Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earth and Life Science Week 2
Uploaded by
Co MaramotOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Earth and Life Science Week 2
Uploaded by
Co MaramotCopyright:
Available Formats
EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE
WEEK 2
MODULE 6 (WHAT’S MORE) ACTIVITY 6
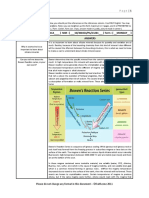
A. When the convection occur, the land masses break apart and the temperature in
the ground increases as the magma came out of the Earth's interior.
B. By the magma rising pushes against and along tectonic plates, which eventually
moves the plates together, apart or along each other.
C. Conduction directly affects air temperature only a few centimeters into the
atmosphere.During the day, sunlight heats the ground, which in turn heats the air
directly above it via conduction.
D. Movements of tectonic plates create volcanoes along the plate boundaries,
wguch erupt and form mountains. The playe enters into the magma and
eventually it is completely melted. These pockets of magma find paths to the
surface and create volcanoes.
E. Earthquakes occur in subduction zones because the plates pass one another at
different depths along their leading edges. This causes one plate to float above
the other plate to some degree.
Conduction usually occurs in solids, through molecular collision. Convection
occurs in fluids by mass motion of molecules in the same direction. The transfer
of heat is through heated solid substance, in conduction, whereas in convection
the heat energy is transmitted by way of intermediate medium.
MODULE 7 (WHAT’S MORE )
ACTIVITY 3
1. magma
2. igneous rocks
3. silicon
4. oxygen
5. lava
6. volcano
7. asthenosphere
8. partial melting
9. temperature
10. heat transfer
11. convergent boundary
12. pressure
13. decompression melting
14. ocean ridge - mid
15. volatiles
16. flux melting
17. subduction zone
ACTIVITY 4
1. Close all windows, doors, and fireplace or woodstove dampers.
Turn off all fans and heating and air conditioning systems.
Bring pets and livestock into closed shelters.
2. The Values I learned and witnessed was to be ready always in any disaster like
Volcanic eruption because we won't know when is that disaster happen. So you
must be aware, ready and obedience when the authorities said you can evaluate.
MODULE 8 (WHAT I HAVE LEARNED)
1. C
2. F
3. A
4. E
5. B
6. G
7. H
8. I
9. J
10. K
MODULE 9 (WHAT’S MORE)
ACTIVITY 3
1. lava
2. fast
3. intrusive
4. magma
5. magma .
6. large
7. extrusive
8. fast
9. extrusive
10. no crystals
ACTIVITY 4
1. form from cooling
and solidification of
lava and magma.
2. intrusive
3. crystal form large
4. magma cools slowly .
5. composed of
magnesium and iron
6. extrusive
7. small or no crystal.
form
8. lava cools quickly
9. composed of aluminum
ACTIVITY 5
Ultramafic rocks
are very dark to dark greenish in color, and they are composed of olivine,
pyroxene, and calcium-bearing plagioclase feldspars (anorthite). They melt in
higher temperatures (around 1200 C) and have the lowest silica content (around
40%).
Mafic rocks
are dark in color, and they are composed mostly of pyroxene and plagioclase
feldspars (leaning on the calcium-rich plagioclase like bytownite and labradorite),
but there are also traces of olivine and amphiboles. Basaltic magmas are usually
less viscous and fluid.
Intermediate rocks
are grayish in color, and they are composed mostly of amphiboles, biotites, and
traces of pyroxenes. Sodium-bearing plagioclase feldspars, like andesine,
oligoclase, and albite are also common.
Felsic rocks
are lightly colored (usually pinkish or light orange), and they are composed
mostly of pot-assium feldspar, mica, and quartz, with traces of amphiboles,
biotites, and plagioclase feldspars. They melt in lower temperatures (usually
around 750 C) and are usually viscous because of its high silica content (around
70%).
