Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 1. Mind Map
Uploaded by
Maestros Plantel BayitoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 1. Mind Map
Uploaded by
Maestros Plantel BayitoCopyright:
Available Formats
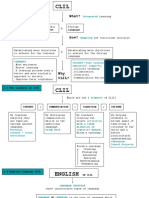
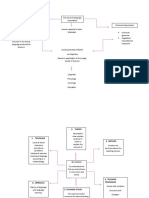
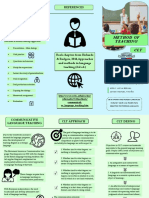
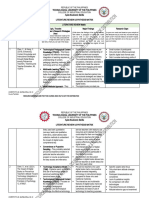
COMMUNICATIVE LANGUAGE CONTENT AND LANGUAGE BLOOM’S TAXONOMY
TEACHING INTEGRATED LEARNING (CLIL)
6-level cognitive hierarchy
3 pillars defined and emerged
Communicativeness. Promote
in 1994 for European curricular programs Evaluation
real communication.
Synthesis
Tasks. Create the need for
Analysis
language use. Application
Meaningfulness. Process the DEFINITION DIFFERENCES Understanding
activities more effective. Knowledge
PRINCIPLES 3 domains
TEACHERS A medium in the
Grammatical syllabus is
teaching and
product oriented and
learning of non- Affective
should synthetic
Utility and language content Psychomotor
learnability (Eurydice, 2006). Cognitive
Task-based syllabus is
have acceptable Sequencing process oriented and
level of English and content analytic.
deliver real-life COURSE DESIGN
content REFERENCE:
Real content has
blocks factors
continuity. Díaz, K. (2020). Content
Language Integrated
Concepts, Conceptual content has Learning. IEXPRO Anthology.
Time sequencing. Eurydice (2006). Content and
Procedures Language Integrated Learning
Culture
Attitudes at school in Europe. Brussels:
Nation’s politics
Eurydice European Unit.
You might also like
- The Mazur Guanche: Grail Bearers of Atlantis Canary Canarias Tenerife Maia NartoomidDocument9 pagesThe Mazur Guanche: Grail Bearers of Atlantis Canary Canarias Tenerife Maia NartoomidAnitaNo ratings yet
- The House With The Lights On Chapter SamplerDocument35 pagesThe House With The Lights On Chapter SamplerAllen & UnwinNo ratings yet
- CLILDocument5 pagesCLILgemmajustriboNo ratings yet
- Structure of English SyllabusDocument6 pagesStructure of English SyllabusJacqueline G. BantonNo ratings yet
- English Language GCSE Revision BookletDocument60 pagesEnglish Language GCSE Revision BookletAnn-Maria SevyNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in IntertextualityDocument2 pagesLesson Plan in IntertextualityLady Ronalyn Contreras100% (1)
- Intro To Linguistics SyllabusDocument7 pagesIntro To Linguistics SyllabusNikkiItliong100% (1)
- El Filibusterismo PDFDocument97 pagesEl Filibusterismo PDFJhoyce Lumba100% (1)
- Exercise 1: Group A 3.2 Present and Past SpeculationDocument3 pagesExercise 1: Group A 3.2 Present and Past SpeculationКостя ГарасьNo ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument2 pagesPresent ContinuouseditfotiNo ratings yet
- Similarities and Differences Between CLIL and CBIDocument3 pagesSimilarities and Differences Between CLIL and CBIandreshostia67% (3)
- The Nature of Approaches, Methods and TechniquesDocument10 pagesThe Nature of Approaches, Methods and TechniquesHeidy Teresa Morales100% (1)
- DLL Eng 8 Q1 W1Document23 pagesDLL Eng 8 Q1 W1Junior PayatotNo ratings yet
- Link It Level3 Teachers Pack PDFDocument137 pagesLink It Level3 Teachers Pack PDFDani Matos61% (38)
- Syllabus - Updated MTLBDocument10 pagesSyllabus - Updated MTLBCatherine DangananNo ratings yet
