Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Assessment and Diagnosis for a Patient with Pleural Effusion
Uploaded by
Al Theó0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views4 pagesOriginal Title
NCP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views4 pagesNursing Assessment and Diagnosis for a Patient with Pleural Effusion
Uploaded by
Al TheóCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
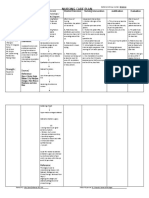
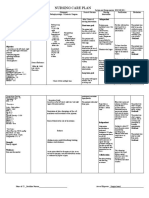
Rationale/ Goals/Desired Nursing
Assessment Cues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Evaluation
Pathophysiologic Basis Outcome Intervention
Subjective Cues: Acute Pain r/t the Predisposing Precipitating After 8hrs of nursing INDEPENDENT: After 8 hours of
The patient persistent Factors: Factors intervention, client Monitor the To identify nursing intervention,
-68 years old -Smoker for
verbalized, “Ga coughing aeb will be able to: patient’s vital signs changes in the client was able to:
-Male 10 years
sakit akon tiyan Reports of -History of hell heart rate or blood
kada mag ubo-ubo discomfort: hypertension -Onset of Verbalize relief from pressure which Verbalize relief from
ko.” pleuritic chest & DM underlying pain or management could indicate pain or managing
pain, headache, condition of pain at a tolerable patient pain at a tolerable
-Retired
Patient had muscle/joint pain. level using the pain experiencing pain level using the pain
Seaman
verbalized pain as scale scale. Patient
7/10 using the pain Definition: -Check the patient's To monitor for the verbalized “Subong
V
scale Unpleasant breathing rate, patient’s daw indi na
sensory and characteristics, respiratory status. masyado kasakit
Accumulation of excess
Objective Cues: emotional including the Changes in kun mag ubo ko.
fluid in the lung space
experience involvement of patient’s breathing Daw 4/10 nlng”
between the membrane
T 36.2°C associated with accessory muscles pattern may GOAL MET.
lining.
PR 82bpm actual or when breathing, and indicate patient
RR 26cpm potential tissue Verbalize any other irregular suffering from Verbalize
V
BP 140/80 damage or understanding of pain breathing patterns. painful episodes understanding of
described in such management pain management
Interference in the
-Drain tube terms of damage techniques for pain Auscultate the lungs To establish a techniques for pain
function of fluid
insertion on the left relief and monitor for baseline. Gas relief. Patient had
production or re-
and CTT insertion adventitious breath exchange is stated that “Subong
absorption lead to fluid
on the right Source/ sounds. affected by rapid maginhawa ko
excess and build-up
Reference: and shallow dalum ukon
between the tissues.
Laboratories NANDA breathing punggan ko akon
Results: International, patterns, as well as tiyan mag ubo para
V
Nursing hypoventilation. indi sobra kasakit”
CXR: Diagnoses, Hypoxia, on the GOAL MET.
The presence of pleural
Bilateral moderate Eleventh Edition, other hand, is
fluid, which aids in the
pleural effusion Nettina, Sandra characterized by
with fissural M. (2003) breathing mechanism Exhibit pain an increased Exhibit pain
insuation on the Lippincott’s during lung expansion and management respiratory rate, management
right. pocket manual of relaxation, has abnormally behaviors during the employment behaviors during
nursing practice. increased. episodes of pain. of accessory episodes of pain.
CBC: 2nd edition.o muscles, nasal Patient
Hematocrit: 0.03 V flaring, diaphragm demonstrated how
breathing to do deep breathing
Blood Chemistry: Patient cannot effectively exercises as well as
Creatinine: 0.7 get enough oxygen. chest splinting. The
mg/dL patient had
Blood uric acid: V verbalized “Indi sya
12.2mg/dL Constantly monitor To detect tuod amo na kasakit
LDH:190 IU/L The body is unable to the patient's oxygen abnormalities in kun mag amo ko ni
Total protein: 5.9 eliminate carbon dioxide. saturation through a the patient’s kada mag ubo gale
g/dL pulse oximeter. oxygenation noh”
Globulin: 2mg/dL V status. Significant GOAL PARTIALLY
oxygenation MET
Strength: Oxygen excess or concerns are
-Strong family deficiency at the alveolar indicated by an
support. capillary membrane, oxygen saturation
-Cooperative resulting in impaired of less than 90% or
-Tells the concern carbon dioxide elimination a partial pressure
pertaining to his of oxygen of less
self. V than 80.
