Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment 1 - Voltage Measurement
Experiment 1 - Voltage Measurement
Uploaded by
Itsuka RarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment 1 - Voltage Measurement
Experiment 1 - Voltage Measurement
Uploaded by
Itsuka RarCopyright:
Available Formats
EXPERIMENT 1
VOLTAGE MEASUREMENT
To begin this experiment, participants are required to understand the
basic of the following subjects:
• DC and AC voltages.
• Measuring instrument accuracy.
• Measuring instrument sensitivity.
• Relative error.
• The procedures to use a voltmeter and how does it work.
• The RMS value, and the average value of AC magnitude.
1.1 DC VOLTAGE MEASUREMENT
Objective : To evaluate the voltmeter accuracy.
Introduction : Upon this experiment, we are going to measure a
voltage value using different types of voltmeter. The
reading on each voltmeter will be compare with each of
the voltmeter accuracy.
Equipment :
1. DC Power source
2. Voltmeter
Procedures :
1. Pay attention to the measuring instrument manual book, and
record its specifications on the following Table 1.1
Table 1.1 Specifications of Voltage Measuring Instrument
VM 1 VM 2
Brand and Types: BK Precision, 889B Brand and Types: BK Precision, 2709B
Analog/Digital: Analog/Digital:
DC volt. Measuring range: DC volt. Measuring range:
DC volt. Measuring accuracy: DC volt. Measuring accuracy:
AC volt. Measuring range: AC volt. Measuring range:
AC volt. Frequency range: AC volt. Frequency range:
AC volt. Measuring accuracy: AC volt. Measuring accuracy:
True RMS (yes/no): True RMS (yes/no):
Additional notes: Additional notes:
VM 3
Brand and Types: BK Precision, 2709B
Analog/Digital:
DC volt. Measuring range:
DC volt. Measuring accuracy:
AC volt. Measuring range:
AC volt. Frequency range:
AC volt. Measuring accuracy:
True RMS (yes/no):
Additional notes:
2. Pay attention to your module. Make sure that you are aware of the
voltage terminal positions of the voltmeter.
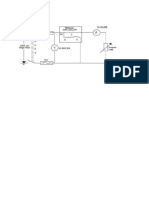
3. Make sure the SW1 and SW2 switches are in position 1, as
shown in figure 1. The SW3 works for determine what type of
voltmeter that we are going to use to measuring.
Figure 1
4. Record the voltage value accuracy of each voltmeter in Table 1.2
Table 1.2 Voltage Measuring Instrument Accuracy
Voltmeter Accuracy (%)
VM1
VM2
VM3
5. Adjust the PC power source output by referring to Table 1.3. The
output value of the DC power source is obtain by observing the
display of the DC power source. Record the observed value in
Table 1.3
Ruang B204 dan AJ302, Departemen Teknik Elektro
Fakultas Teknologi Elektro dan Informatika Cerdas
Table 1.3 DC Voltage Measurement Records
Voltage VM1 Range VM2 Range VM3 Range
(V) (V) VM1 (V) (V) (V) VM3
5
10
NOTES:
1. If using a multi-range measuring device, start the procedure by setting the
range to the highest position. Then slowly decrease the range until the actual
deflection obtained.
2. To improve the measuring accuracy, use the range that will lead the closest
reading to the full scale.
3. Make sure the measuring instrument is at the correct setting and connected
to the correct terminal as well. (i.e. if measuring a DC voltage, then the
terminal must correctly connected at the DC measuring terminal, and etc.)
MODUL ASSIGNMENTS:
1. Calculate the accuracy of each measuring instruments (VM1,
VM2, and VM3), and record the results in Table 1.4
Table 1.4 DC Voltage Measurement Evaluations
Function Generator (V)
Parameters
5 10
Accuracy (± V)
VM1 (V)
VM1
Error (V)
Exceed the limit (Y / N)
Accuracy (± V)
VM2 (V)
VM2
Error (V)
Exceed the limit (Y / N)
Accuracy (± V)
VM3 (V)
VM3
Error (V)
Exceed the limit (Y / N)
2. Calculate the error from VM1, VM2, and VM3 in volts, and record
it in Table 1.4.
