Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prelim Lecture Notes On Auditap
Uploaded by
Charvie Kyle RamirezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prelim Lecture Notes On Auditap
Uploaded by
Charvie Kyle RamirezCopyright:
Available Formats
PRELIM - AUDITAP
AUDITING THEORY: INTRODUCTION TO ASSURANCE, NON-
ASSURANCE AND AUDITING
Auditing Theory in CPA Board Exams
AUDITING AND ASSURANCE STANDARDS COUNCIL (AASC)
AASC is tasked to assist BOA to establish and promulgate
auditing standards in the Philippines.
AUDITING AND ASSURANCE STANDARDS COUNCIL (AASC)
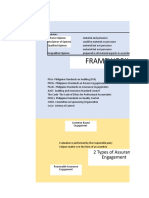
Elements of Assurance Engagement
1. Three-party Relationship
Practitioner
- Is broader than the term auditor.
- must be independent
- is governed by ethical requirements (i e professional competence)
regarding the conduct of the engagements
Standards Governing Professional Services by CPAs - may use the work of experts
- responsible for determining the nature, timing or extent of procedures
In addition to the standards promulgated by AASC, practitioners required by the engagement.
are also governed by the following:
Responsible Party
Philippine Framework for Assurance Engagements (PFAE)
- Is the person/s responsible to the subject matter, the subject matter
Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants in the Philippines (COEPAP) information, or both
- may or may not be the engaging party to the practitioner
- may or may not be from the same organization with the intended
users of the engagements
FUNDAMENTALS OF ASSURANCE SERVICES
- may be one of the intended user
Governing standards:
Intended Users
Philippine Framework for Assurance Engagements
- are the person/s for whom the practitioner prepares the assurance
Definition report
- in case of broad range of interests by the readers of assurance report,
Assurance Engagement (or Services) intended user may be limited to major stockholders with significant
and common interests
- Means an engagement in which a practitioner expresses a - may be identified by agreement between the practitioner and the
conclusion designed to enhance the degree of confidence of the responsible party or engaging party, or by law.
intended users other than the responsible party about the outcome of
the evaluation or measurement of a subject matter against criteria.
2. Appropriate Subject Matter
Assurance
Subject Matter
- Refers to the practitioner’s satisfaction as to the reliability of an
assertion being made by one party for use by another party. - Is the nature of the assertion the practitioner gathers
sufficient evidence
Subject Matter Information
- Pertains to the outcome of the evaluation or measurement of the When is evidence considered sufficient and appropriate? IT IS A MATTER
subject matter It is for which the practitioner gathers sufficient OF PROFESSIONAL JUDGMENT.
appropriate evidence to provide a reasonable basis for expressing a
conclusion in an assurance report. Materiality
- Identifiable, and capable of consistent evaluation or measurement
against the identified criteria and - Materiality is relevant when the practitioner determines the nature,
- Can be subjected to procedures for gathering sufficient appropriate timing and extent of evidence gathering procedures, and when
evidence. assessing whether the subject matter information is free of
misstatement
- LOWER materiality level leads to obtaining MORE audit
evidence
Assurance Engagement Risk
- Assurance engagement risk is the risk that the practitioner
expresses an inappropriate conclusion when the subject matter
information is materially misstated
- LOWER acceptable level of audit risks, MORE evidence must be
obtained
Cost Benefit Consideration and Level of Difficulty
- Considers the relationship between the cost and the usefulness of
the information obtained
- “the benefits that will be derived from obtaining the evidence
should exceed the cost of obtaining it”
Professional Skepticism
3. Suitable Criteria
- The practitioner plans and performs an assurance engagement with
Criteria Definition an attitude of professional skepticism recognizing that
circumstances may exist that cause the subject matter information
- The benchmarks used to evaluate or measure the subject matter
to be materially misstated
including, where relevant, benchmarks for presentation and
- Auditor makes a CRITICAL assessment with questioning mind
disclosure.
