Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Head and Neck Patho Quick Guide
Uploaded by
TMC PGI GENER MICKO0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pages1. Dental caries is the focal demineralization of tooth structures by sugar fermentation products. Gingivitis is the inflammation of the oral mucosa surrounding teeth. Dental plaque is the biofilm that collects between and on teeth surfaces due to poor oral hygiene.
2. Periodontitis is the inflammatory process that affects the supporting structures of the tooth. The organisms associated with periodontitis include Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, Porphyromonas gingivalis, and Prevotella intermedia.
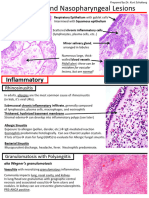
3. Aphthous ulcers are single or multiple, shallow ulcers covered by a thin exudate and rimmed by
Original Description:
Original Title
head-and-neck-patho-quick-guide
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Dental caries is the focal demineralization of tooth structures by sugar fermentation products. Gingivitis is the inflammation of the oral mucosa surrounding teeth. Dental plaque is the biofilm that collects between and on teeth surfaces due to poor oral hygiene.
2. Periodontitis is the inflammatory process that affects the supporting structures of the tooth. The organisms associated with periodontitis include Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, Porphyromonas gingivalis, and Prevotella intermedia.
3. Aphthous ulcers are single or multiple, shallow ulcers covered by a thin exudate and rimmed by
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesHead and Neck Patho Quick Guide
Uploaded by
TMC PGI GENER MICKO1. Dental caries is the focal demineralization of tooth structures by sugar fermentation products. Gingivitis is the inflammation of the oral mucosa surrounding teeth. Dental plaque is the biofilm that collects between and on teeth surfaces due to poor oral hygiene.
2. Periodontitis is the inflammatory process that affects the supporting structures of the tooth. The organisms associated with periodontitis include Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, Porphyromonas gingivalis, and Prevotella intermedia.
3. Aphthous ulcers are single or multiple, shallow ulcers covered by a thin exudate and rimmed by
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
HEAD & NECK PATHOLOGY
CRACKING D’ BOARDS REVIEW CENTER
Focal demineralization of tooth structures by products of sugar Dental caries
fermentation
Inflammation of the oral mucosa surrounding teeth Gingivitis
Biofilm that collects between and on the surface of teeth due to poor Dental plaque
oral hygiene
Inflammatory process that affects the supporting structures of the Periodontitis
tooth, alveolar bone, and cementum
Organisms associated with periodontitis Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans
Porphyromonas gingivalis
Prevotella intermedia
Single or multiple, shallow, hyperemic mucosal ulcerations covered by Aphthous ulcers
a thin exudate and rimmed by a narrow zone of erythema
Fibrous proliferative lesions Irritation fibroma pyogenic granuloma peripheral ossifying fibroma
peripheral giant cell granuloma
Submucosal nodular mass of fibrous connective tissue stroma Irritation fibroma
Red to purple exophytic inflammatory lesion characterized by highly
vascularized proliferation of granulation tissue Pyogenic granuloma
Aggregates of multinucleate, foreign body-like giannt cells with a Peripheral giant cell granuloma
fibrovascular stroma
Usual presentation of oral herpes in: Children
Adults
Immunocompromised
Children: gingivostomatitis
Adults: pharyngitis i
Mmunocompromise: chronic mucocutaneous infections
Microscopic examination of vesicle fluid Tzanck test
Tropism for herpes simplex virus Nerves
Characteristic cpe of herpes simplex Eosinophilic intranuclear inclusions
Manifestation of reactivation of latent hsv Recurrent herpetic stomatitis
Disease entities caused by epstein-barr virus Infectious mononucleosis
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Lymphoma
Diseases caused by enterovirus Herpangina