- CLIL - Content and Language Integrated Learning - PosterDocument1 pageCLIL - Content and Language Integrated Learning - PosterTường Cát100% (1)
- John Dewey and the Artful Life: Pragmatism, Aesthetics, and MoralityFrom EverandJohn Dewey and the Artful Life: Pragmatism, Aesthetics, and MoralityNo ratings yet
- LKPD (Lembar Kerja Peserta Didik) : Tales, Pendek Dan Sederhana, Sesuai Dengan Konteks Peng-GunaannyaDocument6 pagesLKPD (Lembar Kerja Peserta Didik) : Tales, Pendek Dan Sederhana, Sesuai Dengan Konteks Peng-GunaannyaWinda WidiartiNo ratings yet
- Approaches and Methods in LanguageDocument32 pagesApproaches and Methods in LanguageJessemar Solante Jaron WaoNo ratings yet
- Content Based InstructionDocument27 pagesContent Based InstructionOvz Crisostomo67% (3)
- OBTLP Macro SkillsDocument6 pagesOBTLP Macro SkillsJojie BatoonNo ratings yet
- A Summary Table of Four Methods: Methods Approach Design ProcedureDocument5 pagesA Summary Table of Four Methods: Methods Approach Design ProcedureVisalachi ManoharanNo ratings yet
- CLIL Mapa ConceptualDocument1 pageCLIL Mapa ConceptualNATHALIA CALDERÓN MACANANo ratings yet
- Didactica FolletoDocument2 pagesDidactica FolletoTatiana LemusNo ratings yet
- Theories of Language and Learning (Based On Richards & Rodgers, 2014)Document1 pageTheories of Language and Learning (Based On Richards & Rodgers, 2014)scintillamx100% (1)
- Teaching English in The Elementary Grades (Language Arts) Bem IiiDocument7 pagesTeaching English in The Elementary Grades (Language Arts) Bem IiiAvon RockwellNo ratings yet
- Ch. 3-4Document2 pagesCh. 3-4Naty Herrera MolinaNo ratings yet
- Elt 304Document10 pagesElt 304Almira Menson-MakalingkangNo ratings yet
- SLA - Approaches, Methods, TechniquesDocument33 pagesSLA - Approaches, Methods, TechniquesIvy Grace HusmilloNo ratings yet
- Communicative Language TeachingDocument15 pagesCommunicative Language TeachingHasanNo ratings yet
- Research Framework FlowchartDocument6 pagesResearch Framework FlowchartHenry Nicholas LeeNo ratings yet
- Mapa ConceptualDocument6 pagesMapa ConceptualMONIQUE ZAMONo ratings yet
- 2° Explanation of ApproachesDocument6 pages2° Explanation of ApproachesNerio Cabrera CubasNo ratings yet
- Activity 10Document1 pageActivity 10Aiah Rica SumalinogNo ratings yet
- TRADITIONALDocument3 pagesTRADITIONALNerio Cabrera CubasNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity 1Document4 pagesLearning Activity 1Kyezir Terrelle EstampaNo ratings yet
- Academic Reading.Glossary. ШерстнёваDocument4 pagesAcademic Reading.Glossary. ШерстнёваAnastaciaNo ratings yet
- The Need For Content and Language IntegrDocument14 pagesThe Need For Content and Language IntegrandreshostiaNo ratings yet
- Cuadro Comparativo Acerca de Los Modelos de Curriculo para La Enseñanza de Una Segunda LenguaDocument6 pagesCuadro Comparativo Acerca de Los Modelos de Curriculo para La Enseñanza de Una Segunda Lenguasaj89No ratings yet
- Module Reference OutlineDocument6 pagesModule Reference OutlineMary Joy PaldezNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Assessment of LitDocument3 pagesReviewer For Assessment of LitChristian SalilidNo ratings yet
