Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dokumen - Pub - Structural Analysis in Si Units 10nbsped 1292247134 9781292247137 - 5
Dokumen - Pub - Structural Analysis in Si Units 10nbsped 1292247134 9781292247137 - 5
Uploaded by
visanuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dokumen - Pub - Structural Analysis in Si Units 10nbsped 1292247134 9781292247137 - 5
Dokumen - Pub - Structural Analysis in Si Units 10nbsped 1292247134 9781292247137 - 5
Uploaded by
visanuCopyright:
Available Formats
46 Chapter 1 types of struCtures a n d
L o a d s
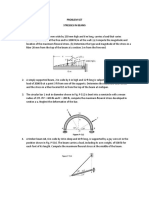
1–9. The “New Jersey” barrier is commonly used during
highway construction. Determine its weight per meter of
length if it is made from plain stone concrete.
1
100 mm
758
300 mm 558
Prob. 1–12
150 mm
1–13. Wind blows on the side of a fully enclosed 9.1 m-high
hospital located on open flat terrain where V = 200 km>h.
600 mm Determine the design wind pressure acting over the windward
wall of the building at the heights 4.6 m, 6.1 m, 7.6 m and 9.1 m.
Prob. 1–9 The roof is flat. Take Ke = 1.0.
1–10. The floor of a light storage warehouse is made of
150-mm-thick lightweight plain concrete. If the floor is a
slab having a length of 7 m and width of 3 m, determine the
resultant force caused by the dead load and the live load.
1–11. The precast inverted T-beam has the cross section
shown. Determine its weight per meter of length if it is
made from reinforced stone concrete and twelve 20-mm-
diameter cold-formed steel reinforcing rods.
225 mm
Prob. 1–13
900 mm
1–14. Determine the resultant force acting on the face
of the truss-supported sign if it is placed on open flat terrain
where V = 38 m/s. The sign has a width of 12 m and a height
300 mm of 3 m as indicated.
1200 mm
3m
Prob. 1–11
*1–12. Wind blows on the side of the fully enclosed 3m
hospital located on open flat terrain where V = 200 km>h.
Determine the external pressure acting on the leeward wall,
if the length and width of the building are 60 m and the
height is 9.1 m. Take Ke = 1.0.
Prob. 1–14
You might also like
- Bending Stress and Shearing Stress in Timber BeamDocument98 pagesBending Stress and Shearing Stress in Timber BeamCharizza Montarin CE100% (2)
- Managing TeamsDocument42 pagesManaging TeamsAudrey Cawis50% (2)
- Prestressed-Concrete Chapter 4Document17 pagesPrestressed-Concrete Chapter 4Renz Ryan Dolor50% (2)
- 123Document13 pages123Meee koooNo ratings yet
- Charles E. Cobb Jr.-This Nonviolent Stuff'll Get You Killed - How Guns Made The Civil Rights Movement Possible-Basic Books (2014) PDFDocument321 pagesCharles E. Cobb Jr.-This Nonviolent Stuff'll Get You Killed - How Guns Made The Civil Rights Movement Possible-Basic Books (2014) PDFdNo ratings yet
- Masonry Tutorial PDFDocument2 pagesMasonry Tutorial PDFRabindraUpretiNo ratings yet
- Jan-25 and 26Document14 pagesJan-25 and 26betvwyNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 PrestressDocument4 pagesQuiz 1 PrestressHeiro KeystrifeNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentMamuye Busier YesufNo ratings yet
- Superimposed, Reinforced, Built-Up Timber BeamsDocument16 pagesSuperimposed, Reinforced, Built-Up Timber Beamsmnmusor0% (1)
- Feb - 8 To 19Document18 pagesFeb - 8 To 19betvwyNo ratings yet
- CE6702 PSCS Rejinpaul Important QuestionsDocument2 pagesCE6702 PSCS Rejinpaul Important QuestionsPar NawNo ratings yet
- NR 410110 Prestressed ConcreteDocument8 pagesNR 410110 Prestressed ConcreteSrinivasa Rao G100% (2)
- TutorialDocument4 pagesTutorialtiwari.dipesh001No ratings yet
- 12d20106a Prestressed ConcreteDocument1 page12d20106a Prestressed ConcretesubbuNo ratings yet
- Jan-22 and 23Document13 pagesJan-22 and 23betvwyNo ratings yet
- Design of Prestressed Concrete Structures 15cese2005-1 PDFDocument2 pagesDesign of Prestressed Concrete Structures 15cese2005-1 PDFvineela saiNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: 07 Ce 6324: Design of Prestressed Concrete StructuresDocument8 pagesQuestion Bank: 07 Ce 6324: Design of Prestressed Concrete StructuresIyrin John100% (1)
