Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PT Ana Functions
Uploaded by
Rin Manalo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageThe document summarizes the functions of 10 major cell organelles and provides analogous structures within an airport to help explain their functions. Specifically, it compares the cell membrane to the entrance and exit of an airport, the cytoplasm to the roof and floor of an airport, and the nucleus to the airport manager who facilitates all sectors of the airport.
Original Description:
Original Title
pt ana functions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the functions of 10 major cell organelles and provides analogous structures within an airport to help explain their functions. Specifically, it compares the cell membrane to the entrance and exit of an airport, the cytoplasm to the roof and floor of an airport, and the nucleus to the airport manager who facilitates all sectors of the airport.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pagePT Ana Functions
Uploaded by
Rin ManaloThe document summarizes the functions of 10 major cell organelles and provides analogous structures within an airport to help explain their functions. Specifically, it compares the cell membrane to the entrance and exit of an airport, the cytoplasm to the roof and floor of an airport, and the nucleus to the airport manager who facilitates all sectors of the airport.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Ivy Koreen P.
Manalo
G10 – St. Alphonsus
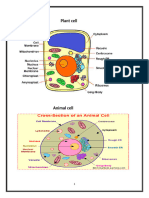
Organelle Name Organelle Function Analogous Structure Analogy Explanation
a) Cell Membrane A cell membrane, which is a semipermeable phospholipid bilayer, This is where the
surrounds all cells. The cell membrane regulates which substances Entrance and Exit of the passengers enter and exit
enter and exit the cell and also separates the cell's interior from its Airport. upon boarding and landing.
external environment.
b) Cytoplasm The cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance that fills the cell's interior
space. It's mostly water, but it also has salts, enzymes, and other The roof and the floor of
organic molecules. The cytoplasm surrounds and protects the cell's Roof and Floor of the Airport. the protects and support
organelles and is the site of many cellular processes (such as protein the airport.
synthesis and glycolysis).
c) Nucleus The nucleus is the cell's main controller and contains all of the genetic
information. Normally, a cell has a single nucleus that contains all of The Airport Manager
its DNA molecules; however, some cells (such as skeletal muscle cells) The Airport Manager facilitates all sectors of the
have multiple nuclei. The nucleus helps to protect the DNA of the cell airport.
while managing all other cellular activities such as cell division,
growth, protein production, and cell death.
d) Golgi Apparatus When newly synthesized substances leave the ER, they are directed The Airport Cashiers are
to the Golgi apparatus. This is a collection of flattened, membrane- The Airport’s Cashiers the ones who receives our
bound sacs that transport substances to the outer cell membrane, tickets before boarding.
where they either become part of the lipid bilayer or exit the cell.
e) Nucleolus The nucleolus is considered as the brain of the nucleus, covering The Owner of the Airport The Owner of the airport
nearly 25% volume of the nucleus. owns the whole facility.
f) Nuclear A nuclear membrane is a double membrane that surrounds the The Pilot and FA’s place are
Membrane nucleus of a cell. Its purpose is to keep the chromosomes separate The Crew’s Area separated from the
from the rest of the cell. passengers and airport
workers.
g) Mitochondria Cells require energy to power their biochemical reactions, and
mitochondria provide the majority of that energy. Mitochondria are Bagging Area The Baggage Area is where
the sites of respiration and the cellular "powerhouses," pumping out we store our luggage
energy that is then stored in ATP (adenosine triphosphate). before boarding.
h) Ribosomes The blueprints for all of the proteins produced by a cell are also
contained in the DNA molecules housed in the nucleus. Ribosomes, Flight Information Display This is where all the flight
which are the site of protein production in plant and animal cells, read System details are posted.
and interpret these blueprints.
i) Endoplasmic The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes inside the cell They are the one who plans
Reticulum that processes and transports new materials. Endoplasmic reticulum Flight Planning Services the available flights and
is classified into two types: rough ER and smooth ER. how passengers could
transport.
j) Lysosome Lysosomes are small, spherical organelles loaded with digestive The Scanning or the X-ray
enzymes. Their primary function is to degrade and recycle unwanted Scanning/ X-ray Area of our luggage area is
cell material, such as old cell parts or invading bacteria and viruses. where the unnecessary
Lysosomes are also involved in apoptosis (AKA programmed cell materials we bring as per
death). entering the premises of
the airport are confiscated.
k) Vacuole The vacuole is a very large organelle that can occupy up to 90% of the Overhead compartments This is where we store our
interior space of plant cells. One of its key functions is storage. luggage on the airplane
itself.
