Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Brochure
Uploaded by
wherrera68160 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesOriginal Title
cell brochure
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesCell Brochure
Uploaded by
wherrera6816Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
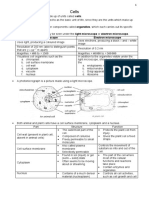
Genetic Material = Wires (the wires send
Similarities between a cell instructions so the car can move and so does
and car parts? genetic material)
Nucleus = Engine (the nucleus gives life to
Nucleolus = Energy (Helps make ribosomes
the cell the same way an engine does)
which contain proteins. Energy helps run
Cell Wall = Frame of car (the cell wall is like the car)
the base for the car because it’s a stiff
Nuclear Envelope = Doors (Helps allow the
structure)
passage of people and things just like the
Cell Membrane = Windows (windows nuclear envelope)
protect from the noise and sight of the
environment)
Chloroplast = A/C (when the A/C is on it
changes the temperature and gives relief
like the chloroplast gives food)
Mitochondrion = Battery (mitochondrion
help produce energy and the battery also
helps)
Ribosome = Oil ( without RNA and proteins
the cell will die and without oil the car will
not turn on)
Vesicle = Tire (they are both filled with air)
Golgi Apparatus = Steering Wheel (it helps
Cell Brochure
with transport)
Carlos Herrera
Central Vacuole = Gas tank (The gas tank Mod 1
holds the gas and the central vacuole also
Due 5/31/17
holds important things)
Smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum =
The cylinders of a car (the cylinders help
transport gas and the endoplasmic
reticulum also helps to transport)
Cells are fun!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Smooth and Rough endoplasmic
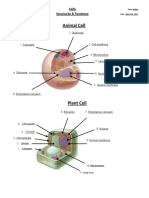
Cell Parts
reticulum: a network of tubular membranes
Cell Membrane: A flexible covering that within the cytoplasm of the cell, occurring either
with a smooth surface (smooth endoplasmic
protects the inside of a cell from the
reticulum) or a rough surface (rough
environment outside a cell.
endoplasmic reticulum)
Cell Wall: A stiff structure outside the cell
membrane. Nucleus: the central and most important part of
an object, movement, or group, forming the
Chloroplast: A plastid that contains basis for its activity and growth.
chlorophyll and in which photosynthesis takes
place. Genetic Material: the medium by which
instructions are transmitted from one generation
Mitochondrion: An organelle found in large of organisms to the next.
numbers in most cells, in which the biochemical
Nucleolus: a small dense spherical structure
processes of respiration and energy production
in the nucleus of a cell during interphase.
occur.
Nuclear Envelope: The double-layered
Ribosome: A minute particle consisting of
membrane enclosing the nucleus of a
RNA and associated proteins, found in large
eukaryotic cell. The nuclear envelope has pores
numbers in the cytoplasm of living cells.
that allow the passage of materials into and out
of the nucleus.
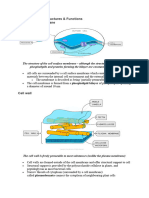
What is a cell? Vesicle: A fluid- or air-filled cavity or sac, in
particular. Parts of a Cell Picture:
Cells can be described in many Cytoskeleton: A microscopic network of
protein filaments and tubules in the cytoplasm
ways because there are different of many living cells, giving them shape and
types but a cell is the smallest unit coherence.
of life.
Golgi Apparatus: A complex of vesicles and
folded membranes within the cytoplasm of most
eukaryotic cells, involved in secretion and
intracellular transport.
Central Vacuole: A cellular organelle found
in plant cells. It is often the largest organelle in
the cell. It is surrounded by a membrane and
functions to hold materials and wastes.
