Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Newton's Law of Motion
Uploaded by
Kyla Mari Valdueza0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesNewton's laws of motion describe the relationship between an object and the forces acting upon it. The first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an external force. The second law states that acceleration is directly proportional to force and inversely proportional to mass. The third law states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Friction opposes motion between objects in contact.
Original Description:
Original Title
Newton’s Law of Motion
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNewton's laws of motion describe the relationship between an object and the forces acting upon it. The first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an external force. The second law states that acceleration is directly proportional to force and inversely proportional to mass. The third law states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Friction opposes motion between objects in contact.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesNewton's Law of Motion
Uploaded by
Kyla Mari ValduezaNewton's laws of motion describe the relationship between an object and the forces acting upon it. The first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an external force. The second law states that acceleration is directly proportional to force and inversely proportional to mass. The third law states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Friction opposes motion between objects in contact.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Newton’s Law of Motion Example:
Introduction -Marathoner Running beyond Finish Line
-A Ball Rolling on the Ground
In classical mechanics, Newton's laws of -A rock at rest
motion are three laws that describe the
relationship between the motion of an object 2. SECOND LAW OF MOTION (LAW OF
and the forces acting on it. ACCELERATION)
Free fall -states that the acceleration of an object is
directly proportional to the applied force but
-is a motion under the influence or effect of inversely proportional to the mass of an
the gravity. Motion thrown upward and object.
downward also and those who are released
in rest is also experiencing a freefall. Newton’s 2nd Law of motion can be
described by this equation:
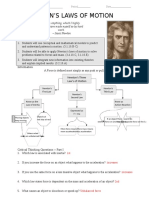
1. FIRST LAW OF MOTION (LAW OF How much force is needed to accelerate a
INERTIA) 1400 kilogram car 2 meters per second per
second(m/s/s)
-states that a body at rest will remain at rest Write the Formula
and a body on move keep on moving unless F=mxa
there is external force acting upon it. Inertial Fill the given Numbers and Units
Frame of Reference is frame of reference or F = 1400 kg x 2 m/s/s
position where the object stays at rest or in Solve the Unknown
constant motion unless external force acts F = 2800kg/m/s/s or 2800 N
upon it.
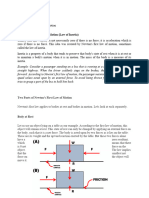
3. THIRD LAW OF MOTION 3. Friction
( LAW OF INTERACTION)
-is a force that opposes relative motion
-states that for every action there is an equal between two systems in contact.
and opposite Reaction.
-Two forces action and reaction Two Types of Friction:
Example: a. Static Friction -It keeps an object at rest.
-Propulsion of fish through water b. Kinetic Friction- slows down a moving
-The flight of the bird object.
-Rowing
KEY TERMS
Force is a Push or Pull
Classic Mechanics -deals with the question
Types of Force of how an object moves when it is subjected
to various forces, and also with the question
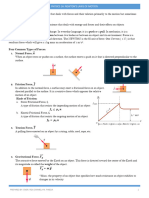
1. Normal Force of what forces act on an object which is not
moving.
-is a type force exerted in an object that is in Force - push or pull on an object with a
contact with another object. Normal force is specific magnitude and direction
called as supporting force. Free Fall- situation in which the only force
acting on an object is gravity.
For example: apple on the top of the table. Inertia -ability of an object to resist changes
in its motion
2.Tension Newton – SI unit of force
9.8 m/s/s – acceleration of gravity, free fall
-is a force along the length of a medium like or Earth gravity equivalent.
rope or cable. The Tension is the rope must
equal the weight of supported mass. Derived
form a Second Law of Motion.
T = mg
A 10 kg ball is hanging from the ceiling.
What is the tension force being applied by
the rope in the ball.