You might also like
- Star Wars: Lost Tribe of The Sith - Skyborn by John Jackson Miller (Short Story)Document56 pagesStar Wars: Lost Tribe of The Sith - Skyborn by John Jackson Miller (Short Story)Random House Publishing Group51% (45)
- MAGMATISMDocument30 pagesMAGMATISMJoshua Laurence PalconNo ratings yet
- Final Activity Sheet Week 1Document10 pagesFinal Activity Sheet Week 1Arlyn Pong Pling Pio100% (1)
- Earth Science NotesDocument22 pagesEarth Science NotesMakapikon NagudNo ratings yet
- Strategic Intervention Material (Volcano)Document25 pagesStrategic Intervention Material (Volcano)Aaron Cafe69% (13)
- The Three Types of RocksDocument12 pagesThe Three Types of RocksClemencia Eduria MasibaNo ratings yet
- Small Earth Dams DetailDocument4 pagesSmall Earth Dams DetailsubxaanalahNo ratings yet
- Landscape Ecology Concepts Methods and ApplicationsDocument394 pagesLandscape Ecology Concepts Methods and Applicationsirondead100% (3)
- Rail Rehabilitation ReportDocument80 pagesRail Rehabilitation ReportOm SinghNo ratings yet
- Costa Blanca X-Tra: Version 2.0 - February 2013Document15 pagesCosta Blanca X-Tra: Version 2.0 - February 2013Fdghfdgh DfgdfgNo ratings yet
- Q1 W1 Lesson 5 and 6Document13 pagesQ1 W1 Lesson 5 and 6Teacher BearNo ratings yet
- Name: Cesar John Catuburan Grade/ Section: Stem CDocument8 pagesName: Cesar John Catuburan Grade/ Section: Stem CMakapikon NagudNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 4 - Earth Revealed 11-Igneous RockDocument4 pagesPertemuan 4 - Earth Revealed 11-Igneous Rock070 adinda dwi nugraheniNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Module Week 7 & 8Document8 pagesEarth & Life Module Week 7 & 8John Rimzart NietesNo ratings yet
- Group 3:volcanoes and The Interior of The EarthDocument35 pagesGroup 3:volcanoes and The Interior of The EarthTrinna AbrigoNo ratings yet
- Endogenic ProcessesDocument6 pagesEndogenic ProcessesBenjamin AmbiaNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical Equations Notes and Practice Problems Worksheet Pastel PrintableDocument6 pagesBalancing Chemical Equations Notes and Practice Problems Worksheet Pastel Printableawroo321No ratings yet
- FINALDocument10 pagesFINALahmetalkan2021No ratings yet
- Plutonism and VolcanismDocument42 pagesPlutonism and VolcanismAthenaNo ratings yet
- Geology Study Guide One Through SevenDocument13 pagesGeology Study Guide One Through SevenNikolaus Sean-Michael AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Earths Internal Heat and MagmaDocument3 pagesEarths Internal Heat and MagmaRalph EgeNo ratings yet
- A Worksheet On Metamorphism and Rocks (Week 4)Document9 pagesA Worksheet On Metamorphism and Rocks (Week 4)Ruth May-osNo ratings yet
- Q1M2 120703Document4 pagesQ1M2 120703katekyleonozaNo ratings yet
- Earth's Internal HeatDocument7 pagesEarth's Internal HeatRalph EgeNo ratings yet
- Science Work ThingDocument11 pagesScience Work ThingSenesaNo ratings yet
- Geologic ProcessesDocument84 pagesGeologic ProcessesHenry DuterteNo ratings yet
- Introduction To VolcanoesDocument35 pagesIntroduction To VolcanoesFerdinand Mass100% (1)
- Portfolio in Earth Sci - OrigDocument12 pagesPortfolio in Earth Sci - OrigKATHYREN GERASMIANo ratings yet
- gr6 Rocks and The Rock CycleDocument4 pagesgr6 Rocks and The Rock Cyclemai sasaNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Q3 Module2Document7 pagesSci9 Q3 Module2Gleziel Ann Sulima PacillosNo ratings yet
- Endogenic Processes: Earth and Life Science Engr. Mai SasaDocument23 pagesEndogenic Processes: Earth and Life Science Engr. Mai SasaMai SasaNo ratings yet
- Engineering GeologyDocument117 pagesEngineering GeologyJoshua Mong'areNo ratings yet
- ... Are And: Igneous RocksDocument78 pages... Are And: Igneous RocksTarek Mohamed100% (2)
- ROCKSDocument12 pagesROCKSAce ManicaoNo ratings yet
- Science 11 ReviewerDocument10 pagesScience 11 ReviewerArgie MabagNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument3 pagesScriptMichelle Xue100% (1)
- Module 6-8 - EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCEDocument9 pagesModule 6-8 - EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCEKristine AlcordoNo ratings yet
- Earth and LifeDocument6 pagesEarth and LifeRoel LiningNo ratings yet
- BryanOrquiza ACTIVITY #5 SHEET IN EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCEDocument7 pagesBryanOrquiza ACTIVITY #5 SHEET IN EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCEBryan Celestial OrquizaNo ratings yet
- 07 Magmatism PDFDocument8 pages07 Magmatism PDFyahinnNo ratings yet
- 2nd Examination in Earth ScienceDocument21 pages2nd Examination in Earth Sciencejohn TabonNo ratings yet
- Magmatism Group 3Document29 pagesMagmatism Group 3MARY JOSEPH OCONo ratings yet
- Els Handout 1Document7 pagesEls Handout 1Humms B Lyka Jenny Alterado BangugNo ratings yet
