Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Epidemiology of Injuries
Uploaded by
Alaa BahjatCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Epidemiology of Injuries
Uploaded by
Alaa BahjatCopyright:
Available Formats
Epidemiology of Injuries
Accident
Definition
• Unexpected, unplanned occurrence of an event which may
involve injury.
• Occurrence in a sequence of events which usually produce
unintended injury, damage or property death.
What are Injuries?
A body lesion due to acute exposure to energy beyond the physiological tolerance
Why have epidemiologists taken an interest in injuries?
• Injuries have been identified as a leading cause of mortality and morbidity in both the developed and
developing world.
• They present a challenge to epidemiologists to understand
✓ The basic underpinnings of their occurrence (the frequency in which they occur,
✓ the risk factors for their occurrence and to develop intervention programs to reduce their impact
Types of accidents
Road Traffic Accidents (RTA) *Industrial Accidents *Domestic accidents *Railway accidents *Violence
Causes of Injuries
Abnormal Energy Transfer
*Mechanical Energy (moving objects) *Thermal *Electric *Chemical *Radiation
Causes of accidents
Accidents are complex phenomena with multiple causation
Etiological factors are classified to
*Human (Age, Gender, Education, ……) *Environmental (Road, weather,…..) *Agent
Human factor Environmental Vehicles:
Age:15-44 yrs(50% mortality)
• Sex: More in males Related to Roads: High speed
• Education: Low educational – Defective and narrow roads Poorly maintained vehicles
status – Defective lay out of cross- Overloaded bus
• Medical condition (illness, Heart roads, Low driving standards
attack, Impaired vision, Fatigue, … – speed breakers Risk factors for motor vehicle
• Lack of protection – Poor lighting crashes
– Helmet Bad Weather
– Safety belts
Do injury patterns differ around the world?
How to Measure the Problem of Accident
Mortality:
Mortality Rate
Number of deaths due to accidents out of 100 total deaths
Death Rate per 1000 registered vehicles per year
Number of accidents or fatalities as a ratio of number of vehicles per km OR passenger per km.
Morbidity:
Measured in terms of
Slight injury *Serious injury
Disability: Measured in terms of
• Temporary or Permanent disability • Partial or Total disability
Injury Prevention
Accident Investigation
*Who was present? *What activities were occurring? *What happened? *Where and what time? *Why did it
happen?
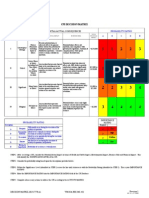
The Haddon Matrix
use for planning, resource
allocation, strategy identification
Effective prevention should::
*be permanent , not temporary * depend on passive not on active contribution of individuals
• not affect productivity * not transfer the risk to another place * be applicable to similar sites
You might also like
- AccidentsDocument41 pagesAccidentssivanayakNo ratings yet
- HEA 101 Lecture # 4 Section # 2Document29 pagesHEA 101 Lecture # 4 Section # 2mahfuzNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of RTIs and Home AccidentsDocument27 pagesEpidemiology of RTIs and Home AccidentsJake MillerNo ratings yet
- ACCIDENTS Presentation - SEH001 - Olaitan Oyedun - UpdatedDocument23 pagesACCIDENTS Presentation - SEH001 - Olaitan Oyedun - UpdatedLateef TaiwoNo ratings yet
- Traffic Psychology, Road Safety, and Health:: The Decade of ActionDocument40 pagesTraffic Psychology, Road Safety, and Health:: The Decade of ActionuykuykNo ratings yet
- Overview of Childhood InjuryDocument26 pagesOverview of Childhood InjuryhananNo ratings yet