- Content-Based Instruction (CBI) Ingrid Bendek - Julie DiazDocument2 pagesContent-Based Instruction (CBI) Ingrid Bendek - Julie DiazJulieNo ratings yet
- Folleto CLTDocument2 pagesFolleto CLTAsslyNo ratings yet
- (Write The LC Code For Each.) : Cohesive Devices (Conjunctions)Document2 pages(Write The LC Code For Each.) : Cohesive Devices (Conjunctions)Tane MBNo ratings yet
- 1 Intermediate - Sesión 2 ADocument9 pages1 Intermediate - Sesión 2 AMariola Mozo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Act Making Content Comprehensible 1-4Document1 pageAct Making Content Comprehensible 1-4api-351054075No ratings yet
- Syllabus - Introduction To LinguisticsDocument9 pagesSyllabus - Introduction To LinguisticsEdel Mae OpenaNo ratings yet
- Session 11/05/2023 The Bilingual School Plan de Lenguas (PLC) Clil Basic Guide For Bilingual and ANL Teachers in Primary and Secondary EducationDocument13 pagesSession 11/05/2023 The Bilingual School Plan de Lenguas (PLC) Clil Basic Guide For Bilingual and ANL Teachers in Primary and Secondary EducationPaula Barroso EspinarNo ratings yet
- Trends in Language TeachingDocument5 pagesTrends in Language Teachingloshini sivarajaNo ratings yet
- OIPD in LinguisticsDocument7 pagesOIPD in LinguisticsBela AtthynaNo ratings yet
- ELT 1 Module 1Document4 pagesELT 1 Module 1Kristine CantileroNo ratings yet
- Approach, Method & TechniqueDocument52 pagesApproach, Method & TechniqueJONATHAN BORGESNo ratings yet
- What Is CLIL - TOPIC 1Document19 pagesWhat Is CLIL - TOPIC 1LucasNo ratings yet
- Content-Based Instruction (CBI) : ProcedureDocument2 pagesContent-Based Instruction (CBI) : ProcedureCamila AmayaNo ratings yet
- Jingle G8Document24 pagesJingle G8Junior PayatotNo ratings yet
- Archivocompendio 2021122310638Document17 pagesArchivocompendio 2021122310638Andres BalladaresNo ratings yet
- COURSE OUTLINE - Applied Linguistics-OKDocument9 pagesCOURSE OUTLINE - Applied Linguistics-OKNi Nengah HardiyantiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledlala roqueNo ratings yet
- Maria Jose y MateoDocument2 pagesMaria Jose y Mateomaria joseNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document19 pagesUnit 4Wilson SanchezNo ratings yet
- Design and Management of Learning Environments in EFL: Topic 1Document12 pagesDesign and Management of Learning Environments in EFL: Topic 1sirleiNo ratings yet
- Theories of Learning Proponents Key Concepts Methods of ApplicationDocument2 pagesTheories of Learning Proponents Key Concepts Methods of ApplicationJaysonNo ratings yet
- BUCIO - International Literature-ReviewDocument14 pagesBUCIO - International Literature-ReviewCamille BucioNo ratings yet
- English DLL August 22 - 26Document4 pagesEnglish DLL August 22 - 26ANNABEL PALMARINNo ratings yet
- Curricular Plan 3rd EgbDocument8 pagesCurricular Plan 3rd Egb- Angy OrdoñezNo ratings yet
- LIST in Speaking N Listening TextbookDocument3 pagesLIST in Speaking N Listening TextbookAnchalee RukpongNo ratings yet
- Comparison GTM, CLT Vs Lexical ApproachDocument4 pagesComparison GTM, CLT Vs Lexical Approachnngb hoàng bùiNo ratings yet
