Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CSE Narrative Report
Uploaded by
susaine100%(7)100% found this document useful (7 votes)
2K views3 pagesComprehensive sexuality education is a curriculum that teaches children and young people about cognitive, emotional, physical and social aspects of sexuality. It aims to empower them to make informed decisions about relationships, gender equality, and their health and well-being. Evidence shows that sexuality education improves knowledge and attitudes without increasing risky behavior when delivered through school-based programs complemented by parent and community involvement. The revised international guidance on comprehensive sexuality education positions it as important for overall well-being and development, not just HIV prevention.
Original Description:
Original Title
CSE Narrative report
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentComprehensive sexuality education is a curriculum that teaches children and young people about cognitive, emotional, physical and social aspects of sexuality. It aims to empower them to make informed decisions about relationships, gender equality, and their health and well-being. Evidence shows that sexuality education improves knowledge and attitudes without increasing risky behavior when delivered through school-based programs complemented by parent and community involvement. The revised international guidance on comprehensive sexuality education positions it as important for overall well-being and development, not just HIV prevention.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(7)100% found this document useful (7 votes)
2K views3 pagesCSE Narrative Report
Uploaded by
susaineComprehensive sexuality education is a curriculum that teaches children and young people about cognitive, emotional, physical and social aspects of sexuality. It aims to empower them to make informed decisions about relationships, gender equality, and their health and well-being. Evidence shows that sexuality education improves knowledge and attitudes without increasing risky behavior when delivered through school-based programs complemented by parent and community involvement. The revised international guidance on comprehensive sexuality education positions it as important for overall well-being and development, not just HIV prevention.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
What is Comprehensive Sexuality Education?
Comprehensive sexuality education is a curriculum-based process of teaching and
learning about the cognitive, emotional, physical and social aspects of sexuality. It aims
to equip children and young people with knowledge, skills, attitudes and values that will
empower them to realize their health, well-being and dignity; develop respectful social
and sexual relationships; consider how their choices affect their own well-being and that
of others; and understand and ensure the protection of their rights throughout their lives.
Why do young people need comprehensive sexuality education?
Too many young people receive confusing and conflicting information about
relationships and sex, as they make the transition from childhood to adulthood. This has
led to an increasing demand from young people for reliable information, which prepares
them for a safe, productive and fulfilling life. When delivered well, CSE responds to this
demand, empowering young people to make informed decisions about relationships and
sexuality and navigate a world where gender-based violence, gender inequality, early
and unintended pregnancies, HIV and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs) still
pose serious risks to their health and well-being. Equally, a lack of high-quality, age-
and developmentally-appropriate sexuality and relationship education may leave
children and young people vulnerable to harmful sexual behaviours and sexual
exploitation.
CSE plays a crucial role in addressing the health and well-being of children and young
people. Applying a learner-centered approach, CSE not only provides children and
young people with age-appropriate and phased education on human rights, gender
equality, relationships, reproduction, sexual behaviours risks and prevention of ill health,
but also provides an opportunity to present sexuality with a positive approach,
emphasizing values such as respect, inclusion, non-discrimination, equality, empathy,
responsibility and reciprocity.
What does the evidence say about CSE?
There is significant evidence on the impact of sexuality education. It emphasizes that:
Sexuality education has positive effects, including increasing young people’s
knowledge and improving their attitudes related to sexual and reproductive health
and behaviors.
Sexuality education – in or out of schools – does not increase sexual activity,
sexual risk-taking behaviour or STI/HIV infection rates.
Programmes that promote abstinence as the only option have been found to be
ineffective in delaying sexual initiation, reducing the frequency of sex or reducing
the number of sexual partners. Programmes that combine a focus on delaying
sexual activity with other content are effective.
‘Gender-focused’ programmes are substantially more effective than ‘gender-
blind’ programmes at achieving health outcomes such as reducing rates of
unintended pregnancy or STIs..
Sexuality education has the most impact when school-based programmes are
complemented with the involvement of parents and teachers, training institutes
and youth-friendly services.
Why have technical Guidance on sexuality education?
