Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AEE311L - Experiment 2
Uploaded by
Peecha PaiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AEE311L - Experiment 2
Uploaded by
Peecha PaiCopyright:
Available Formats
AEE 311L – INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS, LAB
EXPERIMENT 2
VOLTAGE MULTIPLIER
OBJECTIVES:
Demonstrate the operation of both the half-wave and the full-wave voltage
doublers.
Design a voltage tripler/quadrupler.
INTRODUCTION:
Voltage multiplier circuits are employed to maintain a relatively low
transformer peak voltage while stepping up the peak output voltage to two, three, four,
or more times the peak rectified voltage.
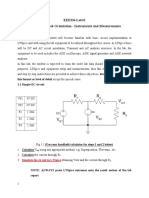
The half-wave voltage doubler is actually a positive clamper followed by a
half-wave rectifier with a capacitor input filter (peak detector). It charges a series
capacitor on each positive half-cycle. Consequently, the ripple frequency is the same
as the input frequency.
Figure 1. Half-wave Voltage Doubler
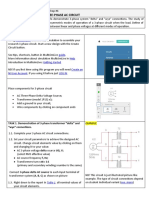
The full-wave voltage doubler, on the other hand, has the same rectified peak
output voltage as the half-wave doubler. It charges one of two series capacitors on the
first half-cycle, while the other capacitor is charged on the remaining half-cycle.
Therefore, it has a ripple frequency that is twice the input frequency. Consequently,
for the same filter time constant, the peak-to-peak ripple voltage is smaller when a full-
wave voltage doubler is used.
Figure 2. Full-wave Voltage Doubler
PROCEDURE:
Half-wave Voltage Doubler
Figure 3. Half-wave Voltage Doubler
1. Using Multisim, build the half-wave voltage doubler shown in Figure 3.
2. Measure the voltages across each components and record it in Table 1.
3. Compare these voltages with your manual calculations.
Full-wave Voltage Doubler
Figure 4. Full-wave Voltage Doubler
1. Using Multisim, build the full-wave voltage doubler shown in Figure 4.
2. Measure the voltages across each components and record it in Table 1.
3. Compare these voltages with your manual calculations.
Voltage Multiplier Design
1. Design your own voltage tripler/quadrupler. That is, build the circuit complete
with its corresponding component values.
2. Run the simulation to measure the voltages across each components.
3. Record these measurements in tabular form (as that of Table 1).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS:
(with screenshots and calculations)
Half-wave Full-wave
Parameters
Simulated Calculated Simulated Calculated
𝑽𝑹𝟏
𝑽𝑪𝟏
𝑽𝑪𝟐
𝑽𝒓𝒊𝒑𝒑𝒍𝒆
Table 1. Voltage Doubler Data
CONCLUSION:
(with documentation)
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Power SupplyDocument22 pagesPower Supplyandree w100% (1)
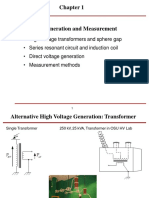
- High Voltage GenerationDocument6 pagesHigh Voltage Generationdp500100% (1)
- Rectifier Lab ReportDocument7 pagesRectifier Lab ReportRupin Mathur0% (2)
- Laboratory Experiment No. 3 Group 2 EE2203B 1Document20 pagesLaboratory Experiment No. 3 Group 2 EE2203B 1Alzen Galpao Enage100% (1)
- TeslaDocument42 pagesTeslaRicardo Martinez ArteagaNo ratings yet
- 23 Seriesand Parallel CircDocument7 pages23 Seriesand Parallel CircAshley O'Neal50% (2)
- Eee334 Lab#1 Ltspice and Lab Orientation - Instruments and MeasurementsDocument9 pagesEee334 Lab#1 Ltspice and Lab Orientation - Instruments and Measurementsplaystation0% (1)