You might also like
- Astral Projection ExercisesDocument5 pagesAstral Projection Exercisesmightyr0% (1)
- Anaphy Topic 3Document4 pagesAnaphy Topic 3RAYNE CHLOIE LASTANo ratings yet
- Obstetric Analgesia and AnesthesiaDocument51 pagesObstetric Analgesia and AnesthesiaHerbert David100% (1)
- Lingualized Occlusion in RDPDocument37 pagesLingualized Occlusion in RDPmujtaba100% (1)
- Liver Function Lecture NotesDocument9 pagesLiver Function Lecture NotesMarie Bernadette DigoNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- 1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesDocument45 pages1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesMaham AdnanNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument146 pagesCell TheoryGynewNo ratings yet
- 10 Emotional DevelopmentDocument33 pages10 Emotional Developmentnurul kamariahNo ratings yet
- Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy A Systems Approach Paperback 8Th Edition Frank H Netter MD Full ChapterDocument67 pagesNetter Atlas of Human Anatomy A Systems Approach Paperback 8Th Edition Frank H Netter MD Full Chapterjohn.quinn22591% (11)
- IB Biology Study NotesDocument134 pagesIB Biology Study NotesManav Parikh100% (2)
- Digestive Tract of The PigDocument3 pagesDigestive Tract of The Pigmihai2242No ratings yet
- Cell AnalogyDocument15 pagesCell AnalogySirisha ChigurupatiNo ratings yet
- Pemf FrequenciesDocument13 pagesPemf FrequenciescumbredinNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nerve InjuriesDocument29 pagesPeripheral Nerve InjuriesbrillniksNo ratings yet
- Cells 1Document4 pagesCells 1ayahcalanticanNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology NotesDocument6 pagesCell Biology Notessaadc786100% (1)
- Answer Each Question of This Workshop With The Sources of Information That Are in The Last Page of This FileDocument7 pagesAnswer Each Question of This Workshop With The Sources of Information That Are in The Last Page of This Filejorge luis torresNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Rishabh Roy - Cell Organelles 2Document8 pagesKami Export - Rishabh Roy - Cell Organelles 2bloomington369No ratings yet
- MC3 Lec 2 Microbial Cell StructureDocument4 pagesMC3 Lec 2 Microbial Cell StructureCrishaGarraNo ratings yet
- Bio Cells ReviewerDocument4 pagesBio Cells ReviewerKimberly LuistroNo ratings yet
- Cells NoteDocument6 pagesCells NoteYolanda JesslinaNo ratings yet
- The Cell and Biological Membranes Structure and FunctionDocument9 pagesThe Cell and Biological Membranes Structure and FunctionAvaneesh HNo ratings yet
- Cell AnalogyDocument2 pagesCell AnalogyAlessandra AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- L2 - Prokaryotic Eukaryotic CellhgfhfgDocument65 pagesL2 - Prokaryotic Eukaryotic CellhgfhfgNoriko MatsumotoNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Activity On The Cell Parts - Written Output No. 2Document2 pagesAsynchronous Activity On The Cell Parts - Written Output No. 2Eunice DascoNo ratings yet
- Fundal Elaine Mae 11 CurieDocument11 pagesFundal Elaine Mae 11 CurieFundal Elaine Mae UmbaoNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Cell OrganellesDocument1 pageStructure and Function of Cell Organellesemmamarietaylor1597No ratings yet
- Rganisation of The Organism: 1 Cell Structure and OrganisationDocument26 pagesRganisation of The Organism: 1 Cell Structure and OrganisationGasterNo ratings yet
- Ani Me Hi MeDocument3 pagesAni Me Hi MeEinan NamsuNo ratings yet
- Organelle - WikipediaDocument42 pagesOrganelle - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- 12.1 Cell Structure and Function - PP PresentationDocument41 pages12.1 Cell Structure and Function - PP PresentationAlfred GeradaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles 2Document13 pagesCell Organelles 2Sadeeq ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Cell AnaogyDocument3 pagesCell AnaogySomeoneNo ratings yet
- Genbio I ReviewerDocument12 pagesGenbio I Reviewerjustanony92No ratings yet
- Cell AnalogyDocument17 pagesCell AnalogyJianne CabildoNo ratings yet
- A Specialized Structure Occurring in Most Cells and Separated From The Rest of The Cell by A Double Layer, The Nuclear MembraneDocument3 pagesA Specialized Structure Occurring in Most Cells and Separated From The Rest of The Cell by A Double Layer, The Nuclear MembraneGian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cell and Eukaryotic CellDocument3 pagesProkaryotic Cell and Eukaryotic CellJake GopitaNo ratings yet
- C3 - Cell StructureDocument4 pagesC3 - Cell StructureLorrine MagramoNo ratings yet
- Cell BrochureDocument2 pagesCell Brochurewherrera6816No ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesCell - The Unit of Lifeharifire050No ratings yet
- Review Workshop 5THDocument5 pagesReview Workshop 5THjairo gomezNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument28 pagesCell OrganellesPrecy Ann ReyesNo ratings yet
- BIOL107 - Different Cell TypesDocument4 pagesBIOL107 - Different Cell TypesJahsuah OrillanedaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Biology: Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument7 pagesCellular Biology: Cell Structure and TaxonomyFelyn Roseann AretaNo ratings yet
