 pagesLecture 4Neo ChanNo ratings yet
- Anggun Wening F - 1304617073 - Biolistrik Pada Sistem SarafDocument8 pagesAnggun Wening F - 1304617073 - Biolistrik Pada Sistem SarafRosa AmaliaNo ratings yet
- LKM 3bDocument10 pagesLKM 3bAsnawi SaragihNo ratings yet
- Lap Pap 2 Daun Monokotil Dan Dikotil-WahDocument13 pagesLap Pap 2 Daun Monokotil Dan Dikotil-WahChaya Stia ClaluiNo ratings yet
- CBR General BiologyDocument15 pagesCBR General Biologyrizka0% (1)
- Lichen Classification and PhotosDocument5 pagesLichen Classification and PhotoswidyaNo ratings yet
- SExl FSDocument93 pagesSExl FSMas Joko100% (1)
- (Revisi Terbaru) Kelimpahan Gastropoda Dan Bivalvia Di Daerah MakroalgaDocument10 pages(Revisi Terbaru) Kelimpahan Gastropoda Dan Bivalvia Di Daerah Makroalgashabrina syifaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis FactsDocument8 pagesMitosis and Meiosis FactsLeonita SwandjajaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Tumbuhan PakuDocument0 pagesJurnal Tumbuhan PakuAri Masturi100% (1)
- Proses Perkembangan Embrio Pada Tahapan CleavageDocument43 pagesProses Perkembangan Embrio Pada Tahapan CleavageAnton TubagusNo ratings yet
- LaporanDocument21 pagesLaporanAnnisa FitriNo ratings yet
- From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Jump To: ,: LeucosoleniaDocument62 pagesFrom Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Jump To: ,: LeucosoleniaSuci AgustianiNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Kladodia, Filodia, Daun DikotilDocument5 pagesAnatomi Kladodia, Filodia, Daun Dikotilanandakhoirunnisa44No ratings yet
- Embryo Development StagesDocument5 pagesEmbryo Development StagesdindaNo ratings yet
- Brazil turtle species profilesDocument15 pagesBrazil turtle species profilesMuhammad Poggy SaputraNo ratings yet
- 2006dhe PDFDocument123 pages2006dhe PDFZahra Salsa BilaNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 3-SIstem PencernaanDocument103 pagesKelompok 3-SIstem PencernaanNurul Fadhillah IsaNo ratings yet
- Uji Daya Tumbuh Stek Tanaman Alpukat (Perseaamericana Mill) DENGAN PEMBERIAN BIO ZPT URINE KambingDocument21 pagesUji Daya Tumbuh Stek Tanaman Alpukat (Perseaamericana Mill) DENGAN PEMBERIAN BIO ZPT URINE Kambingdikidbandto11No ratings yet
- Climate Change Scientist Takes A Roomful of SkepticsDocument3 pagesClimate Change Scientist Takes A Roomful of SkepticsJerome Earl AmarantoNo ratings yet
- Klasifikasi Mikroorganisma Berdasarkan KarakteristikDocument25 pagesKlasifikasi Mikroorganisma Berdasarkan KarakteristikRunoff0% (1)
- Embryo Development StagesDocument5 pagesEmbryo Development StagesdindaNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Organ AkarDocument32 pagesAnatomi Organ AkarDevon SimdayNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Systems of Mice, Koi Fish, Catfish, Frogs, Lizards and ChickensDocument5 pagesReproductive Systems of Mice, Koi Fish, Catfish, Frogs, Lizards and ChickensAldi Rusmana0% (1)
- Ordo Rosales by DELA NAVARINDocument18 pagesOrdo Rosales by DELA NAVARINDela NavarinNo ratings yet
- KiBi Posforilasi Karboksilasi IhsanDocument9 pagesKiBi Posforilasi Karboksilasi Ihsanaisyah teremNo ratings yet
- Kunci Jawaban KTDocument35 pagesKunci Jawaban KTRisza Nuril SamsiyahNo ratings yet
- Snail Activity And DistanceDocument25 pagesSnail Activity And DistanceNurul Fitrah 2008No ratings yet
- Red Algae Classification and Observation TableDocument6 pagesRed Algae Classification and Observation TableriskaNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Histokimia Organ Generatif Amorphophallus MuelleriDocument7 pagesAnatomi Dan Histokimia Organ Generatif Amorphophallus Muellerikarnayah 23No ratings yet
- Lepidoptera Sema Ran Gray ADocument46 pagesLepidoptera Sema Ran Gray ASultan IzdiharNo ratings yet
- Anthurium Jurnal PDFDocument11 pagesAnthurium Jurnal PDFanisa kurniatiNo ratings yet
- Genetic traits comparison chartDocument1 pageGenetic traits comparison chartKristianFelixNo ratings yet