- Experiment 1 Tumambing Evan John C PDFDocument31 pagesExperiment 1 Tumambing Evan John C PDFRafael AclanNo ratings yet
- Course - Section: - ECE20L-2 - E06 Group Number: Group MembersDocument11 pagesCourse - Section: - ECE20L-2 - E06 Group Number: Group MembersLuch ÜNo ratings yet
- ECE20L - 2 - Expt4Document10 pagesECE20L - 2 - Expt4Niko de LemosNo ratings yet
- Eee5451 Lab3Document24 pagesEee5451 Lab3sekelanilunguNo ratings yet
- Analysis Three-Phase Ac Circuit: Work Purpose: To Demonstrate 3-Phase System "Delta" and "Wye" Connections. The Study ofDocument9 pagesAnalysis Three-Phase Ac Circuit: Work Purpose: To Demonstrate 3-Phase System "Delta" and "Wye" Connections. The Study ofnikitaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: EM 222 Circuit Analysis IiDocument6 pagesLaboratory Manual: EM 222 Circuit Analysis IiHarun KahramanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits For Biological Engineering Laboratory: BE154L/A43/4Q1920Document28 pagesElectronic Circuits For Biological Engineering Laboratory: BE154L/A43/4Q1920Kylle SaligumbaNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab ReportDocument4 pagesPower Electronics Lab ReportOmr Darwish100% (1)
- Single Phase Half Wave Voltage Multiplier PDFDocument5 pagesSingle Phase Half Wave Voltage Multiplier PDFJoshua Amiel javinesNo ratings yet
- AC Ckt. Lab Work No. 1Document7 pagesAC Ckt. Lab Work No. 1Ricelle Ann ParaleNo ratings yet
- Function Generator Op-Amp Summing Circuits Pulse Width Modulation LM311 ComparatorDocument7 pagesFunction Generator Op-Amp Summing Circuits Pulse Width Modulation LM311 ComparatorMuhammad JunaidNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 1 StalagmiteDocument6 pagesLaboratory 1 StalagmiteAlejandro PalacioNo ratings yet
- ECE 420 Experiment O. 1 Spring 2007 On-Campus Three Phase TransformersDocument11 pagesECE 420 Experiment O. 1 Spring 2007 On-Campus Three Phase TransformersWai JunNo ratings yet
- 325 Lab 3 ReportDocument13 pages325 Lab 3 Reportapi-241454978No ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Half Wave RectifierDocument8 pagesExperiment 2 - Half Wave RectifierRandred GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lab 5. Single-Phase Transformer Experimental Testing - ManualDocument10 pagesLab 5. Single-Phase Transformer Experimental Testing - ManualnikitaNo ratings yet
- DocumentationDocument4 pagesDocumentationEugene Paul Brian SebiloNo ratings yet
- OPERATION AMPLIFIER - Voltage Follower Configuration Learning OutcomeDocument3 pagesOPERATION AMPLIFIER - Voltage Follower Configuration Learning OutcomeAzriey HafizieyNo ratings yet
- LRC Circuits Resonances - George Ricarrson 2501987261Document14 pagesLRC Circuits Resonances - George Ricarrson 2501987261George RY100% (1)
- Modeling of Integrated Monitoring On Power Transformer Using LabviewDocument10 pagesModeling of Integrated Monitoring On Power Transformer Using LabviewNituNo ratings yet
- Electronics Laboratory DC Power Supply CircuitsDocument10 pagesElectronics Laboratory DC Power Supply CircuitsDen CelestraNo ratings yet
- نسخة EXPER - 1تقريرDocument9 pagesنسخة EXPER - 1تقريرx98w9p6z9kNo ratings yet
- Lab 1-Bjt AmplifierDocument8 pagesLab 1-Bjt Amplifierhasnain3257100% (1)
- Lab Guide Lab1 - RectifiersDocument5 pagesLab Guide Lab1 - RectifiersxDavidx :VNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - AC MeasurementDocument7 pagesExperiment 1 - AC MeasurementmixchescakeNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document18 pagesLab 4abuzai0% (1)