Countries are increasingly acknowledging the importance of equipping young people
with knowledge and skills to make responsible choices for their lives. CSE supports
young people’s empowerment by improving their analytical, communication and other
life skills for health and well-being in relation to sexuality, human rights, values, healthy
and respectful relationships, cultural and social norms, gender equality, non-
discrimination, sexual behaviour, violence and gender-based violence, consent, sexual
abuse and harmful practices.
What is new in the revised Guidance?
The original international technical Guidance published in 2009 positioned sexuality
education primarily as part of the HIV response. However, while HIV prevention remains
important, evidence and practice demonstrate that sexuality education has a much
broader relevance to other issues, not only for young people’s sexual and reproductive
health but also for their overall wellbeing and personal development.
The revised Guidance presents sexuality with a positive approach, recognizing that
CSE goes beyond educating about reproduction, risks and disease. It reaffirms the
position of sexuality education within a framework of human rights and gender equality.
It and reflects the contribution of sexuality education to the realization of several
internationally agreed commitments in relation to sexual and reproductive health, as
well as the achievement of the goals in the 2030 Agenda in relation to health and well-
being, quality and inclusive education, gender equality and women and girls
empowerment.
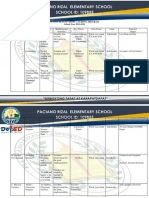
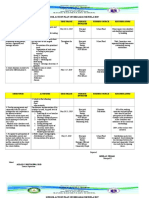
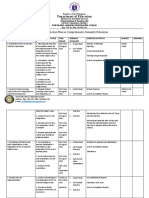
NARRATIVE REPORT
You might also like
- Accomplishment Report On Child-Friendly SchoolDocument2 pagesAccomplishment Report On Child-Friendly SchoolRachelle Annie Tagam100% (2)
- Child Friendly Narrative Reports 2021-2022Document2 pagesChild Friendly Narrative Reports 2021-2022William Felisilda100% (2)
- Naungan Elementary School 4th Quarter Portfolio Day ReportDocument4 pagesNaungan Elementary School 4th Quarter Portfolio Day ReportBraddock Mcgrath DyNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument6 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesJanine Bernadette MacasoNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Accomplishment Report On Advocating Child ProtectionDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Accomplishment Report On Advocating Child ProtectionJade Millante100% (2)
- ACR On OK Sa DepEdDocument5 pagesACR On OK Sa DepEdCristine may Danaytan100% (1)
- Implementation of The Integration of Comprehensive Sexuality Education of Core TopicsDocument6 pagesImplementation of The Integration of Comprehensive Sexuality Education of Core Topicsjethro123_69100% (2)
- Primals 4-6: Addressing Reading DifficultiesDocument5 pagesPrimals 4-6: Addressing Reading DifficultiesApril Pristine Ole75% (4)
- Saint Columban's Child Protection DataDocument4 pagesSaint Columban's Child Protection Datarose100% (1)
- Jomarie B. TorepelDocument2 pagesJomarie B. TorepelRhye Pabilona LocionNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report On PEACEDocument10 pagesAccomplishment Report On PEACEMary Kris Basa100% (2)
- Narrative Report On Limited Face-To-FaceDocument3 pagesNarrative Report On Limited Face-To-FaceAiza Mae CabactulanNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument2 pagesNarrative ReportTcherKamilaNo ratings yet
- NARRATIVE REPORT ON StakeholdersDocument1 pageNARRATIVE REPORT ON StakeholdersMichelle Fuentes Villoso100% (1)
- Department of Education: Narrative Report On The Conduct of Early Registration 2020Document2 pagesDepartment of Education: Narrative Report On The Conduct of Early Registration 2020Emilia Malabanan100% (1)
- Virtual In-Service Training For Public School Teachers 2021: Doña Concepcion H. Umali Elementary SchoolDocument1 pageVirtual In-Service Training For Public School Teachers 2021: Doña Concepcion H. Umali Elementary SchoolGlaiza Laya100% (1)