- Rse Unit 5Document17 pagesRse Unit 5Aishwarya BNo ratings yet
- New Drivers' Handbook PDFDocument184 pagesNew Drivers' Handbook PDFDelloStrittoNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 PDFDocument10 pagesChapter5 PDFJustine CosicoNo ratings yet
- Ch13 Unintentional InjuriesDocument19 pagesCh13 Unintentional InjuriesAnanyaBandyopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Pencegahan CederaDocument35 pagesPencegahan CederaDini Novita SariNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document51 pagesUnit 1Muthukumar ANo ratings yet
- INJURY AND DEATH by DR Ifeanyi J. NkwokaDocument12 pagesINJURY AND DEATH by DR Ifeanyi J. NkwokaDfaid NGNo ratings yet
- By-Ramray Tudu 4 Year M.B.B.S, S.C.B MCH, CuttackDocument19 pagesBy-Ramray Tudu 4 Year M.B.B.S, S.C.B MCH, CuttackRamray TuduNo ratings yet
- Chapter3a Hazards IdentificationDocument24 pagesChapter3a Hazards IdentificationMohammed BahramNo ratings yet
- Chapter3a Hazards Identification Sem7OGEDocument24 pagesChapter3a Hazards Identification Sem7OGEMohammed Khaled Al-ThobhaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter3a Hazards IdentificationDocument24 pagesChapter3a Hazards Identificationmohammed.bm106No ratings yet
- Accident StudiesDocument63 pagesAccident Studiesmanaliamit100% (1)
- 3945 14044 1 PBDocument5 pages3945 14044 1 PBkumaran.rdaNo ratings yet
- Risk MGMTDocument20 pagesRisk MGMTManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Accident Data: Unit 01 - Health & Safety Btec Construction in The Built Environment Level 3 Hugh MclellandDocument22 pagesAccident Data: Unit 01 - Health & Safety Btec Construction in The Built Environment Level 3 Hugh Mclellandjim123No ratings yet
- Epidemiologi CederaDocument38 pagesEpidemiologi CederaWida WtpNo ratings yet
- Risk AssessmentDocument2 pagesRisk Assessmentandra14No ratings yet
- Safety, Accidents, and Human ErrorDocument32 pagesSafety, Accidents, and Human ErrorLorence Claire OstilNo ratings yet
- Safety Topic 1 - Introduction To SafetyDocument60 pagesSafety Topic 1 - Introduction To Safetysaidyharuna000No ratings yet
- Unsafe Human ErrorDocument32 pagesUnsafe Human ErrorAzad pravesh khanNo ratings yet
- Kespar - Travel Medicine InjuriesDocument31 pagesKespar - Travel Medicine InjuriesSulindri IntanNo ratings yet
- A Study On Awareness and Behaviour of Adolescent Towards Road Traffic AccidentDocument8 pagesA Study On Awareness and Behaviour of Adolescent Towards Road Traffic AccidentcksNo ratings yet
- 2021 Module A RiskDocument86 pages2021 Module A RiskFathia OlaitanNo ratings yet
- Module 2. A Systematic Approach UpdatedDocument35 pagesModule 2. A Systematic Approach UpdatedEric Nyame-BaafiNo ratings yet
- Risk AssessmentDocument104 pagesRisk AssessmentDimpi ShahNo ratings yet
- Traffic Accident Problems-Contributory Factors PDFDocument51 pagesTraffic Accident Problems-Contributory Factors PDFSiyuanLiNo ratings yet
- Traffic Accident ThesisDocument6 pagesTraffic Accident ThesisKatie Naple100% (2)
- Safe CommunityDocument3 pagesSafe CommunityRaja AlfatihNo ratings yet
- CH 18 Accidents Errors Safety 325 - 22Document65 pagesCH 18 Accidents Errors Safety 325 - 22azuresteowNo ratings yet
- Information About Writing A Risk Assessment and Management PlanDocument6 pagesInformation About Writing A Risk Assessment and Management PlanRanny CornejoNo ratings yet
- Road Safety Suggestion To Supreme Court Committee To Control Fatalities in IndiaDocument122 pagesRoad Safety Suggestion To Supreme Court Committee To Control Fatalities in IndiaSanjay KulshresthaNo ratings yet