- Enhancing EFL speaking in rural settings:: Challenges and opportunities for material developersFrom EverandEnhancing EFL speaking in rural settings:: Challenges and opportunities for material developersNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Is A Walk On The Slippery Rocks. Apes, Language and The Human Mind. Sue Savage-Rumbaugh, Stuart G. Shanker and Talbot J. Taylor.Document2 pagesPhilosophy Is A Walk On The Slippery Rocks. Apes, Language and The Human Mind. Sue Savage-Rumbaugh, Stuart G. Shanker and Talbot J. Taylor.ron potterNo ratings yet
- Sem1 Unit I WelcomeDocument3 pagesSem1 Unit I WelcomeyaniNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy: (Quarter 1-Module 1 /week 1) Introduction To MilDocument19 pagesMedia and Information Literacy: (Quarter 1-Module 1 /week 1) Introduction To MilEliza LucinaNo ratings yet
- English Speaking Test For Grade 10 - The 1 SemesterDocument3 pagesEnglish Speaking Test For Grade 10 - The 1 SemesterPhương LinhNo ratings yet
- Literature-Based Language TeachingDocument3 pagesLiterature-Based Language TeachingFRANCIS CALUBAYANNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 RooftopsDocument2 pagesUnit 1 RooftopsmariacarlosmariaNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE TEST 1810 (TR Reading II Và Writing I) : EntlyDocument14 pagesPRACTICE TEST 1810 (TR Reading II Và Writing I) : EntlyLinh Đỗ KiềuNo ratings yet
- "Beekeeper" Job Description and Jobs Job DescriptionDocument4 pages"Beekeeper" Job Description and Jobs Job DescriptionPatrick Lawrence YeeNo ratings yet
- Parashat V'zot Habrakhah Torah Reading (Deuteronomy 33v1-34v12) in English Transtropilation (Len Fellman 2019)Document6 pagesParashat V'zot Habrakhah Torah Reading (Deuteronomy 33v1-34v12) in English Transtropilation (Len Fellman 2019)hum fujNo ratings yet
- GA ANH 7 (2021-2022) Chi UyenDocument109 pagesGA ANH 7 (2021-2022) Chi UyenHạnh ThươngNo ratings yet
- Comparative and Superlative Session 4Document3 pagesComparative and Superlative Session 4fahril gamingNo ratings yet
- Upsc Syllabus 2020 PDFDocument5 pagesUpsc Syllabus 2020 PDFHHP CHEVELLA100% (1)
- Oxo Ieng1 0304 ws01 XxaannDocument2 pagesOxo Ieng1 0304 ws01 XxaanntiurNo ratings yet
- Đế Số 08 Hsg Anh 9 (Huyện) : Chú ý: - Thí sinh làm bài trực tiếp vào đề thiDocument10 pagesĐế Số 08 Hsg Anh 9 (Huyện) : Chú ý: - Thí sinh làm bài trực tiếp vào đề thiHai AhnhNo ratings yet
- Employing Appropriate Communicative StylesDocument14 pagesEmploying Appropriate Communicative StylesMorris Carreal100% (1)
- Remainig Student List - NewDocument39 pagesRemainig Student List - NewSanika PatilNo ratings yet
- 1 Aunt Agatha Speaks Her MindDocument2 pages1 Aunt Agatha Speaks Her MindanneNo ratings yet
- Makalah (Deducing Meaning From The Context)Document10 pagesMakalah (Deducing Meaning From The Context)zx15100% (1)
- A22948Vacacional I-2022 - Pearson English Interactive 2 2022-07-07 14.42.25 62c6f0d1b66acDocument594 pagesA22948Vacacional I-2022 - Pearson English Interactive 2 2022-07-07 14.42.25 62c6f0d1b66acELKIN JULIAN PAEZ DIAZNo ratings yet
- Annual Exam - REVISION QP Grade 6 - Eng - Set A PDFDocument5 pagesAnnual Exam - REVISION QP Grade 6 - Eng - Set A PDFyou susNo ratings yet
- Basic Collection Answer Key 2Document36 pagesBasic Collection Answer Key 2Melike KeleşNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Text File InglesiiiDocument6 pagesAssignment 2 Text File InglesiiiEstrella De SantiagoNo ratings yet