Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organization & Management Notes (Q1-W1)
Uploaded by
Honey SevillaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organization & Management Notes (Q1-W1)
Uploaded by
Honey SevillaCopyright:
Available Formats
Organization & Management recruited, and some internal or
external pressures.
Leading - Entails Influencing or
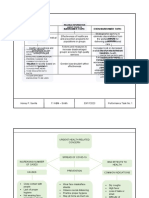
MANAGEMENT is the process of
motivating subordinates to do their
planning, organizing, leading, and controlling
best so that they would be able to
the activities of an organization effectively
help the organization's endeavor to
and efficiently to achieve its goals.
attain their set goals.
Controlling - Involves evaluating and,
FUNCTIONS OF MANAGEMENT
if necessary, correcting the
Planning
performance of the individuals or
work groups or teams to ensure that
they are all working toward the
Controlling Organizing previously set goals and plans of the
Management organization.
Functions
EFFICIENCY - the character of being able
Leading Staffing
to yield the maximum output from a
minimum amount of input.
Planning - Involves determining the The ability to maximize output with
organization's goals or performance minimum input
objectives, defining strategic actions “doing things right”
that must be done to accomplish Seeks to limit the wasted input
them, and developing coordination It requires things to be done quickly
and integration activities. to avoid wasting time and effort
Organizing - Demands assigning tasks, EFFECTIVENESS – being adapted to
setting aside funds, and bringing produce an effect that will help the
harmonious relations among the organization attain it aims.
individuals and work groups or teams The capacity to attain an intended
in organization. objective/result
Staffing - Indicates filling in the “doing the right thing”
different job positions in the Meet the desired goal regardless of
organization's structure; the factors the amount of input required
that influence this function include: Careful analysis and critical thinking
size of the organization, types of Things that need to be done are
jobs, number of individuals to be prioritized to achieve that goal
THE CLASSICAL THEORY 4. Impersonal connections with on
Systematic study of management another
began with the Classical Approach Bureaucracy is “the exercise of control on
Oldest and widely accepted viewpoint the basis of knowledge” – Weber
in management Administrative Management Theory
It emphasizes that there is “one In 1914, Henri Fayol delineated
best way” to manage management functions
Scientific Management 14 Principles of Management
It makes use of the step by step, 1. Division of work into specialized
scientific methods for finding the tasks, with specific duties and
single best way for doing a job responsibilities given to individuals
Frederick W. Taylor – Father of Scientific 2. Authority of managers to delegate
Management work and tasks to the employees.
To Increase production, the following The employees, in turn, are expected
principles must be observed: to comply and exercise their tasks
1. Develop a science for each element of responsibly
an individual's work to replace the 3. Discipline where expectations should
old rule of thumb method; be clearly set and violators of rules
2. Scientifically select and then train, must be punished
teach, and develop the workers: 4. Unity of command where an
3. Heartily cooperate with the workers employee should only report to one
so as to ensure that all work is done supervisor
in accordance with the principles of 5. Unity of direction which means that
the science that has been developed; the efforts of the employees are
4. Divide work and responsibility almost guided toward the attainment of
equally between management and organizational objectives
workers. 6. Predominance of the general interest
Bureaucratic Management of the organization over the
Max Weber believed to increase individual interests of employees
efficiency; the ideal bureaucracy has 7. Remuneration of the efforts of the
to be based on rational authority. employees which should be
Dimensions of The Ideal Bureaucracy: systematically rewarded in line with
1. Division of labor the organization's vision and mission
2. Hierarchal identification of job 8. Centralization where the roles of all
positions employees are clarified, with emphasis
3. Detailed rules and regulations
on distinction between superior and
subordinate roles
9. Scalar chain which means that
communication should be open within
chain of command
10.Order where the organization of jobs