of the validity of evidence obtained
Classification
Formal
Less formal
Established
Specifically developed
Characteristics of Suitable Criteria
Reliability
Understandability
Neutrality
Completeness
Relevance
Communication to Intended Users 5. Written assurance report
- The practitioner provides a written report containing a conclusion
Publicly or an opinion that conveys the assurance obtained about the subject
Through inclusion in a clear manner in the presentation of the matter information
subject matter information
Through inclusion in a clear manner in the assurance report
By general understanding
4. Sufficient Appropriate Evidence
- All information used by the practitioner in arriving at the
conclusions on which the auditor’s opinion is based
- The practitioner performs the engagement with an attitude of
professional skepticism to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence
about whether the subject matter information is free from material
misstatement
Consideration when Planning and Performing the Engagement
Quantity (SUFFICIENCY)and quality (APPROPRIATENESS) of
Levels and Forms of Assurance
evidence
Materiality The levels (high or moderate) and forms (positive or negative) of
Assurance engagement risk assurance provided by the practitioner are dependent on the type of assurance
Cost-benefit consideration engagement being rendered.
Professional skepticism
Types of Engagement as to Assurance Level
Reasonable assurance engagement
The objective is a reduction in assurance engagement risk to an
acceptably low level in the circumstances of the engagement as the basis for a
positive form of expression of the practitioner’s conclusion Such form
conveys “reasonable assurance”
Limited assurance engagement
The objective is a reduction in assurance engagement risk to a
level that is acceptable in circumstances of the engagement, but where the risk
is greater than for a reasonable assurance engagement, as a basis for a
negative form of expression of the practitioner’s conclusion This form
conveys “limited assurance”
Types of Engagement as to Structure
Attestation Engagements
Attestation engagement is an engagement in which a practitioner is
engaged to issue, or does issue, a written communication that expresses a
conclusion about the reliability of a written assertion that is the responsibility
of another party
Attestation engagement may further be classified depending on the
availability of the assertions made by the responsible party to intended users
Assertion based engagements
assurance
engagements that the evaluation or measurement of the subject matter is
performed by the responsible party, and the subject matter information is in
the form of
an assertion by the responsible party that is made available to the intended
users
Direct
reporting engagements
assurance
engagements that the practitioner either directly performs the evaluation or
measurement of the subject matter, or obtains a representation from the
responsible
party that has performed the evaluation or measurement that is not available to
the
intended users in the assurance reports
Direct Engagements
You might also like
- Internal and External Communication Matrix (7.4)Document1 pageInternal and External Communication Matrix (7.4)Css100% (3)
- Task 4 Difference Analysis P1 - QuesDocument4 pagesTask 4 Difference Analysis P1 - QuesNgọc Trâm Trần0% (1)
- Auditing Midterm NotesDocument25 pagesAuditing Midterm NotesAmanda Claro0% (2)
- Team Handbook Downloadable Worksheets Plus CatalogDocument31 pagesTeam Handbook Downloadable Worksheets Plus CatalogNguyên CátNo ratings yet
- Unit Code: SITXWHS003 Unit Name: Implement and Monitor Work Health and Safety PracticesDocument11 pagesUnit Code: SITXWHS003 Unit Name: Implement and Monitor Work Health and Safety Practicessandeep kesarNo ratings yet