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease
Acute lymphonodular pharyngitis
Most common fungal infection of the oral cavity Candida albicans
Pseudomembranous form of oral candidiasis Oral thrush
Oral lesion on the lateral tongue caused by EBV in Hairy leukoplakia
immunocompromised patients
Strawberry and raspberry tongue Scarlet fever
Koplik spots Measles
Acute atp with white exudative membranes with enlargement of the Infectious mononucleosis
lymph nodes
Dirty white fibrinosuppurative, tough membrane over the Diphtheria
retropharynx
Gingival hyperplasia Phenytoin
Ad with multiple congenital telangiectasias of the oral cavity and lips Osler-weber-rendu syndrome
White patch or plaque that cannot be scraped off and cannot be Leukoplakia
characterized clinically or pathologically as any other disease
Red, velvety flat lesion, usually atypical Erythroplakia
Most common carcinoma of the head and neck Squamous cell carcinoma
Most common cause of scca of the oropharynx Hpv
Risk factors for scca Smoked tobacco
Alcohol
Betel quid and paan
Actinic radiation
Pipe smoking
Hpv variant most commonly associated with hpv Hpv 16
Multiple individual primary tumors develop independently in an area Field cancerization
due to exposure to carcinogens
Histologic subtype of hpv-negative scca Keratinizing scca
Surrogate marker for hpv P16
Focal protrusions of the mycosa caused by recurrent attacks of rhinitis Inflammatory nasal polyp
Sinusitis, bronchiectasis, and situs inversus Kartagener syndrome
Very lethal lymphoma of the nasopharynx that usually leads to Extranodal nk/t-cell lymphoma
lymphoma spread and cranial vault invasion
Most common causes of pharyngitis and tonsillitis Rhinovirus
Echovirus
Adenovirus
Benign highly vascular tumor that occurs in adolescent males Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
Benign papilloma arising from the respiratory mucosa lining the nasal Sinonasal papilloma
cavity and paranasal sinuses
Mutation associated with nasopharyngeal angiofibromas Beta catenin
Forms of sinonasal papilloma Exophytic
Endophytic
Oncocytic
Arise from neuroectodermal olfactory cells within the mucosa Olfactory neuroblastoma
Extremely aggressive carcinoma and resistant to conventional therapy, Nut midline carcinoma
always found in the midline
Causative agent of nasopharyngeal carcinoma EBV
Patterns of nasopharyngeal carcinoma Keratinizing
Non-keratinizing
Basaloid
Standard therapy for nasopharyneal ca Radiotherapy
Found in vocal cords of heavy smokers or those who impose great Reactive nodules
strain on their vocal cords
Benign neoplasms located on the true vocal cords that form soft, Squamous papilloma
exophytic proliferations composed of slender, fingerlike projections
supported by a central fibrovascular core
Most common carcinoma of the larynx Squamous cell carcinoma
Most common cause of acute and chronic otitis media Viral
Superimposed infections in otitis S. Pneumoniae
H. Influenzae
M. Catarrhalis
Abnormal bone deposition int eh middle ear near the rim of the oval Otosclerosis
window into which the footplate of the stapes fits
Most common malignancy of the external ear Basal cell carcinoma
Benign cystic lesions lined by sse containing lymphoid tissue Branchial cyst (cervical lymphoepithelial cyst)
Origin of branchial cysts 2nd branchial arch
Failure of the thyroid anlage to descend from the foramen cecum Thyroglossal duct cyst
Tumors of neuroendocrine cells associated with sympathetic and Paraganglioma
parasympathetic nervous systems
Most common location of extra-adrenal paragangliomas Head and neck
Adrenal paragangliomas Pheochromocytoma
Nests of chief cells with abundant, round to ovoid nuclei. Zellballen
Dry mouth resulting from a decrease in the production of saliva Xerostomia
Most common viral cause of sialadenitis Mumps
Most prevalent form of sialadenitis Mucocele
Or rupture of a salivary gland duct Mucocele
Epithelial-lined cysts that arise when the duct of the sublingual gland Ranula
has been damaged
Most common cause of sialolithiasis Staphylococcus aureus
Streptococcus viridans
Most common location of salivary gland tumors Parotid gland