- Pre Stress Sample ProblemsDocument2 pagesPre Stress Sample ProblemsJC AldeaNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Concrete Structures - AssignmentDocument14 pagesPrestressed Concrete Structures - AssignmentGanesh MistercoolNo ratings yet
- Control of Ground Movements For A Multi-Level Anchored Diaphragm Wall During ExcavationDocument7 pagesControl of Ground Movements For A Multi-Level Anchored Diaphragm Wall During ExcavationMarco NevesNo ratings yet
- Seatwork 03 (R3) - 2023.12.13Document5 pagesSeatwork 03 (R3) - 2023.12.13reynesmarygen9No ratings yet
- Seismic Retrofitting of Unreinforced Masonry Walls by Cable SystemDocument15 pagesSeismic Retrofitting of Unreinforced Masonry Walls by Cable SystemDamit SuranaNo ratings yet
- Deep Foundations TutorialDocument1 pageDeep Foundations TutorialHajahaNo ratings yet
- Tek 14-03a PDFDocument4 pagesTek 14-03a PDFdaveshitNo ratings yet
- Guide To Load TableDocument1 pageGuide To Load TablekikaniNo ratings yet
- 18CV81Document16 pages18CV81Nagaraja M LNo ratings yet
- UBC Shear Wall DesignDocument5 pagesUBC Shear Wall DesignAJBAJBNo ratings yet
- MDB Prob Set Stresses in BeamsDocument1 pageMDB Prob Set Stresses in BeamsFerrolinoLouieNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument13 pagesFormulasSandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Prestressed ConcreteDocument5 pagesPrestressed ConcreteSamNo ratings yet
- H.W Chapter 12Document1 pageH.W Chapter 12Ghassan HazmiNo ratings yet
- Slope Stability Analysis Using FlacDocument17 pagesSlope Stability Analysis Using FlacSudarshan Barole100% (1)
- Analysis of Prestress and Bending Stress: Force 170 KNJ.)Document5 pagesAnalysis of Prestress and Bending Stress: Force 170 KNJ.)Kim JunmyeonNo ratings yet
- Bolted Cross Section ExamplesDocument17 pagesBolted Cross Section ExamplesmandregomesNo ratings yet
- Dos Iii - Unit Iv Masonry WallDocument26 pagesDos Iii - Unit Iv Masonry WallMohamed ArzathNo ratings yet
- Design of BeamsDocument4 pagesDesign of BeamsStephanie Gallos0% (1)
- Plate No.1Document10 pagesPlate No.1Marvin Bryant MedinaNo ratings yet
- Erath WireDocument3 pagesErath WireAli OthmanNo ratings yet
- RMR - Support Guidelines RMR - Semi-Empirical Support GuidelinesDocument100 pagesRMR - Support Guidelines RMR - Semi-Empirical Support GuidelinesSusett M TNo ratings yet
- Tutorial No. 9 Pile Foundation UCE 613 Foundation EngineeringDocument1 pageTutorial No. 9 Pile Foundation UCE 613 Foundation EngineeringDushyant Sharma0% (1)
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitleddivyen gamitNo ratings yet
- Design of Retaining Walls: Suez Canal University Faculty of EngineeringDocument8 pagesDesign of Retaining Walls: Suez Canal University Faculty of EngineeringAmr Abdelraouf MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Water TankDocument8 pagesLecture On Water Tankabdul samadNo ratings yet
- Take Home QuizDocument1 pageTake Home QuizBlezzie Ann ObraNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2022 - Prestressed ConcreteDocument2 pagesCE Board Nov 2022 - Prestressed ConcretetwicetacsNo ratings yet
- TDS Proofex 3000 Saudi ArabiaDocument3 pagesTDS Proofex 3000 Saudi Arabiarangarajan1989No ratings yet
- Article On Residential EarthingDocument4 pagesArticle On Residential EarthingAbul Kalam AzadNo ratings yet
- APL104 Solid Mechanics Tutorial 9Document1 pageAPL104 Solid Mechanics Tutorial 9Pratham VermaNo ratings yet
- Instruction: Answer All Question: Assignment 1 Analysis of Prestress and Bending Stress BFS 40303Document4 pagesInstruction: Answer All Question: Assignment 1 Analysis of Prestress and Bending Stress BFS 40303tashadzureenNo ratings yet
- Seismic Protection of The Guadalfeo Bridge by Viscous DampersDocument10 pagesSeismic Protection of The Guadalfeo Bridge by Viscous Dampersavmurugan87No ratings yet
- Retaining WallDocument25 pagesRetaining WalldhaifanNo ratings yet