- Yeditepe University Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Ee 232 Introduction To ElectronicsDocument5 pagesYeditepe University Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Ee 232 Introduction To Electronicstarafe5509No ratings yet
- Half-Wave and Full-Wave RectDocument11 pagesHalf-Wave and Full-Wave RectSunghoonie KangNo ratings yet
- Dee 3043-Electronic Circuit: PTSS - JKE - DEE3043 - LAB1Document8 pagesDee 3043-Electronic Circuit: PTSS - JKE - DEE3043 - LAB1nixsone357No ratings yet
- Electronics System: Lab. Session 3: Electrical ActuatorsDocument8 pagesElectronics System: Lab. Session 3: Electrical ActuatorsMarti SoucheironNo ratings yet
- LRC CircuitsDocument10 pagesLRC CircuitsleisllyNo ratings yet
- Circuits 2 Power Factor LabDocument3 pagesCircuits 2 Power Factor LabJulian ThrashNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: Unified Electronics Laboratory-IiDocument28 pagesLaboratory Manual: Unified Electronics Laboratory-IiAtul SainiNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - AC Circuits: RMS, Peak, and Peak-to-Peak VoltageDocument2 pagesWeek 2 - AC Circuits: RMS, Peak, and Peak-to-Peak VoltageMark CyrulikNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 7 Single-Phase Half Wave Voltage Multiplier 7-1 ObjectDocument2 pagesExperiment - 7 Single-Phase Half Wave Voltage Multiplier 7-1 ObjectMohammed Dyhia AliNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical EnggDocument5 pagesBasic Electrical EnggRohit HAndoreNo ratings yet
- PHY 112L Activity 8 Series RLC Circuit - 2: ResonanceDocument3 pagesPHY 112L Activity 8 Series RLC Circuit - 2: Resonanceقويه TasmanNo ratings yet
- Power and Maximum Power TransferDocument9 pagesPower and Maximum Power TransferNathan ButronNo ratings yet
- Exp. 1 ManualDocument4 pagesExp. 1 Manualf20212001No ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument12 pagesOhm's LawMHNo ratings yet
- Lab Handouts # 3Document6 pagesLab Handouts # 3Kashif Mujeeb Abdul MujeebNo ratings yet
- Ti Adc 2012 Team 28 4 Phase 1aDocument13 pagesTi Adc 2012 Team 28 4 Phase 1ahv_chillal88No ratings yet
- Project 1: Voltage RegulatorDocument26 pagesProject 1: Voltage RegulatordanielNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 1Document6 pagesLaboratory 1Alejandro PalacioNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering DepartmentDocument10 pagesElectrical Engineering DepartmentNicoNo ratings yet
- ME1 - Voltage DividerDocument5 pagesME1 - Voltage DividerMajeed BANo ratings yet
- Electronics 2 Lab ManualDocument75 pagesElectronics 2 Lab ManualLuisa Marie Bernardo Rañada100% (1)
- Semiconductors and Amplifiers LabDocument18 pagesSemiconductors and Amplifiers LabDurshil MungraNo ratings yet
- Lab Session: 3: Demonstrate The Behavior of A Silicon Diode in Half Wave RectifierDocument7 pagesLab Session: 3: Demonstrate The Behavior of A Silicon Diode in Half Wave RectifierFatima AmjadNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document11 pagesLab 1Fatin ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 Power ElectronicsDocument11 pagesLab 9 Power ElectronicsFahad IftikharNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- HV Circuits Nut N BoltsDocument14 pagesHV Circuits Nut N Boltsamit281276No ratings yet
- PS 3 PDFDocument22 pagesPS 3 PDFDragoslav IvankovicNo ratings yet