and materials must be done in an
orderly fashion
11. Equity which means that fairness and
order must be practiced to maintain
employee commitment
12.Stability and tenure of personnel to
actively promote employee loyalty to
the organization
13.Initiative to encourage employees to
act on their own in support of the
organization's objectives
14.Esprit de corps to promote
teamwork and the unity of interest
between the employees and the
management
THE NEO-CLASSICAL THEORY
Behavioral science approach
Gives importance to human and social
aspects of the worker and his
relations in the organization
Robert Owen (1771-1858)
Increased profit ability for the firm
and reduced hardships for workers are
the positive result of showing
concern for workers
He disapproved of his colleagues’
failure to appreciate human element,
which when given careful attention
can result to 50% return of
investment
You might also like
- Building Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsFrom EverandBuilding Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsNo ratings yet
- Organization & Management: First Semester - First Quarter Week - 1Document9 pagesOrganization & Management: First Semester - First Quarter Week - 1Mira Joey AradoNo ratings yet
- TACN VOCAB - Sheet1Document6 pagesTACN VOCAB - Sheet1maihoangxuan.2211No ratings yet
- Organization and ManagementDocument2 pagesOrganization and ManagementAnn Sherley Baynosa SottoNo ratings yet
- Om Unit 1 NotesDocument7 pagesOm Unit 1 NotesRonaldine Julie PunongNo ratings yet
- Om First QuarterDocument10 pagesOm First QuarterBatilaran Nico Jan G.No ratings yet
- Organization and Management: Quarter 1Document45 pagesOrganization and Management: Quarter 1Jocet GeneralaoNo ratings yet
- OM ReviewerDocument18 pagesOM ReviewerJAVELOSA, YUAN ALDRICH M.No ratings yet
- Org - and Mngt. LAS Part 1Document41 pagesOrg - and Mngt. LAS Part 1Ai CaidenNo ratings yet
- Handouts Org. and MangamentDocument8 pagesHandouts Org. and MangamentBrian Omaña Deconlay EmhayNo ratings yet
- Org and Management Module 1Document11 pagesOrg and Management Module 1Juicy SaniatanNo ratings yet
- Aim Reviewer Elective 1Document4 pagesAim Reviewer Elective 1ChrisAlmerRamosNo ratings yet
- Org & Mgt-MarsloDocument2 pagesOrg & Mgt-MarslolordwygneNo ratings yet
- Accbp100 Lesson-2 UlobDocument42 pagesAccbp100 Lesson-2 UlobEgieMae GarcesNo ratings yet
- Inbound 639025605988810050Document22 pagesInbound 639025605988810050Ashlie ValdezNo ratings yet
- Raphaelle Marie H. Amoroso Bs Socwk - 2A: Perspectives Highlights/Assumptions/PrinciplesDocument7 pagesRaphaelle Marie H. Amoroso Bs Socwk - 2A: Perspectives Highlights/Assumptions/PrinciplesRaphaelle Marie AmorosoNo ratings yet
- Lab Management - Notes Term 01Document24 pagesLab Management - Notes Term 01Janus FideliNo ratings yet
- OrgMa Reviewer 1 1Document10 pagesOrgMa Reviewer 1 1potato langNo ratings yet
- Org & MGT 1Document10 pagesOrg & MGT 1Jennis Rollen MaagadNo ratings yet
- Org. & Mgt. ReviewerDocument7 pagesOrg. & Mgt. ReviewerlapNo ratings yet
- CE 413 - Lecture Notes (Outline)Document5 pagesCE 413 - Lecture Notes (Outline)Zennielle RayponNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Meaning and Function of ManagementDocument4 pages1.1 Meaning and Function of ManagementHannah Denise BatallangNo ratings yet
- HBM 111 ReviewerDocument4 pagesHBM 111 ReviewerClaire EdogawaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Management PDFDocument99 pagesLaboratory Management PDFPam Fajardo100% (5)
- OM - Q1 - Lesson 1Document32 pagesOM - Q1 - Lesson 1jofel yarciaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Operations ManagementDocument8 pagesBasics of Operations Managementarabela joyce manimtimNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management Chap 3Document3 pagesPrinciples of Management Chap 3Andrea OlescoNo ratings yet
- FBM Chapter 2Document44 pagesFBM Chapter 2Claire Evann Villena EboraNo ratings yet
- Notes in Psyc 011Document4 pagesNotes in Psyc 011이삐야No ratings yet
- NSG 129: Nursing Leadership and ManagementDocument13 pagesNSG 129: Nursing Leadership and ManagementJOHN PEARL FERNANDEZ100% (1)
- b5fc2f59-1c57-48ef-b5d8-06873af947b9Document14 pagesb5fc2f59-1c57-48ef-b5d8-06873af947b91624zainzain1624No ratings yet
- 1 Intro To Engineering Management Part 2Document24 pages1 Intro To Engineering Management Part 2Lily CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 BmecDocument5 pagesChapter 6 BmecaisNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 NotesDocument22 pagesUNIT 3 NotesMadan RVNo ratings yet
- 1.NCM 119 - ManagementDocument56 pages1.NCM 119 - ManagementEdgar Rebuyas100% (1)