- Filum Protozoa Dan PoriferaDocument5 pagesFilum Protozoa Dan PoriferaDidik PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- Genus: Rosa: FamilyDocument5 pagesGenus: Rosa: FamilyMakara MeanNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum Taksonomi Vertebrata RDocument10 pagesLaporan Praktikum Taksonomi Vertebrata RMuhammad Fahreza Rizky WNo ratings yet
- Alaydrus, 2013Document6 pagesAlaydrus, 2013Muh HidayatNo ratings yet
- Laju Respirasi HewanDocument8 pagesLaju Respirasi HewanAqsha InezaNo ratings yet
- ParthenogenesisDocument17 pagesParthenogenesisAndi Kurniawan PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Persepsi Guru Biologi Sma Kota Padang Terhadap Pembelajaran EvolusiDocument7 pagesPersepsi Guru Biologi Sma Kota Padang Terhadap Pembelajaran EvolusiResma WahyuniNo ratings yet
- Cemara Pua-Pua BenefitsDocument2 pagesCemara Pua-Pua BenefitsdaniaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum Ekologi Terestrial Ekosistem TerestrialDocument8 pagesLaporan Praktikum Ekologi Terestrial Ekosistem Terestrialkentang mcdNo ratings yet
- Germination and seedling development of two tropical plant speciesDocument12 pagesGermination and seedling development of two tropical plant speciesDimaz IrawanNo ratings yet
- Laporan Sistem SirkulasiDocument10 pagesLaporan Sistem SirkulasiRosa AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Struktur Morfologi Dan Anatomi Burung Endemik Sulawesi Cabai Panggul-Kelabu (Dicaeum Celebicum Műller, 1843)Document7 pagesStruktur Morfologi Dan Anatomi Burung Endemik Sulawesi Cabai Panggul-Kelabu (Dicaeum Celebicum Műller, 1843)SaadatulNo ratings yet
- Pengantar NanobiologiDocument47 pagesPengantar NanobiologiInnes Putri MonikaNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy, External Morphology, and Species Identification: Scientific and Vernacular NamesDocument20 pagesTaxonomy, External Morphology, and Species Identification: Scientific and Vernacular NamesKarlo SalazarNo ratings yet
- Evolusi Invertebrata Hingga ProtovertebrataDocument31 pagesEvolusi Invertebrata Hingga Protovertebratakhoirotul wijayantiNo ratings yet
- Osmoregulation of Aquatic Animals ExplainedDocument5 pagesOsmoregulation of Aquatic Animals ExplainedFira Julia PutriNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Suksesi Ekologi KiyahhhhhDocument3 pagesJurnal Suksesi Ekologi KiyahhhhhMelda Aprilya SolinNo ratings yet
- Slide For Presentation Leaf DevelopmentDocument13 pagesSlide For Presentation Leaf DevelopmentJalal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mollusca and ArthropodaDocument7 pagesMollusca and ArthropodaRegina LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Portofolio EvolusiDocument100 pagesPortofolio EvolusiNabila MahgfiraNo ratings yet
- Transpor Pasif Melintasi Membran Tanpa Mengeluarkan Energi: June 2020Document9 pagesTranspor Pasif Melintasi Membran Tanpa Mengeluarkan Energi: June 2020Susani khairinaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Micros PDFDocument3 pagesJournal of Micros PDFHayon YantoNo ratings yet
- Antibody Diversity:Variable Joining Sites and Somatic MutationsDocument11 pagesAntibody Diversity:Variable Joining Sites and Somatic MutationsFemi Mega LestariNo ratings yet
- 01 Laporan Genetika MONOHYBRID AND DIHYBRID CROSSES IN DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTERDocument5 pages01 Laporan Genetika MONOHYBRID AND DIHYBRID CROSSES IN DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTERhananNo ratings yet
- 06 Laporan Genetika DNA ISOLATIONDocument5 pages06 Laporan Genetika DNA ISOLATIONhananNo ratings yet
- 02 Laporan Genetika POLYPLOIDY IN PTERIDOOPHYTADocument4 pages02 Laporan Genetika POLYPLOIDY IN PTERIDOOPHYTAhananNo ratings yet
- 03 Laporan Genetika IMITASI RATIO FENOTIPEDocument8 pages03 Laporan Genetika IMITASI RATIO FENOTIPEhananNo ratings yet
- 01 Laporan Genetika MONOHYBRID AND DIHYBRID CROSSES IN DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTERDocument5 pages01 Laporan Genetika MONOHYBRID AND DIHYBRID CROSSES IN DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTERhananNo ratings yet
- Arundhati Roys The God of Small Things As A Postmodern NovelDocument7 pagesArundhati Roys The God of Small Things As A Postmodern NovelRoshni KhanNo ratings yet