- Las 2 (Biology)Document12 pagesLas 2 (Biology)Renz GahumNo ratings yet
- Cell Size and ShapeDocument23 pagesCell Size and ShapenmsarmaNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts & Functions TableDocument2 pagesCell Parts & Functions TableJerene BrownNo ratings yet
- Organelle - WikipediaDocument21 pagesOrganelle - Wikipediamae mahiyaNo ratings yet
- MedicalterminologyDocument85 pagesMedicalterminologySamm ParillaNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellAlexa MacailoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Plant CellsDocument6 pagesLesson 2: Plant CellslalaNo ratings yet
- As BiologyDocument45 pagesAs BiologyShanzay DkhanNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument28 pagesCell StructureBANQUERIGO I.G. (2201427)No ratings yet
- (Zoolone) Animal CellDocument5 pages(Zoolone) Animal CellRenee Margarette GrapilonNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocument8 pagesCell Organelles WorksheetVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Structures Notes SVDocument10 pagesEukaryotic Cell Structures Notes SValkbbushra25No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic CellsDocument8 pagesProkaryotic CellsbbhoeeNo ratings yet
- M2 Lesson 1. Check in Activity QuizDocument5 pagesM2 Lesson 1. Check in Activity QuizElla PadillaNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and FunctionsDocument21 pagesCell Parts and FunctionsMarievic DavidNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Cell 1. NucleusDocument2 pagesParts of A Cell 1. NucleusVon Lester SanchezNo ratings yet
- Cell UltrastructureDocument19 pagesCell Ultrastructurezaydharoon419No ratings yet
- Structural and Functional Manifestation of LifeDocument6 pagesStructural and Functional Manifestation of LifeKaila StefanieNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionADMModule - Grade12 - Quarter1STEM - BIO12 Ia C 2Document14 pagesCell Structure and FunctionADMModule - Grade12 - Quarter1STEM - BIO12 Ia C 2Lyka Mae BenitoNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument18 pagesEnzymesIrllyshouldslepepNo ratings yet
- Session 4 (Organelles)Document4 pagesSession 4 (Organelles)MARO BGNo ratings yet
- 1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesDocument45 pages1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesMaham AdnanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-8 Cell: The Unit of LifeDocument6 pagesChapter-8 Cell: The Unit of LifeShreyas JaiwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter-8 Cell: The Unit of LifeDocument6 pagesChapter-8 Cell: The Unit of LifeNanbanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology SenthilDocument67 pagesRespiratory Physiology SenthilSenthilkumarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Head and NeckDocument25 pagesAnatomy Head and NeckMARISOL GALLEGO DUQUENo ratings yet
- 21 Neural Control N Coordination-NCERT Questions N AnswersDocument6 pages21 Neural Control N Coordination-NCERT Questions N AnswersGuru SrinivaasNo ratings yet
- Module 10-Digestive SystemDocument27 pagesModule 10-Digestive SystemDarlene FrueldaNo ratings yet
- Ascites BY: Muhammad Javaid Iqbal PGR Paediatric Surgery Services Hospital LahoreDocument40 pagesAscites BY: Muhammad Javaid Iqbal PGR Paediatric Surgery Services Hospital LahoreJavaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Teaching With The Teen Brain in Mind: 10 Top TipsDocument2 pagesTeaching With The Teen Brain in Mind: 10 Top TipschrisNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Antigenic StructureDocument36 pagesBacterial Antigenic Structuredearsaran0% (1)
- Valeriana.: Specific Indications.-Cerebral Anemia Hysteria Chorea HemicraniaDocument22 pagesValeriana.: Specific Indications.-Cerebral Anemia Hysteria Chorea HemicraniaDr Rushen SinghNo ratings yet
- Pysiology of Digestive SystemDocument26 pagesPysiology of Digestive SystemSamreen SammarNo ratings yet
- Cleavage in MammalsDocument51 pagesCleavage in MammalsIrfan Azram100% (4)
- Murali S MDocument116 pagesMurali S MSuman MondalNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2Document4 pagesLesson Plan 2api-248521749No ratings yet
- I. Purposes of Antenatal ExerciseDocument4 pagesI. Purposes of Antenatal ExercisePabhat KumarNo ratings yet
- UWI Exam Timetable Draft 1Document15 pagesUWI Exam Timetable Draft 1Marly MarlNo ratings yet
- Yawning Actual TestDocument4 pagesYawning Actual TestThu Hương BạchNo ratings yet
- Glucose Quiz 1 @ukrok1Document4 pagesGlucose Quiz 1 @ukrok1Omran BashirNo ratings yet
- Interplay Between Autophagy and Metabolic Syndrome-FrontiersDocument224 pagesInterplay Between Autophagy and Metabolic Syndrome-Frontiersdonmd98No ratings yet
- Effect of Bhastrika Pranayama and Exercise On Lung.1655Document2 pagesEffect of Bhastrika Pranayama and Exercise On Lung.1655Adrian ScurtuNo ratings yet
- G10 Mid-Term RevisionDocument239 pagesG10 Mid-Term RevisionMartria EhabNo ratings yet
- Urticaria Angioedema AlwiDocument53 pagesUrticaria Angioedema AlwiOkto Sofyan HasanNo ratings yet
- Use of A Passy-Muir Speaking Valve in A Non-Ventilated PatientDocument7 pagesUse of A Passy-Muir Speaking Valve in A Non-Ventilated PatientGian Franco Fariña VeraNo ratings yet