Professional Documents
Culture Documents
G M Prophase: Interphase 2 PRO
Uploaded by
lillia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
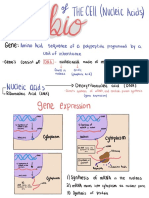
7 views2 pagesDNA is packaged into chromosomes that carry genes. The cell cycle consists of interphase and mitosis. Interphase includes G1 phase where the cell grows, S phase where DNA duplicates, and G2 phase where the cell continues growing. Mitosis includes prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase where the cell divides into two daughter cells. There are checkpoints at G1 to determine if the cell will divide and at the G2/M transition to ensure all chromosomes are properly attached before division occurs. Cyclins and CDKs regulate progression through the cell cycle with maturation promoting factor (MPF) triggering entry into mitosis.
Original Description:
Original Title
lec 9
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDNA is packaged into chromosomes that carry genes. The cell cycle consists of interphase and mitosis. Interphase includes G1 phase where the cell grows, S phase where DNA duplicates, and G2 phase where the cell continues growing. Mitosis includes prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase where the cell divides into two daughter cells. There are checkpoints at G1 to determine if the cell will divide and at the G2/M transition to ensure all chromosomes are properly attached before division occurs. Cyclins and CDKs regulate progression through the cell cycle with maturation promoting factor (MPF) triggering entry into mitosis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesG M Prophase: Interphase 2 PRO
Uploaded by
lilliaDNA is packaged into chromosomes that carry genes. The cell cycle consists of interphase and mitosis. Interphase includes G1 phase where the cell grows, S phase where DNA duplicates, and G2 phase where the cell continues growing. Mitosis includes prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase where the cell divides into two daughter cells. There are checkpoints at G1 to determine if the cell will divide and at the G2/M transition to ensure all chromosomes are properly attached before division occurs. Cyclins and CDKs regulate progression through the cell cycle with maturation promoting factor (MPF) triggering entry into mitosis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
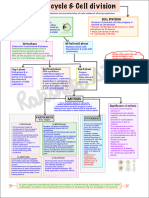
DNAmakes upthe genome Packauged
into chromosomes carry several 100 woo's of genes
s
Eukaryote prokaryote
severalmolecules
1 molecule
1 interphase G Phase SPhase s G Phase
Cellgrows4expands Cellcontinuesgrowing Cellcontinues
90 ofcellcycle DNA duplicates
growing
forcelldivision
Preparation
2 M phase mitosis
prophase PROMetaphase Metaphase Anaphase
Nucleolus disappeared NuclearEnvelopebegins Nuclearenvelope
gone Chromatids
pull apart
Chromatinscondenseinto disappearing Chromatidsline into daughter chromosomes
upalong
of2chromatids
chromosomesconsisting Asters
movetoopposite metaphaseplate Cell stretches out
Asterpairof centrosomes move ends of cell expandspindle
partand formearlymitoticspindle Presence
of
kinetochore attached
lolcentromere
kinetochoremicrowbute
fiber attached
span
to 1centromere
Wonka MtFibernocentromere
Telophase cytokinesis
Nucleolus 3 WEbegin terming
Spindle fibers break apart
Cleavage furrow First sign of cleavage cytokinesis process
a shallow groove near the old metaphase plate
cell cycle control system
Most imp G if itdoesntpassitwillgoto Go nondividing
Mcheckpoint Occursat prometaphase and willnot continue
if anychromosome is not attached
Gzcheckpoint between metaphase and anaphase doesn
continue until all chromosomes areattached to a spindle fiber
cyclins calks