Weakness: S/S: Signs of basal rales -Constantly check To identify
-Poor health both lung fields the results of blood patient’s ABG
seeking behaviors chemistry and status. Elevated
V arterial blood gases Carbon dioxide
(ABG). levels and
Impaired Gas Exchange r/t diminishing levels
the altered supply of of oxygen may
oxygen secondary to indicate
pleural effusion aeb basal respiratory
rales both lung fields. acidosis and
hypoxemia (low
level of blood
oxygen,
Source/Reference: particularly in the
Nettina, Sandra M. (2003) arteries)
Lippincott’s pocket manual
of nursing practice. 2nd
edition Place the patient in a To promote chest
high or semi- expansion for
Fowler's position optimized
with the head of the breathing and
bed elevated. decrease episodes
of pain.
-Conduct health To promote
teaching on pain independent
management management of
techniques such as pain during painful
deep breathing episodes.
exercises and visual Coughing and
distraction. deep breathing
exercises will help
the patient
evacuate
secretions from his
lungs. Visual
Imagery or Noise
distraction may
shift focus from
pain and relieve
patient.
Dependent
Interventions
Administer oxygen To improve
therapy as oxygenation status
prescribed. of the patient.
Improved
oxygenation
promotes better
circulation and
decreased pain
episodes
Administer To promote
medications as pharmacologic
prescribed. effect of
medication.
You might also like
- The Basics: A Comprehensive Outline of Nursing School ContentFrom EverandThe Basics: A Comprehensive Outline of Nursing School ContentRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Brain-Gut Interactions And Somatization in Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)From EverandBrain-Gut Interactions And Somatization in Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)No ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- Corrected NCP Case 3 Intrapartum NCPDocument2 pagesCorrected NCP Case 3 Intrapartum NCPReyzel PahunaoNo ratings yet
- Actual NCP - PESCADERO 4CDocument3 pagesActual NCP - PESCADERO 4COrlando VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Post-Operative Cataract Extraction Pain ManagementDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Post-Operative Cataract Extraction Pain ManagementOrlando VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Barrientos Case StudyDocument6 pagesBarrientos Case StudyCalvin Dante BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Colon Cancer PatientDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for Colon Cancer PatientCyril Joy N. FernandoNo ratings yet
- NUR 103A RLE Learning Activity - PneumothoraxDocument8 pagesNUR 103A RLE Learning Activity - PneumothoraxLaica & AivanNo ratings yet
- Pascual Janine Krista E. NCPDocument3 pagesPascual Janine Krista E. NCPCzarina Mae LomboyNo ratings yet
- The Appropriate Amount of Oxygen Is Continuously Delivered So That The Patient Does Not DesiderateDocument4 pagesThe Appropriate Amount of Oxygen Is Continuously Delivered So That The Patient Does Not DesideratezheeraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan PneumoniaIsaac KipkemoiNo ratings yet
- Alvarez, Kheeney - Case For Orthopedics WardDocument9 pagesAlvarez, Kheeney - Case For Orthopedics WardKheeney AlvarezNo ratings yet
- NCP Ectopic PregnancyDocument2 pagesNCP Ectopic PregnancykatrinajhorelletillesNo ratings yet
- Assessing Ectopic Pregnancy Risk and Fluid DeficitDocument2 pagesAssessing Ectopic Pregnancy Risk and Fluid DeficitAleeyah Krizle EstabilloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Labor and DeliveryDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan for Labor and DeliveryTrisha Dianne RaquenioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Intervention for Cough and Chest PainDocument2 pagesNursing Intervention for Cough and Chest PainDiana Anne MarisNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Acute PainDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Acute PainEvet VaxbmNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Labor and DeliveryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Labor and DeliverykimtalaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for UTIDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for UTIAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan (NCP)Sha PinedaNo ratings yet