You might also like
- General Physics: Newton Law of MotionDocument4 pagesGeneral Physics: Newton Law of MotionJewel ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 MotionDocument4 pagesLecture 2 MotionAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Force and MotionDocument8 pagesForce and MotionForsythe LearningNo ratings yet
- LM5 - Newton's Laws of Motion and Applications - GPHYS1Document53 pagesLM5 - Newton's Laws of Motion and Applications - GPHYS1burner accNo ratings yet
- Module 3 PhysciDocument124 pagesModule 3 Physciburner accNo ratings yet
- Writing BibliographyDocument12 pagesWriting BibliographyPrincess CarstenNo ratings yet
- Newton'S Laws of Motion: Name KeyDocument13 pagesNewton'S Laws of Motion: Name KeyMingNo ratings yet
- General Physics PrefinalsDocument3 pagesGeneral Physics PrefinalssarmientojoonsunNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion Class 11 Notes NEET 2023 Physics - Free PDF DownloadDocument22 pagesLaws of Motion Class 11 Notes NEET 2023 Physics - Free PDF Downloadayushdangi5635No ratings yet
- Week 1 ScienceDocument38 pagesWeek 1 ScienceEyphrille UmandapNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in ScienceDocument6 pagesReviewer in ScienceBAD-E, JUSTINE ALEXIS BALBUENANo ratings yet
- Physics Tutorial: Andalas UniversityDocument26 pagesPhysics Tutorial: Andalas UniversityMiranda Febriani TanjungNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion NotesDocument2 pagesForce and Motion NotesChaela ApplebyNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 8, Quarter 1: Force and MotionDocument3 pagesScience Grade 8, Quarter 1: Force and MotionMin Yoongi92% (12)
- ScienceDocument1 pageScienceChaela ApplebyNo ratings yet
- Stem BL - Gre RefugiaDocument6 pagesStem BL - Gre RefugiaMichaela RefugiaNo ratings yet
- Sci 2 LESSONSDocument34 pagesSci 2 LESSONSAnnely Jane DarbeNo ratings yet
- Nkdievid 2Document10 pagesNkdievid 2nik100% (2)
- MotionDocument51 pagesMotionJohanna Marie SorianoNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument55 pagesLaws of MotionRalphNeilMarananNo ratings yet
- 10physics2 2 PDFDocument6 pages10physics2 2 PDFSami NeriNo ratings yet
- MANIPAL Newtons Laws of MotionDocument25 pagesMANIPAL Newtons Laws of MotionLeong Mun FaiNo ratings yet
- Phy - NLM PDFDocument48 pagesPhy - NLM PDFKushagraNo ratings yet
- Physics 2Document1 pagePhysics 2Willow ItchiroNo ratings yet
- Module 1 3 LectureDocument2 pagesModule 1 3 LectureaileenNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument43 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionNasr UllahNo ratings yet
- Statistics of Rigid BodiesDocument7 pagesStatistics of Rigid BodiesAphaedes AlcalaNo ratings yet
- FORCE and MOTIONDocument3 pagesFORCE and MOTIONKristineMaeFernandezCarmeloNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument29 pagesNewton's Laws of Motionpbayes83% (6)
- Physics (CETs)Document9 pagesPhysics (CETs)AkiNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Newton MechanicsDocument16 pagesCh1 Newton MechanicsRana JahanzaibNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of Elements ListDocument7 pagesPeriodic Table of Elements ListMin YoongiNo ratings yet
- ForceDocument11 pagesForceAnastasia LarasatiNo ratings yet
- Physics - Force and MotionDocument10 pagesPhysics - Force and MotionÅBanDonNo ratings yet
- Physics ch-1.5 (Forces and Motion)Document3 pagesPhysics ch-1.5 (Forces and Motion)Safiul FaiyazNo ratings yet
- Wk6 GenPhys1 - 0926 30Document8 pagesWk6 GenPhys1 - 0926 30JenRose Gadon SoliguenNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 NotesDocument2 pagesGrade 8 NotesRocel U. GinooNo ratings yet
- Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsDocument1 pageRotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicskaeppjangedNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws of MotionDocument52 pagesNewtons Laws of MotionOluwaferanmi OgunleyeNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Due To Gravity ForcesDocument28 pagesAcceleration Due To Gravity Forcesfelipee20No ratings yet
- Newtons 1 and 2 Law: ST NDDocument15 pagesNewtons 1 and 2 Law: ST NDApoorva TalankiNo ratings yet
- 3 - DynamicsDocument2 pages3 - DynamicsStephen CamsolNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law's of MotionDocument19 pagesNewtons Law's of MotionAira YamuyamNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 - Fundamental Physics (Forces)Document6 pagesPhysics 1 - Fundamental Physics (Forces)Claire FabellarNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Mechanics IntroDocument12 pagesChap 1 Mechanics Introfortunato dilaoNo ratings yet
- Classical Mechanics Block 1/4Document70 pagesClassical Mechanics Block 1/4Chethan PrathapNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Unit 9Document2 pagesPhysical Science Unit 9Bluematwo TwoNo ratings yet
- Phy 2. Force and Laws of MotionDocument15 pagesPhy 2. Force and Laws of MotionShreyash MauryaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Module in Science: Quarter 1Document5 pagesGrade 8 Module in Science: Quarter 1Min Yoongi100% (1)
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument17 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionJuan Pablo Penagos LosadaNo ratings yet
- Group 5Document23 pagesGroup 5Gavin avNo ratings yet
- Mechanics IntroDocument23 pagesMechanics Introfortunato dilaoNo ratings yet
- Unit2keyconcepts 1Document4 pagesUnit2keyconcepts 1ansonng16888No ratings yet
- LM5b - Newton - S Laws of Motion - GPHYS1Document40 pagesLM5b - Newton - S Laws of Motion - GPHYS1burner accNo ratings yet
- Review Review Im CryingggDocument11 pagesReview Review Im CryingggMaryann San JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument6 pagesNewton's Laws of Motionrizki siwiNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws: Al-Basra University College of Engineering Department of MechanicsDocument12 pagesNewton's Laws: Al-Basra University College of Engineering Department of MechanicsZahra 9oNo ratings yet
- Various Art Forms in TheDocument4 pagesVarious Art Forms in TheKyla Mari ValduezaNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy andDocument3 pagesWork, Energy andKyla Mari ValduezaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structures Formulas and NamesDocument4 pagesAtomic Structures Formulas and NamesKyla Mari ValduezaNo ratings yet
- Text StructureDocument2 pagesText StructureKyla Mari ValduezaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - The Nature of VariablesDocument4 pagesLesson 2 - The Nature of VariablesKyla Mari ValduezaNo ratings yet
- Units of MeasurementsDocument3 pagesUnits of MeasurementsKyla Mari ValduezaNo ratings yet
- Eq Missing Mass CorrectionDocument6 pagesEq Missing Mass CorrectionTejashri SalunkheNo ratings yet
- Metering Solution For Custody Transfer ApplicationsDocument8 pagesMetering Solution For Custody Transfer ApplicationsTallal joiyaNo ratings yet
- Appendix GDR 00.1 001 CDocument81 pagesAppendix GDR 00.1 001 Cluce gianniNo ratings yet
- Amend - 1 To IRS - S - 63 - 2014 03 - 07Document12 pagesAmend - 1 To IRS - S - 63 - 2014 03 - 07Singla CablesNo ratings yet
- C - 15 - 58 Project ProposalDocument35 pagesC - 15 - 58 Project ProposalklklklNo ratings yet
- ch14 1Document7 pagesch14 1jiholee1117No ratings yet
- JAGADEESHDocument139 pagesJAGADEESHMannam Sarath Sarath0% (1)
- sm1 014Document2 pagessm1 014Paulo Henrique D. FavarettoNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0997754621000212 MainDocument16 pages1 s2.0 S0997754621000212 MainAnimesh KumarNo ratings yet