Most common location of salivary gland malignancies Parotid gland
Most common salivary gland neoplasm Pleomorphic adenoma
Histology of PA Epithelial cells arranged in ducts, acini, tubules or sheets in a loose
myxoid and hyaline matrix
Malignancy arising from a pa Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma
Second most common salivary gland neoplasm Warthin tumor
Greatest risk factor for warthin tumor Smoking
Histology of warthin tumor Cystic lesion lined by double layer of oncocytic cells, columnar in the
inner layer, cuboidal at the outer with lymphoepithelial elements
Most common primary malignancy of the salivary gland Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
Translocation associated with mec Crtc1-maml2 fusion
Components of mec Squamous, intermediate and mucus cells
Characteristic architecture of adenoid cystic carcinoma Cribriform (swiss-cheese)
You might also like
- Fammed Family Life CycleDocument3 pagesFammed Family Life CycleTMC PGI GENER MICKONo ratings yet
- ORTHO by Target 200 PlusDocument21 pagesORTHO by Target 200 PlusTMC PGI GENER MICKONo ratings yet
- Study Guide Key CH - 23 - MicroevolutionDocument5 pagesStudy Guide Key CH - 23 - Microevolutionrulz65100% (1)
- Bacterial Infections of Oral CavityDocument63 pagesBacterial Infections of Oral CavityAkash Anilkumar Malini60% (5)
- Isolation and Characterization of RNADocument3 pagesIsolation and Characterization of RNAEvans DionNo ratings yet
- Elements of EPIDocument2 pagesElements of EPIMichelle Gambol50% (2)
- OMIC 311 Lecture 17 Human Papilloma, Herpes, Hepatits VirusDocument51 pagesOMIC 311 Lecture 17 Human Papilloma, Herpes, Hepatits VirusMaryam XANo ratings yet
- Approach in Lymphadenopathy in ChildrenDocument14 pagesApproach in Lymphadenopathy in Childrennahiry100% (1)
- LymphadenopathyDocument18 pagesLymphadenopathyIin RosalinaeNo ratings yet
- Neoplasms of Nose & para Nasal SinusesDocument171 pagesNeoplasms of Nose & para Nasal SinusesJulian HobbsNo ratings yet
- Notes EntDocument43 pagesNotes Entadriana azmanNo ratings yet
- Ent MBBS NotesDocument23 pagesEnt MBBS NotesDr.Riashat azimNo ratings yet
- Head and NeckDocument8 pagesHead and Neckstudy with maineNo ratings yet
- DefaultDocument1 pageDefaultAhmed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Sino NasalDocument13 pagesSino NasalClaudia EpureNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Disorders: Chapter OutlineDocument43 pagesEpithelial Disorders: Chapter Outlineitza andradeNo ratings yet
- Git 1 PDFDocument24 pagesGit 1 PDFafaq alismailiNo ratings yet
- 1.pathology-Practical - Disease Affecting Uper Respiratory TractDocument34 pages1.pathology-Practical - Disease Affecting Uper Respiratory TractSounds of MindNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PathologyDocument3 pagesRespiratory PathologyDawan SherkoNo ratings yet
- 5th Year SummaryDocument198 pages5th Year SummaryomeerulrafieNo ratings yet
- Nasal Discharge & ObstructionDocument70 pagesNasal Discharge & ObstructionRajhmuniran KandasamyNo ratings yet
- Otolaryngologic Clinical Manifestations On Hiv PatientsDocument21 pagesOtolaryngologic Clinical Manifestations On Hiv PatientsCamille MagatNo ratings yet
- Head PDFDocument22 pagesHead PDFAye PhattheeraNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary PathologyDocument134 pagesPulmonary PathologyFor ChristNo ratings yet
- Chancroid and Genital Herpes REPORTDocument24 pagesChancroid and Genital Herpes REPORTKyla RamonesNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Diseases of The PharynxDocument33 pagesAcute and Chronic Diseases of The Pharynxnena twtNo ratings yet
- Tumors: of The Nose, Sinuses and NasopharynxDocument69 pagesTumors: of The Nose, Sinuses and Nasopharynxapi-19770621No ratings yet
- Text 1 Text 2Document8 pagesText 1 Text 2azrkxNo ratings yet
- TP Fungal RhinosinusitisDocument44 pagesTP Fungal RhinosinusitisBucex DyanNo ratings yet
- Infections of The Oral MucosaDocument154 pagesInfections of The Oral MucosarizwanNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology: Dr. Tasnim Hamdan Graduated From University of ValenciaDocument160 pagesOral Pathology: Dr. Tasnim Hamdan Graduated From University of ValenciaMariam Abd ElhadiNo ratings yet