- Library Hub ReportDocument5 pagesLibrary Hub ReportEva May BaguioNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report On Lardo/PardoDocument2 pagesNarrative Report On Lardo/PardoAngel Gelig100% (2)
- LAC SESSION Mental HealthDocument2 pagesLAC SESSION Mental Healthgayle badoraya100% (1)
- Accomplishment Report in Guidance Grade Vi S.Y 2015-2016: Maljo-Jubasan Elem. SchoolDocument3 pagesAccomplishment Report in Guidance Grade Vi S.Y 2015-2016: Maljo-Jubasan Elem. SchoolJoevelyn CubianNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report On The Conduct of Parents Orientation About SLCPDocument2 pagesNarrative Report On The Conduct of Parents Orientation About SLCPM Ivy EstoqueNo ratings yet
- PFA training helps teachers cope with pandemic stressDocument2 pagesPFA training helps teachers cope with pandemic stressChristian Barrientos100% (1)
- Home Guidance-NARRATIVEDocument5 pagesHome Guidance-NARRATIVECATHERINE FAJARDO100% (1)
- Championing Learning in the New NormalDocument3 pagesChampioning Learning in the New NormalJade Jayvee100% (3)
- ACR Brigada Eskwela 2022-2023Document5 pagesACR Brigada Eskwela 2022-2023Joel Gaut100% (1)
- Hrpta ReportDocument5 pagesHrpta ReportIlyn Domingo Nupat100% (1)
- Accomplishment Report InsetDocument2 pagesAccomplishment Report InsetPrince Genesis G. Gunhuran100% (1)
- Narrative Report World Toilet DayDocument2 pagesNarrative Report World Toilet DayBithao Daisy84% (19)
- Action Plan in Adopt A School Program School Year 2019-2020Document4 pagesAction Plan in Adopt A School Program School Year 2019-2020Malyn Menorca67% (3)
- Narrative Report - Inset January 24, 2024 - Mikka AguadoDocument5 pagesNarrative Report - Inset January 24, 2024 - Mikka AguadoMikka Aguado100% (2)
- Narrative Report: Kalatagbak Elementary SchoolDocument1 pageNarrative Report: Kalatagbak Elementary SchoolAnonymous 6gthRen0% (1)
- Grade 2 - Narrative Report KickoffDocument3 pagesGrade 2 - Narrative Report KickoffGanie Mae Talde CasuncadNo ratings yet
- Brigada Eskwela Acton Plan 2Document7 pagesBrigada Eskwela Acton Plan 2Reymart Tandang Ada100% (1)
- Narrative Report On February 2017 DewormingDocument6 pagesNarrative Report On February 2017 DewormingRiz BangeroNo ratings yet
- Synchronized SSG Election ReportDocument4 pagesSynchronized SSG Election ReportRd David100% (2)
- Deworming NarrativeDocument3 pagesDeworming NarrativeccmmcNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report On Launching of Project RBB: (Restrospect Batang Batangueno)Document2 pagesNarrative Report On Launching of Project RBB: (Restrospect Batang Batangueno)Jane Ilagan VizcoNo ratings yet
- Lac Session Reflection 3Document2 pagesLac Session Reflection 3Aiza Abanto100% (1)
- Baroy South District Maliwanag Elementary SchoolDocument3 pagesBaroy South District Maliwanag Elementary SchoolNoeme VillarealNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Sexuality Education Action Plan: Bulalacao Elementary SchoolDocument1 pageComprehensive Sexuality Education Action Plan: Bulalacao Elementary SchoolLiezel Joyce Amigo Quezada100% (1)
- GAD Session GuideDocument6 pagesGAD Session GuideEirren Dela Cruz BagosNo ratings yet
- Alejandro ES facility upgradesDocument10 pagesAlejandro ES facility upgradesPinky Jane Piadozo PapaNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report in Homeroom Guidance Q2 2021 2022Document5 pagesNarrative Report in Homeroom Guidance Q2 2021 2022Charles Carl GarciaNo ratings yet
- Cluster Based Training On Gender and Development Awareness: Narrative ReportDocument1 pageCluster Based Training On Gender and Development Awareness: Narrative Reportmichelle c lacad50% (2)
- School Learning Action Cell Session On Violence Against Women and Children (VAWC)Document2 pagesSchool Learning Action Cell Session On Violence Against Women and Children (VAWC)Divina Arena100% (1)