- C-Arm Parts and PrinciplesDocument10 pagesC-Arm Parts and PrinciplesErshad SohailNo ratings yet
- CasingTables 2008Document53 pagesCasingTables 2008Timothy PopikNo ratings yet
- Timber Ridge Beam Calculation Report 2Document5 pagesTimber Ridge Beam Calculation Report 2CartecSyriaNo ratings yet
- MGS Capacity CalculatorDocument13 pagesMGS Capacity CalculatorRodolfo MendezNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Textile Application of Poly Methyl Methacrylate Co Methacrylic Acid N Octadecane and N Eicosane MicrocapsulesDocument13 pagesPreparation and Textile Application of Poly Methyl Methacrylate Co Methacrylic Acid N Octadecane and N Eicosane MicrocapsulesFelipe Vázquez DávilaNo ratings yet
- CE 5101 Structural Analysis-Ii Unit-I BY S K Singh: Lecture No 01Document14 pagesCE 5101 Structural Analysis-Ii Unit-I BY S K Singh: Lecture No 01धीरज कुमारNo ratings yet
- 2021 Uzem Chemistry Ch09 - 2 Solubility and Complex-Ion EquilibriaDocument102 pages2021 Uzem Chemistry Ch09 - 2 Solubility and Complex-Ion EquilibriaErdem AltunNo ratings yet
- Science - Satrun Voyager 1981 PDFDocument30 pagesScience - Satrun Voyager 1981 PDFLuis Romero100% (2)
- 1.chemical KineticsDocument24 pages1.chemical KineticsVinod AgrawalNo ratings yet
- ThermoDynamics Conversion Table PDFDocument1 pageThermoDynamics Conversion Table PDFCloie Chavez100% (1)
- Thermochemical Properties Estimation For Biodiesel Related MixturesDocument11 pagesThermochemical Properties Estimation For Biodiesel Related Mixturesalberth_carantónNo ratings yet
- Ashrae 55Document74 pagesAshrae 55Temitope Vic100% (1)
- 09C Polymer Structure and Properties (2.5 MB)Document22 pages09C Polymer Structure and Properties (2.5 MB)FâtïMâ ZâhřæNo ratings yet
- Particle Size Analysis Cocoa PowdersDocument3 pagesParticle Size Analysis Cocoa PowdersAhmad S MohamadNo ratings yet
- 6 EntropyDocument18 pages6 EntropyRasel khanNo ratings yet
- Mech Eng DsDocument11 pagesMech Eng Ds路人丁No ratings yet
- Engineering Standards Manual - Welding Standards M Anual - Volume 3 Welding Procedure SpecificationsDocument3 pagesEngineering Standards Manual - Welding Standards M Anual - Volume 3 Welding Procedure Specificationslaz_k50% (2)
- Radiation Heat Transfer: By: Ankit SinghDocument27 pagesRadiation Heat Transfer: By: Ankit SinghAnkit SinghNo ratings yet
- HDG Steel Combined With Al-AlloyDocument9 pagesHDG Steel Combined With Al-AlloySreedhar Patnaik.MNo ratings yet
- General Welding Procedures (0679, 7000) (REHS1841-23)Document73 pagesGeneral Welding Procedures (0679, 7000) (REHS1841-23)Anderson Oliveira SilvaNo ratings yet
- Level Ii Questions - RTDocument7 pagesLevel Ii Questions - RTViral ThankiNo ratings yet
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyFrom EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (410)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (49)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (157)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1396)
- AP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeFrom EverandAP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeNo ratings yet
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- The 60 Minute Quantum Physics Book: Science Made Easy For Beginners Without Math And In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandThe 60 Minute Quantum Physics Book: Science Made Easy For Beginners Without Math And In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- A Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itFrom EverandA Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessFrom EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- What If?: Serious Scientific Answers to Absurd Hypothetical QuestionsFrom EverandWhat If?: Serious Scientific Answers to Absurd Hypothetical QuestionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)