Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bow Els
Uploaded by
Rhenn Bagtas SongcoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bow Els
Uploaded by
Rhenn Bagtas SongcoCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OFFICE OF BATAAN
DR. VICTORIA B. ROMAN MEMORIAL HIGH SCHOOL
PANTINGAN, PILAR, BATAAN
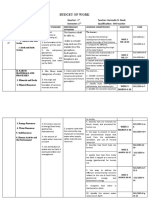
BUDGET OF WORK
Earth and Life Science
(Quarter 1)
Content Standard Performance Most Essential Code Duration
Standard Learning Competencies
The learners The learners should Recognize the uniqueness S11/12ES-Ia-e- Week 1
demonstrate be of Earth, being the only 3
understanding of 1. able to conduct a planet in the solar system
the formation of the survey to with properties
universe and the solar assess the possible necessary to support life.
system geologic/
2. the subsystems hydrometeorologica Explain that the Earth S11/12ES-Ia-e-
(geosphere, l consists of four 4
hydrosphere, hazards that your subsystems,
atmosphere, and community may across whose boundaries
biosphere) that make experience. matter and energy flow.
up
the Earth
3. the Earth’s internal
structure
1. the three main Identify common rock- S11/12ES-Ia-9
categories forming minerals using their
of rocks physical and chemical
2. the origin and properties
environment of
formation
of common minerals
and Classify rocks into igneous, S11/12ES-Ib-10 Week 2
rocks sedimentary, and
3. geologic processes Metamorphic
that
occur on the surface explain how the products of S11/12ES-Ib-12
of the weathering are
Earth such as carried away by erosion
weathering, and deposited elsewhere
erosion, mass
wasting, and Describe where the Earth’s S11/12ES-Ib-14 Week 3
sedimentation internal heat comes
(include the from.
role of ocean basins
in the describe how magma is S11/12ES-Ic-15
formation of formed (magmatism)
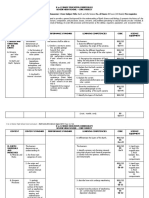
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OFFICE OF BATAAN
DR. VICTORIA B. ROMAN MEMORIAL HIGH SCHOOL
PANTINGAN, PILAR, BATAAN
sedimentary Describe the physical and S11/12ES-Ic-18 Week 4
rocks) chemical changes in rocks
4. geologic processes due to changes in pressure
that and temperature
occur within the Earth (metamorphism)
5. the folding and
faulting compare and contrast the
of rocks formation of the
6. plate tectonics different types of igneous
7. how the planet rocks
Earth Explain how the movement S11/12ES-Id-22 Week 5
evolved in the last 4.6 of plates leads to the
billion years (including formation of folds and
the faults
age of the Earth,
major Describe how layers of S11/12ES-Ie-25
geologic time rocks (stratified rocks) are
subdivisions, Formed
and marker fossils).
Describe the different S11/12ES-Ie-26
methods (relative and
absolute dating) to
determine the age of
stratified
rocks
Explain how relative and S11/12ES-Ie-27 Week 6
absolute dating were
used to determine the
subdivisions of geologic
1. the different time
hazards
caused by geological Describe how the Earth’s S11/12ES-Ie-29
processes history can be
(earthquakes, interpreted from the
volcanic eruptions, geologic time scale
and
landslides)
2. the different Using hazard maps, identify S11/12ES-If-31 Week 7
hazards areas prone to
caused by hazards brought about by
hydrometeorological earthquakes, volcanic
phenomena (tropical eruptions, and landslides
cyclones, monsoons,
floods, Identify human activities
and tornadoes or ipo- that speed up or trigger S11/12ES-If-33
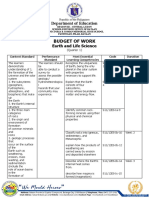
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OFFICE OF BATAAN
DR. VICTORIA B. ROMAN MEMORIAL HIGH SCHOOL
PANTINGAN, PILAR, BATAAN
ipo) Landslides
3. the different Describe how coastal S11/12ES-Ih-38 Week 8
hazards processes result in coastal
caused by coastal erosion, submersion, and
processes saltwater intrusion
(waves, tides, sea-