- Sinonasal/Nasopharyngeal Tumors: BenignDocument9 pagesSinonasal/Nasopharyngeal Tumors: BenignIsa EnacheNo ratings yet
- HIV Head Neck Pic 1010 10Document25 pagesHIV Head Neck Pic 1010 10Justine NyangaresiNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Medicine Medical Education-Damietta University: Level 1 Semester IIDocument34 pagesFaculty of Medicine Medical Education-Damietta University: Level 1 Semester IISounds of MindNo ratings yet
- Non-Huma Primate PathologyDocument27 pagesNon-Huma Primate PathologyDr. Vikram SinghNo ratings yet
- Microbial Aspect of Respiratory TrackDocument23 pagesMicrobial Aspect of Respiratory TrackNovi AdriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Head and NeckDocument8 pagesChapter 16 - Head and NeckAgnieszka WisniewskaNo ratings yet
- Hy Pulmonary TMG - PicsDocument38 pagesHy Pulmonary TMG - PicsblablalbablablablaNo ratings yet
- Neck TumorsDocument7 pagesNeck TumorsJose SirittNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis in ENTDocument10 pagesDifferential Diagnosis in ENTPushkar Raaj PatidarNo ratings yet
- BreastDocument9 pagesBreastyaraabdulkaderaliNo ratings yet
- Laryngitis: Wahyu Priatmoko 1301 1207 0197 Ilman Fathony 1301 1207 007Document74 pagesLaryngitis: Wahyu Priatmoko 1301 1207 0197 Ilman Fathony 1301 1207 007Arief FakhrizalNo ratings yet
- Specific OsteomyelitisDocument14 pagesSpecific OsteomyelitisOmnia SamiNo ratings yet
- Granulo 3Document94 pagesGranulo 3Sathvika BNo ratings yet
- VESICULOBULLOUS DISEASE by AMDocument4 pagesVESICULOBULLOUS DISEASE by AMbasitcontentNo ratings yet
- Candidiasis Kandidiasis/ KandidosisDocument19 pagesCandidiasis Kandidiasis/ KandidosisAulya ArchuletaNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Infection, by MahrukhDocument11 pagesAnaerobic Infection, by MahrukhImran Niaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Benign and Malignant Neoplasia of URTDocument48 pagesBenign and Malignant Neoplasia of URTsahirbuleNo ratings yet
- DR - Gaurav Shukla DR - Jyoti Batra DR - Uma SridharDocument101 pagesDR - Gaurav Shukla DR - Jyoti Batra DR - Uma SridharGaurav shuklaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Muhartono, M.Kes, SP - PADocument29 pagesDr. Muhartono, M.Kes, SP - PADada DoniNo ratings yet
- AdenotonsilitisDocument42 pagesAdenotonsilitisELIA RICHARDNo ratings yet
- Benign Mucosal Lesions of The Oral Cavity: Dr. Ronald P. Cabral, M.D., D.S.TDocument61 pagesBenign Mucosal Lesions of The Oral Cavity: Dr. Ronald P. Cabral, M.D., D.S.TcabralmdNo ratings yet
- Cornea and External DiseasesDocument18 pagesCornea and External DiseasesMiguel C. DolotNo ratings yet
- ASOMDocument41 pagesASOMArunkumar S KumarNo ratings yet
- Malignant Catahrral Fever MCFDocument48 pagesMalignant Catahrral Fever MCFhhes8116No ratings yet
- Atypical Ulcer Palate Terciary Syphilis Ooo2019Document6 pagesAtypical Ulcer Palate Terciary Syphilis Ooo2019DIEGO MAURICIO PAZ GARCIANo ratings yet
- Lesiones Benignas y MalignasDocument23 pagesLesiones Benignas y MalignasValeria DellarossaNo ratings yet
- LMR Ent - Throat: Diseases of Oral Cavity and Salivary GlandsDocument8 pagesLMR Ent - Throat: Diseases of Oral Cavity and Salivary GlandsYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Module - Practical PathologyDocument30 pagesRespiratory Module - Practical PathologyfasdfNo ratings yet
- Important Topics of ENT For MBBSDocument2 pagesImportant Topics of ENT For MBBSDr.Riashat azimNo ratings yet
- Sur Mucosal Lesions-207Document207 pagesSur Mucosal Lesions-207megahedhazeemNo ratings yet
- Dr. Muhartono, M.Kes, SP - PADocument29 pagesDr. Muhartono, M.Kes, SP - PAVidi IndrawanNo ratings yet
- HPV Benign Lesions SummaryDocument2 pagesHPV Benign Lesions SummaryzainNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The LarynxDocument28 pagesDiseases of The LarynxDon AkmalNo ratings yet
- Virology RationaleDocument6 pagesVirology RationaleTMC PGI GENER MICKONo ratings yet
- A2 Congestive Heart FailureDocument44 pagesA2 Congestive Heart FailureTMC PGI GENER MICKONo ratings yet