- Organization & Management - 1ST Semi-Quarterly - Grade 11 - AbmDocument7 pagesOrganization & Management - 1ST Semi-Quarterly - Grade 11 - AbmJullianaNo ratings yet
- Concepts of ManagementDocument15 pagesConcepts of ManagementShekhar SunthaNo ratings yet
- Outline For The Report in Intro To PA - Organizing, Staffing, Controlling and DirectingDocument10 pagesOutline For The Report in Intro To PA - Organizing, Staffing, Controlling and DirectingDenn Icent Matthew MendarosNo ratings yet
- Handout in OrgaDocument4 pagesHandout in OrgaMay-Ann S. CahiligNo ratings yet
- NCM 119 Chap 5Document4 pagesNCM 119 Chap 5GEN COLLANTESNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment QuestionsDocument5 pagesSelf Assessment QuestionsErreix NNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document7 pagesChapter 1Pam GuillermoNo ratings yet
- MS PDFDocument65 pagesMS PDFThamil ArasanNo ratings yet
- Nature and Concepts of ManagementDocument16 pagesNature and Concepts of ManagementPercephone RazonableNo ratings yet
- OrganisingDocument29 pagesOrganisingAnsh RawatNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management NotesDocument19 pagesOrganization and Management NotesSchanelle RenoballesNo ratings yet
- Classical Neo Classical Theories of ManagementDocument11 pagesClassical Neo Classical Theories of ManagementDonabel CondonarNo ratings yet
- PPM Notes Unit 1Document68 pagesPPM Notes Unit 1megha bhatiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document11 pagesChapter 02Jomar TeofiloNo ratings yet
- Unit 6: Organizing: BBS Notes - 1st Year Principles of Management - WWW - Edunepal.infoDocument17 pagesUnit 6: Organizing: BBS Notes - 1st Year Principles of Management - WWW - Edunepal.infoSatish Kumar RanjanNo ratings yet
- 01 Org&Manage ReviewerDocument10 pages01 Org&Manage Reviewerortega.johnrhonlieNo ratings yet
- Orgman ReviewerDocument29 pagesOrgman ReviewerTini GarciaNo ratings yet
- PA 203 2nd Sem 2020 2021Document105 pagesPA 203 2nd Sem 2020 2021inshiraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction HSMDocument151 pagesUnit 1 Introduction HSMBazezew TakeleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 OrgmngtDocument32 pagesChapter 4 OrgmngtMargretheNo ratings yet
- ANIZINGDocument7 pagesANIZINGGiana CalloNo ratings yet
- Mpa Un3Document101 pagesMpa Un3Janani ChandrasekaranNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document34 pagesTopic 1SarahNo ratings yet
- ABM104 ModuleDocument4 pagesABM104 ModuleKeith BumaatNo ratings yet
- Organization StructureDocument27 pagesOrganization StructureDeepika SinghNo ratings yet
- FABM (Group 1)Document35 pagesFABM (Group 1)Honey SevillaNo ratings yet
- Clicking Through ChallengesDocument6 pagesClicking Through ChallengesHoney SevillaNo ratings yet
- USCP NotesDocument4 pagesUSCP NotesHoney SevillaNo ratings yet
- FABM 1 NotesDocument6 pagesFABM 1 NotesHoney SevillaNo ratings yet
- FABM 1 (Group Activity)Document2 pagesFABM 1 (Group Activity)Honey SevillaNo ratings yet
- R&WS PT 1Document2 pagesR&WS PT 1Honey SevillaNo ratings yet
- USCP EssayDocument1 pageUSCP EssayHoney Sevilla100% (1)
- Topic 7Document7 pagesTopic 7Honey SevillaNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science Q1-M1Document3 pagesEarth & Life Science Q1-M1Honey SevillaNo ratings yet
- 21ST CLPW Q1-PT1Document1 page21ST CLPW Q1-PT1Honey SevillaNo ratings yet
- 21st CLPW Q1-M1Document1 page21st CLPW Q1-M1Honey SevillaNo ratings yet
- 21ST Century Literature From The Philippines and The World Q1-W1Document2 pages21ST Century Literature From The Philippines and The World Q1-W1Honey SevillaNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Q1 - PT1Document2 pagesGen Math Q1 - PT1Honey SevillaNo ratings yet
- Applied Econ. Q1-W1Document2 pagesApplied Econ. Q1-W1Honey SevillaNo ratings yet
- Eapp Q1-W1Document4 pagesEapp Q1-W1Honey SevillaNo ratings yet
- DRRR - Activity #2 FinDocument3 pagesDRRR - Activity #2 FinHoney SevillaNo ratings yet
- Performance TaskDocument2 pagesPerformance TaskHoney Sevilla100% (1)
- DRRR - Activity #2 FinDocument2 pagesDRRR - Activity #2 FinHoney SevillaNo ratings yet
- Performance TaskDocument2 pagesPerformance TaskHoney SevillaNo ratings yet
- DRRR - Activity #3-4 MidDocument9 pagesDRRR - Activity #3-4 MidHoney SevillaNo ratings yet
- Making Friends British English StudentDocument8 pagesMaking Friends British English StudentMily ArrayaNo ratings yet
- Inkubator TransportDocument8 pagesInkubator TransportYassarNo ratings yet
- PATMD-LW Series Trifold 20200212Document2 pagesPATMD-LW Series Trifold 20200212Taacsa MatrizNo ratings yet