level cite ways to prevent or S11/12ES-Ii-41
changes, crustal mitigate the impact of
movement, land development, waste
and storm surges) disposal, and
construction of structures
on control coastal
processes
Submitted by: Approved by:
RHENN B. SONGCO FELISA C. BRAVO, EdD
Teacher II School Principal II
You might also like
- (Marc Loudon, Jim Parise) Organic Chemistry PDFDocument1,595 pages(Marc Loudon, Jim Parise) Organic Chemistry PDFPriyankaSaha95% (19)
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument4 pagesEarth and Life ScienceArmelin AlipayoNo ratings yet
- Exp 5 Gas ChromatographyDocument8 pagesExp 5 Gas Chromatographylebogang75% (4)
- Budget of Work - Earth and Life ScienceDocument7 pagesBudget of Work - Earth and Life ScienceAngela Francisca Bajamundi-Veloso100% (2)
- MELCs in Earth and Life ScienceDocument5 pagesMELCs in Earth and Life ScienceAdonis Besa100% (14)
- PC PH DiagramsDocument37 pagesPC PH DiagramsKenny Pabón Cevallos100% (1)
- Earth and Life Science MelcsDocument6 pagesEarth and Life Science MelcsGeraldine V. LantanoNo ratings yet
- Final K To 12 MELCS ELSDocument4 pagesFinal K To 12 MELCS ELSMiraflor RandingNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument8 pagesEarth and Life ScienceMeldie Ann B. LeopoldoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science MELCsDocument4 pagesEarth and Life Science MELCsValiant TiaciNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Budget of WorkDocument3 pagesEarth and Life Science Budget of Workrubelyn.caratikitNo ratings yet
- Earth and LifeDocument8 pagesEarth and LifeLeslie Lara DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Cordillera Administrative RegionDocument5 pagesDepartment of Education: Cordillera Administrative RegionRuth May-osNo ratings yet
- Earth and LifeDocument8 pagesEarth and LifeLeslie Lara DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Budget of Work for Quinabigan National High SchoolDocument8 pagesEarth and Life Science Budget of Work for Quinabigan National High SchoolShiery annNo ratings yet
- Table of Specifications (Tos) Midterm Examination: Earth and Life Science in GRADE 11Document4 pagesTable of Specifications (Tos) Midterm Examination: Earth and Life Science in GRADE 11Julene Joy AbeladaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Lesson on Rocks and Geological ProcessesDocument3 pagesEarth Science Lesson on Rocks and Geological Processesdexter salemNo ratings yet
- Understanding Geologic ProcessesDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Geologic ProcessesAlvin Pabores100% (2)
- Budget-of-Work-Earth and Life ScienceDocument5 pagesBudget-of-Work-Earth and Life Sciencejoei Arquero100% (1)
- PRETESTDocument55 pagesPRETESTMedy Lumagui MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Quarterly Exam ReviewDocument13 pagesEarth and Life Science Quarterly Exam ReviewArjune PantallanoNo ratings yet
- JKLDocument18 pagesJKLjanice alquizarNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Core GuideDocument5 pagesEarth Science Core GuideLoren Marie Lemana AceboNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life TOS Q1Q3 DONE-1Document3 pagesEarth and Life TOS Q1Q3 DONE-1villecapeNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Test Specifications for Las Piñas CityDocument5 pagesEarth Science Test Specifications for Las Piñas CityGenesis AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- CIM in ELS - Q1Document2 pagesCIM in ELS - Q1JESSA SUMAYANGNo ratings yet
- Jigs BowDocument4 pagesJigs BowHarnadin NoohNo ratings yet
- SHS Core - Earth ScienceDocument5 pagesSHS Core - Earth ScienceFeinrirNo ratings yet
- SHS Core - Earth Science CG PDFDocument5 pagesSHS Core - Earth Science CG PDFJohn David YermoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument11 pagesEarth and Life ScienceMark Gil Jandusay YpantoNo ratings yet