- GAD Training Promotes Gender Equality at Rizal Science HSDocument5 pagesGAD Training Promotes Gender Equality at Rizal Science HSBright AppleNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report: School Based Feeding Program S.Y. 2020-2021Document1 pageNarrative Report: School Based Feeding Program S.Y. 2020-2021Dianne Encienzo100% (3)
- Department of Education: School Action Plan in Comprehensive Sexuality EducationDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: School Action Plan in Comprehensive Sexuality EducationDhanessa Condes92% (26)
- SBFP Best Practices Buhatan Es 2017Document25 pagesSBFP Best Practices Buhatan Es 2017MarlynAzurin100% (1)
- Narrative Report On NationalismDocument2 pagesNarrative Report On NationalismAdora SarcinoNo ratings yet
- Annex 9 - Project Work Plan & Budget Matrix On Anti Bullying ProgramDocument1 pageAnnex 9 - Project Work Plan & Budget Matrix On Anti Bullying ProgramNemfa Gaco Tumacder100% (3)
- Second Quarter Accomplishment ReportDocument2 pagesSecond Quarter Accomplishment ReportKristine Grace Venturillo Asuque100% (1)
- Division Consolidated Least Learned Competencies and Technical Assistance ProvidedDocument2 pagesDivision Consolidated Least Learned Competencies and Technical Assistance ProvidedRyangaaSiquera80% (5)
- Narrative-Report Student Protection Policy For FacultyDocument2 pagesNarrative-Report Student Protection Policy For FacultyRocel Roxas100% (1)
- Narrative Report School Based Feeding Program Orientation September 12 2023Document3 pagesNarrative Report School Based Feeding Program Orientation September 12 2023Alvin Gajerana FloresNo ratings yet
- ACR-Global Hand Washing Day 2021Document2 pagesACR-Global Hand Washing Day 2021Katy Chenee Napao Perez100% (1)
- ACR - BrigadaDocument3 pagesACR - Brigadacelsalazar81077No ratings yet
- Narrative Report On The In-Service Training (Inset) in ScienceDocument2 pagesNarrative Report On The In-Service Training (Inset) in Sciencemeriam tamayo100% (2)
- Closing SLAC DocumentationDocument7 pagesClosing SLAC DocumentationRichard R AvellanaNo ratings yet
- Behh..debate ToDocument17 pagesBehh..debate ToMicah Jenelle BironganNo ratings yet
- IRRESSEDocument4 pagesIRRESSEsusaineNo ratings yet
- Masterlist-Of-Participating-Learners 6sectionDocument7 pagesMasterlist-Of-Participating-Learners 6sectionsusaineNo ratings yet
- RPMS PPST 2021 2022Document23 pagesRPMS PPST 2021 2022susaineNo ratings yet
- Video Lesson - Susaine, Edna, AnnaDocument28 pagesVideo Lesson - Susaine, Edna, AnnasusaineNo ratings yet
- New-flat-Template-ENGLISH OrangeDocument12 pagesNew-flat-Template-ENGLISH OrangesusaineNo ratings yet
- Sample Activity SheetsDocument17 pagesSample Activity SheetssusaineNo ratings yet
- Distribution and Retrieval of ModulesDocument11 pagesDistribution and Retrieval of ModulessusaineNo ratings yet
- Teen PregnancyDocument3 pagesTeen PregnancyRoxan Joy MondiaNo ratings yet
- Sex Ed Rough DraftDocument7 pagesSex Ed Rough Draftapi-346202905No ratings yet
- Research Paper-CHAPTER IIDocument5 pagesResearch Paper-CHAPTER IIkcthon100% (2)
- Female Chauvinist Pigs PDFDocument17 pagesFemale Chauvinist Pigs PDFmaseaua36No ratings yet
- RH Bill provides universal access to family planningDocument32 pagesRH Bill provides universal access to family planningIrene JuarezNo ratings yet
- Sex Talk Tips From A My LangDocument2 pagesSex Talk Tips From A My LangMariana UzcateguiNo ratings yet
- LAC MANUAL DRAFT As of 27 Nov 2019Document168 pagesLAC MANUAL DRAFT As of 27 Nov 2019Elwin Vergara MoradosNo ratings yet
- The Prevalence of Hotels in Cabanatuan CityDocument35 pagesThe Prevalence of Hotels in Cabanatuan CityCristine Fajardo100% (1)
- Reflection in Sexually Transmitted DiseaseDocument1 pageReflection in Sexually Transmitted Diseasewenna janeNo ratings yet
- Integrating Sex Education in Basic Education Curriculum Perceptions Level of Knowledge and Acceptance of DLSU D Grade 12 Senior High SchoolDocument80 pagesIntegrating Sex Education in Basic Education Curriculum Perceptions Level of Knowledge and Acceptance of DLSU D Grade 12 Senior High SchoolKelly Shane Bernabe100% (9)