You might also like
- Tour of The CellDocument60 pagesTour of The Celladisty sncNo ratings yet
- Strawberry Dna Extract KitDocument18 pagesStrawberry Dna Extract KitIcunLelah Hatilelah SekaliampebngungdirisndriNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Topic 3Document4 pagesAnaphy Topic 3RAYNE CHLOIE LASTANo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- 1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesDocument45 pages1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesMaham AdnanNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Gizmo Answer KeyDocument4 pagesCell Structure Gizmo Answer KeyJonathan o00% (1)
- MCQs in Objective PathologyDocument97 pagesMCQs in Objective Pathologyvinayguru82100% (6)
- Anemia in PregnancyDocument212 pagesAnemia in Pregnancysalah subbah100% (1)
- Chapter 5: "The Fundamental Unit of Life"Document66 pagesChapter 5: "The Fundamental Unit of Life"Tejous TejousNo ratings yet
- Genbio ExamDocument13 pagesGenbio Examharry pottahNo ratings yet
- ADN vs. ARNDocument3 pagesADN vs. ARNDiana Bio100% (1)
- Biology AS ClassifiedDocument209 pagesBiology AS ClassifiedMaaz Rashid100% (2)
- FTS-12 (Code-B) SolutionDocument12 pagesFTS-12 (Code-B) SolutionGnapika dgNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument72 pagesThe Cellbir.email013No ratings yet
- Summarising First Chap WipDocument30 pagesSummarising First Chap Wiprehan nimnadaNo ratings yet
- Cell: Cell Is Called The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument6 pagesCell: Cell Is Called The Fundamental Unit of LifeShrinivasan HariprasanthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-CellDocument6 pagesChapter 2-CellAlthea BayolaNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between A Plant (Palisade) Cell and An Animal (Liver) CellDocument3 pagesComparison Between A Plant (Palisade) Cell and An Animal (Liver) CellOctaviano SimonNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure: Structural Functional Unit: UnitDocument13 pagesCell Structure: Structural Functional Unit: UnitHaya Attieh100% (1)
- 1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesDocument45 pages1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesMaham AdnanNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Rishabh Roy - Cell Organelles 2Document8 pagesKami Export - Rishabh Roy - Cell Organelles 2bloomington369No ratings yet
- Week 2: September 20-25: MC 2: BiochemistryDocument6 pagesWeek 2: September 20-25: MC 2: BiochemistryMary Rose CuentasNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument24 pagesThe CellCaren AdongoNo ratings yet
- 2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsDocument37 pages2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsJuan Jaylou AnteNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellAlexa MacailoNo ratings yet
- As BiologyDocument45 pagesAs BiologyShanzay DkhanNo ratings yet
- Cells NoteDocument6 pagesCells NoteYolanda JesslinaNo ratings yet
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument54 pagesCell The Fundamental Unit of LifeAxyahh 99No ratings yet
- Eukaryote Cell GuideDocument4 pagesEukaryote Cell GuideStephania AldanaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 (BioChem)Document33 pagesModule 1 (BioChem)cariagatrishaclaireNo ratings yet
- Chapter-8 Cell: The Unit of LifeDocument6 pagesChapter-8 Cell: The Unit of LifeNanbanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-8 Cell: The Unit of LifeDocument6 pagesChapter-8 Cell: The Unit of LifeShreyas JaiwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: "The Fundamental Unit of Life"Document7 pagesChapter 5: "The Fundamental Unit of Life"Zeel ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure 2Document5 pagesCell Structure 2slombez 150% (1)
- Acfrogahwtgjhymcdbhqd9juy0ihb5dgzqyobwgygm44pyrxkeh Dixuo Odyslryl Jpqgjhd4udt63zm6ot2mgudp GWKKKDFLLJD 4nxfp5i Pvcee 9pyuxltmliuwhn9qmanxfhy82jt1l4Document8 pagesAcfrogahwtgjhymcdbhqd9juy0ihb5dgzqyobwgygm44pyrxkeh Dixuo Odyslryl Jpqgjhd4udt63zm6ot2mgudp GWKKKDFLLJD 4nxfp5i Pvcee 9pyuxltmliuwhn9qmanxfhy82jt1l4s20003No ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Structures Notes SVDocument10 pagesEukaryotic Cell Structures Notes SValkbbushra25No ratings yet
- Cell & TissueDocument11 pagesCell & TissuerahulpanditkgpNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Study of Cellular NucleusDocument25 pagesA Comprehensive Study of Cellular NucleusAnita ShuklaNo ratings yet
- 03 The CellDocument20 pages03 The CellJasmine JuitNo ratings yet
- 2 - Cell+WSDocument3 pages2 - Cell+WSRohan SoniNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesCell - The Unit of Lifeharifire050No ratings yet
- Louie John L. Caballero BSMT 1Y1 - 2: Happ Experiment #3Document3 pagesLouie John L. Caballero BSMT 1Y1 - 2: Happ Experiment #3Louie John CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument54 pagesCell The Fundamental Unit of LifeAxyahh 99No ratings yet
- Historical Background:: Chapter 4: Cell StructureDocument6 pagesHistorical Background:: Chapter 4: Cell Structureanon_975930740No ratings yet
- MaryamDocument23 pagesMaryamHabiba SaeedNo ratings yet
- Introductiontophysiologylecture 101020230212 Phpapp02Document34 pagesIntroductiontophysiologylecture 101020230212 Phpapp02DR KARSHAN NANDANIYANo ratings yet