- Adcon Group 14Document34 pagesAdcon Group 14TMC PGI GENER MICKONo ratings yet
- 6 Antimicrobial 2Document6 pages6 Antimicrobial 2TMC PGI GENER MICKONo ratings yet
- Phys - 1S04 - SynapseDocument9 pagesPhys - 1S04 - SynapseTMC PGI GENER MICKONo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus NewDocument97 pagesDiabetes Mellitus NewTMC PGI GENER MICKONo ratings yet
- Spine and Extremities Script KTRCDocument1 pageSpine and Extremities Script KTRCTMC PGI GENER MICKONo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Lymphatic SystemDocument24 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Lymphatic Systemamber tariqNo ratings yet
- (13384376 - Agriculture (Pol'nohospodárstvo) ) Characterization and Evaluation of Bacillus Siamensis Isolate For Its Growth Promoting Potential in TomatoDocument9 pages(13384376 - Agriculture (Pol'nohospodárstvo) ) Characterization and Evaluation of Bacillus Siamensis Isolate For Its Growth Promoting Potential in TomatoSajib AmanulNo ratings yet
- Sample Test Questions: MedicineDocument17 pagesSample Test Questions: MedicinePrince NathanNo ratings yet
- Tosoh Bioscience Tosoh Bioscience: CL Aia-Pack ReagentsDocument2 pagesTosoh Bioscience Tosoh Bioscience: CL Aia-Pack ReagentsAleksandar MisicNo ratings yet
- By DR SIWILA DRINKING WATER QUALITY - STUDENT VERSIONDocument77 pagesBy DR SIWILA DRINKING WATER QUALITY - STUDENT VERSIONjames mbinjoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument2 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsWallen LagradaNo ratings yet
- 2.BMD Study Guide Final 6.4.2023Document42 pages2.BMD Study Guide Final 6.4.2023Phyo Wai KyawNo ratings yet
- Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of Probiotic YeastsDocument5 pagesPhenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of Probiotic YeastsChi TranNo ratings yet
- Upper Urinary Tract. InfectionDocument11 pagesUpper Urinary Tract. InfectionnadhifNo ratings yet
- CMV Pregnancy 20Document20 pagesCMV Pregnancy 20Татьяна ТутченкоNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterología y Hepatología: Scientific LettersDocument2 pagesGastroenterología y Hepatología: Scientific LettersAswin ArinataNo ratings yet
- PN Panel Quick GuideDocument2 pagesPN Panel Quick GuidecassNo ratings yet
- Granulomatous Colitis: More Than A Canine Disease? A Case of Escherichia Coli-Associated Granulomatous Colitis in An Adult CatDocument5 pagesGranulomatous Colitis: More Than A Canine Disease? A Case of Escherichia Coli-Associated Granulomatous Colitis in An Adult Catclara FNo ratings yet
- Overview of Immunity and Its Different TypesDocument11 pagesOverview of Immunity and Its Different TypesPalwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- VASCULITIS para DummiesDocument7 pagesVASCULITIS para DummiesTatiana PotesNo ratings yet
- 1.endo PerioLesionPartIThePathogenesisDocument8 pages1.endo PerioLesionPartIThePathogenesisMaulida SyafarinaNo ratings yet
- MyocarditisDocument29 pagesMyocarditispanvilai0% (1)
- ChleraDocument26 pagesChleraadelekeyusufNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGY HOMEWORK SET A-QuestionsDocument2 pagesMICROBIOLOGY HOMEWORK SET A-QuestionschristinejoanNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Coagulation FactorsDocument35 pagesDisorders of Coagulation FactorsMelesNo ratings yet
- Biopreservation and ProbioticsDocument11 pagesBiopreservation and ProbioticsDandapani Varsha100% (1)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms Friend and FoeDocument10 pagesNCERT Exemplar Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms Friend and FoePradipti VermaNo ratings yet
- Gene Transfer Teniques in PlantDocument21 pagesGene Transfer Teniques in PlantRakesh GedalaNo ratings yet
- Serologicchartv 8Document1 pageSerologicchartv 8Gautamu ZalavadiyaNo ratings yet
- Microbial Metabolism and Biotechnology Tutorial WorksheetDocument4 pagesMicrobial Metabolism and Biotechnology Tutorial WorksheetPaulina AntczakNo ratings yet
- L04 - FC - Water and MoistureDocument29 pagesL04 - FC - Water and MoistureEsteban RobayoNo ratings yet
- 10 1038@ncomms9614Document6 pages10 1038@ncomms9614Cagar Irwin TaufanNo ratings yet