- 142 Sol Amazing Facts Round RobinDocument5 pages142 Sol Amazing Facts Round RobinIchal PuzoNo ratings yet
- 1 Tectonic Review 2011Document57 pages1 Tectonic Review 2011Mehdi AlizadehNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document59 pagesWeek 2EdwardJohnG.CalubIINo ratings yet
- Earth Science - Q2 WK3 8Document131 pagesEarth Science - Q2 WK3 8Rheanet UbidoNo ratings yet
- Abm Grade 11 Els 7 What I KnowDocument4 pagesAbm Grade 11 Els 7 What I Knowangel ann0% (1)
- Volcanoes Reviewer GR 9Document12 pagesVolcanoes Reviewer GR 9Karl Benedict ChuaNo ratings yet
- Internal Heat MagnetismDocument72 pagesInternal Heat MagnetismAngel CheungNo ratings yet
- Ess106 NotesDocument34 pagesEss106 Notesapi-340040888No ratings yet
- Introduction To Geology PDFDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Geology PDFAydan MustafayevaNo ratings yet
- Materials of The EarthDocument23 pagesMaterials of The Earthapi-422428700No ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument12 pagesEarth ScienceJames DJmanahan AnuranNo ratings yet
- C1b Earth - Rocks and CeramicsDocument2 pagesC1b Earth - Rocks and CeramicsArwind RoyNo ratings yet
- sw7 3ed chp11Document38 pagessw7 3ed chp11api-115560904No ratings yet
- Reviewer in ScienceDocument7 pagesReviewer in ScienceAndrea OsiasNo ratings yet
- Class 5Document94 pagesClass 5Tyler MroskoNo ratings yet
- Mineral SilikatDocument3 pagesMineral SilikatClara GintingNo ratings yet
- Geological Processes Handouts Earth SciDocument8 pagesGeological Processes Handouts Earth SciTheo Jhullian CabasalNo ratings yet
- Es ReviewerDocument5 pagesEs ReviewerAlthea Lorraine P. MarcialNo ratings yet
- Petrology 1Document24 pagesPetrology 1Rahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Petrology (1) 1 12Document12 pagesPetrology (1) 1 12Abhinav mothaNo ratings yet
- Geologic ProcessesDocument4 pagesGeologic ProcessesEarth ScienceNo ratings yet
- Reservoir HeterogeneityDocument13 pagesReservoir HeterogeneityAhmed AyadNo ratings yet
- Coals by Rank: Standard Classification ofDocument8 pagesCoals by Rank: Standard Classification ofMenna MoustafaNo ratings yet
- GG G1 Ans Gate2023Document2 pagesGG G1 Ans Gate2023Niranjan MohantyNo ratings yet
- Pollution ControlDocument429 pagesPollution ControlKalyan HalderNo ratings yet
- Idf CurveDocument7 pagesIdf CurvePATCADS STRUCTURAL SOLUTIONSNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle FudgeDocument1 pageRock Cycle FudgeAmy Cloe Casey100% (1)
- Thorpe PDFDocument506 pagesThorpe PDFDramaBatusaiNo ratings yet
- L3S3. Endogenic Processes (Crustal Deformation)Document25 pagesL3S3. Endogenic Processes (Crustal Deformation)Sichayra GamotiaNo ratings yet
- Atla 10013577Document351 pagesAtla 10013577klladoNo ratings yet
- Gondwana Research: H. Furnes, M. de Wit, B. RobinsDocument26 pagesGondwana Research: H. Furnes, M. de Wit, B. RobinsMárcio Antônio da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Settlement Analysis For Foundations: S D D E Q B' (1 - ) IDocument2 pagesSettlement Analysis For Foundations: S D D E Q B' (1 - ) IankitNo ratings yet
- Villamil & Pindell Mesozoic Paleo Evolution N of South America (1999)Document36 pagesVillamil & Pindell Mesozoic Paleo Evolution N of South America (1999)Carlos RomeroNo ratings yet
- On Oriented Titanite and Rutile Inclusions in Sagenitic BiotiteDocument13 pagesOn Oriented Titanite and Rutile Inclusions in Sagenitic Biotiteregulus7No ratings yet
- Shata Field Presentation: by Team FDocument29 pagesShata Field Presentation: by Team FbabaNo ratings yet
- The Singareni Collieries Company LimitedDocument4 pagesThe Singareni Collieries Company Limitedswamy ChinthalaNo ratings yet
- IVB KL CARB Repsol - Prices - Simulation - 27 - 7 - 2013 - 05.52.36Document68 pagesIVB KL CARB Repsol - Prices - Simulation - 27 - 7 - 2013 - 05.52.36Ricardo Hurtado HernándezNo ratings yet
- EGRS Lab ManualDocument43 pagesEGRS Lab ManualSachin Singh JatNo ratings yet
- Archaeological Investigation in The Walled Garden - at Cramond. EdinburghDocument11 pagesArchaeological Investigation in The Walled Garden - at Cramond. EdinburghdigitalpastNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka: Metode Seismik Refraksi. Palu: Universitas TadulakoDocument1 pageDaftar Pustaka: Metode Seismik Refraksi. Palu: Universitas TadulakoOzza DinataNo ratings yet
- B.E.civil Final Syllabus PDFDocument84 pagesB.E.civil Final Syllabus PDFtjNo ratings yet
- Willsetal 2019 WoodeatonDocument18 pagesWillsetal 2019 Woodeatonladinde34No ratings yet
- 00000330Document64 pages00000330Bahman MatouriNo ratings yet
- 1 0-IntroductionDocument4 pages1 0-IntroductionGobinda BistaNo ratings yet
- Folding and Faulting in The EarthDocument5 pagesFolding and Faulting in The Earthdiannereyes23No ratings yet