- Minimum Thickness For Ductile RC Structural Walls: Y.H. Chai, S.K. KunnathDocument12 pagesMinimum Thickness For Ductile RC Structural Walls: Y.H. Chai, S.K. KunnathDavid FloresNo ratings yet
- Wsa Unit and Co Wise AssignmentsDocument9 pagesWsa Unit and Co Wise AssignmentsJohn WickNo ratings yet
- CE5710 Assignment IDocument1 pageCE5710 Assignment INani RujaNo ratings yet
- "No Copying and Sharing of Answers ": Finals ExaminationDocument5 pages"No Copying and Sharing of Answers ": Finals ExaminationArvin LopezNo ratings yet
- RCD Assignment 3Document2 pagesRCD Assignment 3CE-Cret KuyaaDeeeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3. Prestressed ConcreteDocument4 pagesTutorial 3. Prestressed ConcreteNisarg SutharNo ratings yet
- Strength Of Beams, Floor And Roofs - Including Directions For Designing And Detailing Roof Trusses, With Criticism Of Various Forms Of Timber ConstructionFrom EverandStrength Of Beams, Floor And Roofs - Including Directions For Designing And Detailing Roof Trusses, With Criticism Of Various Forms Of Timber ConstructionNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Some of the Equations used in Constructing a Suspension BridgeFrom EverandA Guide to Some of the Equations used in Constructing a Suspension BridgeNo ratings yet
- Design Construction Manual2002 - 10Document1 pageDesign Construction Manual2002 - 10visanuNo ratings yet
- Bentonite 1Document1 pageBentonite 1visanuNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills Basics - 6Document1 pageCommunication Skills Basics - 6visanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering - 8Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 8visanuNo ratings yet
- Bentonite 4Document1 pageBentonite 4visanuNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills Basics - 7Document1 pageCommunication Skills Basics - 7visanuNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills Basics - 1Document1 pageCommunication Skills Basics - 1visanuNo ratings yet
- Design Construction Manual2002 - 6Document1 pageDesign Construction Manual2002 - 6visanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering - 15Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 15visanuNo ratings yet
- Bentonite 6Document1 pageBentonite 6visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 2Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 2visanuNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills Basics - 2Document1 pageCommunication Skills Basics - 2visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 3Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 3visanuNo ratings yet
- Bentonite 3Document1 pageBentonite 3visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 4Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 4visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 3Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 3visanuNo ratings yet
- Bentonite 2Document1 pageBentonite 2visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 1Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 1visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 1Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 1visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 3Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 3visanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering - 13Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 13visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 6Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 6visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 4Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 4visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 2Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 2visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 5Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 5visanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering - 11Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 11visanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering - 14Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 14visanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering - 9Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 9visanu100% (1)