- Traffic Accident InvestigationsDocument32 pagesTraffic Accident InvestigationsAbdullah ZubairNo ratings yet
- RTA ManagementDocument48 pagesRTA ManagementthehexhealthNo ratings yet
- Lect12 Highway SafetyDocument39 pagesLect12 Highway SafetyBALQEES HAMADNo ratings yet
- Road Traffic Accidents in Tunisia: A Man Made DisasterDocument20 pagesRoad Traffic Accidents in Tunisia: A Man Made DisasterReena GangurdeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document89 pagesUnit 1Rudra Sai SandeepNo ratings yet
- Road Traffic Accidents in Tunisia: A Man Made DisasterDocument20 pagesRoad Traffic Accidents in Tunisia: A Man Made DisastersdffefzffNo ratings yet
- Course01 - Handout - What Is Patient SafetyDocument4 pagesCourse01 - Handout - What Is Patient SafetySalsa Nabila Rianti PutriNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Introduction To Road Safety ManagementDocument12 pagesTopic 1 Introduction To Road Safety ManagementMAURICE KIOKONo ratings yet
- Accidents and Injuries in Childhood: Maha Mohamed El Gaafary Ass. Prof. of Public HealthDocument45 pagesAccidents and Injuries in Childhood: Maha Mohamed El Gaafary Ass. Prof. of Public HealthAbo AmgadNo ratings yet
- Seminar HADDONS MATRIXDocument30 pagesSeminar HADDONS MATRIXSasmita bisoyiNo ratings yet
- Road Traffic Accident: Purpose of Medico-Legal InvestigationDocument33 pagesRoad Traffic Accident: Purpose of Medico-Legal InvestigationAmirul AminNo ratings yet
- Industrial Safety and Health L1Document100 pagesIndustrial Safety and Health L1AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Usmanu Dan Fodiyo University Sokoto, Sokoto StateDocument18 pagesUsmanu Dan Fodiyo University Sokoto, Sokoto Statebuhari rabiuNo ratings yet
- Optician Vision of Eyesight Vector PowerPoint Templates StandardDocument39 pagesOptician Vision of Eyesight Vector PowerPoint Templates Standardtahirabeer50No ratings yet
- Group 6 TranspoDocument110 pagesGroup 6 TranspoCE-Velasquez, AndreaNo ratings yet
- Critical Incident ReportingDocument44 pagesCritical Incident Reportingsushil@irdNo ratings yet
- Elem 1 Foundations of Health and Safety PDFDocument21 pagesElem 1 Foundations of Health and Safety PDFabood aslmanNo ratings yet
- Elem 1 Foundations of Health and Safety PDFDocument21 pagesElem 1 Foundations of Health and Safety PDFabood aslmanNo ratings yet
- Artikel 4Document6 pagesArtikel 4Amalia Augustina FadlilahNo ratings yet
- TI Project ProposalDocument14 pagesTI Project ProposalAnonymous 7NDbF3No ratings yet
- 4 - MVA For DistributionDocument65 pages4 - MVA For DistributionCarl Christian V. DonaireNo ratings yet
- Car Accidents Handbook: Why Car Accident Victims Deserve a Book to Protect Their RightsFrom EverandCar Accidents Handbook: Why Car Accident Victims Deserve a Book to Protect Their RightsRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- AsthmaDocument12 pagesAsthmaAlaa BahjatNo ratings yet
- Histo KidneyDocument3 pagesHisto KidneyAlaa BahjatNo ratings yet
- Enteric Fever and Dysentery (Typhoid FeverDocument2 pagesEnteric Fever and Dysentery (Typhoid FeverAlaa BahjatNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Quality of Life of Disabled PeopleDocument2 pagesAssessing The Quality of Life of Disabled PeopleAlaa BahjatNo ratings yet
- تجميعات النساDocument4 pagesتجميعات النساAlaa BahjatNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Health StatusDocument3 pagesMeasurement of Health StatusAlaa BahjatNo ratings yet
- Occupational Dermatoses2Document3 pagesOccupational Dermatoses2Alaa BahjatNo ratings yet