- Cell Structure - Part II Updated 01-11-2016Document47 pagesCell Structure - Part II Updated 01-11-2016Abdulaziz AHNo ratings yet
- CELL STRUCTURE Chapter 3Document18 pagesCELL STRUCTURE Chapter 3Micaela BobierNo ratings yet
- Cell Ncert Solution: SolnDocument6 pagesCell Ncert Solution: Soln비KeerthuNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 GROUP ACTIVITYDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology 1 GROUP ACTIVITYLoseriaga Vince TristanNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes (YR11)Document42 pagesBio Notes (YR11)nguyenbohaeNo ratings yet
- Biology VCE Chapter 1Document8 pagesBiology VCE Chapter 1Rachel JNo ratings yet
- Introduction CellDocument48 pagesIntroduction CellabdNo ratings yet
- #1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument3 pages#1 Cell Structure and FunctionCharlene EpilepsiaNo ratings yet
- More Cells. The Cell Theory Can Be Summarized As:: Biology 12 - Cell Structure & Function: Chapter NotesDocument7 pagesMore Cells. The Cell Theory Can Be Summarized As:: Biology 12 - Cell Structure & Function: Chapter NotesJaveed KassamNo ratings yet
- w1 Introduction of CellsDocument60 pagesw1 Introduction of CellsNur Bahiyah Binti Abdul Wahab IPGKTINo ratings yet
- Biochemistry PDFDocument2 pagesBiochemistry PDFMuhammad EhsanNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer 2Document3 pagesAnaphy Reviewer 2Christopher Valle ArgelNo ratings yet
- CHP 2 (N) - Cell Structures and FunctionDocument62 pagesCHP 2 (N) - Cell Structures and FunctionSIMBA The Lion KingNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Intl A Levels Biology Unit 2 Wbi12 v1Document14 pagesEdexcel Intl A Levels Biology Unit 2 Wbi12 v1seif nimerNo ratings yet
- Revision: Cell Division 20 MARCH 2013: Lesson DescriptionDocument19 pagesRevision: Cell Division 20 MARCH 2013: Lesson DescriptionKaylaNo ratings yet
- DR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Document14 pagesDR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Cole- Min Khant KyawNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellDocument41 pagesAnimal and Plant CellSabrina LavegaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Plant CellsDocument6 pagesLesson 2: Plant CellslalaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure ASDocument40 pagesCell Structure ASYasmine HadiastrianiNo ratings yet
- PLANT CELL: Parts and FunctionsDocument2 pagesPLANT CELL: Parts and FunctionsnniChaNo ratings yet
- Cell UltrastructureDocument19 pagesCell Ultrastructurezaydharoon419No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Diagnostic Microbiology 4th Edition MahonDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Diagnostic Microbiology 4th Edition MahonEricBlankenshipkcfes100% (40)
- Stage 3 Worksheets 8-11Document5 pagesStage 3 Worksheets 8-11api-314389226No ratings yet
- Discussion Bio460Document2 pagesDiscussion Bio460MUHAMMAD SYAHMI BIN AZMINo ratings yet
- Module 9 - Weeks 1,2Document15 pagesModule 9 - Weeks 1,2Jomar CarabotNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument45 pagesMitosis and MeiosisJhon dave SurbanoNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Karyotype Revision2 NondisjuncDocument2 pagesMeiosis Karyotype Revision2 NondisjuncKerem Sezai BaşNo ratings yet
- Botany ReviewerDocument14 pagesBotany ReviewerTherese EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Histology 1532547893Document233 pagesVeterinary Histology 1532547893Teguh ArinataNo ratings yet
- KARYOTYPEDocument23 pagesKARYOTYPELucia AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 - Handout For Lectures 1-6 (Summary)Document1 pageBio 11 - Handout For Lectures 1-6 (Summary)Steffi GatdulaNo ratings yet
- Pre Test BiotechDocument3 pagesPre Test BiotechMichaelAbdonDomingoFavoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1,2 - Plant Cell Structure - DFQDocument10 pagesLecture 1,2 - Plant Cell Structure - DFQUmarNo ratings yet
- Assignment Research: CELLS Second PeriodDocument7 pagesAssignment Research: CELLS Second PeriodMaria FabianNo ratings yet
- 2ND Periodical ExamDocument4 pages2ND Periodical Examjhong rabangNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 GROUP ACTIVITYDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology 1 GROUP ACTIVITYLoseriaga Vince TristanNo ratings yet
- Trisomy 21Document5 pagesTrisomy 21pongidaeNo ratings yet
- Sri Chaitanya Educational Institutions, India: NEET Grand TestDocument5 pagesSri Chaitanya Educational Institutions, India: NEET Grand TestVikash ReddyNo ratings yet
- Experiment9 PlastidDocument4 pagesExperiment9 PlastidRahaizuddin RaniNo ratings yet
- Biota Quiz Bee Mock Test Part 1Document2 pagesBiota Quiz Bee Mock Test Part 1Ken Juliana Fe IsaacNo ratings yet
- 3 Tseng PDFDocument24 pages3 Tseng PDFAyman AbdoNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of Life To Improvement in Food Resources ChaptersDocument104 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life To Improvement in Food Resources ChaptersSARANSH oPNo ratings yet
- IB Released Questions On 01 Cell BiologyDocument50 pagesIB Released Questions On 01 Cell BiologyZuzanna BaligaNo ratings yet
- Biology Entrance Exam For G11 & G12 From 1995 - 2011Document60 pagesBiology Entrance Exam For G11 & G12 From 1995 - 2011Azure Fikadu100% (1)