Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Exam Open Notes
Uploaded by
Erica Rose Ramales0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesLipids are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They function to store energy and make up cell membranes. The three main types of lipids are triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids. Carbohydrates are the primary energy source and are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The simplest forms are monosaccharides like glucose. Proteins are made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. They provide structure, regulate cell functions, transport molecules, and act as enzymes and hormones. Nucleic acids contain genetic information and are made of nucleotides containing nitrogen bases, sugars, and phosphates. DNA stores and transmits hereditary information while RNA assists in protein synthesis.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLipids are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They function to store energy and make up cell membranes. The three main types of lipids are triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids. Carbohydrates are the primary energy source and are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The simplest forms are monosaccharides like glucose. Proteins are made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. They provide structure, regulate cell functions, transport molecules, and act as enzymes and hormones. Nucleic acids contain genetic information and are made of nucleotides containing nitrogen bases, sugars, and phosphates. DNA stores and transmits hereditary information while RNA assists in protein synthesis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesScience Exam Open Notes
Uploaded by
Erica Rose RamalesLipids are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They function to store energy and make up cell membranes. The three main types of lipids are triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids. Carbohydrates are the primary energy source and are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The simplest forms are monosaccharides like glucose. Proteins are made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. They provide structure, regulate cell functions, transport molecules, and act as enzymes and hormones. Nucleic acids contain genetic information and are made of nucleotides containing nitrogen bases, sugars, and phosphates. DNA stores and transmits hereditary information while RNA assists in protein synthesis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
II.
Multiple choice (Biomolecules)
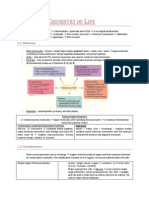
The digestive process is occurring. In order for organisms to LIPIDS: FATS AND OILS
live and function they require energy. Eating and digesting
Function: Store energy, Insulates your body
food provides the body with chemical energy in the form of
(maintains homeostasis), and make up the cell
ATP.
membrane, Made mainly of carbon and hydrogen
CARBOHYDRATES (few oxygen), Fat best method of STORING, forms
cell membranes, Insulates nerve cells (myelin),
Most common organic molecule
Elements: C-H-O
Function: Primary energy source our body needs Monomer (Building blocks): glycerol & 3 fatty acids
Supplies energy to our brain Polymer: Phospholipids, triglycerides
Provide quick energy to our body Example: Steroids, cholesterol, fats, Oils, Nuts,
Elements present: C, H, O (1:2:1 ratio) Waxes, and make up part of the cell membrane
Monomer (building block):
Monosaccharides (Glucose is most common) Lipids are Hydrophobic (water fearing) and do not dissolve in
water!
Polymer: Polysaccharides (starch, Glycogen, Cellulose,
Chitin) SATURSTED: The bonds between all the carbons are single
Examples: Chocolate, Bread, Pasta, Fruits, Vegetables bonds.
beans, milk, popcorn, potatoes, cookies, spaghetti, soft
Solid at room temperature
drinks, corn, and cherry pie.
Mainly animal fats (bacon grease, lard)
MONOSACCHARIDES are the simplest form of
carbohydrates. Examples: Glucose, Fructose Galactose UNSATURATED: There is at least one double or triple bond
between carbons present.
POLYSACCHARIDES many
Liquid at room temperature
DISACCHARIDES two
Mainly plant based fats (olive oil, peanut oil) as well as oily
MONOSACCHARIDES one
fish (Tuna, Sardines)
PROTEINS Function of Proteins
Elements: C-H-O-N Provides us with building blocks for life!