- Lab Session: 5: Demonstrate The Uses of Diodes in Voltage Multiplier Circuits. ObjectiveDocument4 pagesLab Session: 5: Demonstrate The Uses of Diodes in Voltage Multiplier Circuits. ObjectiveFatima AmjadNo ratings yet
- Godown Wiring - MechatroficeDocument2 pagesGodown Wiring - MechatroficeKush SharmaNo ratings yet
- L 6: V M I: AB Oltage UltipliersDocument5 pagesL 6: V M I: AB Oltage UltipliersMuhammad Nauman ZakkiNo ratings yet
- VolVoltage Doubler Desulfatortage Doubler Desulfator Design in Pulse Charging and DesuDocument15 pagesVolVoltage Doubler Desulfatortage Doubler Desulfator Design in Pulse Charging and DesukobyxNo ratings yet
- Ee 3101 Electronics I Laboratory Experiment 2 Lab Manual Power Supply Design ConsiderationsDocument8 pagesEe 3101 Electronics I Laboratory Experiment 2 Lab Manual Power Supply Design ConsiderationsAnurag PatelNo ratings yet
- Principles and Applications of The ICL7660 CMOS Voltage Converter PDFDocument10 pagesPrinciples and Applications of The ICL7660 CMOS Voltage Converter PDFPeter JordanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Diode ApplicationsDocument84 pagesChapter 2 Diode ApplicationssaadatNo ratings yet
- List of Edc ManualDocument88 pagesList of Edc ManualPatricia Grace PerezNo ratings yet
- Soumaya Almorabeti V2Document7 pagesSoumaya Almorabeti V2Abdullah AloglaNo ratings yet
- Der 447Document81 pagesDer 447ekupovina.djordjevic.mil87No ratings yet
- High Efficiency 2.45 GHZ Low Power Hybrid Junction Rectifier For RF Energy HarvestingDocument4 pagesHigh Efficiency 2.45 GHZ Low Power Hybrid Junction Rectifier For RF Energy HarvestingPrakash SunnyNo ratings yet
- Diode 1 SWDocument16 pagesDiode 1 SWNani Chori ShresthaNo ratings yet
- 22esc143 Iec Module-1 NotesDocument26 pages22esc143 Iec Module-1 Notesskus0426No ratings yet
- Generation of High Direct Current VoltagesDocument68 pagesGeneration of High Direct Current VoltagesMaria JoseeNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic Circuits Explained - Beginner's Guide To Electronics - Homemade Circuit ProjectsDocument85 pagesBasic Electronic Circuits Explained - Beginner's Guide To Electronics - Homemade Circuit ProjectsJuan fernando RoldanNo ratings yet
- EE 468 - Chapter 1 - SlidesDocument45 pagesEE 468 - Chapter 1 - SlidesُIBRAHEEM ALHARBINo ratings yet
- Unit Iii: Staff Incharge Dr.S.V.KayalvizhiDocument81 pagesUnit Iii: Staff Incharge Dr.S.V.KayalvizhiSuryaNo ratings yet
- Dynamo-Powered LED Light Circuits For BicyclesDocument22 pagesDynamo-Powered LED Light Circuits For BicyclesDharani KumarNo ratings yet
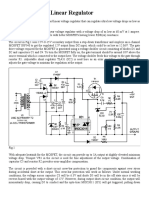
- Elliott Sound Products - Linear Power Supply DesignDocument26 pagesElliott Sound Products - Linear Power Supply Designksb9790No ratings yet
- Bridge Voltage Doubler With Active Diodes - ImpDocument4 pagesBridge Voltage Doubler With Active Diodes - ImpMajdi M. AbabnehNo ratings yet
- Charge PumpsDocument7 pagesCharge Pumpsjofinjv3194100% (1)
- EE1402 HVE NotesDocument96 pagesEE1402 HVE NotesKarthikeyanKarunNo ratings yet
- Ultra Low Drop Linear RegulatorDocument2 pagesUltra Low Drop Linear RegulatorJose Helio PalmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Clippers, Clampers & Voltage MultipliersDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Clippers, Clampers & Voltage MultipliersTarisai DoroNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap Ve Diode 1Document43 pagesBai Tap Ve Diode 1maithuong85100% (1)