- Quinto, Gemma (NCP & DRUG STUDY)Document13 pagesQuinto, Gemma (NCP & DRUG STUDY)Mariam Yiani Aspiras RacelesNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationBiancaGabatinoAbarcaNo ratings yet
- Labor Pain NCPDocument4 pagesLabor Pain NCPBea Dela Cena60% (5)
- Risk For Acute Pain Related To Surgical IncisionDocument4 pagesRisk For Acute Pain Related To Surgical IncisionMia Grace Garcia100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NnananaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (Acute Cholecystitis) - NAVARRADocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan (Acute Cholecystitis) - NAVARRAami forevsNo ratings yet
- Delivery Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesDelivery Nursing Care PlanKayelyn-Rose CombateNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective: Short Term GoalDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective: Short Term GoalEYANAH DELOS REYESNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPYette Polillo CondeNo ratings yet
- Readiness For Enhanced Health ManagementDocument6 pagesReadiness For Enhanced Health ManagementJIMENEZ, TRISHA MARIE D.No ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals/Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals/Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Managing Labor Pain for First-Time MotherDocument2 pagesManaging Labor Pain for First-Time MotherNovilyn TendidoNo ratings yet
- NCP Ob WardDocument3 pagesNCP Ob WardAbby AusteroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Gallbladder StonesDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Gallbladder StonesKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- NCP FileDocument3 pagesNCP FileJaneenne Fe Nicole SilvanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing-Care-Plan 4Document4 pagesNursing-Care-Plan 4Christine CornagoNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1Khrisha DavilloNo ratings yet
- Chloe Jacoba NCMA 113 BSN 1-YC-6: Subjective IndependentDocument1 pageChloe Jacoba NCMA 113 BSN 1-YC-6: Subjective IndependentPatricia ParagguaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Case ScenarioDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan: Case ScenarioShelvin Jules LayvaNo ratings yet
- 123cardos Sga NCPDocument7 pages123cardos Sga NCPGabrielle CardosNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationREOLALAS, Mariane JoyNo ratings yet
- Sultan - NCP 1 (Preterm Labor)Document2 pagesSultan - NCP 1 (Preterm Labor)Johanisa SultanNo ratings yet
- Villanueva Bsn-1a - NcplecDocument6 pagesVillanueva Bsn-1a - NcplecKhyra Ysabelle VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Ehr PDFDocument31 pagesEhr PDFNicolai MabituinNo ratings yet
- A Nursing Care Plan Presented To The Faculty of The Nursing DepartmentDocument4 pagesA Nursing Care Plan Presented To The Faculty of The Nursing DepartmentAnge MinguitoNo ratings yet
- NCP Hydatidiform Mole PDFDocument2 pagesNCP Hydatidiform Mole PDFKimNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationAgnes GeolinaNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute Pain DiarrheaDocument4 pagesNCP Acute Pain DiarrheaBARRISTERFLOWERSEAURCHIN6No ratings yet
- Acute Pain Related To Complications of Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever As Evidenced by Enlarged LiverDocument3 pagesAcute Pain Related To Complications of Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever As Evidenced by Enlarged LiverAlyssa marieNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions Relieve Chest Pain Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument4 pagesNursing Interventions Relieve Chest Pain Acute Myocardial InfarctionDienizs LabiniNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument2 pagesNCP Acute PainJeiza AvelinoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan #1 - Acute Pain ManagementDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan #1 - Acute Pain Managementunnamed personNo ratings yet
- Norbe COMFORT MEASURESDocument10 pagesNorbe COMFORT MEASURESMarlo Dañez NorbeNo ratings yet
- Proper Hygiene Prevents Spread of PathogensDocument4 pagesProper Hygiene Prevents Spread of PathogensSheda BondNo ratings yet