Monomer (Building Block): amino acids (20 different Also regulate most functions in a cell.
ones!) Glycoproteins (antigens)
Polymer: proteins (tons) Combines w/DNA to form chromosomes
Examples of proteins: hemoglobin in red blood cells, Turns genes on and off
albumin in eggs, enzymes that control reactions in the Antibodies (fights disease)
body, and antibodies Provides structure & strength (fibers)
Found in: fish, eggs, meat Transports molecules in & out cells
“R” groups represent one of the 20 Amino Acids! (so, each Hemoglobin (transports O2)
amino acid has something different in that spot) Enzymes (speeds up rxns)- has –ase suffix
Acts as hormones (insulin)- many proteins have suffix
MONOMER: Amino Acids
of -in
Contains C, H, O, N
20 types
Has both hydrophobic & hydrophylic ends
Differ in R-group
R-group can be acidic, basic or neutral
Makes polypeptide then makes proteins
POLYMER: Polypeptide (peptide means bond)
Formed by dehydration synthesis
Sequence determined by DNA
3-D and folds to take up less space
NUCLEIC ACIDS Contains phosphorus & oxygen
Polymer: polynucleotide
Function:
Provide our genetic information Function Polypeptide: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
Holds the instructions to make proteins.
contains the genetic code
Elements: C-H-O-N-P
stores & transmit heredity/genetic information
Monomer : nucleotides
found in the nucleus (mitochondria)
A nucleotide is made up of:
Sugar Double stranded (double helix)
Phosphate Function Polypeptide: RNA (ribonucleic acid)
Nitrogen Base: A, T, G, C, or U
Polymer: DNA, RNA and ATP Carries info from DNA to cell
Helps in protein synthesis
Nucleotide: Nitrogen Bases found in ribosomes & nucleoli
5 types Single stranded
Cytosine Polypeptide: ATP
Guanine
Adenine Contains adenine, ribose sugar, 3 phosphates
Thymine (in DNA only) Stores and releases energy
Uracil (in RNA only)
Purines or pyrimidines
Nucleotides: 5-carbon sugar and phosphate group
2 types of sugars
Ribose (in RNA only)
Deoxyribose (in DNA only)
Phosphate group
You might also like
- SBI4U Biochemistry NotesDocument13 pagesSBI4U Biochemistry NotesAli MalikNo ratings yet
- Ralph Alan Dale 1972 Hypnotism and EducationDocument21 pagesRalph Alan Dale 1972 Hypnotism and EducationFrancis Gladstone-Quintuplet100% (2)
- Bio MoleculesDocument32 pagesBio MoleculesCarrie Lhee BoadoNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules - Chapter 4Document9 pagesBiological Molecules - Chapter 4Bimbo, Arabela June G.No ratings yet
- Macromolecules. Monomers: Bio 11O Topic 5 - BiomoleculesDocument8 pagesMacromolecules. Monomers: Bio 11O Topic 5 - BiomoleculesYda TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: You Are What You Eat!Document39 pagesBiomolecules: You Are What You Eat!Joanna Ruth SeproNo ratings yet
- Biological Macromolecules PDFDocument31 pagesBiological Macromolecules PDFAngeline CortezNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week 3 - 4Document13 pagesQ4 Week 3 - 4MARILES PRUDENCIANO0% (1)
- Ace Biochemistry by Wong ReviewDocument222 pagesAce Biochemistry by Wong ReviewReham QueNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument26 pagesBiological MacromoleculesGomez Agustin LeslieNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument52 pagesBiomoleculesTrixie Rose Ebona CortezNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules PPT ReviewDocument40 pagesBiomolecules PPT ReviewBernard Enriquez SorianoNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument83 pagesBiomoleculesZairaJallorinaNo ratings yet
- Komatsu d65px 16 Parts BookDocument20 pagesKomatsu d65px 16 Parts Booklaura100% (54)
- Landis System 3200 Software User's ManualDocument135 pagesLandis System 3200 Software User's ManualjoshibocanegraNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument47 pagesBio Moleculesᜆᜑᜒᜇᜒᜐ ᜉᜀᜎᜃᜒᜓNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledMarien Mae VillarinNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: The Raw Materials of Cell The Building Blocks of Life The Molecules of CellsDocument61 pagesBiomolecules: The Raw Materials of Cell The Building Blocks of Life The Molecules of CellsKenneth NicolasNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 NotesDocument38 pagesUnit 2 NotesElen Mae PadugaNo ratings yet