- Ahs13 Filipino Sa Piling Larangan Akademik Week 2 PDFDocument6 pagesAhs13 Filipino Sa Piling Larangan Akademik Week 2 PDFJoy RamosNo ratings yet
- 1stQTOS EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCEDocument2 pages1stQTOS EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCENajmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- SHS Core - Earth and Life Science CG PDFDocument12 pagesSHS Core - Earth and Life Science CG PDFRejaelSenoro85% (13)
- Earth Lifescience Tos DatDocument4 pagesEarth Lifescience Tos Datcarl pahuyoNo ratings yet
- SHS Core - Earth Science CG - Spideylab - Com - 2017Document5 pagesSHS Core - Earth Science CG - Spideylab - Com - 2017Aienna Lacaya MatabalanNo ratings yet
- Definitive Budget of Work for SY 2021-2022Document8 pagesDefinitive Budget of Work for SY 2021-2022Jesmar Quirino TutingNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Unpacked (1) 1st QuarterDocument11 pagesEarth Science Unpacked (1) 1st QuarterGenalyn Cirpo TayoneNo ratings yet
- Intervention Earth and LifeDocument3 pagesIntervention Earth and LifeVannie MonderoNo ratings yet
- Learn Earth Science essentialsDocument6 pagesLearn Earth Science essentialsJake Arman PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Table of SpecificationsDocument2 pagesEarth and Life Science Table of SpecificationsReymartNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Earth and Life ScienceDocument6 pagesQ2 - Earth and Life Sciencejessica ignacioNo ratings yet
- Teachers GuideDocument108 pagesTeachers GuideMea-Ann OscianasNo ratings yet
- Core - Earth and Life Science Learning GuideDocument3 pagesCore - Earth and Life Science Learning GuideJerico Karlos Logarta CortesNo ratings yet
- Shs Core Earth Science CGDocument6 pagesShs Core Earth Science CGHenn liNo ratings yet
- Budget of Lesson: Ma. Antonette L. CorpinDocument12 pagesBudget of Lesson: Ma. Antonette L. CorpinYoilie RedNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Quarter 1 Week 1Document9 pagesEarth and Life Science Quarter 1 Week 1aiahNo ratings yet
- K-12 Science Curriculum Grade 10 Earth and Space: Edited By: Jevy Dacunes-CarbonquilloDocument65 pagesK-12 Science Curriculum Grade 10 Earth and Space: Edited By: Jevy Dacunes-CarbonquilloMark Jesson DatarioNo ratings yet
- SHS Core - Earth and Life Science CG - With Tagged Sci EquipmentDocument11 pagesSHS Core - Earth and Life Science CG - With Tagged Sci EquipmentZorayda SarabiNo ratings yet
- Walkthrough in EARTH AND LIFE G11 SLM Q1Document6 pagesWalkthrough in EARTH AND LIFE G11 SLM Q1Cecille Robles San JoseNo ratings yet
- Learning Continuity Plan SY 2020 - 2021Document5 pagesLearning Continuity Plan SY 2020 - 2021allanrnmanalotoNo ratings yet
- SHS Core - Earth and Life Science CG - 0Document10 pagesSHS Core - Earth and Life Science CG - 0Jhullienne Jabat100% (1)
- Division of Lapu-Lapu City: ProcedureDocument1 pageDivision of Lapu-Lapu City: Procedurezenaida a academiaNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Course SyllabusDocument1 page1st Quarter Course Syllabusmark gonzalesNo ratings yet
- TOS-2ndDocument3 pagesTOS-2ndNazer M. LacaboNo ratings yet
- SHS Core Earth and Life Science CG With Tagged Sci EquipmentDocument15 pagesSHS Core Earth and Life Science CG With Tagged Sci EquipmentJimuel AbadillaNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 First Quarter: K To 12 Senior High School Core CurriculumDocument13 pagesGrade 11 First Quarter: K To 12 Senior High School Core CurriculumShen EugenioNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Standards and CompetenciesDocument6 pagesEarth and Life Science Standards and CompetenciesBaby Yanyan100% (3)
- Sedimentary Crisis at the Global Scale 2: Deltas, A Major Environmental CrisisFrom EverandSedimentary Crisis at the Global Scale 2: Deltas, A Major Environmental CrisisNo ratings yet