- Basic Civil Engineering - 10Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 10visanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering - 12Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 12visanuNo ratings yet
- Numpy UserDocument502 pagesNumpy UserkartiNo ratings yet
- Learning Task - Mapeh8 - Week-2Document5 pagesLearning Task - Mapeh8 - Week-2mpaynor26No ratings yet
- SML10 SystemDocument33 pagesSML10 SystemgilbertoNo ratings yet
- Publication SAW SOUR SERVICE 2023 PDFDocument7 pagesPublication SAW SOUR SERVICE 2023 PDFPako RosasNo ratings yet
- STM Lab ManualDocument87 pagesSTM Lab ManualKrishna Chowdary ChallaNo ratings yet
- The Avr Instruction SetDocument4 pagesThe Avr Instruction SetSundari Devi BodasinghNo ratings yet
- Acts of Teaching Chapter 14Document2 pagesActs of Teaching Chapter 14api-350726106No ratings yet
- Phillppe Sollers - Writing and The Experience of Limits (European Perspectives) - Columbia University Press (1983) PDFDocument119 pagesPhillppe Sollers - Writing and The Experience of Limits (European Perspectives) - Columbia University Press (1983) PDFDavid Antonio Bastidas100% (1)
- Specifications For LG 42WS50BS-BDocument4 pagesSpecifications For LG 42WS50BS-BRPhillipsVMPNo ratings yet
- SocializationDocument18 pagesSocializationCamile BercesNo ratings yet
- SAMURAI Anti-Vibration Tool - Sigma Toolings, Fine Boring Tools, Cutting Tools ManufacturerDocument28 pagesSAMURAI Anti-Vibration Tool - Sigma Toolings, Fine Boring Tools, Cutting Tools ManufacturerSigma ToolingsNo ratings yet
- EBusiness ModelsDocument7 pagesEBusiness ModelsamindradesilvaNo ratings yet
- Java Loops II - Java QuestionDocument4 pagesJava Loops II - Java QuestionBlake PayriceNo ratings yet
- An Ideal Gas Monte CarloDocument19 pagesAn Ideal Gas Monte CarloVyassa BarathamNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To MorphologyDocument15 pagesAn Introduction To MorphologyKakar KakarNo ratings yet
- Telkomsel Lte FDD Interworking Strategy For l1800 Amp U900 U2100Document10 pagesTelkomsel Lte FDD Interworking Strategy For l1800 Amp U900 U2100achmad amrullohNo ratings yet
- Teacher's ClearanceDocument1 pageTeacher's ClearanceShairuz Caesar Briones DugayNo ratings yet
- April 29 Homework Solutions: Mechanical Engineering 390 Fluid MechanicsDocument6 pagesApril 29 Homework Solutions: Mechanical Engineering 390 Fluid MechanicsLaliethaNo ratings yet
- AUDISON Prima AP8 9 Bit Tech SheetDocument1 pageAUDISON Prima AP8 9 Bit Tech SheetErwin HernandezNo ratings yet
- Malaysia Form 4 Mathematics Chapter 4.1 and 4.2 (Mathematical Reasoning)Document2 pagesMalaysia Form 4 Mathematics Chapter 4.1 and 4.2 (Mathematical Reasoning)Tsuey XinNo ratings yet
- Strategi Bisnis Umkm Selama Pandemi Covid-19Document9 pagesStrategi Bisnis Umkm Selama Pandemi Covid-19nabila zhafirah100% (1)
- Taylor 168 User ManualDocument47 pagesTaylor 168 User ManualFama Banks EdrevopmacNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal Communication StudyDocument13 pagesInterpersonal Communication StudySameer KhanNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Reading: Parlin Pardede Fkip-Uki JakartaDocument12 pagesThe Nature of Reading: Parlin Pardede Fkip-Uki JakartaParlin PardedeNo ratings yet
- Primetime: Golden Timing Signoff Solution and EnvironmentDocument7 pagesPrimetime: Golden Timing Signoff Solution and Environmentsubrahmanya_rao_1No ratings yet
- Unit 2.2 MmworldDocument41 pagesUnit 2.2 MmworldAveryNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet For Bechem GreaseDocument1 pageTechnical Data Sheet For Bechem GreaseSandeepNo ratings yet
- Yesterday 10Document7 pagesYesterday 10Christopher OjoNo ratings yet