Ruang B204 dan AJ302, Departemen Teknik Elektro
Fakultas Teknologi Elektro dan Informatika Cerdas
3. Determine whether the readings on VM1, VM2, and VM3 are
exceeding the accuracy limits of each voltmeter or not. Record it
in Table 1.4.
4. Write down your comments and draw a conclusion from this
experiment.
===============================
1.2 AC SINUSOIDAL VOLTAGE MEASUREMENT
Objective : To evaluate the effect of AC sinusoidal voltage
frequency to a voltmeter measurement.
Introduction : Every voltmeter has its own specifications regarding
the frequency limits of the measured voltage value.
Upon this experiment, we are going to measure the AC
voltage value on various frequency.
Equipment :
1. Function Generator
2. Voltmeter
Procedures :
1. The AC voltage value that are going to be measured coming from
the function generator which set to generating sinusoidal wave.
2. Adjust the function generator output to generate 4 VRMS at 50 Hz.
(We are going to assume that VM1 has a very wide frequency
spectrum and uses it as our reference).
3. Record the readings of VM2 and VM3 using various frequency.
Record it on Table 1.5.
Table 1.5 AC Voltage Measurement Records
Frequency VM1 VM2 VM3
(Hz) (V) (V) (V)
50
500
5k
50k
MODUL ASSIGNMENTS:
1. From the instrument brand and type, find the specifications that
related to the device’s frequency spectrum and error.
2. AC voltage values consist of different parameters (i.e. RMS
value, average value, maximum values, etc). In this experiment,
what are the exact parameters that you read from the voltmeter?
Ruang B204 dan AJ302, Departemen Teknik Elektro
Fakultas Teknologi Elektro dan Informatika Cerdas
3. Write down your comments and draw a conclusion from this
experiment.
===============================
1.3 AC NON-SINUSOIDAL VOLTAGE MEASUREMENT
Objective : To evaluate the results of AC non-sinusoidal
measurements on
a voltmeter
Introduction : Regarding to the AC voltage measurement,
there are two methods commonly applied by the
measuring instrumentations. Which consist of AC
average rectified measurement, and true RMS
measurement.
In sinusoidal wave, the instrument measures the
average value of AC voltage and multiply it with
multiplying factor of the instrument. This method results
will come as an RMS value. Therefore, in non-
sinusoidal wave measurements, if the instruments
implementing this method, the instrument will show
inaccurate readings.
Upon this experiment, we are going to measure
the AC non-sinusoidal voltage value and compare the
results with the calculated RMS value.
Equipment :
1. Function Generator
2. Voltmeter
Procedures :
1. The AC voltage value that are going to be measured coming from
the function generator which set to generate triangle and square
wave.
2. Adjust the output of function generator to generate 4 VRMS
(measured using VM1) at 50 Hz.
3. Record the readings on VM1 and VM2 using various frequency
and record it on Table 1.6.
Ruang B204 dan AJ302, Departemen Teknik Elektro
Fakultas Teknologi Elektro dan Informatika Cerdas
Table 1.6 AC Non-Sinusoidal Voltage Measurement Records
Function
VM1 VM2
Wave Generator
(V) (V)
(V)
10 Vpp
Triangle
5 rms
10 Vpp
Square
5 rms
MODUL ASSIGNMENTS:
1. VM1 uses in this experiment is a voltmeter with true RMS
specifications, where we are using it as our reference. For other
voltmeter, find its specifications related to how to measure the
voltage RMS value.
2. Upon this experiment, readings on every voltmeter might be
different. Write down your comments and draw a conclusion from
this experiment.