- Questão 13: Technology Anticipates Fast-Food Customers' OrdersDocument3 pagesQuestão 13: Technology Anticipates Fast-Food Customers' OrdersOziel LeiteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document3 pagesChapter 11Kristine TiuNo ratings yet
- Microtronics Technologies: GSM Based Vehicle Theft Detection SystemDocument3 pagesMicrotronics Technologies: GSM Based Vehicle Theft Detection Systemابراهيم الثوبريNo ratings yet
- ATP Parts Guide-B3Z Mechanical Seal PumpDocument1 pageATP Parts Guide-B3Z Mechanical Seal PumpRony FloresNo ratings yet
- Phy Interface Pci Express Sata Usb31 Architectures Ver43 PDFDocument99 pagesPhy Interface Pci Express Sata Usb31 Architectures Ver43 PDFRaj Shekhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- DBMS NotesDocument6 pagesDBMS Notesᴠɪᴄɪᴏᴜs ᴄᴜʀsᴇNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper For Class 9 Maths 2021 Set 1Document6 pagesCBSE Sample Paper For Class 9 Maths 2021 Set 1Aryaman TiwariNo ratings yet
- VC2200 Vibration MonitorsDocument16 pagesVC2200 Vibration MonitorsAnonymous HrTzKENo ratings yet
- Literature Review Topics RadiographyDocument8 pagesLiterature Review Topics Radiographyea7w32b0100% (1)
- Competency Based Learning Materials: Housekeeping NciiDocument54 pagesCompetency Based Learning Materials: Housekeeping NciiNickolodian AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Lethal Dose TableDocument1 pageLethal Dose TableRochie DiezNo ratings yet
- 2course Codes For 1 SEMESTER S.Y. 2021-2022: GE 2/ GE 1: Readings in The PhilippineDocument10 pages2course Codes For 1 SEMESTER S.Y. 2021-2022: GE 2/ GE 1: Readings in The PhilippineRexson Dela Cruz TagubaNo ratings yet
- Dual Shield 7100 Ultra: Typical Tensile PropertiesDocument3 pagesDual Shield 7100 Ultra: Typical Tensile PropertiesDino Paul Castro HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Romanian Association of Drilling Contractors ACFRDocument83 pagesRomanian Association of Drilling Contractors ACFRFuBasho33% (3)
- Pseudomonas AeruginosaDocument26 pagesPseudomonas AeruginosaNur AzizahNo ratings yet
- PLC Anupam Samanta 2010JE0976Document64 pagesPLC Anupam Samanta 2010JE0976Anupam SamantaNo ratings yet
- AutoCad 2012 ReadmeDocument2 pagesAutoCad 2012 Readmema_basith50% (2)
- Comprehensive Land Use Plan-Tagaytay CityDocument87 pagesComprehensive Land Use Plan-Tagaytay CityCet R. Cabahug50% (4)
- Physiology 102Document5 pagesPhysiology 102Javed AkhlaqNo ratings yet
- Cutlist Cistern TankDocument10 pagesCutlist Cistern TankAilyn O. DungogNo ratings yet
- Honkon Laser PDFDocument18 pagesHonkon Laser PDFEvolution MedNo ratings yet
- Prologue: Managerial Accounting and The Business EnvironmentDocument156 pagesPrologue: Managerial Accounting and The Business EnvironmentMarcus MonocayNo ratings yet
- Agrasar Lecture and Demonstration Programme On Water, Food and Climate ChangeDocument20 pagesAgrasar Lecture and Demonstration Programme On Water, Food and Climate ChangeMinatiBindhaniNo ratings yet
- Module 6.1 Plan Training SessionDocument16 pagesModule 6.1 Plan Training Sessioncyrene cayananNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Work MeasurementDocument24 pagesCHAPTER 5 Work MeasurementAiman SupniNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Set (Queing Model)Document5 pagesTutorial Set (Queing Model)Samuel kwateiNo ratings yet
- The Way of the Shepherd: Seven Secrets to Managing Productive PeopleFrom EverandThe Way of the Shepherd: Seven Secrets to Managing Productive PeopleRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (112)
- Getting Along: How to Work with Anyone (Even Difficult People)From EverandGetting Along: How to Work with Anyone (Even Difficult People)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Hire With Your Head: Using Performance-Based Hiring to Build Outstanding Diverse TeamsFrom EverandHire With Your Head: Using Performance-Based Hiring to Build Outstanding Diverse TeamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- 12 Habits Of Valuable Employees: Your Roadmap to an Amazing CareerFrom Everand12 Habits Of Valuable Employees: Your Roadmap to an Amazing CareerNo ratings yet
- The 5 Languages of Appreciation in the Workplace: Empowering Organizations by Encouraging PeopleFrom EverandThe 5 Languages of Appreciation in the Workplace: Empowering Organizations by Encouraging PeopleRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (46)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0From EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Five Dysfunctions of a Team SummaryFrom EverandThe Five Dysfunctions of a Team SummaryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (58)