- The unexpected onset of acute pain reminds the patient to seek support, assistance, and reliefDocument1 pageThe unexpected onset of acute pain reminds the patient to seek support, assistance, and reliefJUN JUN PALISOCNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Skills Lab NCPDocument1 pageNCM 107 Skills Lab NCPMoises Clerick BalloguingNo ratings yet
- J.REPORT NCP BernabeLoveriel V.Document3 pagesJ.REPORT NCP BernabeLoveriel V.Lovi DVNo ratings yet
- Eugenio (NCP and Patient Education)Document6 pagesEugenio (NCP and Patient Education)Sam EugenioNo ratings yet
- JMJ Marist Brothers Notre Dame of Marbel University College of Arts and Sciences - Nursing Department Alunan Avenue, Koronadal City, South CotabatoDocument1 pageJMJ Marist Brothers Notre Dame of Marbel University College of Arts and Sciences - Nursing Department Alunan Avenue, Koronadal City, South CotabatoJoevence Gazo CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- University of St. La Salle College of Nursing Nursing Care Plan Name of Student: - Artillo, Aljean Altheo L Name of CIDocument2 pagesUniversity of St. La Salle College of Nursing Nursing Care Plan Name of Student: - Artillo, Aljean Altheo L Name of CIAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Lacerated Wound Forms (Artillo)Document9 pagesLacerated Wound Forms (Artillo)Al TheóNo ratings yet
- HTP Lacerated Wound Case 1 Group1 BN3BDocument9 pagesHTP Lacerated Wound Case 1 Group1 BN3BAl TheóNo ratings yet
- NCP Stab Wound (Artillo)Document7 pagesNCP Stab Wound (Artillo)Al TheóNo ratings yet
- ARTILLO Losartan Drug StudyDocument3 pagesARTILLO Losartan Drug StudyAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Tita Senal RN, MN, PHD - Area of Exposure: - Bacolod City Mental Health Care CenterDocument4 pagesTita Senal RN, MN, PHD - Area of Exposure: - Bacolod City Mental Health Care CenterAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Research Ethics Review Committee: Urc@usls - Edu.phDocument3 pagesResearch Ethics Review Committee: Urc@usls - Edu.phAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Aljean Altheo L. Artillo BSN-3B "Describe Your Community" Location/Address of Your Communit: Block 2 Lot 5, Alida Residences, Silay CityDocument9 pagesAljean Altheo L. Artillo BSN-3B "Describe Your Community" Location/Address of Your Communit: Block 2 Lot 5, Alida Residences, Silay CityAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Mental Status Exam (MSE-ABC) - 1Document1 pageMental Status Exam (MSE-ABC) - 1Al TheóNo ratings yet
- Aljean Altheo L. Artillo BSN-3B Anxiety LogDocument1 pageAljean Altheo L. Artillo BSN-3B Anxiety LogAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Who Surgical Safety Checklist: Be Polite. Thank EveryoneDocument1 pageWho Surgical Safety Checklist: Be Polite. Thank EveryoneAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia (DS)Document7 pagesSchizophrenia (DS)Al TheóNo ratings yet
- Medication Sheet: Complete Name and Initials of Medication NurseDocument1 pageMedication Sheet: Complete Name and Initials of Medication NurseAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing: Community Health Profile Worksheet (Worksheet “CDocument15 pagesCommunity Health Nursing: Community Health Profile Worksheet (Worksheet “CAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Date: November 6, 2021 Date: Date:: Date Hospital Days Post-Op/Post-Partu Hour AM PM AM PM AM PM Pulse Rate 150Document1 pageDate: November 6, 2021 Date: Date:: Date Hospital Days Post-Op/Post-Partu Hour AM PM AM PM AM PM Pulse Rate 150Al TheóNo ratings yet
- Artillo-Fdar Nurses NotesDocument2 pagesArtillo-Fdar Nurses NotesAl TheóNo ratings yet
- My COPD Action Plan: Green Zone: I Am Doing Well Today ActionsDocument2 pagesMy COPD Action Plan: Green Zone: I Am Doing Well Today ActionsAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Surgery Case Scenario 1Document5 pagesSurgery Case Scenario 1Al TheóNo ratings yet