- MGT211 RecruitmentDocument16 pagesMGT211 RecruitmentEdward N MichealNo ratings yet
- Integrating JasperReports To PHPDocument10 pagesIntegrating JasperReports To PHPrupinder_3061463No ratings yet
- Asian Studies Vol 49 No 2 - 2013Document218 pagesAsian Studies Vol 49 No 2 - 2013Ari Dodol100% (1)
- Handout-Wisdom QuestionsDocument1 pageHandout-Wisdom Questionsapi-369459770No ratings yet
- 100 transaction cycle in VisionPLUS banking systemDocument7 pages100 transaction cycle in VisionPLUS banking systemGoushik Balakrishnan100% (1)
- Wealth Management Asia: ParsimonyDocument3 pagesWealth Management Asia: ParsimonyJohn RockefellerNo ratings yet
- Arctic Monkeys Do I Wanna KnowDocument4 pagesArctic Monkeys Do I Wanna KnowElliot LangfordNo ratings yet
- En Subject C08Document13 pagesEn Subject C08jmolfigueiraNo ratings yet
- XMLvsJSON-40charDocument7 pagesXMLvsJSON-40charPrakashNo ratings yet
- Pdic LawDocument30 pagesPdic LawDadangNo ratings yet
- Biraogo vs. Philippine Truth CommissionDocument3 pagesBiraogo vs. Philippine Truth CommissionJulesMillanarNo ratings yet
- 2010 - Octenidine Dihydrochloride, A Modern Antiseptic For Skin, Mucous Membranes and WoundsDocument15 pages2010 - Octenidine Dihydrochloride, A Modern Antiseptic For Skin, Mucous Membranes and Woundsnovia100% (2)
- Bca SYNOPSISDocument31 pagesBca SYNOPSISjigyasha oarmarNo ratings yet
- The BarographDocument8 pagesThe BarographNazre ShahbazNo ratings yet
- TRW WHP PDFDocument20 pagesTRW WHP PDFmonica_codNo ratings yet
- IN THE COURT OF - SUIT/APPEAL No. - JURISDICTION OF 2017Document1 pageIN THE COURT OF - SUIT/APPEAL No. - JURISDICTION OF 2017Adv Pooja AroraNo ratings yet
- Advanced Engineering Mathematics 10th EditionDocument7 pagesAdvanced Engineering Mathematics 10th EditionsamuelNo ratings yet
- The Structure of PoetryDocument3 pagesThe Structure of PoetryRose Razo100% (1)
- Grade 6 Quarter 3 WHLP WEEK 4Document3 pagesGrade 6 Quarter 3 WHLP WEEK 4JaneDandanNo ratings yet
- International Organizations and RelationsDocument3 pagesInternational Organizations and RelationsPachie MoloNo ratings yet
- ProComp 2 Service Manual SM7008P-01Document22 pagesProComp 2 Service Manual SM7008P-01cobramcNo ratings yet
- Year 11 GCSE Revision Guidance and Exam Booklet Solihull PDFDocument27 pagesYear 11 GCSE Revision Guidance and Exam Booklet Solihull PDFNoor Ulain Nabeela83% (6)
- Vicarious LiabilityDocument12 pagesVicarious LiabilitySoap MacTavishNo ratings yet
- Keerai BenefitsDocument3 pagesKeerai BenefitsjnaguNo ratings yet
- StudenttextDocument29 pagesStudenttextapi-195130729No ratings yet
- Summative Test 1Document3 pagesSummative Test 1Glenda AstodilloNo ratings yet
- Quam SingulariDocument2 pagesQuam SingulariMichael WurtzNo ratings yet
- IT Industry in India: Indian Education SystemDocument9 pagesIT Industry in India: Indian Education SystemPradeep BommitiNo ratings yet
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (215)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Eels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishFrom EverandEels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (30)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Superlative: The Biology of ExtremesFrom EverandSuperlative: The Biology of ExtremesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (51)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- The Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineFrom EverandThe Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- Younger for Life: Feel Great and Look Your Best with the New Science of AutojuvenationFrom EverandYounger for Life: Feel Great and Look Your Best with the New Science of AutojuvenationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Darwin's Dangerous Idea: Evolution and the Meaning of LifeFrom EverandDarwin's Dangerous Idea: Evolution and the Meaning of LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (523)
- Fearfully and Wonderfully: The Marvel of Bearing God's ImageFrom EverandFearfully and Wonderfully: The Marvel of Bearing God's ImageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (40)
- The Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (632)