- The Power of People Skills: How to Eliminate 90% of Your HR Problems and Dramatically Increase Team and Company Morale and PerformanceFrom EverandThe Power of People Skills: How to Eliminate 90% of Your HR Problems and Dramatically Increase Team and Company Morale and PerformanceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (22)
- The Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and GrowthFrom EverandThe Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and GrowthRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (101)
- Powerful Phrases for Dealing with Difficult People: Over 325 Ready-to-Use Words and Phrases for Working with Challenging PersonalitiesFrom EverandPowerful Phrases for Dealing with Difficult People: Over 325 Ready-to-Use Words and Phrases for Working with Challenging PersonalitiesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Summary: Who Moved My Cheese?: An A-Mazing Way to Deal with Change in Your Work and in Your Life by Spencer Johnson M.D. and Kenneth Blanchard: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Who Moved My Cheese?: An A-Mazing Way to Deal with Change in Your Work and in Your Life by Spencer Johnson M.D. and Kenneth Blanchard: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Organizational Behaviour: People, Process, Work and Human Resource ManagementFrom EverandOrganizational Behaviour: People, Process, Work and Human Resource ManagementNo ratings yet
- Inspiring Accountability in the Workplace: Unlocking the brain's secrets to employee engagement, accountability, and resultsFrom EverandInspiring Accountability in the Workplace: Unlocking the brain's secrets to employee engagement, accountability, and resultsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- The Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and GrowthFrom EverandThe Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and GrowthRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (12)
- Developing Coaching Skills: A Concise IntroductionFrom EverandDeveloping Coaching Skills: A Concise IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Strength-Based Leadership Coaching in Organizations: An Evidence-Based Guide to Positive Leadership DevelopmentFrom EverandStrength-Based Leadership Coaching in Organizations: An Evidence-Based Guide to Positive Leadership DevelopmentRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Coaching and Mentoring: Practical Techniques for Developing Learning and PerformanceFrom EverandCoaching and Mentoring: Practical Techniques for Developing Learning and PerformanceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Irresistible: The Seven Secrets of the World's Most Enduring, Employee-Focused OrganizationsFrom EverandIrresistible: The Seven Secrets of the World's Most Enduring, Employee-Focused OrganizationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Mastering the Instructional Design Process: A Systematic ApproachFrom EverandMastering the Instructional Design Process: A Systematic ApproachNo ratings yet
- Goal Setting: How to Create an Action Plan and Achieve Your GoalsFrom EverandGoal Setting: How to Create an Action Plan and Achieve Your GoalsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- The Art of Active Listening: How People at Work Feel Heard, Valued, and UnderstoodFrom EverandThe Art of Active Listening: How People at Work Feel Heard, Valued, and UnderstoodRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- The Burnout Epidemic: The Rise of Chronic Stress and How We Can Fix ItFrom EverandThe Burnout Epidemic: The Rise of Chronic Stress and How We Can Fix ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Crucial Conversations: Tools for Talking When Stakes are High, Third EditionFrom EverandCrucial Conversations: Tools for Talking When Stakes are High, Third EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads 2023: The Definitive Management Ideas of the Year from Harvard Business Review (with bonus article "Persuading the Unpersuadable" By Adam Grant)From EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads 2023: The Definitive Management Ideas of the Year from Harvard Business Review (with bonus article "Persuading the Unpersuadable" By Adam Grant)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Project Management For Beginners: The ultimate beginners guide to fast & effective project management!From EverandProject Management For Beginners: The ultimate beginners guide to fast & effective project management!Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)