- Audit&Assurance Ireneo-Summary NotesDocument7 pagesAudit&Assurance Ireneo-Summary NotesMa. BeatriceNo ratings yet
- ACCP301 NotesDocument6 pagesACCP301 NotesAngelica RubiosNo ratings yet
- 01 Intro To Audit and AssuranceDocument7 pages01 Intro To Audit and AssuranceBts Army ForeverNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Auditing and Assurance ServicesDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Auditing and Assurance ServicesEdgie Trinidad TusiNo ratings yet
- Report That Limits Its Use To Those Users or ThatDocument7 pagesReport That Limits Its Use To Those Users or Thatkate bautistaNo ratings yet
- Framework of Assurance ServicesDocument14 pagesFramework of Assurance ServicesI am JacobNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Assurance ServicesDocument4 pagesFundamentals of Assurance ServicesMitzi CatemprateNo ratings yet
- c6 Aud TheoryDocument11 pagesc6 Aud TheoryRachel Anne RascoNo ratings yet
- Assurance Engagements & Other Services of A PractitionerDocument22 pagesAssurance Engagements & Other Services of A PractitionerkngnhngNo ratings yet
- Auditing Theory: Elements of An Assurance Engagement 1.) Suitable CriteriaDocument14 pagesAuditing Theory: Elements of An Assurance Engagement 1.) Suitable CriteriaIm NayeonNo ratings yet
- 0 Audit P ReviewerDocument66 pages0 Audit P ReviewerRiza Mae Ramos AddatuNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Audit and Assurance ServicesDocument50 pagesFundamentals of Audit and Assurance ServicesAndrea ValdezNo ratings yet
- Assurance Engagements: Appropriate Subject MatterDocument12 pagesAssurance Engagements: Appropriate Subject MatterNezhreen MaruhomNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Fundamentals of Assurance ServicesDocument28 pagesChapter 6 Fundamentals of Assurance ServicesJoyce Anne Garduque100% (1)
- Preliminary Discussion Assurance Engagements 5 Elements of Assurance EngagementDocument3 pagesPreliminary Discussion Assurance Engagements 5 Elements of Assurance EngagementChristine NionesNo ratings yet
- PSA 100 Phil Framework For Assurance EngagementsDocument4 pagesPSA 100 Phil Framework For Assurance EngagementsSkye LeeNo ratings yet
- At Ho Overview of AuditDocument3 pagesAt Ho Overview of AuditJamikka DistalNo ratings yet
- 03 Fundamentals of Assurance Services1Document3 pages03 Fundamentals of Assurance Services1carloNo ratings yet
- Assurance and Non Assurance EngagementsDocument4 pagesAssurance and Non Assurance EngagementsHazel BawasantaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Assurance, Auditing, and Other ServicesDocument12 pagesOverview of Assurance, Auditing, and Other ServicesCarms St ClaireNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoDocument5 pagesLecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoDenny June CraususNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document43 pagesPresentation 1Ma. Elene MagdaraogNo ratings yet
- Assurance Engagements OverviewDocument5 pagesAssurance Engagements OverviewprestinejanepanganNo ratings yet
- Auditing - Assurance Engagements NotesDocument2 pagesAuditing - Assurance Engagements NotesCharlize Natalie ReodicaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Fundamentals of Assurance Services I. The Concept of AssuranceDocument11 pagesChapter One Fundamentals of Assurance Services I. The Concept of AssuranceJeremy Lorenzo Teodoro VirataNo ratings yet
- AT01Document3 pagesAT01kara albueraNo ratings yet
- Framework: 2 Types of Assurance EngagementDocument41 pagesFramework: 2 Types of Assurance EngagementJerah TorrejosNo ratings yet
- Aap M1-3Document9 pagesAap M1-3Patricia CruzNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Operational Audit FrameworkDocument6 pagesModule 2 Operational Audit FrameworkEric CauilanNo ratings yet
- Auditing ReviewerDocument2 pagesAuditing Reviewerjerdelynvillegas7No ratings yet