Ruang B204 dan AJ302, Departemen Teknik Elektro
Fakultas Teknologi Elektro dan Informatika Cerdas
Ruang B204 dan AJ302, Departemen Teknik Elektro
Fakultas Teknologi Elektro dan Informatika Cerdas
You might also like
- R2019 49P1MSDocument29 pagesR2019 49P1MSSkruzdelyte MielaNo ratings yet
- 1.O.C. & S.C. Tests On Single Phase TransformerDocument6 pages1.O.C. & S.C. Tests On Single Phase Transformerchandrakanth100% (3)
- Expalanation Text About ThunderDocument2 pagesExpalanation Text About ThunderAzmiFarizNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Testing InstrumentDocument8 pagesModule 2 Testing Instrumentnelson ijeboimenNo ratings yet
- Measurement ElectricityDocument4 pagesMeasurement ElectricityMd HamzaNo ratings yet
- Experiment1-Multimeter, Oscilloscope and Function GeneratorDocument11 pagesExperiment1-Multimeter, Oscilloscope and Function GeneratorHilmi SulimanNo ratings yet
- International Islamic University, Islamabad: Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyDocument10 pagesInternational Islamic University, Islamabad: Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyLovely JuttNo ratings yet
- Experiment 10 - Calibration of Wattmeter by Phantom LoadingDocument2 pagesExperiment 10 - Calibration of Wattmeter by Phantom LoadingFALSERNo ratings yet
- Machine Lab Manuals Final Modified On 12-2-2019Document67 pagesMachine Lab Manuals Final Modified On 12-2-2019Danyal NasirNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measurements - FormDocument5 pagesElectrical Measurements - FormmariaNo ratings yet
- DC EECE1315 Lab 02 F18Document5 pagesDC EECE1315 Lab 02 F18Simon Roa (MortalSix02)No ratings yet
- Semiconductor Devices and Circuits LaboratoryDocument53 pagesSemiconductor Devices and Circuits LaboratoryKaryampudi RushendrababuNo ratings yet
- ELE8923 Labs Part 1 W2011Document25 pagesELE8923 Labs Part 1 W2011Rob GchukNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Wattmeter DirectloadingDocument12 pagesCalibration of Wattmeter DirectloadingMurugan RNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Energy MeterDocument4 pagesCalibration of Energy MeterKalyana Sundaram M.SNo ratings yet
- EE306 Lab5 Multi-Range Voltmeter Using GalvanometerDocument3 pagesEE306 Lab5 Multi-Range Voltmeter Using GalvanometerTalha Abdul Khaliq0% (1)
- Experiment 2Document3 pagesExperiment 2Nurfazira RashidNo ratings yet
- Lablab MokoDocument5 pagesLablab MokoOtepNo ratings yet
- Saint Louis UniversityDocument8 pagesSaint Louis Universitynahj.fernandez69No ratings yet
- Making Low Level AC Voltage Measurements With DVM: G.B. Gubler, N.S. AlekseevaDocument2 pagesMaking Low Level AC Voltage Measurements With DVM: G.B. Gubler, N.S. AlekseevaGNo ratings yet
- Book LastDocument83 pagesBook LastZirk De LeonNo ratings yet
- FINAL EXPERIMENT 1 (29.11.2019) - With FigsDocument8 pagesFINAL EXPERIMENT 1 (29.11.2019) - With FigsMd HamzaNo ratings yet
- pc20tk 1 44 8Document1 pagepc20tk 1 44 8Ryan LeeNo ratings yet
- EET223-W22-EXP 1 - Uncontrolled RectifiersDocument8 pagesEET223-W22-EXP 1 - Uncontrolled Rectifiersjohnathan.donnellyNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Lab Manual - 2020-21Document32 pagesBasic Electronics Lab Manual - 2020-21Chandra VinnakotaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 BEEL 1125Document8 pagesLab 1 BEEL 1125Denayshan SelvarajooNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment 4Document4 pagesLab Experiment 4Saad AliKhanNo ratings yet
- Circuit Diagram:: Experiment No: 1 Title: Calibration of A Milliammeter As A Voltmeter. ObjectivesDocument2 pagesCircuit Diagram:: Experiment No: 1 Title: Calibration of A Milliammeter As A Voltmeter. ObjectivesAsrar Hussain Bhat100% (1)