- DissertationDocument54 pagesDissertationRakesh Insan100% (1)
- Speech 001 Persuasive SpeechDocument9 pagesSpeech 001 Persuasive Speechapi-263312360100% (1)
- Baby Dumping Essay OutlineDocument4 pagesBaby Dumping Essay OutlineCharlene CathrineNo ratings yet
- Findings Background: Sex Education and CommunicationDocument1 pageFindings Background: Sex Education and CommunicationruthNo ratings yet
- Teaching Human Development Sexual Health With ConfidenceDocument5 pagesTeaching Human Development Sexual Health With Confidenceapi-348016142No ratings yet
- Changes in Elementary and Middle School Sexual Education Spark DiscussionDocument2 pagesChanges in Elementary and Middle School Sexual Education Spark Discussionapi-377600529No ratings yet
- ChauhanDocument28 pagesChauhanapi-450874030No ratings yet
- Sex Education: And-Cons-Of-Single-Gender-ClassroomsDocument4 pagesSex Education: And-Cons-Of-Single-Gender-ClassroomsrechelannlavillaNo ratings yet
- Mansci G16 Final PaperDocument21 pagesMansci G16 Final PaperAllan Patrick AlsimNo ratings yet
- Apr 2015 REALityDocument6 pagesApr 2015 REALityJohn LawsNo ratings yet
- Adolescent Reproductive Health EducationDocument16 pagesAdolescent Reproductive Health Educationapi-253732526No ratings yet
- Sex Education in SchoolDocument14 pagesSex Education in SchoolfiraNo ratings yet
- A Primer For Teaching Sexual Health EducationDocument54 pagesA Primer For Teaching Sexual Health EducationpepotchNo ratings yet
- Teenage Pregnant DilemmaDocument3 pagesTeenage Pregnant DilemmaAunice IdananNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Knowledge and Practices About Menstrual HygieneDocument6 pagesAssessment of Knowledge and Practices About Menstrual HygieneChikita Artia SariNo ratings yet
- Sample AE2 Writing - Final Test-30-3-19Document7 pagesSample AE2 Writing - Final Test-30-3-19Ngân VõNo ratings yet
- The Phenomenon of Teenage Pregnancy in The PhilippinesDocument21 pagesThe Phenomenon of Teenage Pregnancy in The PhilippinesKen PalNo ratings yet
- The Phenomenon of Teenage Pregnancy in The Philippines: ArticleDocument21 pagesThe Phenomenon of Teenage Pregnancy in The Philippines: ArticleMary Ann Leona SelgaNo ratings yet
- Issues and Possible Solution Ped266Document7 pagesIssues and Possible Solution Ped266Dan PradesNo ratings yet
- Sex Education Should Not Be Taught in SchoolsDocument6 pagesSex Education Should Not Be Taught in SchoolsCiamin YeapNo ratings yet
- You Can Thrive After Narcissistic Abuse: The #1 System for Recovering from Toxic RelationshipsFrom EverandYou Can Thrive After Narcissistic Abuse: The #1 System for Recovering from Toxic RelationshipsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (16)
- Tears of the Silenced: An Amish True Crime Memoir of Childhood Sexual Abuse, Brutal Betrayal, and Ultimate SurvivalFrom EverandTears of the Silenced: An Amish True Crime Memoir of Childhood Sexual Abuse, Brutal Betrayal, and Ultimate SurvivalRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (136)
- Unwanted Advances: Sexual Paranoia Comes to CampusFrom EverandUnwanted Advances: Sexual Paranoia Comes to CampusRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (22)
- The Longest Race: Inside the Secret World of Abuse, Doping, and Deception on Nike's Elite Running TeamFrom EverandThe Longest Race: Inside the Secret World of Abuse, Doping, and Deception on Nike's Elite Running TeamRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (59)
- I Love You Baby Girl... A heartbreaking true story of child abuse and neglect.From EverandI Love You Baby Girl... A heartbreaking true story of child abuse and neglect.Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- Unspeakable: Surviving My Childhood and Finding My VoiceFrom EverandUnspeakable: Surviving My Childhood and Finding My VoiceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (59)