- 1 Fundamentals of Auditing and Assurance Services RESADocument5 pages1 Fundamentals of Auditing and Assurance Services RESArandomlungs121223No ratings yet
- CH1. FUNDAMENTALS OF AUDITING AND ASSURANCE SERVICES pt2 2Document17 pagesCH1. FUNDAMENTALS OF AUDITING AND ASSURANCE SERVICES pt2 2Jyle ManiagoNo ratings yet
- Mod2-Assurance Engagements & Other Services HandoutDocument14 pagesMod2-Assurance Engagements & Other Services HandoutDonise Ronadel SantosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Assurance EngagementsDocument7 pagesLesson 1 Assurance EngagementsMark TaysonNo ratings yet
- AudTheo NoteDocument2 pagesAudTheo NoteJorelyn Rose BaronNo ratings yet
- 1 UlDocument11 pages1 UlYae'kult VIpincepe QuilabNo ratings yet
- LS 1 CombinedDocument35 pagesLS 1 CombinedSkye LeeNo ratings yet
- LS 1.00 - PSA 100 Phil Framework For Assurance EngagementsDocument4 pagesLS 1.00 - PSA 100 Phil Framework For Assurance EngagementsSkye LeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Aud TheoDocument37 pagesChapter 1 Aud TheoAlice WuNo ratings yet
- At 01 Assurance Engagements and Related ServicesDocument7 pagesAt 01 Assurance Engagements and Related ServicesJobby JaranillaNo ratings yet
- Accounting and Assurance Principles Notes - Sir PerlasDocument7 pagesAccounting and Assurance Principles Notes - Sir PerlasScarlet DragonNo ratings yet
- Colegio de La Purisima Concepcion: School of The Archdiocese of Capiz Roxas CityDocument3 pagesColegio de La Purisima Concepcion: School of The Archdiocese of Capiz Roxas CityJhomel Domingo GalvezNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Assurance Services FinalDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Assurance Services FinalLv ValenzonaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 An Auditor's ServicesDocument22 pagesChapter 4 An Auditor's ServicesAisa TriNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Fundamentals of Audit and Assurance EngagementDocument24 pagesTopic 1 Fundamentals of Audit and Assurance EngagementEricka Alipio AusteroNo ratings yet
- Philippine Framework For Assurance EngagementsDocument5 pagesPhilippine Framework For Assurance EngagementsAdan EveNo ratings yet
- AT-01 (Fundamentals of Auditing & Assurance Services)Document5 pagesAT-01 (Fundamentals of Auditing & Assurance Services)Allan MarquezNo ratings yet
- Edited Lesson 1 - Introduction To Assurance Services and EngagementsDocument16 pagesEdited Lesson 1 - Introduction To Assurance Services and EngagementsS RNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. ASSURANCE SERVICESDocument4 pagesChapter 1. ASSURANCE SERVICESyo poNo ratings yet
- Summary NotesDocument11 pagesSummary NotesAhmad Noainy AntapNo ratings yet
- Rodriguez Zyra-Denelle 01 JournalDocument10 pagesRodriguez Zyra-Denelle 01 JournalDaena NicodemusNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Auditing and Assurance ServicesDocument27 pagesFundamentals of Auditing and Assurance ServicesjennyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Assurance Services: Edner TDocument22 pagesFundamentals of Assurance Services: Edner TPb CunananNo ratings yet
- Audtheory - Fundamentals of Assurance ServicesDocument1 pageAudtheory - Fundamentals of Assurance Servicesfarah mae raquinioNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Philippine Framework For Assurance EngagementsDocument7 pagesSummary Notes - Philippine Framework For Assurance EngagementsLaila ContadoNo ratings yet
- Philippine Framework For Assurance EngagementsDocument9 pagesPhilippine Framework For Assurance EngagementsKlo MonNo ratings yet
- Edited Lesson 2 - Assurance and Non-Assurance EngagementDocument37 pagesEdited Lesson 2 - Assurance and Non-Assurance EngagementS RNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Auditing and Assurance ServicesDocument41 pagesFundamentals of Auditing and Assurance Servicesnotchu latteNo ratings yet