- Lab 1 Introduction To Workbench Apparatus: ObjectiveDocument51 pagesLab 1 Introduction To Workbench Apparatus: ObjectiveOsama Ahmed OfficialNo ratings yet
- AC Watt Meter ProjectDocument14 pagesAC Watt Meter ProjectYung SangNo ratings yet
- Part2 PDFDocument33 pagesPart2 PDFSYAFIQAH ISMAILNo ratings yet
- ECE 381L No1aDocument6 pagesECE 381L No1aNakunaru GretserNo ratings yet
- Differential Pair Using MOS TransistorsDocument5 pagesDifferential Pair Using MOS TransistorsSatish BojjawarNo ratings yet
- Electrical & Electronics Measurement (EEMMI) Subject Code: 303Document31 pagesElectrical & Electronics Measurement (EEMMI) Subject Code: 303Blue eyes India kiNo ratings yet
- Ee6312-Homework Iii: Problem 1Document6 pagesEe6312-Homework Iii: Problem 1Shahab PoshtkouhiNo ratings yet
- Measurement Devices (Dee10013) Practical TestDocument4 pagesMeasurement Devices (Dee10013) Practical TestMohd IskandarNo ratings yet
- BXE Experiment No.2Document12 pagesBXE Experiment No.2DsgawaliNo ratings yet
- AC ApparatusDocument4 pagesAC ApparatusMark manuelNo ratings yet
- Multimeter GUIDELINEDocument14 pagesMultimeter GUIDELINEAmirul SyazwanNo ratings yet
- EMSL Cycle 2 ExptsDocument25 pagesEMSL Cycle 2 ExptsVarun ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Calibration WattmeterDocument2 pagesCalibration WattmeterVARAPRASADNo ratings yet
- EE1071 - Lab Manual PDFDocument22 pagesEE1071 - Lab Manual PDFSidhanth NoduNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document178 pagesModule 3eee.22beec97No ratings yet
- Report Long MicroprocessorDocument8 pagesReport Long MicroprocessorFaris SyahmiNo ratings yet
- DC Source ExtractDocument4 pagesDC Source ExtractJusticeNo ratings yet
- 9 LLResistWhitePaperDocument14 pages9 LLResistWhitePaperLingesh K VNo ratings yet
- EML Manual (2019 2023)Document43 pagesEML Manual (2019 2023)Areeba NasirNo ratings yet
- Electronics - Mechanic - 1st - Year - (Volume - I - of - II) - TP (1) - 123-124-1Document2 pagesElectronics - Mechanic - 1st - Year - (Volume - I - of - II) - TP (1) - 123-124-1Chinmay MahindrakarNo ratings yet
- Me170a - Lab 01 - Instrumentation Handout - Edited2015Document8 pagesMe170a - Lab 01 - Instrumentation Handout - Edited2015andman753No ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 2A (Measurement)Document6 pagesEXPERIMENT 2A (Measurement)Lim sui phing Lim sui phingNo ratings yet
- Experiment #2 Multistage Amplifiers: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesExperiment #2 Multistage Amplifiers: ObjectiveMUHAMMAD AMIN HAMDANNo ratings yet
- 7 PotentiometerDocument4 pages7 PotentiometerBreno Oliveira0% (1)
- Introduction To Operational AmplifierDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Operational AmplifierkhalidNo ratings yet
- ECE 140 L C: Inear IrcuitsDocument10 pagesECE 140 L C: Inear IrcuitsPaola RamírezNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgCqMBIt9H4SGXoNbXT-GN-A9BhEOWL3VO9AanTPs6DGeV10cYwyieLlBwEA3k36t FjyG68rM9GJHU9s-V3hVT2PJDvCl9ggaCLeBc zAJaHKcNH9hdIuVnO6t0DjQJ3KBhluInkic 29MjDocument18 pagesACFrOgCqMBIt9H4SGXoNbXT-GN-A9BhEOWL3VO9AanTPs6DGeV10cYwyieLlBwEA3k36t FjyG68rM9GJHU9s-V3hVT2PJDvCl9ggaCLeBc zAJaHKcNH9hdIuVnO6t0DjQJ3KBhluInkic 29MjEzekiel IyamuNo ratings yet
- EMI Previous Question Papers Topic Wise PDFDocument24 pagesEMI Previous Question Papers Topic Wise PDFjaganmohanrsNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Laboratory 2BDocument8 pagesPower Electronics Laboratory 2Bkibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines I29012020Document73 pagesElectrical Machines I29012020fake1542002No ratings yet