- Fallen Idols: A Century of Screen Sex ScandalsFrom EverandFallen Idols: A Century of Screen Sex ScandalsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- Unbound: My Story of Liberation and the Birth of the Me Too MovementFrom EverandUnbound: My Story of Liberation and the Birth of the Me Too MovementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (147)
- The Longest Race: Inside the Secret World of Abuse, Doping, and Deception on Nike's Elite Running TeamFrom EverandThe Longest Race: Inside the Secret World of Abuse, Doping, and Deception on Nike's Elite Running TeamNo ratings yet
- QAnon & the #Pizzagates of Hell: Unreal Tales of Occult Child Abuse by the CIAFrom EverandQAnon & the #Pizzagates of Hell: Unreal Tales of Occult Child Abuse by the CIARating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Invisible Abuse - Instantly Spot the Covert Deception and Manipulation Tactics of Narcissists, Effortlessly Defend From and Disarm Them, and Effectively Recover: Deep Relationship Healing and RecoveryFrom EverandInvisible Abuse - Instantly Spot the Covert Deception and Manipulation Tactics of Narcissists, Effortlessly Defend From and Disarm Them, and Effectively Recover: Deep Relationship Healing and RecoveryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- What Is a Girl Worth?: My Story of Breaking the Silence and Exposing the Truth about Larry Nassar and USA GymnasticsFrom EverandWhat Is a Girl Worth?: My Story of Breaking the Silence and Exposing the Truth about Larry Nassar and USA GymnasticsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- Dear Professor: A Woman's Letter to Her StalkerFrom EverandDear Professor: A Woman's Letter to Her StalkerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (79)
- Becoming a Church that Cares Well for the AbusedFrom EverandBecoming a Church that Cares Well for the AbusedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- On the Threshold of Hope: Opening the Door to Healing for Survivors of Sexual AbuseFrom EverandOn the Threshold of Hope: Opening the Door to Healing for Survivors of Sexual AbuseRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Dear Professor: A Woman's Letter to Her StalkerFrom EverandDear Professor: A Woman's Letter to Her StalkerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (157)
- Scoundrel: How a Convicted Murderer Persuaded the Women Who Loved Him, the Conservative Establishment, and the Courts to Set Him FreeFrom EverandScoundrel: How a Convicted Murderer Persuaded the Women Who Loved Him, the Conservative Establishment, and the Courts to Set Him FreeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (19)
- Girls Like Us: Fighting for a World Where Girls Are Not for Sale, an Activist Finds Her Calling and Heals HerselfFrom EverandGirls Like Us: Fighting for a World Where Girls Are Not for Sale, an Activist Finds Her Calling and Heals HerselfRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (49)
- On Guard: Preventing and Responding to Child Abuse at ChurchFrom EverandOn Guard: Preventing and Responding to Child Abuse at ChurchRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Freedom from Shame: Trauma, Forgiveness, and Healing from Sexual AbuseFrom EverandFreedom from Shame: Trauma, Forgiveness, and Healing from Sexual AbuseNo ratings yet
- Unspeakable: Surviving My Childhood and Finding My VoiceFrom EverandUnspeakable: Surviving My Childhood and Finding My VoiceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Daddy’s Little Earner: A heartbreaking true story of a brave little girl's escape from violenceFrom EverandDaddy’s Little Earner: A heartbreaking true story of a brave little girl's escape from violenceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Somebody's Daughter: Inside an International Prostitution RingFrom EverandSomebody's Daughter: Inside an International Prostitution RingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Rescuing the 'Inner Child': Therapy for Adults Sexually Abused as ChildrenFrom EverandRescuing the 'Inner Child': Therapy for Adults Sexually Abused as ChildrenNo ratings yet