- MoleculesDocument60 pagesMoleculesCharlize Jeneah MedinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of MacromoleculesDocument1 pageChapter 5: The Structure and Function of MacromoleculesPrithvi MohanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Basis of LifeDocument26 pagesChemical Basis of LifeEla SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document8 pagesChapter 2Kate Wen GuanNo ratings yet
- DrMinaSamuel-BioEST-ACT-AP-Notes-3&4-Biochemistry & Enzymes-2022Document17 pagesDrMinaSamuel-BioEST-ACT-AP-Notes-3&4-Biochemistry & Enzymes-2022Nour ShahdNo ratings yet
- 2DY Bio Macromolecules (Oct 2020)Document31 pages2DY Bio Macromolecules (Oct 2020)B BizzleNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesBiomoleculesgeecyjane YguintoNo ratings yet
- Biological Macromolecules 2015Document57 pagesBiological Macromolecules 2015Sharreah LimNo ratings yet
- 4 General Biology 1 BiomoleculesDocument34 pages4 General Biology 1 BiomoleculesSteward SantillanNo ratings yet
- To The Point New Ch1,2Document7 pagesTo The Point New Ch1,2m.mansoor3377No ratings yet
- Biochemistry CHAPTER 1Document10 pagesBiochemistry CHAPTER 1Joyce ElizaldeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composotion of The CellDocument38 pagesChemical Composotion of The CelliQalyanaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids are linked by peptide bonds to form formed by linking the α-carboxyl group of one amino acid to the α-amino group of another amino acid with a peptide bond (also called an amide bond)Document2 pagesAmino Acids are linked by peptide bonds to form formed by linking the α-carboxyl group of one amino acid to the α-amino group of another amino acid with a peptide bond (also called an amide bond)Noviemae TuandaNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument58 pagesBio Moleculescheryl tayasNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules TableDocument2 pagesBiomolecules TableJoya HossainNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document87 pagesUnit 1SHIVANSH KASHYAP (RA2011003010988)No ratings yet
- JEE Main Biomolecules Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadDocument9 pagesJEE Main Biomolecules Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadYash SaxenaNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument22 pagesBIOMOLECULESchristian josh magtarayoNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument12 pagesBIOMOLECULESHazel PachecoNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week 3 - 4Document13 pagesQ4 Week 3 - 4Claudie MabiniNo ratings yet
- C, L, P Notes No PicturesDocument35 pagesC, L, P Notes No PicturesFarhadullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Biomolecule ChartDocument5 pagesBiomolecule ChartRachel WrightNo ratings yet
- 2.3 BiomoleculesDocument25 pages2.3 Biomoleculesvivitri.dewiNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes 1Document2 pagesBiology Notes 1Paulo AloroNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument9 pagesBiology NotesAIFASMI HAWANTINo ratings yet
- Bio Notes 2Document11 pagesBio Notes 2ayaka kamisatoNo ratings yet
- Food Chemistry Recovered 69Document3 pagesFood Chemistry Recovered 69Kimberly TrocioNo ratings yet
- Most Important - Glucose - The One Utilized by Mitochondria and AtpDocument4 pagesMost Important - Glucose - The One Utilized by Mitochondria and AtpCharles GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Water, CarbohydratesDocument22 pagesLesson 2 - Water, CarbohydratesDon'tAsK TheStupidOnesNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Organic Compounds - 1) Carbohydrates: - A) Monosaccharaides: (C H O)Document13 pagesBiochemistry: Organic Compounds - 1) Carbohydrates: - A) Monosaccharaides: (C H O)Ziad KandilNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument55 pagesBiological MacromoleculesjeffNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: The Building Blocks of LifeDocument23 pagesBiomolecules: The Building Blocks of LifemalaitamanNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules - Year 9Document19 pagesBiological Molecules - Year 9ArmanNo ratings yet