- Glacial Geology: An Introduction for Engineers and Earth ScientistsFrom EverandGlacial Geology: An Introduction for Engineers and Earth ScientistsN. EylesNo ratings yet
- BOW-General Biology 2Document2 pagesBOW-General Biology 2Rhenn Bagtas SongcoNo ratings yet
- BOW-General PhysicsDocument6 pagesBOW-General PhysicsRhenn Bagtas SongcoNo ratings yet
- Bow ElsDocument3 pagesBow ElsRhenn Bagtas SongcoNo ratings yet
- BOW-Personal DevelopmentDocument2 pagesBOW-Personal DevelopmentRhenn Bagtas Songco100% (1)
- Bow IwrbsDocument4 pagesBow IwrbsRhenn Bagtas SongcoNo ratings yet
- BOW-General PhysicsDocument6 pagesBOW-General PhysicsRhenn Bagtas SongcoNo ratings yet
- BOW-General Biology 2Document2 pagesBOW-General Biology 2Rhenn Bagtas SongcoNo ratings yet
- Rubiag 13Document1 pageRubiag 13ChérubinNo ratings yet
- Michael FaradayDocument33 pagesMichael FaradayRezie Dampog DellavaNo ratings yet
- Widmanstätten StructuresDocument3 pagesWidmanstätten StructuresdantegimenezNo ratings yet
- Ph8253 EceDocument21 pagesPh8253 EceJairusNo ratings yet
- Linezolid 600mg 21142467Document4 pagesLinezolid 600mg 21142467asksameerkumarNo ratings yet
- Bergman5 36Document3 pagesBergman5 36Siddabathula MaheshNo ratings yet
- Manual of Petroleum MeasurementDocument7 pagesManual of Petroleum Measurementsreeyuktha50% (2)
- Paribhashik ShabdawaliDocument5 pagesParibhashik Shabdawalisgangwar2005sg100% (1)
- Kinetics LecturesDocument5 pagesKinetics Lecturesapi-278051982No ratings yet
- TDC in Chemistry (Major) 22Document38 pagesTDC in Chemistry (Major) 22Tamanna boruahNo ratings yet
- Explosive PenetrationDocument3 pagesExplosive PenetrationKaarthicNatarajanNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet 8020, 8022: Acc. To Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 No. of ArticleDocument4 pagesSafety Data Sheet 8020, 8022: Acc. To Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 No. of ArticleManuela Paulina TrejoNo ratings yet
- Agilent HPLC and UHPLC Application HighlightsDocument159 pagesAgilent HPLC and UHPLC Application HighlightsHeather Fleming100% (1)
- Drag EquationDocument4 pagesDrag EquationMspamNo ratings yet
- Free Fall DemoDocument38 pagesFree Fall DemoLogan LeeNo ratings yet
- Tema ExcelDocument8 pagesTema ExcelTeodor OlaruNo ratings yet
- 414CC3 Excel Template Prelim Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design Si UnitsDocument3 pages414CC3 Excel Template Prelim Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design Si UnitsGuruh Mehra MulyanaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals 1Document32 pagesMetals and Non-Metals 1MindOfPrinceNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis: STATIC FRICTION IN RUBBER-METAL CONTACTS WITH APPLICATION TO RUBBER PAD FORMING PROCESSESDocument183 pagesPHD Thesis: STATIC FRICTION IN RUBBER-METAL CONTACTS WITH APPLICATION TO RUBBER PAD FORMING PROCESSESJonathan Xie100% (1)
- Related Substances Calc. and LimitsDocument27 pagesRelated Substances Calc. and LimitsRana MohamedNo ratings yet
- Mechanics - Benjamin CrowellDocument515 pagesMechanics - Benjamin CrowellalpcruzNo ratings yet
- Acid Properties and Fluid Flow CharacteristicsDocument20 pagesAcid Properties and Fluid Flow CharacteristicsPablo SotoNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry: Physical ChemistryDocument22 pagesThermochemistry: Physical ChemistryAaryan KeshanNo ratings yet
- Separators and FiltersDocument15 pagesSeparators and FilterstrpacNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Cell Structure & Function: CellsDocument14 pagesAn Introduction To Cell Structure & Function: Cellsyasser alozaibNo ratings yet
- Isomerization of Aldoximes to Amides Under Neutral ConditionsDocument5 pagesIsomerization of Aldoximes to Amides Under Neutral ConditionsDavideGiacomelliNo ratings yet