- Aml - Ibrahiem - 5-Primary and Secondary Survey in Multiple Trauma PatientDocument62 pagesAml - Ibrahiem - 5-Primary and Secondary Survey in Multiple Trauma PatientAlaa BahjatNo ratings yet
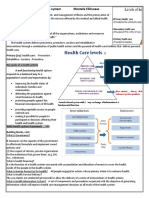
- Health Care System Mostafa ElkhwaasDocument4 pagesHealth Care System Mostafa ElkhwaasAlaa BahjatNo ratings yet
- Probability MethodsDocument106 pagesProbability MethodsebrarrsevimmNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction To Highway and Railroad EngineeringDocument43 pagesModule 1 Introduction To Highway and Railroad EngineeringKenneth FajardoNo ratings yet
- Decision MatrixDocument12 pagesDecision Matrixrdos14No ratings yet
- IV (First Ten)Document12 pagesIV (First Ten)Nika RojasNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No 10054Document2 pagesRepublic Act No 10054Jun Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- A Study On Traffic Management Along EDSA in Metro ManilaDocument8 pagesA Study On Traffic Management Along EDSA in Metro ManilaChinang100% (4)
- Thesis 2018 First Sem Painted IslandsDocument115 pagesThesis 2018 First Sem Painted IslandsBryan Carl LascotaNo ratings yet
- Zoox Safety Report Volume2 2021Document26 pagesZoox Safety Report Volume2 2021dgafghfdgdhNo ratings yet
- (IJCST-V6I6P1) : Gandrapu Gideon, Prof. K. Venkata RaoDocument5 pages(IJCST-V6I6P1) : Gandrapu Gideon, Prof. K. Venkata RaoEighthSenseGroupNo ratings yet
- Indicative Draft Terms of Reference - HPSRP - II (15022018)Document103 pagesIndicative Draft Terms of Reference - HPSRP - II (15022018)Amar NegiNo ratings yet
- Forklift 1Document90 pagesForklift 1syoumans3364100% (1)
- Road Traffic Accident and Its Characteristics in Kathmandu ValleyDocument7 pagesRoad Traffic Accident and Its Characteristics in Kathmandu ValleyrajjaNo ratings yet
- Weekly Safety MeetingsDocument52 pagesWeekly Safety MeetingsparthaNo ratings yet
- Ins200 - Full AssignmentDocument17 pagesIns200 - Full AssignmentFATIMAH MOHAMAD ISANo ratings yet
- Transport Management System of Nepal: Yuba Raj Pandey SecretaryDocument33 pagesTransport Management System of Nepal: Yuba Raj Pandey SecretarySigdel gopalNo ratings yet
- Forensic Examination of VehiclesDocument3 pagesForensic Examination of VehicleskrishnaNo ratings yet
- Traffic Accident ThesisDocument6 pagesTraffic Accident ThesisKatie Naple100% (2)
- Incident ReportDocument3 pagesIncident Reportجميل باكويرين موسنيNo ratings yet
- Research of TrafficDocument20 pagesResearch of Trafficdemelash kasayeNo ratings yet
- Page - 1Document10 pagesPage - 1eka etika sariNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Utilization of Pedestrian Bridges in Batangas CityDocument37 pagesFactors Affecting The Utilization of Pedestrian Bridges in Batangas CityJoana CastilloNo ratings yet
- Guidance On Hazard IdentificationDocument20 pagesGuidance On Hazard Identificationmath62210No ratings yet
- Spouses Anchevara and Valdez V Ramos G.R. No. 175172, September 29, 2009Document12 pagesSpouses Anchevara and Valdez V Ramos G.R. No. 175172, September 29, 2009ChatNo ratings yet
- Disaster Management AssignmentDocument8 pagesDisaster Management AssignmentAdarsh RNo ratings yet
- Owner's Manual VELOZDocument446 pagesOwner's Manual VELOZPeaky Blinders50% (2)
- TrafficInvestigation PDFDocument119 pagesTrafficInvestigation PDFjd_prgrin_coNo ratings yet
- Major ProjectDocument57 pagesMajor Projectshaik shahidNo ratings yet
- Sample Accident Prevention PlanDocument23 pagesSample Accident Prevention PlanPeter GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Road Safety 2013 BergDocument45 pagesRoad Safety 2013 BergjoebriffaNo ratings yet