- Mixed Signal System Lab Sept 2022 - Lab2 ManualDocument5 pagesMixed Signal System Lab Sept 2022 - Lab2 ManualSyahmi KNo ratings yet
- Blah Exp2Document10 pagesBlah Exp2Hero CourseNo ratings yet
- ENGR2200 Lab Manual Lab2Document12 pagesENGR2200 Lab Manual Lab2Sure TipsNo ratings yet
- CLS ENG 23 24 XI Che Target 1 Level 1 Chapter 2Document36 pagesCLS ENG 23 24 XI Che Target 1 Level 1 Chapter 2sarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Motion With Constant AccelerationDocument33 pagesMotion With Constant AccelerationJohn Kristoffer VillarNo ratings yet
- r27 R33Document7 pagesr27 R33Mohamad HafizNo ratings yet
- Slides For Multi Level Inverter in PsimDocument16 pagesSlides For Multi Level Inverter in Psimmuhammad saeedNo ratings yet
- C4 ExamQuestions Chp6 Integration1 GeneralDocument50 pagesC4 ExamQuestions Chp6 Integration1 GeneralBNo ratings yet
- Experiment 24: The Potentiometer: PurposeDocument6 pagesExperiment 24: The Potentiometer: PurposekirtiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Interview Questions and AnswersDocument2 pagesElectrical Engineering Interview Questions and AnswersChandreshDharDubeyNo ratings yet
- Design Data SheetDocument1 pageDesign Data Sheetdriller27No ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning - Unit 2 - Week-1Document4 pagesRefrigeration and Air-Conditioning - Unit 2 - Week-1Kali DassNo ratings yet
- BEL Internship ReportDocument45 pagesBEL Internship ReportAnkitNo ratings yet
- Dakshana Class 11th Unit Test 3 - Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesDakshana Class 11th Unit Test 3 - Laws of MotionullasagwNo ratings yet
- ESO 203: Introduction To Electrical Engineering: Dr. S. ChakrabartiDocument11 pagesESO 203: Introduction To Electrical Engineering: Dr. S. ChakrabartiHimanshu KatheriaNo ratings yet
- M.Tech Power ElectronicsDocument2 pagesM.Tech Power ElectronicsWebsoft Tech-HydNo ratings yet
- Roller Coaster Physics Coursework GcseDocument7 pagesRoller Coaster Physics Coursework Gcseafjwdbaekycbaa100% (2)
- Chem Research PDFDocument2 pagesChem Research PDFFarahNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFvishuNo ratings yet
- Dig Assist 4.0 OBW OperatorDocument54 pagesDig Assist 4.0 OBW OperatorCatalin UrsuNo ratings yet
- Dykewall CalculationDocument4 pagesDykewall CalculationVipul GandhiNo ratings yet
- Is 3 eDocument2 pagesIs 3 emohamedwalyNo ratings yet
- Psych Chart Venmar CES Metric 8.5x11 1Document1 pagePsych Chart Venmar CES Metric 8.5x11 1Ayhu Rahayu NingsihNo ratings yet
- Anexo B Felder 4taedDocument27 pagesAnexo B Felder 4taedIan Oscar Gomez HuamaniNo ratings yet
- Blowers: Blower Motors, Wheels & FansDocument27 pagesBlowers: Blower Motors, Wheels & FansAndrey GyrychNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Fields: Right Hand RulesDocument14 pagesMagnetic Fields: Right Hand RulesFeolo Riel TarayNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0032591007001799 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0032591007001799 MainTomas ZadravecNo ratings yet
- TECKA Air Cooled Screw Chiller (Heat Pump) Unit - Brochure TECKA202103Document10 pagesTECKA Air Cooled Screw Chiller (Heat Pump) Unit - Brochure TECKA202103Guvanch MuradowNo ratings yet
- Lecture 26.20081029.49084b9fe41bc1.76327325.20081029.4908941e13c981.68685807Document9 pagesLecture 26.20081029.49084b9fe41bc1.76327325.20081029.4908941e13c981.68685807Aditya CandratamaNo ratings yet
- Project Report: Faculty of Electrical and Electronic EngineeringDocument16 pagesProject Report: Faculty of Electrical and Electronic Engineeringabdikadir hassanNo ratings yet
- Projectiles I MD I RnsDocument4 pagesProjectiles I MD I RnsKhabi Nada50% (2)