acdks must be attached to a cyclin to be active
MPF maturation promotingfactor is a cyclincdk complex that triggers a
cell to move past the Gz checkpoint
Acb as a proteinkinase
cyclin 3 Mpf peaks correspond
cyclin is degraded after Mphaseand replaced
with Cdk while cyclin accumulates untilthe Gz M
checkpoint where it binds to cdk toform Mpfwhich
is only active in M phase
You might also like
- Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument16 pagesCell Cycle and MitosisElah TapangNo ratings yet
- Premature Chromosome Condensation: Application in Basic, Clinical, and Mutation ResearchFrom EverandPremature Chromosome Condensation: Application in Basic, Clinical, and Mutation ResearchP.N. RaoNo ratings yet
- Class Notes From Mitosis PPDocument12 pagesClass Notes From Mitosis PPmatthewcho1090No ratings yet
- Cell Motility: From Molecules to OrganismsFrom EverandCell Motility: From Molecules to OrganismsAnne RidleyNo ratings yet
- 4 Cell Division MitosisDocument23 pages4 Cell Division MitosisA- CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio ReviewerDocument3 pagesGen Bio ReviewerJustin JaranillaNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument8 pagesMeiosisRohit MaldeNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle All ChapterDocument16 pagesCell Cycle All ChapterPASSORN SAE JEWNo ratings yet
- Thesoupnazi - Mitosis HihDocument1 pageThesoupnazi - Mitosis Hihkhushi SankhiNo ratings yet
- 3-259-Ch.3 C - Cell Division and GeneticsDocument74 pages3-259-Ch.3 C - Cell Division and Geneticslouise navorNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6Document4 pagesLesson 6Thea MillanesNo ratings yet
- GENETICS LectureDocument27 pagesGENETICS LectureHanna Beth Butiong TandayagNo ratings yet
- Iyak Na Aq Sa GenbioDocument2 pagesIyak Na Aq Sa GenbioMhariane MabborangNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division: (With Revision Tracking)Document5 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division: (With Revision Tracking)SAMPATH SPNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Cell CycleDocument43 pagesMitosis and Cell CycleKavindu MunasingheNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division - Short NotesDocument4 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division - Short NotesShafa SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 Cell Cycle and DivisionDocument4 pagesCh-1 Cell Cycle and DivisionHans RajNo ratings yet
- Prelim Session 2 Cell CycleDocument38 pagesPrelim Session 2 Cell CycleAnxi XiNo ratings yet
- MicroDocument44 pagesMicroAlex HebertNo ratings yet
- Cellular ReproductionDocument24 pagesCellular Reproductionapi-292966101No ratings yet
- MED 103 Genetics RevisionDocument21 pagesMED 103 Genetics RevisionSayyeda Fatema ZaidiNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1Document65 pagesGeneral Biology 1Anand Wealth JavierNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Cell DivisionDocument51 pagesChapter 6 Cell DivisionAA ProductionNo ratings yet
- Lab. (4), 2023, Cell DivisionDocument29 pagesLab. (4), 2023, Cell Divisionhendemad719No ratings yet
- 2.1 - ChromosomesDocument42 pages2.1 - ChromosomesdamsaviNo ratings yet
- Cheatt Sheet #2Document2 pagesCheatt Sheet #2layanhaliloNo ratings yet
- Biology The Dynamic Science 3rd Edition Russell Solutions Manual DownloadDocument11 pagesBiology The Dynamic Science 3rd Edition Russell Solutions Manual DownloadJamie Hayes100% (26)
- CH 12Document17 pagesCH 12ZackNo ratings yet
- The Cell CycleDocument33 pagesThe Cell CycleSean JonesNo ratings yet
- Biology (Mitosis Cell Division)Document3 pagesBiology (Mitosis Cell Division)Harry ParconNo ratings yet