- Topic2 Biomolecule PPDocument28 pagesTopic2 Biomolecule PPismail aeryNo ratings yet
- Science10q4 Week3-4Document27 pagesScience10q4 Week3-4ClyzuhNo ratings yet
- 3 Essential Chemicals of Life PPTDocument82 pages3 Essential Chemicals of Life PPTBhoni KumariNo ratings yet
- Molecules of LifeDocument5 pagesMolecules of LifeEmmaNo ratings yet
- Aureus Penicillin G (Parenterally) and Penicillin V (Oral)Document22 pagesAureus Penicillin G (Parenterally) and Penicillin V (Oral)jeffreyNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in General Biology 1Document2 pagesReviewer in General Biology 1Moy ReyesNo ratings yet
- LIPIDS and Nucleic AcidDocument3 pagesLIPIDS and Nucleic AcidHainela Delgado Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument35 pagesBio MoleculesFerlyn KateNo ratings yet
- RMD Topic 1 - Organic Compounds and EnzymesDocument51 pagesRMD Topic 1 - Organic Compounds and Enzymesz4g4v7gkzjNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument39 pagesBiological MacromoleculesMA. FRITZIE DE ASISNo ratings yet
- Caps 5Document4 pagesCaps 5shheNo ratings yet
- Usability Test Report MemoDocument2 pagesUsability Test Report MemoTiffany PetersonNo ratings yet
- Imran Index 1Document11 pagesImran Index 1api-387022302No ratings yet
- Embedded Modules: Pci Express Minicard and Lga Modules High-Speed Multi-Mode 3GDocument4 pagesEmbedded Modules: Pci Express Minicard and Lga Modules High-Speed Multi-Mode 3GYaSeregaNo ratings yet
- Finalizing The Accounting ProcessDocument2 pagesFinalizing The Accounting ProcessMilagro Del ValleNo ratings yet
- ALVAREZ, John Edriane A - Experiment No. 1Document7 pagesALVAREZ, John Edriane A - Experiment No. 1John Edriane AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 832Document40 pages832B. MerkurNo ratings yet
- Cept FinalDocument14 pagesCept FinalVighnesh MalagiNo ratings yet
- Industrial RobotDocument32 pagesIndustrial RobotelkhawadNo ratings yet
- Novena To Our Lady Queen of PeaceDocument4 pagesNovena To Our Lady Queen of PeaceGraciedion MediaNo ratings yet
- Excel Subhadip NandyDocument9 pagesExcel Subhadip NandyNihilisticDelusionNo ratings yet
- Public Value and Art For All?Document20 pagesPublic Value and Art For All?yolandaniguasNo ratings yet
- Tpa6404 q1Document12 pagesTpa6404 q1siogNo ratings yet
- Advanced Concepts of GD&TDocument3 pagesAdvanced Concepts of GD&TPalani Trainer33% (3)
- Formula and Functions in MS ExcelDocument9 pagesFormula and Functions in MS ExcelBhavana SangamNo ratings yet
- Traffic Monitoring SystemDocument16 pagesTraffic Monitoring Systemankit kumarNo ratings yet
- Service Oriented Architecture - Course Notes PDFDocument93 pagesService Oriented Architecture - Course Notes PDFRoberto Luna OsorioNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument91 pagesStrategic ManagementAniket DEORENo ratings yet
- CV TemplateDocument1 pageCV TemplateHimanshu RaghuwanshiNo ratings yet
- A View From Elkab The Tomb and Statues oDocument87 pagesA View From Elkab The Tomb and Statues oBeatriz FélixNo ratings yet
- TDS - 0121 - CapaCare Classic - 201912Document5 pagesTDS - 0121 - CapaCare Classic - 201912ayviwurbayviwurbNo ratings yet
- Pakistan: Nation-State, State-Nation or Multinational State?Document12 pagesPakistan: Nation-State, State-Nation or Multinational State?Asif KhanNo ratings yet
- 1.1.DeFacto Academy enDocument7 pages1.1.DeFacto Academy enYahya AçafNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 SAU 1, Term 4Document5 pagesGrade 10 SAU 1, Term 4Aizat SarsenovaNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument11 pagesTime Value of MoneyRajesh PatilNo ratings yet
- The Enemy Within - v18Document8 pagesThe Enemy Within - v18Matt WillisNo ratings yet
- Management of Developing DentitionDocument51 pagesManagement of Developing Dentitionahmed alshaariNo ratings yet