- Drug study at University of St. La Salle College of NursingDocument5 pagesDrug study at University of St. La Salle College of NursingAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Artillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaDocument5 pagesArtillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Intravenous/Parenteral Fluid SheetDocument1 pageIntravenous/Parenteral Fluid SheetAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Artillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaDocument5 pagesArtillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SitagliptinDocument2 pagesDrug Study SitagliptinAl Theó0% (1)
- Health Teaching: Medication Exercise Treatment Hygiene Outpatient DietDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching: Medication Exercise Treatment Hygiene Outpatient DietAl TheóNo ratings yet
- GRD HeimlichDocument1 pageGRD HeimlichAl TheóNo ratings yet
- ARTILLO-FDAR Nurses NotesDocument2 pagesARTILLO-FDAR Nurses NotesAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario 2 MarioDocument1 pageCase Scenario 2 MarioAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Week 13 CaseDocument1 pageWeek 13 CaseAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario 3 RosellaDocument2 pagesCase Scenario 3 RosellaAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Y8 AP2 Revision LesssonsDocument32 pagesY8 AP2 Revision Lesssons4m44r2010No ratings yet
- Gillis - Sound Concepts For SaxDocument4 pagesGillis - Sound Concepts For SaxBrianna WilliamsNo ratings yet
- ETCO2 ReadingDocument19 pagesETCO2 ReadingTuan TrinhNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4: Chapter 7 - RespirationDocument3 pagesBiology Form 4: Chapter 7 - RespirationGerard Selvaraj100% (1)
- Body Scan English Script (Final)Document1 pageBody Scan English Script (Final)Boris ThingbaijamNo ratings yet
- Emergency Patient Assessment SheetDocument18 pagesEmergency Patient Assessment SheetHaneenNo ratings yet
- English Recovery RoomDocument5 pagesEnglish Recovery RoomRahima PutriNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Failure Vs DistressDocument1 pageRespiratory Failure Vs DistressMutiara Annisa AmadeaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Kundalini Yoga CourseDocument113 pagesIntroduction to Kundalini Yoga CourseMike YonkersNo ratings yet
- Qi GongDocument69 pagesQi GongOudotte100% (3)
- CCA206 - Assessment - 2 - Brief - Case Study Analysis and Developing A Care Plan - Module 4.2 - AO - 13102021Document11 pagesCCA206 - Assessment - 2 - Brief - Case Study Analysis and Developing A Care Plan - Module 4.2 - AO - 13102021Akriti DangolNo ratings yet
- Emergency Exam2Document10 pagesEmergency Exam2Nader Smadi100% (6)
- ARDS With PathophysiologyDocument79 pagesARDS With Pathophysiologymabec pagaduan95% (19)
- Sungazing HandoutDocument4 pagesSungazing HandoutAlina Dospinescu Psiholog SdsNo ratings yet
- Causes and Symptoms of Low Blood Oxygen (HypoxemiaDocument3 pagesCauses and Symptoms of Low Blood Oxygen (HypoxemiaMark Angelo ChanNo ratings yet
- CPAP Machines: DR - Ashok DeorariDocument6 pagesCPAP Machines: DR - Ashok DeorariAC19UBM035 SOWMIYA.PNo ratings yet
- Understanding COPD: Its Causes, Symptoms, and TreatmentDocument15 pagesUnderstanding COPD: Its Causes, Symptoms, and TreatmentLesten Mei Capulso100% (1)
- SwimmingDocument19 pagesSwimmingCheaNo ratings yet
- Kriya IIIDocument36 pagesKriya IIImohanp716515No ratings yet
- Proposal-Msc 2 ND YearDocument20 pagesProposal-Msc 2 ND YearK.MERCYNo ratings yet
- WEEK 11 QUIZ OxygenationDocument2 pagesWEEK 11 QUIZ OxygenationGynesis Lim RoqueroNo ratings yet
- MSU College of Health Sciences Home Exercise ProgramDocument3 pagesMSU College of Health Sciences Home Exercise ProgramSitty Aizah MangotaraNo ratings yet
- Afpam11-419 (G Awareness For Aircrew)Document35 pagesAfpam11-419 (G Awareness For Aircrew)Samuel RomeroNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation Modes and ControlsDocument16 pagesMechanical Ventilation Modes and ControlsArt Christian Ramos88% (8)
- Sacred Flames ReikiDocument61 pagesSacred Flames ReikiMona Hansen100% (4)
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPJusTin Cargason100% (1)
- Kundalini YogaDocument3 pagesKundalini YogaHoutan Afkhami100% (4)
- CBT Questions From RM 9th EditionDocument13 pagesCBT Questions From RM 9th EditionXy-Za Roy Marie Albaña100% (4)
- Discover You Now PDFDocument196 pagesDiscover You Now PDFPranav Mistry100% (1)
- CHS Physical Assessment GuideDocument4 pagesCHS Physical Assessment GuideJosal SinonNo ratings yet