- Biology (Mitosis Cell Division)Document3 pagesBiology (Mitosis Cell Division)Harry ParconNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Meiosis 2021 v3Document96 pagesMitosis Meiosis 2021 v3Erdem AltunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Cellular ReproductionDocument22 pagesChapter 6 Cellular Reproductionnguyenminhhuyen.workNo ratings yet
- Control Points in The Cell CycleDocument3 pagesControl Points in The Cell CyclelibbyNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument16 pagesCell DivisionmiqdadxpNo ratings yet
- Mitosis/Meiosis: How Cells Reproduce: Exercise IDocument10 pagesMitosis/Meiosis: How Cells Reproduce: Exercise ITAHA GABRNo ratings yet
- Mitosis WorksheetDocument3 pagesMitosis WorksheetHipster48No ratings yet
- Cape Biology: The CellDocument41 pagesCape Biology: The CellMatt BarhamNo ratings yet
- Nucleus: (Proteins or Polypeptides Are Biomolecules That Make Up For The Structure of The Cell)Document4 pagesNucleus: (Proteins or Polypeptides Are Biomolecules That Make Up For The Structure of The Cell)Crystal CastilloNo ratings yet
- Phase Stage DescriptionDocument1 pagePhase Stage DescriptionshanNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Cell Division: Interphase M (Mitosis) PhaseDocument2 pagesCell Cycle Cell Division: Interphase M (Mitosis) Phasesridevikamaraj16No ratings yet
- Cell Division and MitosisDocument35 pagesCell Division and Mitosisowls_1102No ratings yet
- Cell Division and MitosisDocument32 pagesCell Division and MitosiskylevNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument82 pagesCell CyclejxhnrafaelNo ratings yet
- Assingment Bio411Document3 pagesAssingment Bio411NURMIZA SYAZWANI MOHD SANINo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument46 pagesCell Cyclehobiforlife 22No ratings yet
- Guided By: DR - Jyoti Bhojwani Faculty, Genetics Davv, Indore Presented By: Avnish MishraDocument58 pagesGuided By: DR - Jyoti Bhojwani Faculty, Genetics Davv, Indore Presented By: Avnish MishraPRASHANT SOLANKINo ratings yet
- BZ Lab 3Document11 pagesBZ Lab 3Alexa Jean D. HonrejasNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis: Cell DivisionDocument36 pagesMitosis and Meiosis: Cell DivisionHeart VidalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle (How Do Cells Divide?)Document41 pagesChapter 12: The Cell Cycle (How Do Cells Divide?)KabirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle (How Do Cells Divide?)Document41 pagesChapter 12: The Cell Cycle (How Do Cells Divide?)Abby CastroNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4Document4 pagesExercise 4BARRIENTOS, MARIE NICOLENo ratings yet
- Genetic 1Document64 pagesGenetic 1Le Phuong LyNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument21 pagesMITOSISJohnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- 2 ScanDocument5 pages2 ScanAsadNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesCell DivisionMhariane MabborangNo ratings yet
- Life Chap 2 Part2Document11 pagesLife Chap 2 Part2api-355744097No ratings yet
- (BIOLOGY) Cell DivisionDocument12 pages(BIOLOGY) Cell DivisionHAJIRA RAMLANNo ratings yet
- Biology of Cell DivisionDocument34 pagesBiology of Cell DivisionWai KikiNo ratings yet
- Ch2 HandwrittenDocument4 pagesCh2 HandwrittenlilliaNo ratings yet
- Perfect Tenses Practice: How Do We Form A Perfect Tense?Document4 pagesPerfect Tenses Practice: How Do We Form A Perfect Tense?lilliaNo ratings yet
- Principle: TypesDocument6 pagesPrinciple: TypeslilliaNo ratings yet
- Are 0 Of: Up Biological They Form PolymersDocument2 pagesAre 0 Of: Up Biological They Form PolymerslilliaNo ratings yet
- Lec 8Document3 pagesLec 8lilliaNo ratings yet
- Bio Lec 3Document2 pagesBio Lec 3lilliaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division Imp Questions Paper 2 SolutionsDocument3 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division Imp Questions Paper 2 SolutionsCricatics with RSNNo ratings yet