- Prelim Lecture Notes On JoserizDocument2 pagesPrelim Lecture Notes On JoserizCharvie Kyle RamirezNo ratings yet
- Prelim Lecture Notes On JoserizDocument2 pagesPrelim Lecture Notes On JoserizCharvie Kyle RamirezNo ratings yet
- Prelim Lecture Notes On JoserizDocument2 pagesPrelim Lecture Notes On JoserizCharvie Kyle RamirezNo ratings yet
- Customs of Tagalogs (Juan Plasencia)Document2 pagesCustoms of Tagalogs (Juan Plasencia)Charvie Kyle RamirezNo ratings yet
- Intacc 1Document3 pagesIntacc 1Charvie Kyle RamirezNo ratings yet
- Illustration IIIDocument1 pageIllustration IIICharvie Kyle RamirezNo ratings yet
- Group 5 QuizDocument2 pagesGroup 5 QuizCharvie Kyle RamirezNo ratings yet
- Board of Directors and Leadership Team - GSKDocument8 pagesBoard of Directors and Leadership Team - GSKkelvinkinergyNo ratings yet
- M U M I: Incom Nderstands The Ining NdustryDocument4 pagesM U M I: Incom Nderstands The Ining NdustryAl-hakimNo ratings yet
- Corrective and Preventative Action (CAPA) Procedure (ISO27001)Document5 pagesCorrective and Preventative Action (CAPA) Procedure (ISO27001)Maulana SyaifullahNo ratings yet
- Category Management Presentation by Dave PorterDocument32 pagesCategory Management Presentation by Dave PorterAlan Veeck100% (1)
- CatalogueDocument76 pagesCatalogueMogahed BarakatNo ratings yet
- Internship Report of Adamjee InsuranceDocument20 pagesInternship Report of Adamjee InsuranceMohsin Rahim100% (4)
- Case Study (Chapter 5-7)Document7 pagesCase Study (Chapter 5-7)Ana Mae CatubesNo ratings yet
- ENG7143 - Shaghayegh Tajik Principle of Project ManagementDocument34 pagesENG7143 - Shaghayegh Tajik Principle of Project ManagementShaghayegh T100% (2)
- Financial Statement Analysis of DellDocument14 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis of Dellfizza amjadNo ratings yet
- English AssignmentDocument45 pagesEnglish AssignmentClésia KassambaNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheets in Fundamentals of Accountanc2Document5 pagesActivity Sheets in Fundamentals of Accountanc2Irish NicolasNo ratings yet
- Telkom Presentation-Syndicate 3Document7 pagesTelkom Presentation-Syndicate 3Alif ArtantoNo ratings yet
- Visitor Handbook 2019Document9 pagesVisitor Handbook 2019erwinNo ratings yet
- Flow Proses Operational Linc TerminalDocument4 pagesFlow Proses Operational Linc Terminaldidanuraida001100% (1)
- CV1 Radhika Khandelwal 61920919Document1 pageCV1 Radhika Khandelwal 61920919Harmandeep singhNo ratings yet
- Total Golden RulesDocument32 pagesTotal Golden Ruleskaizen989489No ratings yet
- Accounting 111E Quiz 5Document3 pagesAccounting 111E Quiz 5Khim NaulNo ratings yet
- Internship JD (Full) 90 DaysDocument73 pagesInternship JD (Full) 90 Daysparika khannaNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Effective Administrative ManagementDocument2 pagesStrategies For Effective Administrative ManagementNatasha BritoNo ratings yet
- Lean Six Sigma White BeltDocument41 pagesLean Six Sigma White BeltMigs DavidNo ratings yet
- ITIL 4 Foundation Sample QuestionsDocument32 pagesITIL 4 Foundation Sample QuestionsSebastian Amaro HinojosaNo ratings yet
- Producer Behavior: Chapter OutlineDocument57 pagesProducer Behavior: Chapter OutlineAbdullahi100% (1)
- February 1, 2022 - Region Viii - 22i00054 - Bid DocsDocument64 pagesFebruary 1, 2022 - Region Viii - 22i00054 - Bid Docszerielyn dagangonNo ratings yet
- Intercompany and Intracompany in GLDocument7 pagesIntercompany and Intracompany in GLHarini YarlagaddaNo ratings yet
- Estate Managemen Jurnal 1Document10 pagesEstate Managemen Jurnal 1Agung Murti NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Number Division Position Scale Code Position ID Req NR: Manager: Building TechnologyDocument2 pagesNumber Division Position Scale Code Position ID Req NR: Manager: Building TechnologyThembelihle HadebeNo ratings yet