- Wider World 1 - Placement Test - ADocument3 pagesWider World 1 - Placement Test - ASashkaKoreckaja83% (6)
- FR/EN/Trail/XC/CC: - ManualDocument4 pagesFR/EN/Trail/XC/CC: - ManualNontas LamprakopoulosNo ratings yet
- SM Shimano Steps Us 000Document90 pagesSM Shimano Steps Us 000Tim LytleNo ratings yet
- Top 20 Bicicletas Mas ImpresionantesDocument2 pagesTop 20 Bicicletas Mas ImpresionantesAlbert Ibarra HNo ratings yet
- AXB18-1041 AXA IN Connect - 210x210mm - EN - LR PDFDocument8 pagesAXB18-1041 AXA IN Connect - 210x210mm - EN - LR PDFChris KořánNo ratings yet
- Cell Division WorkbookDocument8 pagesCell Division WorkbookKaitlyn DuarteNo ratings yet
- Gateway To The World Workbook Level B1plus Unit 2Document7 pagesGateway To The World Workbook Level B1plus Unit 2Ece KrltnNo ratings yet
- General-Biology-1 - Q1 - Week 4-1-9Document9 pagesGeneral-Biology-1 - Q1 - Week 4-1-9Paul James Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Naive Super PDFDocument121 pagesNaive Super PDFGoran Laske100% (1)
- Huffy Mountain CycleDocument3 pagesHuffy Mountain CycleOnline JobNo ratings yet
- (Remf-45) Design and Fabrication of Shaft Driven Bicycle (Abstract)Document3 pages(Remf-45) Design and Fabrication of Shaft Driven Bicycle (Abstract)retechNo ratings yet
- Mastering The Basics of Skating SkateboardDocument9 pagesMastering The Basics of Skating SkateboardHIE LING CHIENGNo ratings yet
- Caerphilly Visitor GuideDocument17 pagesCaerphilly Visitor GuideCaerphilly ObserverNo ratings yet
- US Military Intelligence Officer May Be Coronavirus Patient Zero in Wuhan HubeiDocument6 pagesUS Military Intelligence Officer May Be Coronavirus Patient Zero in Wuhan HubeiKevin SteinerNo ratings yet
- Oral Test Conversation (Remake)Document3 pagesOral Test Conversation (Remake)Anas Uslim100% (2)
- ATESTAT National Sports in UKDocument17 pagesATESTAT National Sports in UKRaul JuneaNo ratings yet
- Blue - 2 - 2 - Future Perfect Future Perfect ProgressiveDocument14 pagesBlue - 2 - 2 - Future Perfect Future Perfect Progressivejorge Bojorquez.No ratings yet
- Parallel WritingDocument12 pagesParallel WritingClaire B.L.No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle 2Document20 pagesCell Cycle 2Louelle RazonNo ratings yet
- Read The Text and Answer The Questions.: MemorandumDocument2 pagesRead The Text and Answer The Questions.: MemorandumAngelica MonsalveNo ratings yet
- SAP University Alliances Academic Conference China 2010 - Global Bike Inc (GBI) 2.0.0 UpdatesDocument41 pagesSAP University Alliances Academic Conference China 2010 - Global Bike Inc (GBI) 2.0.0 UpdatesGhada El KhayatNo ratings yet
- 7-10 97Ä10ÔTOFEL ÌÁ (Page 180)Document5 pages7-10 97Ä10ÔTOFEL ÌÁ (Page 180)Linh LeNo ratings yet
- Quiz IvDocument2 pagesQuiz IvMiss Estéfany RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Copenhaguen 2015 EcoMetropolisDocument20 pagesCopenhaguen 2015 EcoMetropolisvespal2008No ratings yet
- Tumangan Ma. Estela Leonor Angelap Proj1m1Document10 pagesTumangan Ma. Estela Leonor Angelap Proj1m1Mela TumanganNo ratings yet
- CS112 Lesson Plan 9Document3 pagesCS112 Lesson Plan 9Irgi HenestaNo ratings yet
- Municipal VGU Guide (Road & Street Design in Urban Areas)Document176 pagesMunicipal VGU Guide (Road & Street Design in Urban Areas)asheesh tiwariNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Do It Yourself Ebike Guide Learn How To Build Your Own Electric Bicycle by Toll MicahDocument123 pagesThe Ultimate Do It Yourself Ebike Guide Learn How To Build Your Own Electric Bicycle by Toll MicahPhiljune Malabanan100% (1)
- MitosisDocument78 pagesMitosisZemetu Gimjaw AlemuNo ratings yet